Anterior Chamber & Iris
1/137
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
138 Terms
the AC is more shallow in the ____________
periphery
depth and diameter of AC
depth: 3.6 mm
diameter: 11-12 mm
how much fluid can the AC hold
120-170 microns
average IOP
15.5 mmHg
boundaries of AC
anterior: corneal endothelium
peripheral: TM, Schlemm’s canal, CB, iris root
posterior: anterior iris
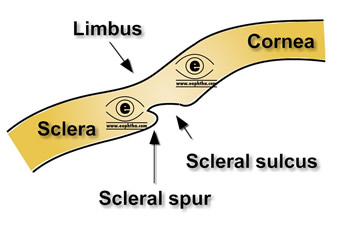
internal scleral sulcus
corneal scleral junction where the aqueous is filtered
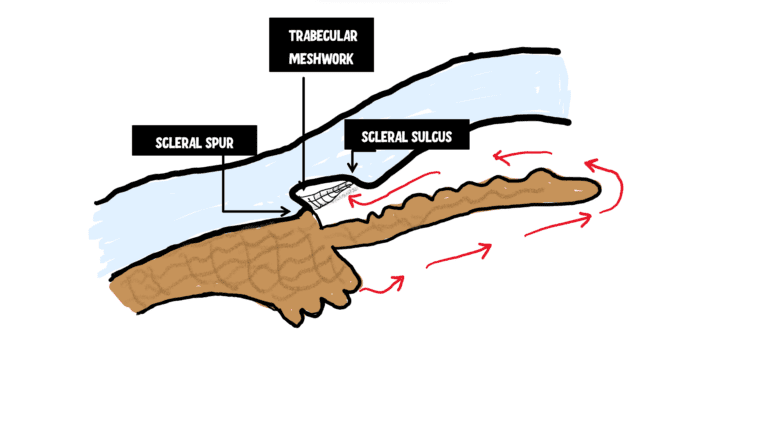
structures in the corneal scleral sulcus (back to front)
peripheral iris, ciliary body, scleral spur, TM, schlemm’s canal, schwalbe’s line
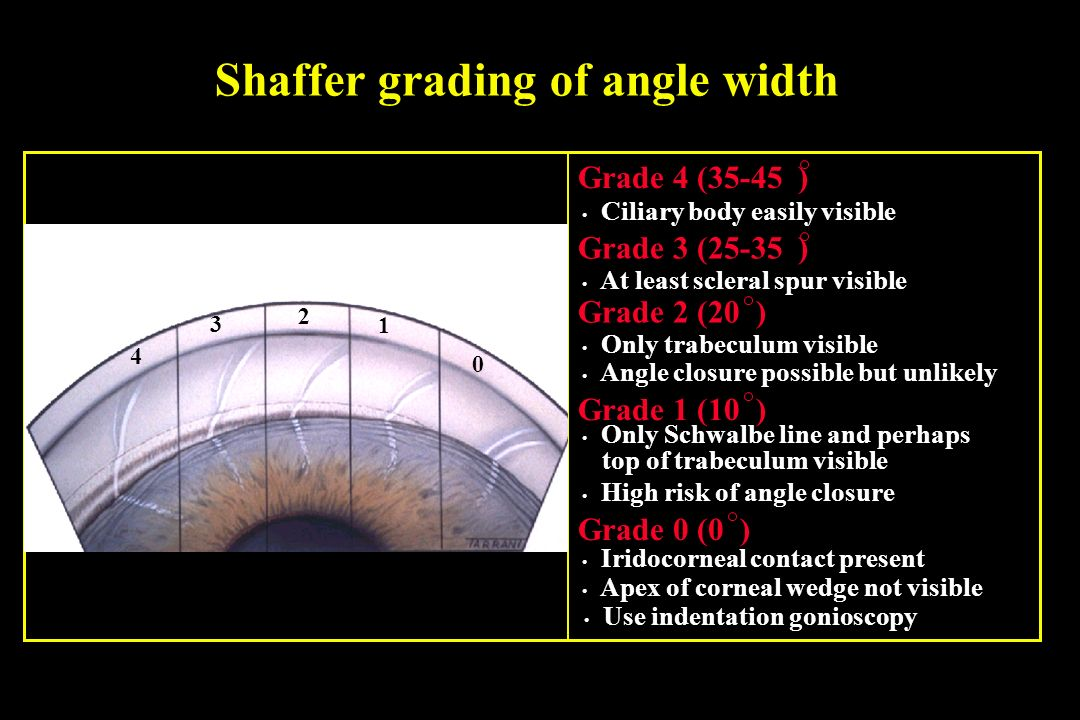
Becker-Schaffer grading system
grades the AC angle based on most posterior structure visible
Becker-Schaffer classification
grade 4: CBB
grade 3: SS
grade 2: 1/3-1/2 TM
grade 1: only anterior TM or Schwalbe’s line
grade 0: no structures visible
Van-Herick grading system
based on width of AC angle compared to width of optic section
