(pt 1) exam #4 - immunohematology (cls 544)
1/79
Earn XP
Description and Tags
donor selection, transfusion transmitted diseases
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
role of transfusion medicine
Blood collection: providing safe, satisfying experiences for our blood donors
Manufacturing: accurately labeling and testing blood bank components provided to our transfusion services
Transfusion service: accurate timely, transfusion to our clinicians and other members of the healthcare team
Blood administration: safe, efficacious blood transfusions to our patients
purpose of blood centers
responsible for supplying a safe and adequate blood supply to community
Recruiting people to donate crucial to ensuring blood available for transfusions
Reporting of adverse events in blood donor and recipients (hemovigilance)
volunteer vs paid donors
Blood components intended for transfusion must indicate on the container label "paid donor" or "volunteer donor"
Payment for donation has the potential to promote dishonestly
Voluntary, non-paid blood donation with no coercion is felt to be the safest
governing agencies for blood collection
Governing agencies for processes including donor selection and donor unit processing
FDA
CFR / CBER
AABB Standards
College of American Pathologists (CAP)
European Union (EU) Standards
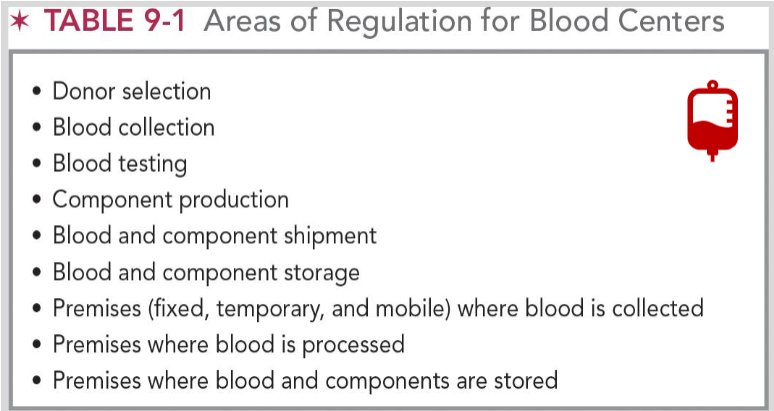
areas of regulation for blood centers
donor selection
blood collection & testing
component production
blood and component shipment / storage
premises (fixed, temporary, and mobile) where blood is collected, processed, and stored
donor health history screening (general)
include donor history questionnaire (DHQ), mini physical examination, and serologic testing of the donor blood
Donor identification and registration requirements confirm donor identity and link the donor to existing donor records
(donor health screening) physical examination & registration
Physical examination
Donor's vital signs taken
Hemoglobin or hematocrit check performed
Registration
Donors must present ID
Demographic information obtained
Donor deferral registry (DDR) or deferred donor director (DDD)
Donors given education materials prior to donating blood
(donor health screening) consent & informed consent
Consent
Obtained prior to actual donation
Often incorporated with DHQ
Informed Consent
AABB standards mandate that informed consent of allogenic, autologous, and apheresis donors be obtained
The donor must be informed of the risks of the procedure and the tests performed to reduce the risk of transmitting infectious disease(s) to the recipient
(donor health screening) confidential unit exclusion (CUE)
confidential way to indicate donor blood should not be used for transfusion
donor history questionnaire (general)
standardized set of risk-factor questions developed by a task force that included representatives from AABB, FDA, and the blood and plasma industry
Determine eligibility of donor; protect donor and recipient
Developed by AABB's donor history task force
Contains more than 40 capture questions
Available in an abbreviated format for use with qualified, frequent donors
