USE OF PREFORMED METAL CROWNS IN PAEDIATRIC DENTISTRY
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
outline preformed metal crowns
3M ESPE surgical grade stainless steel primary molar crowns
6 different sizes per tooth (sizes 2-7)
pre-contoured and pre-crimped
when placing a preformed metal crown, where should the text on the crown be
size and location text should be on the buccal aspect when placed on tooth

how does the text on the PMC come off
via rubbing and toothbrushing overtime
what are indications for the use of PMCs in primary teeth
teeth with large or multi-surface carious lesions
pulp treated teeth
trauma
enamel and dentine defects
abutment for crown-loop space maintainer
infraoccluded teeth to maintain mesial/ distal space
what are infraoccluded teeth
premature stop of eruption so the tooth sits below the occlusal plane compared to adjacent teeth
pulpotomy VS pulpectomy
pulpotomy = partial
pulpectomy = complete
what are contraindications for the use of PMCs in primary teeth
unrestorable tooth
failed pulp therapy
soon to exfoliate teeth
cautions: severe wear/ space loss, pre-cooperative, poor motivation, multiple grossly carious teeth
space loss - 1° teeth often have large contact areas so it may be challenging to get a crown to fit
what are indications for the use of PMCs in permanent teeth
hypomineralised molars e.g. in MIH
amelogenesis imperfecta
dentinogenesis imperfecta
temporary restoration
severe erosion
what are advantages of PMCs
straightforward technique
quick and cheap
evidence of excellent longevity, low failure rates, compare well with other materials
failure - if it occurs - is easily corrected
what are disadvantages of PMCs
poor aesthetics
may impede eruption of adjacent teeth if too big
may cause gingival inflammation if cement is not removed completely
theoretical nickel allergy risk - most modern crowns do not have nickel in them
