Chemistry 14A
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards based on class notes and practice midterm samples/solutions
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
1
New cards
Karl Popper’s Theory
Scientific theories can only be proven incorrect; they can not be proven correct. The goal of science is to discard incorrect theories rather than confirm them.
2
New cards
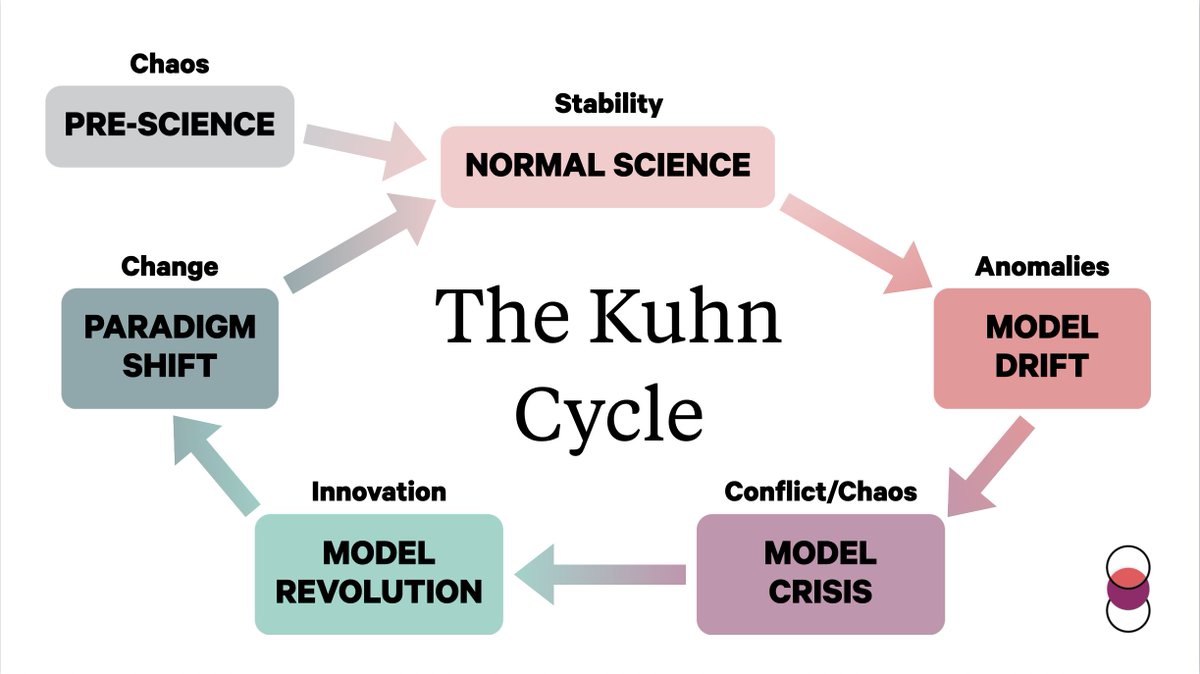
Kuhnian Scheme (By Thomas Kuhn
Kuhn believes that there is a chaotic, pre-scientific stage followed by the establishment of a paradigm within which anomalies arise. When there is complete disagreement among members of a paradigm, a revolution forms to establish a new paradigm.
3
New cards
Law of Conservation of Mass
Mass is neither created nor destroyed. According to this law, the mass of products in a chemical reaction must equal the mass of the reactants: Mass of A + Mass of B = Mass AB
4
New cards
Law of Constant Composition
When two elements combine they will do so in the same proportion
5
New cards

Law of Multiple Proportion (Dalton)
If two elements combine and form more than one compound, the weights of one element that combine with a fixed weight of the other are in a ratio of small whole numbers
6
New cards
Hypothesis
An educated guess, or an untested explanation, that is based upon observations or known facts
7
New cards
Theory
When a hypothesis has been repeatedly tested and verified by other scientists, it may be accepted as a theory. Theories explain observations and laws.
8
New cards
Laws
Laws describe past observations and predict future observations but do not explain how they happen.
9
New cards
Physical change
The identity of the substance does not change, only its physical properties are different
10
New cards
Chemical change
When a substance is transformed into a different substance. Example: hydrogen changing to water
11
New cards
Physical properties
Characteristics that can be observed or measured without changing the identity of the substance. Example: mass, temperature, melting point, hardness, color, state of matter, and density
12
New cards
Chemical properties
The ability of a substance to be changed into another substance. Example: a chemical property of the gas hydrogen is that it reacts with oxygen to produce water
13
New cards
The power of ten that defines kilo-
10^3
14
New cards
The power of ten that defines centi-
10^-2
15
New cards
The power of ten that defines milli-
10^-3
16
New cards
The power of ten that defines micro-
10^-6
17
New cards
nano-
10^-9
18
New cards
Empirical Formula
19
New cards
Finding Maximum Height
h= v^2/2g
20
New cards
Kinetic Energy Formula
K=1/2mv^2