Self-administered questionnaires must be reviewed by trained personnel prior to blood collection
types of deferral (3)
Temporary: donor unable to donate blood for a limited time period
Permanent: donor will never eligible to donate blood for someone else
Indefinite: donor unable to donate blood for someone else for an unspecified period due to current regulatory requirements
medication deferral list
identifies medications that require donor deferral to protect safety of recipient
Many medications restricted due to potential for causing teratogenic effects in the fetus of a female transfusion recipient
Major medications types restricted from donation
Antiplatelet agents (i.e. Plavix, Feldene)
Anticoagulants (Coumadin, Xarelto, Lovenox)
Accutane
Drugs for treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia and alopecia (Proscar, Avodart)
Drugs used to treat psoriasis (Soriatane, Tegison)
Drugs used to treat HIV
list of vaccines with no deferral period
Allergy ; Anthrax
Diphtheria (DPT, TDAP)
Flu (including intranasal live attenuated)
Recombinant vaccines
HPV / Hep B
Gamma globulin (no exposure)
RSV / Hep A (no exposure)
Pneumonia / Paratyphoid
Pertussis / Tetanus
Typhoid (injection) / Polio (injection)
Covid-19 (FDA-approved, nonreplicating, inactivated, mRNA-based)
list of vaccines with 2-week deferral period
Measles (rubeola)
Mumps
Polio (sabin/oral)
Typhoid (oral)
Yellow fever
list of vaccines with 4-week deferral period (3)
German measles (rubella)
Chickenpox/shingles (varicella zoster)
MMR (measles, mumps, rubella)
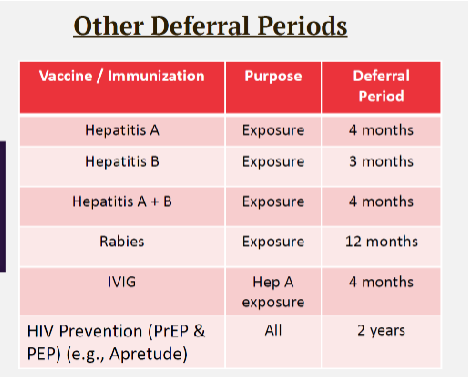
other deferral periods for select vaccines
Hep A = 4 months
Hep B = 3 months
Hep A + B = 4 months
Rabies = 12 months
IVIG = 4 months
HIV prevention (PrEP, PEP) = 2 years
deferral period for juvenile detention, jail, prison
12 months
(miscellaneous deferrals) malaria illness + resident of malarial endemic country
3 years
(miscellaneous deferrals) travel to malarial endemic country for >24 hrs
3 months deferral
(misc deferrals) conditions that have a indefinite deferral
dura mater graft/xenotransplant
person with hep B/C
person with sickle cell disease
(misc deferrals) conditions that have a permament deferral
person w hemophilia/coag deficiencies
polycythemia vera
thalassemia major
primary thrombocytosis
(misc deferrals) conditions that have no deferral period
person recovered from idiopathic TTP
von willebrand’s disease not requiring treatment
cancer in-situ of the vulva, cervix, or breast; papillary thyroid carcinoma treatment complete
lung disease
thalassemia minor trait
(misc deferrals) cancer & leukemia
cancer: 1 year
leukemia: 5 years
(misc deferrals) cardiac bypass surgery, heart attack etc + pregnancy
cardiac bypass surgery & heart attack: 6 month deferral period
pregnancy: 6 week deferral
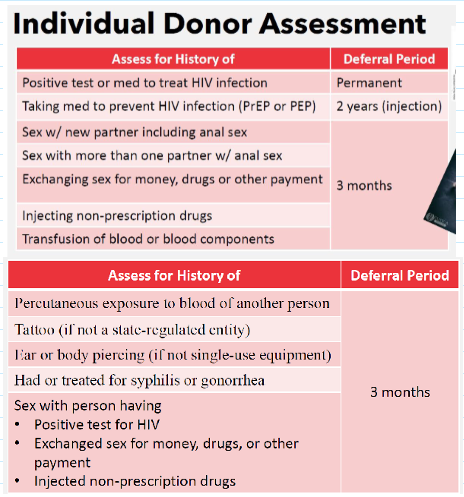
individual donor assessment
Revised donor deferral recommendation for individual with increased risk for transmitted HIV infection
Eliminates screening questions specific to:
Men who have sex w men (MSM)
Women who have sex w MSM
Recommendations: assess eligibility using individual risk-based questions for all donors (regardless of sex or gender