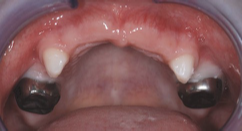
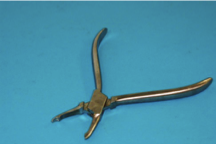
comment on this PMC
the crown is slightly too big
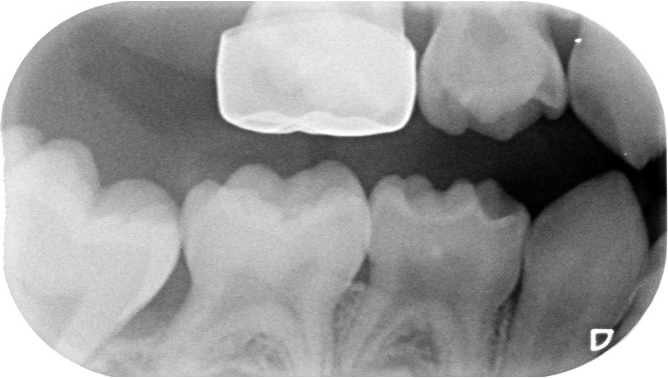
comment on these PMCs
the erupting 6s will get stuck on the PMCs so they will need to be removed
how are PMCs removed
need to drill them off
evidence for PMCs
Cochrane Review (2015)
six studies included
teeth with PMCs were less likely to develop abscesses or cause pain in the long term compared to a conventional restoration
PMC on teeth with caries/ that have had pulp treatment are likely to reduce the risk of major failure or pain in the long term compared to conventional restorations
what are barriers to placing PMCs in children
lack of training esp. at undergraduate level
reluctance to administer LA to children
difficulties in preparation in young children
how can you sell PMCs to children
parents often do not like the look of them
children love them
princess/ barbie teeth
tooth jewellery
pirate tooth
iron man tooth
points to inform the patient/ parent about PMCs
they stay on until the tooth falls out (sometimes reported that the crown feels loose but in reality it is the tooth starting to exfoliate)
they need to be brushed just like normal teeth
the glue (glass ionomer) tastes a bit like lemons/ salt and vinegar crisps
they feel a bit funny to bite on to start with (bigger/ slidey)

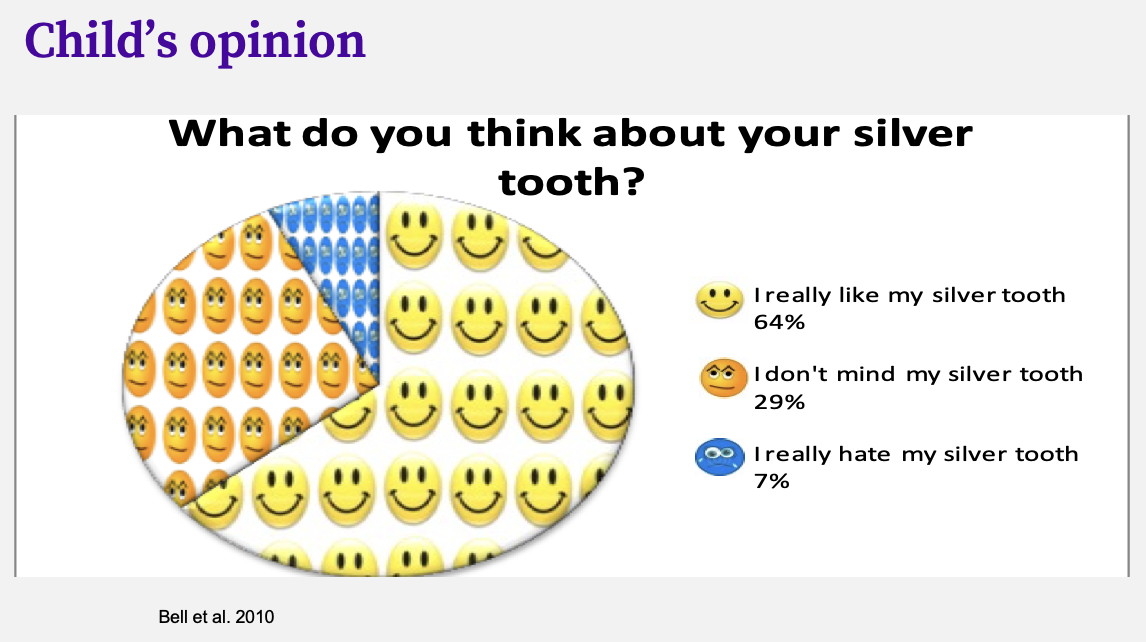
parent’s opinion on PMCs
conventional PMC technique: essential materials
whole box of crowns
topical/ LA
diamond burs
cement
dental tape - knotted
conventional PMC technique: optional materials
rubber dam
crown scissors
crimping pliers
orthodontic band seater
what instrument is this
crown scissors (try to use as little as possible)

what instrument is this
orthodontic band seater
what instrument is this