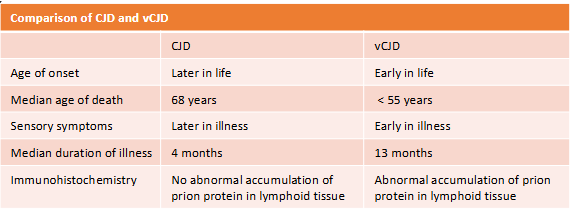
creutzfeldt-jakob disease (CJD) vs variant CJD
CJD--neurological disorders known as transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSE) or prion disease
Sheep, cows, and humans affected
vCJD--a prion disease, human infection with the agent of bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE, "mad cow disease)
Prions--abnormal proteins found in the brain tissue of disease cattle, heat resistant, and UV light resistant
Results in progressive dementia and spongiform alterations in the brain → fatal
types of donations (4)
Autologous donation: donated by donors for their own use = "self"
Allogenic donation: given for use by someone other than donor
Directed or designated donation: for specific recipient
Therapeutic donation: need further evaluation
physicial examination for blood collection (pic)
donor center representative evaluates the prospective donor for the following:
General appearance, weight, temperature, pulse
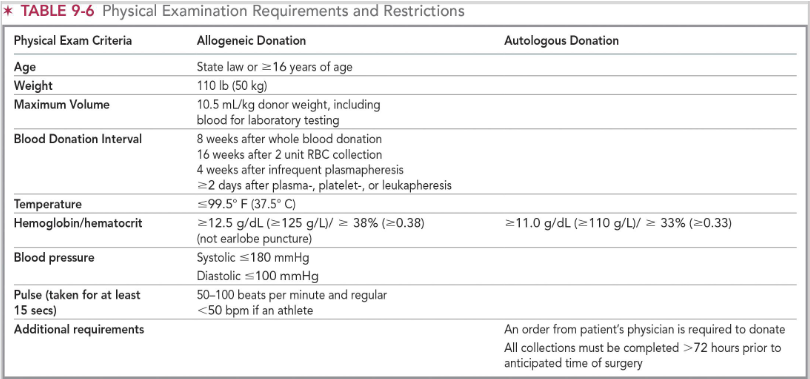
(mini physical) minimum hgb levels for whole blood and plateletpheresis
Females: 12.5 g/dL
Males: 13.0 g/dL
Max: 20 g/dL
Autologous: >/= 11.0 g/dL
(mini physical) minimum hgb levels for DRBC & trima apheresis donation
DRBC apheresis
13.3 g/dL (either gender)
Trima apheresis
Max: 18.4 g/dL
(mini physical) minimum hgb levels for plasmapheresis
Females: 12.5 g/dL
Males: 13.0 g/dL
Maximum 18.3 g/dL
general donation criteria
Generally healthy, feeling well
No infection
No medications from the Medication Deferral List within specified timeframes
Must read education materials (at every donation)
No deferral on file (verify donor eligibility against donor deferral list)
frequency limits of blood/blood product donations
Whole blood (every 56 days)
Power red (every 112 days, up to 3x/year)
Platelet (every 7 days, up to 24x/yr)
Plasma--type AB (every 28 days up to 13x/yr)
whole blood collection sets
WB collection sets are available in a variety of configurations
One primary bag to collect blood contains anticoagulant
Smaller bags (satellite) attached to main bag with plastic tubing
Large-bore needle (16 gauge) attached to collection set
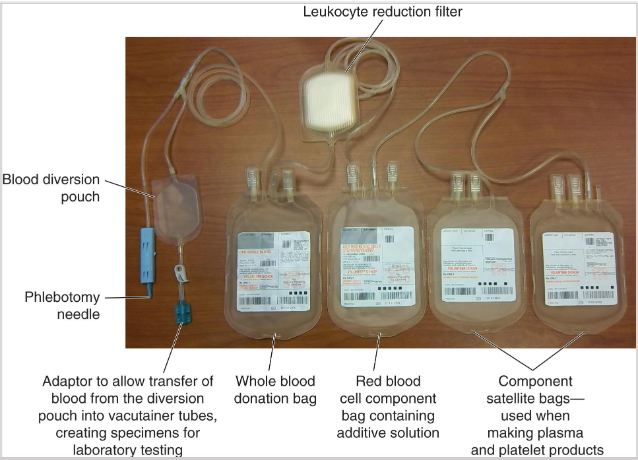
(whole blood collection) anticoagulant preservative solutions
Citrate phosphate dextrose (CPD) / Citrate Phosphate Double Dextrose (CP2D)
Shelf life of 21 days
Citrate phosphate dextrose adenine (CPDA-1)
Adenine is used for making ATP
Shelf life of 35 days
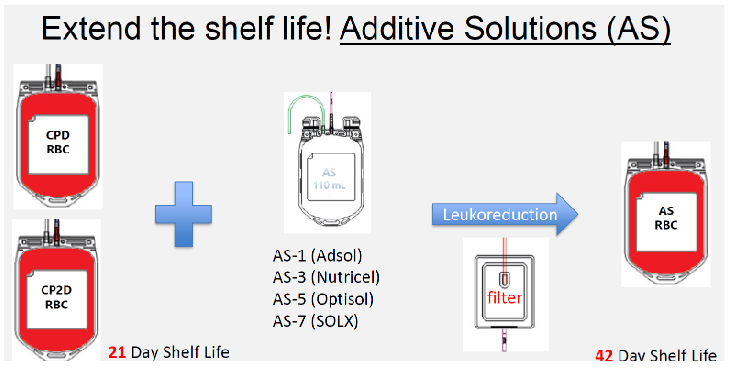
(whole blood collection) additive solutions (AS)
preserving solutions that are added to the RBCs after removal of the plasma with/without plasma
Extends shelf life of pRBCS to 42 days
Currently four additive solutions are licensed in the US
Adsol (AS-1)
Nutricel (AS-3)
Optisol (AS-5)
SOLX (AS-7)
Different formulations of saline, adenine, glucose, and mannitol (SAGM)
process of whole blood collection
First step = confirm the donor's identity
Select vein to be used for venipuncture and clean the area
Once blood collected in diversion pouch, pouch is sealed off
Blood allowed to flow into tubing on other side of Y connector and into blood bag
Important that blood collected is sterile
Most whole blood donations completed within 5 to 10 minutes
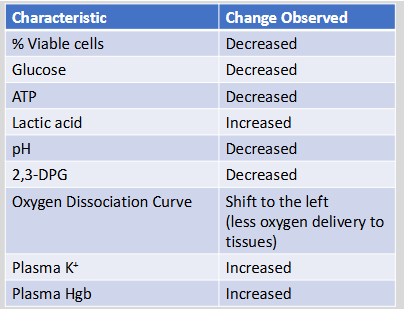
RBC viability and storage lesion
Loss of RBC viability has been correlated with the lesion of storage
Associated with various biochemical changes within the pRBC unit
Glucose, ATP, pH and 2,3-DGP & # of viable cells all decreased
Lactic acid, plasma K+, and plasma Hgb all increased
autologous donations (general)
most autologous blood is used to treat surgical blood loss in very specific situations where there is a reasonable opportunity to avoid homologous transfusions and/or when compatible allogenic blood is not available
Products cannot be placed into regular inventory if not used by the donor
advantages of autologous donations
decreased risk of:
Disease transmission
Transfusion reactions
Alloimmunization
disadvantages of autologous donations
Bacterial contamination
Not permitted to donate if donor has condition for risk of bacteremia
Circulatory overload
Cytokine-mediated reactions and product/recipient misidentification
High cost
methods of obtaining autologous blood (4)
Preoperative Collection or Preoperative Autologous Donation (PAD)
Usually 5-6 weeks prior to surgery
max of 4 donations with 3-7 days in between, final donation no sooner than 3 days prior to surgery / transfusion
Acute Normovolemic Hemodilution
Concurrent collection and replacement with crystalloids (volume replacements)
Intraoperative Collection
Collecting shed blood from surgical site
Postoperative Collection
Collected from a drainage tube placed at the surgical site
directed donation
Collected under the same requirements as allogenic donors but directed toward a specific patient
tag for directed unit is a distinct color (pink)
May lead to increased risk for patients
Infectious disease testing is performed on all directed donation units
If the donor is a blood relative, the unit must be irradiated to prevent GVHD
Allogenic donations from unrelated volunteer donors may be set aside or collected for specific patient because of antigen matching
therapeutic donations
Remove blood from patient, generally due to myeloproliferative disorder or neoplasm causing increased hematocrit
Hereditary hemochromatosis
Secondary polycythemia due to testosterone replacement therapy
May only be performed with physician's order
Done every few weeks as needed
apheresis (automated) collection
automated method for collecting a specific blood component while returning the remaining whole blood components back to the patient
Blood separated into components with centrifugal force based on differences in density
Can be used to collect large volumes of the intended component
Plateletpheresis, plasmapheresis, WBCs (granulocytes), single or double RBCs
Donor requirements generally the same as for whole blood donation—time intervals between donations vary depending on component collected
donor reactions
divided into 3 categories:
Mild--fainting (syncope), nausea/vomiting, hyperventilation, twitching, and muscle spasms
Moderate--includes mild reaction symptoms up to loss of consciousness
Severe--convulsions
what do you do in the case of an adverse donor reaction?