crimping pliers
outline airway protection when placing a PMC
child sitting slightly upright
rubber dam
gauze
adhesive handle
elastoplast tape
conventional PMC technique step-by-step
topical/ LA
remove caries
pulpotomy/ pulpectomy if needed
AIRWAY PROTECTION
prepare tooth
select crown
adapt crown or modify prep
cementation of crown
push down as far as possible
remove excess cement with wet gauze
allow child to bite on band seater/ cotton wool roll
remove further cement with gauze, excavator or probe
floss contact points with knotted floss
outline how the tooth should be prepared using the conventional PMC technique
occlusal reduction: remove about 1mm off occlusal surface following the contours of the tooth
mesial and distal reduction: use a pointy bur and remove tooth tissue mesially and distally, leaving no ledges and ensuring they are parallel
mesial/ distal reduction with ledge
finished tooth preparation
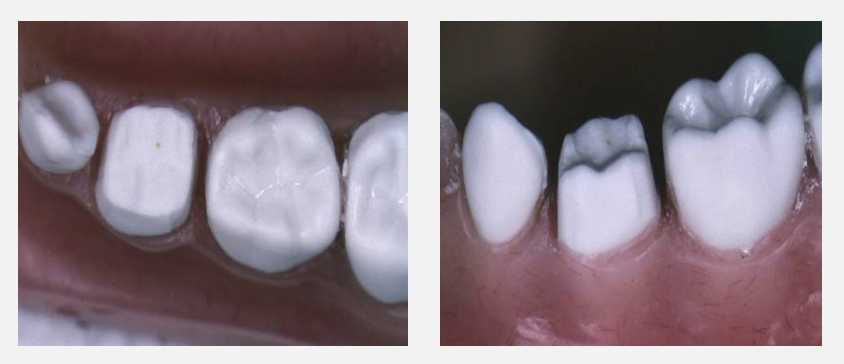
how should a PMC be selected
want it to cover the entire crown of the tooth down to the gingival margin
best way to try on crown size: roll from lingual to buccal, should click into place
why may a crown need to be modified/ adapted
coping with:
poorly adapted crown margins » crimp
space loss » modify shape or use a crown from the opposite side and arch
gingival blanching » will resolve itself
occlusal discrepancies » will resolve
outline PMC cementation
glass ionomer (Aquacem on clinic)
clotted cream consistency
enough to fill the crown (there should be excess)
fit crown on tooth
remove excess with wet gauze and knotted floss
get child to bite down on cotton wool until glue has set
outline the history of the Hall Technique

differences between the conventional technique and the Hall Technique
no tooth preparation
no local analgesia
no full try-in (partial try in done)