Remove tourniquet and withdraw needle
Place cold compress on donor's forehead
Raise donor's legs above the level of head
Loosen tight clothing
Monitor vital signs
donor blood testing
Blood donations must be tested for the following:
ABO/Rh typing
Weak D (when needed)
Antibody screen
Especially for donors with history of pregnancy(ies) and/or blood transfusion
Pathogens (see pic)
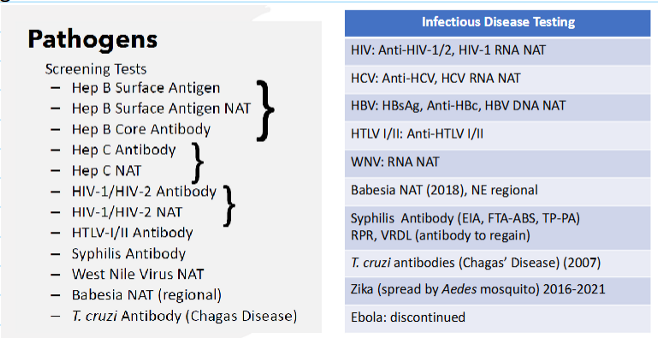
(transfusion transmitted diseases) what types of tests are performed on donated blood?
Hepatitis B virus
Hepatitis C virus
HIV-1/2
HTLV-I/II
Syphilis
West Nile virus
Trypanosoma cruzi (Chagas' disease)
Babesia: in states where testing is required by FDA guidance
(transfusion transmitted diseases) hepatitis A virus (HAV)
Small, non-enveloped single stranded RNA virus in Picornaviridae family--most common of all hepatitis viruses
Transmitted in unsanitary conditions that lead to contaminated food or water, then ingested (fecal-oral route)
Incubation period ~4 weeks
Symptoms include fatigue, fever, jaundice, and vomiting
25% of HAV infected persons are asymptomatic
hepatitis A virus transfusion testing
Rare transmission through blood transfusion
HAV vaccine available since 1995
Resistant to pathogen inactivation procedures due to no envelope
Pathogen inactivation is a process by which blood and blood products are treated to remove (or inactivate) infection agents
(transfusion transmitted diseases) hepatitis B virus (HBV)
Enveloped double-stranded circular DNA viruses in the Hepadnaviridae family
Vaccine available
Transmitted sexually, parenterally, or vertically (from mom to fetus) via bodily fluids
95% of HBV infected persons have acute infection only and often asymptomatic
Virus can survive up to 1 week in dried blood
Symptoms: flu-like, jaundice, fever, vomiting, and elevated liver enzymes
Complications include liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma
transfusion considerations for HBV
Antigens in serum of infected person: HBsAg, HBcAg, and HbeAg
Anti-HBc and anti-HBs can persist for years
Transfusion-transmitted infection (TTI) rates declining due to deferral of high-risk donors, confidential self-exclusion, disease testing, vaccine use
(transfusion transmitted diseases) hepatitis C virus (HCV)
Small enveloped single stranded RNA virus in Flaviviridae family
Transmitted parenterally—e.g. infected needles
Most acute HCV infections asymptomatic
Most cases go unresolved leading to chronic carriers
80% of those infected become chronic carriers
Symptoms include jaundice and elevated liver enzymes
Long-term risks includes cirrhosis or liver and/or development of hepatocellular carcinoma
(transfusion transmitted diseases) hepatitis D virus (HDV)
Small ssRNA virus; referred to as "delta hepatitis" virus
Only virus in the Deltavirus genus
Unique virus dependent on HBV--only occurs as a co-infection
Enveloped HCV particles contain HBsAG
Transmitted through parenteral and sexual routes only in presence of HBV
More severe, acute illness than those infected with HBV alone
Assays to detect antibodies available but not recommended for donor testing
(transfusion transmitted diseases) hepatitis E virus (HEV)
Nonenveloped RNA virus in the Caliciviridae family
Mode of transmission similar to HAV via fecal-oral route
Not sexually transmitted
Most cases are acute and do not proceed to chronic illness
Serologic tests available--not recommended for donor testing
(transfusion transmitted diseases) hepatitis G virus (HGV)
Enveloped RNA virus in Flaviviridae family
GBV-C/HGV
Transmitted parenterally, sexually, and through blood transmission
Does not cause hepatitis-like illness in humans
Assays for identification are available but NOT recommended for donor testing
(transfusion transmitted diseases) HIV 1 / 2 (retroviruses)
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) 1 & 2
Enveloped retrovirus in Retroviridae family
HIV-1 prevalent worldwide whereas HIV-2 is endemic in western Africa
Both are causative agents of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS)
40% of HIV infected persons exhibit flu-like symptoms
Can be asymptomatic for 10 years or longer
transmission and testing of HIV 1 / 2
Transmitted parenterally, sexually, vertically, and through breast milk
In end-stage HIV infection/AIDS, the immune system is depressed, and complications plus opportunistic infections rise
Concerns regarding safety of blood supply led to detailed donor history requirements
The window period has an impact on donor supply due to small percent of donors that present seronegative
Screening: HIV1/HIV-2 antibody and NAT
(transfusion transmitted diseases) HTLV I/II (retroviruses)
Human T-cell lymphocytic virus (HTLV) I/II
<10% incidence in the population
Modes of transmission--parenteral, sexual, breast milk, and via blood transfusion
Cell-associated virus highly concentrated in leukocytes
Refrigerated products (after 7 days) have demonstrated degradation of the virus
Active infection asymptomatic and HTLV infection can be lifelong
Screening: EIA test
(transfusion transmitted diseases) west nile virus (WNV)
single stranded enveloped RNA virus from the Flavivirus family
Found primarily in bird species
Transmitted through infected mosquitoes (Culex)
Most infected persons are asymptomatic
Symptoms : flu-like symptoms, fever, rash, headache, vomiting
Transmissible through blood products
Window period of two weeks
Screening: NAT
Positive: 4 months deferral
(transfusion transmitted diseases) zika virus
arbovirus in the Flaviviridae family
Transmitted through infected mosquitoes (Aedes aegypti)
Most infected persons are asymptomatic
Symptoms: flu-like symptoms, fever, rash, headache and muscle and joint pain
Associated with severe neurological complication during pregnancy
Transmissible through blood products
Screening: NAT, ELISA, and immunofluorescence assay
Positive: 120 days deferral
(transfusion transmitted diseases) cytomegalovirus
DNA virus and a member of herpesvirus group
Transmission: direct contact of blood and body fluids, transfusion, and/or vertically
Can remain latent for years
Can cause severe and potentially life-threatening complications in high-risk groups
Immunosuppressed, fetuses/neonates, and marrow or solid organ transplant recipients
Screening: ELISA, fluorescence assay, indirect hemagglutination, and latex agglutination testing
Leukoreduction of blood products helps limit exposure
(transfusion transmitted diseases) epstein-barr virus (EBV)
Herpesviridae family, dsDNA virus
Acquired through infected saliva—”kissing disease"
Causative agent of infectious mononucleosis
Symptoms include sore throat, enlarged lymph nodes, fever, lethargy, and malaise
Bed rest and increased fluid intake resolves symptoms
Risk population: immunocompromised
Leukoreduction of blood products help limit exposure
(transfusion transmitted diseases) parvovirus B19
Parvovirus B19 is the only known pathogenic human parvovirus
Nonenveloped single stranded DNA virus
Enters the RBC via the P antigen
Infects RBCs and classified as an erythrovirus
Transmitted through the respiratory route
Associated with causing childhood illnesses such as erythema infectiosum or fifth disease
Resistant to pathogen inactivation
(transfusion transmitted diseases) human herpes virus 6 & 8
Human herpes virus 6 (HHV6)
Viral agent causes roseola infantum or sixth disease
Transmitted through saliva, respiratory route
Not known to be transmissible through blood transfusion
Human herpes virus 8 (HHV8)
Associated with Kaposi's sarcoma
Transmitted parenterally
Present in blood, and semen
Concern in immunosuppressed patients
(transfusion transmitted diseases) emerging viruses
Chikungunya Virus (CHIKV)
Enveloped ssRNA virus of the family Togaviridae
Transmitted through mosquito (Aedes family) bite
Not known to be transmissible through blood transfusion
Dengue Virus (DENV)
Enveloped ssRNA virus in Flavivirus
Transmitted through mosquito (Aedes family) bite
Concern in immunosuppressed patients
(transfusion transmitted diseases) prions