caries not removed but sealed into the tooth to isolate it from the mouth
(?) not for extensively carious teeth
what are indications of the Hall Technique
tooth has to be asymptomatic
child not at risk of endocarditis
pre-operative radiograph
must shown no inter-radicular pathology
must be a clear band of dentine between caries and pulp
what may be needed more when using a Hall Technique VS conventional
orthodontic separators
evidence for the Hall Technique (Innes, Evans & Stirrups, 2007)
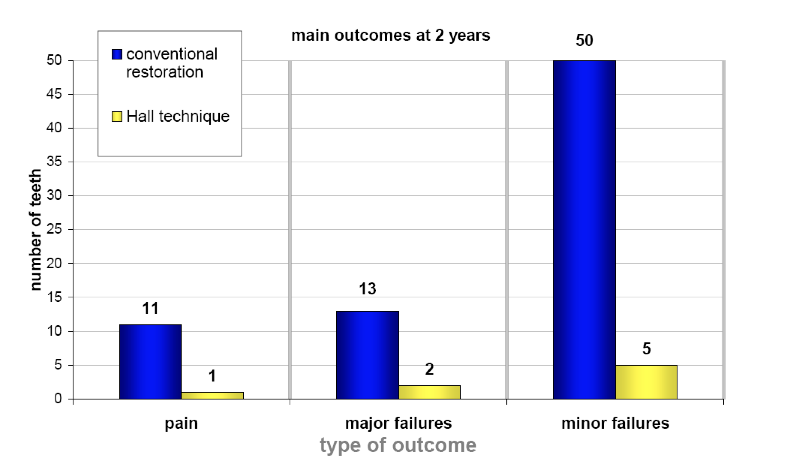
evidence for the Hall Technique (Innes, Evans & Stirrups, 2007)
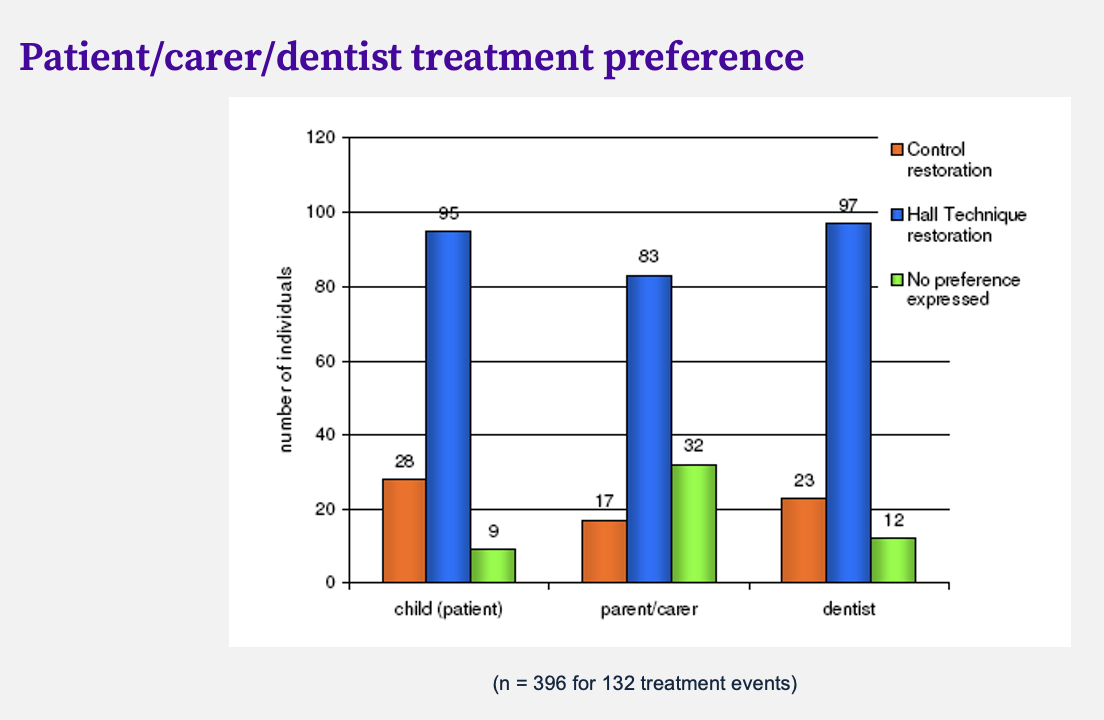
evidence for the Hall Technique (Innes, Evans & Stirrups, 2007)

what is perforation of PMCs
if a child has had PMCs on for a long time it can get worn occlusally esp. if it is contacting enamel
the exposed layer underneath is a layer of glass ionomer
as long as the perforated area is not sharp or annoying, they can be left on until exfoliation

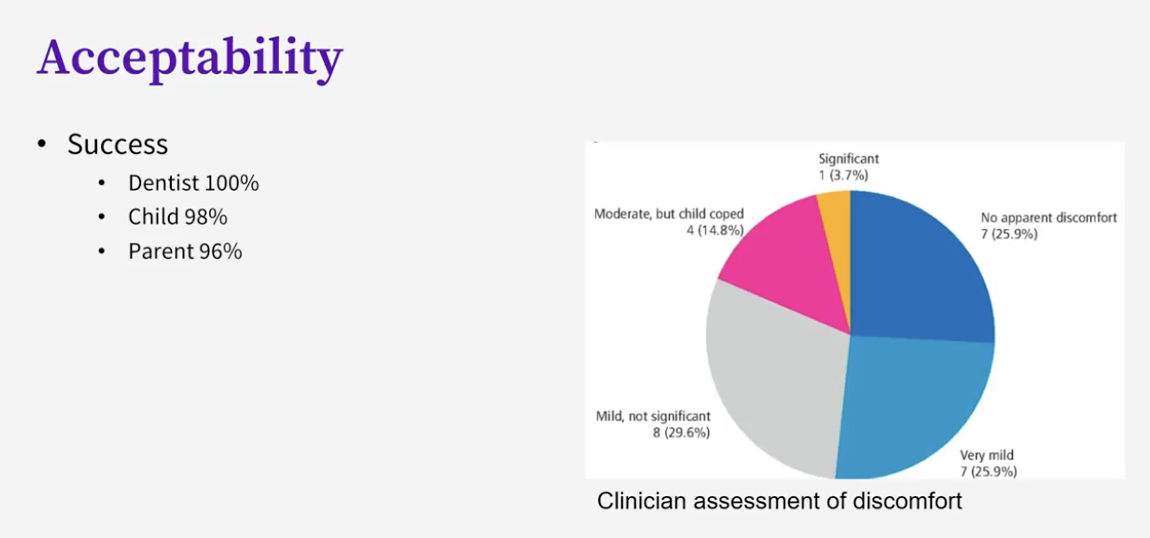
outline the Hall Technique
if necessary place separators 1 week prior (tell patient it will feel like food stuck between teeth)
topical anaesthetic (optional)
choose crown
AIRWAY PROTECTION
try crown to contact point only
cementation of crown
push down as far as possible
remove excess cement with wet gauze
allow child to bite on band seater/ cotton wool roll
remove further cement with gauze, excavator or probe
floss contact points with knotted floss
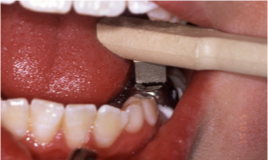
image of band seater being used to fit crown
patient instructions after PMCs
may be a little uncomfortable afterwards - can be tender around gingivae
Calpol/ paracetamol
advice about analgesia
occlusion will be propped open but will settle
gingival blanching is normal and should resolve itself in 3-4h
image showing gingival blanching after PMC placement