Infectious self-replicating proteins that convert normal proteins into abnormal structures
Group of diseases caused by prions called transmissible spongiform encephalitis (TSE)
Affect brain and neurologic function
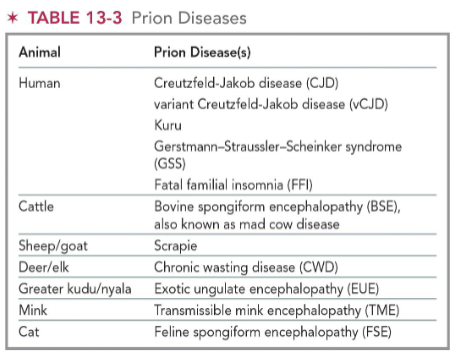
(transfusion transmitted diseases) creutzfeldt-jakob disease CJD
Transmitted through human-derived pituitary growth hormones, infected electrodes for EEGs, neurosurgical equipment, and some transplant materials (cornea or dura mater)
Symptoms:
Rapidly progressing dementia, poor coordination, visual problems, and involuntary movements
All cases eventually fatal
(transfusion transmitted diseases) vCJD
Fatal neurological disease
Symptoms similar to classic CJD
Occurs in persons younger than 55 yrs old
Classic CJD disease primarily seen in elderly persons
Transmissible through blood transfusion
bacterial contamination of blood products
Rare occurrence in RBCs/plasma
Contamination during venipuncture at time of collection or manufacture and handling of blood components
Donor with asymptomatic bacteremia
High incidence of morbidity and mortality can lead to sepsis
Immediate antibiotic treatment recommended
bacterial contamination in platelet products
Platelet products frequently implicated in transfusion-transmitted bacteremia (1 in 2,000)
Staphylococcus,Yersinia, Pseudomonas, Serratia, Enterobacter, Bacillus and Salmonella, etc. have been identified in blood products
Pathogen reduction methods (platelets):
Riboflavin +UVA/UVB
Cerus INTERCEPT: Psoralen + UVA (FDA approved)
UVC light + agitation
Other method: leukoreduction, decontamination
(transfusion transmitted diseases) syphilis
Infection caused by spirochete Treponema pallidum
Spread through sexual contact
Transfusion-transmitted syphilis is rare
Screening: syphilis antibody EIA, FTA-ABS, TP-PA
Positive: 3 months deferral
(transfusion transmitted diseases) lyme disease
Spread by tick bite
Causative agent: spirochete, Borrelia burgdorferi
No cases of transfusion-transmitted Lyme disease have been reported
(transfusion transmitted diseases) babesiosis
Caused: Babesia microti
Transmitted through deer tick bites and known to infect RBCs
Most infected persons are asymptomatic
Symptoms: fever, chills, lethargy, and hemolytic anemia
May be treated with antibiotics
Transfusion transmission reported
Screening: NAT
Positive: 2-year deferral
(transfusion transmitted diseases) chagas disease
Cause: flagellate protozoan Trypanosoma cruzi
Transmitted through bite of reduviid bug
Disease not common in U.S. ; prevalent in Mexico, Central and South America
Screening: antibodies, enzyme strip assay (ESA), one time only
If not properly treated, cardiac problems and other complications can be fatal
Parasite resistant to refrigeration, cryopreservation procedures, and thawing
Positive: permanent deferral
(transfusion transmitted diseases) malaria
Caused: Plasmodium sp parasite
Found mainly in Africa, Asia, and Latin America
Transmitted through mosquito bite
Symptoms: fevers, lethargy, hemolysis or RBCs with resulting anemia
Prognosis good if treated promptly
Screening positive: 3 years deferral
Travel: 3 months deferral
(transfusion transmitted diseases) leishmaniasis
Caused: Leishmania
Transmitted by bite of infected sandfly
Transmitted in blood and body fluids and through blood transfusion
Endemic in Middle Eastern countries
Positive screen: permanent deferral
Travel: 1 year deferral
(transfusion transmitted diseases) toxoplasmosis
Cause: Toxoplasma gondii
Transmitted through undercooked meats and feces from farm animals and household pets
Invades the WBCs
Rare transmissions via blood transfusion reported
Positive: 6-12 months deferral
(transfusion transmitted diseases) risk reduction strategoies
Enhanced regulatory oversight of blood collection process
Establish stringent blood donor eligibility criteria
Tracking of infection rates for new and emerging pathogens
New blood donor screening assays under development
Development of pathogen inactivation methods (heat, organic solvents, and detergents)
Quarantine and Look-Back