Van-Herick classification
grade 4: 1/2-1
grade 3: 1/4-1/2
grade 2: ¼
grade 1: less than ¼
grade 0: no space visible
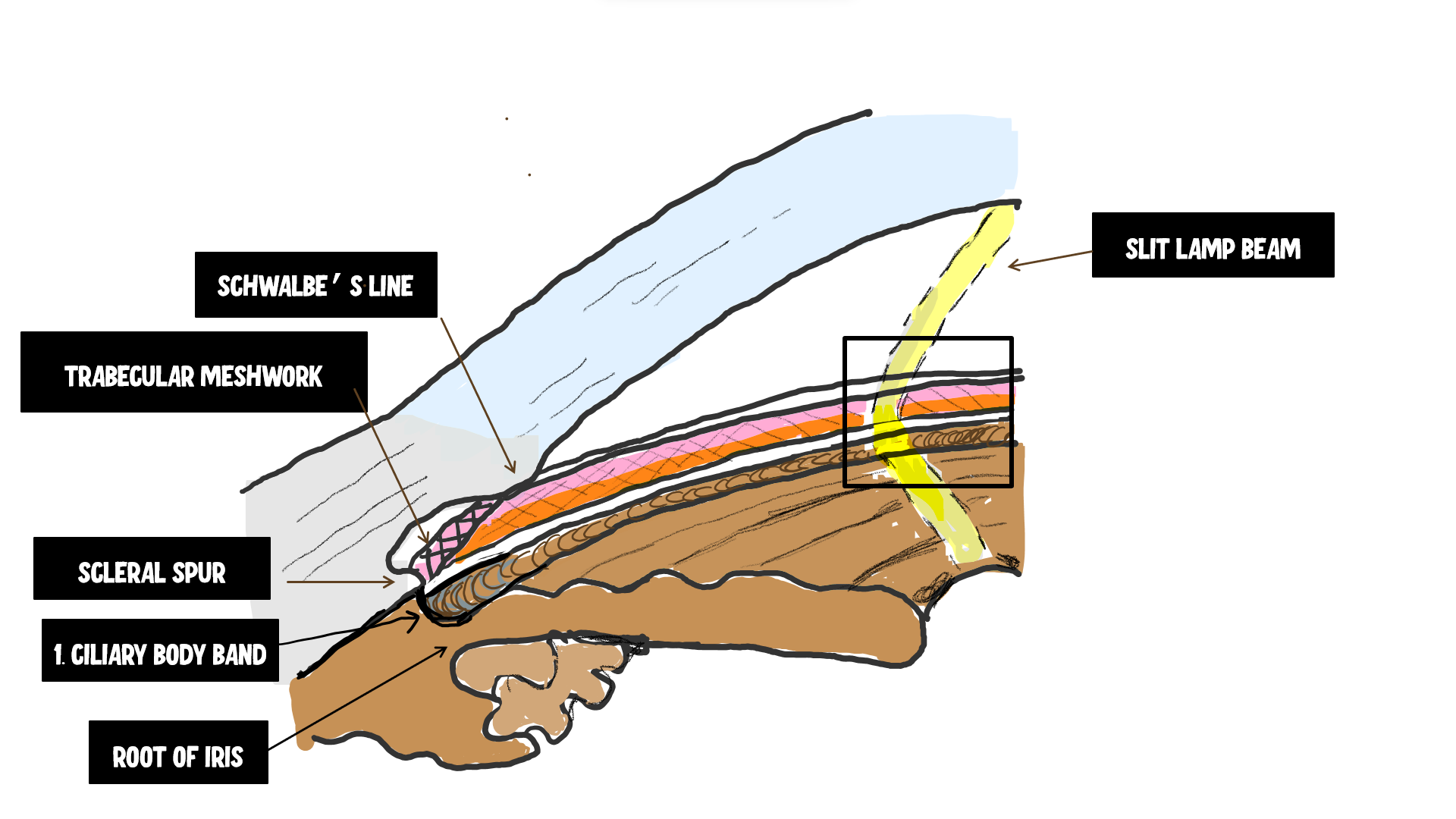
scleral spur
circular band of collagen and elastin that extends from the inner part of the sclera
what structures originate off of the scleral spur
posteriorly: longitudinal ciliary muscle fibers
anteriorly: TM lamellae
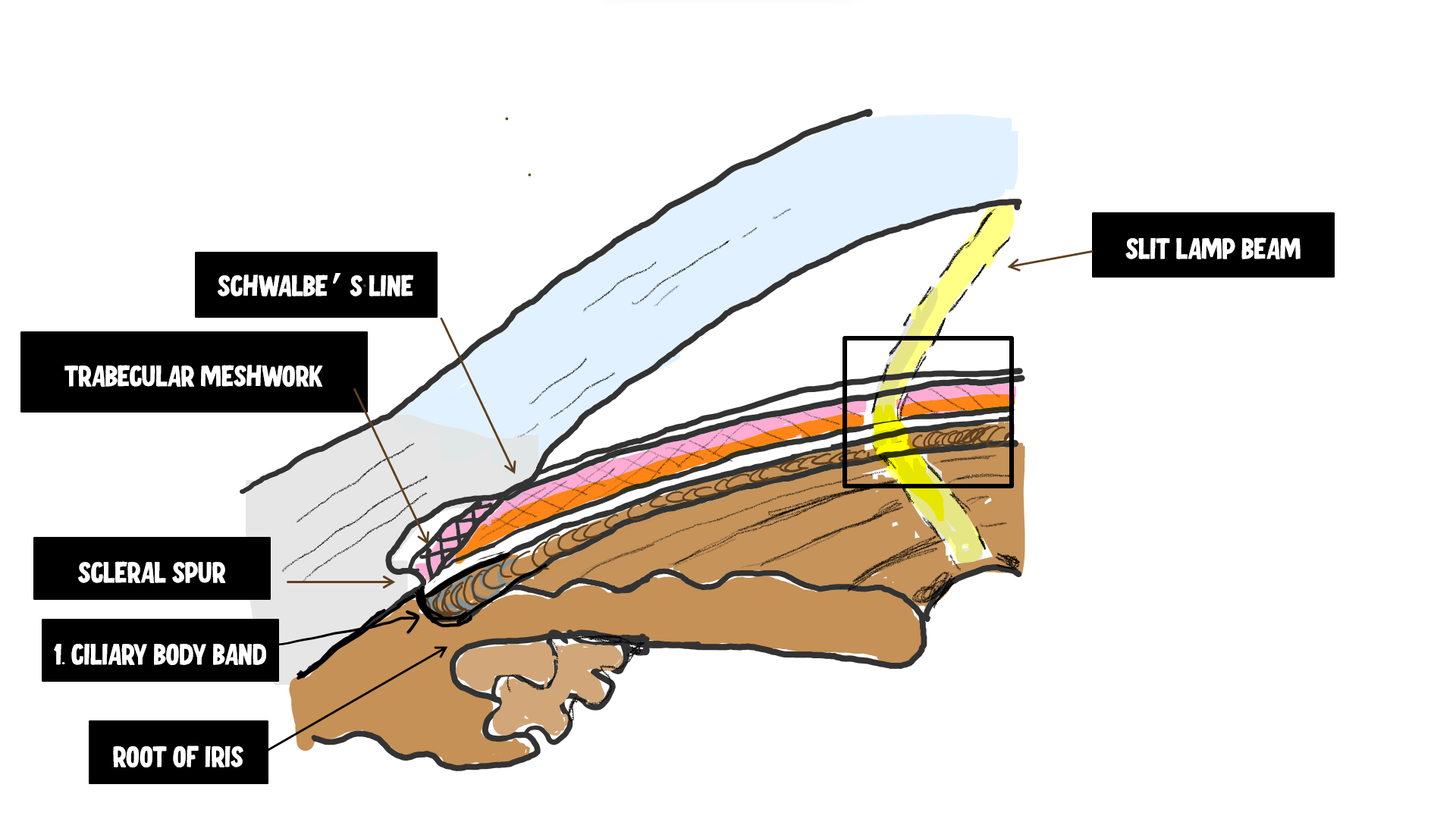
what parts of the sclera contain elastin
scleral spur, lamina cribrosa, lamina fusca
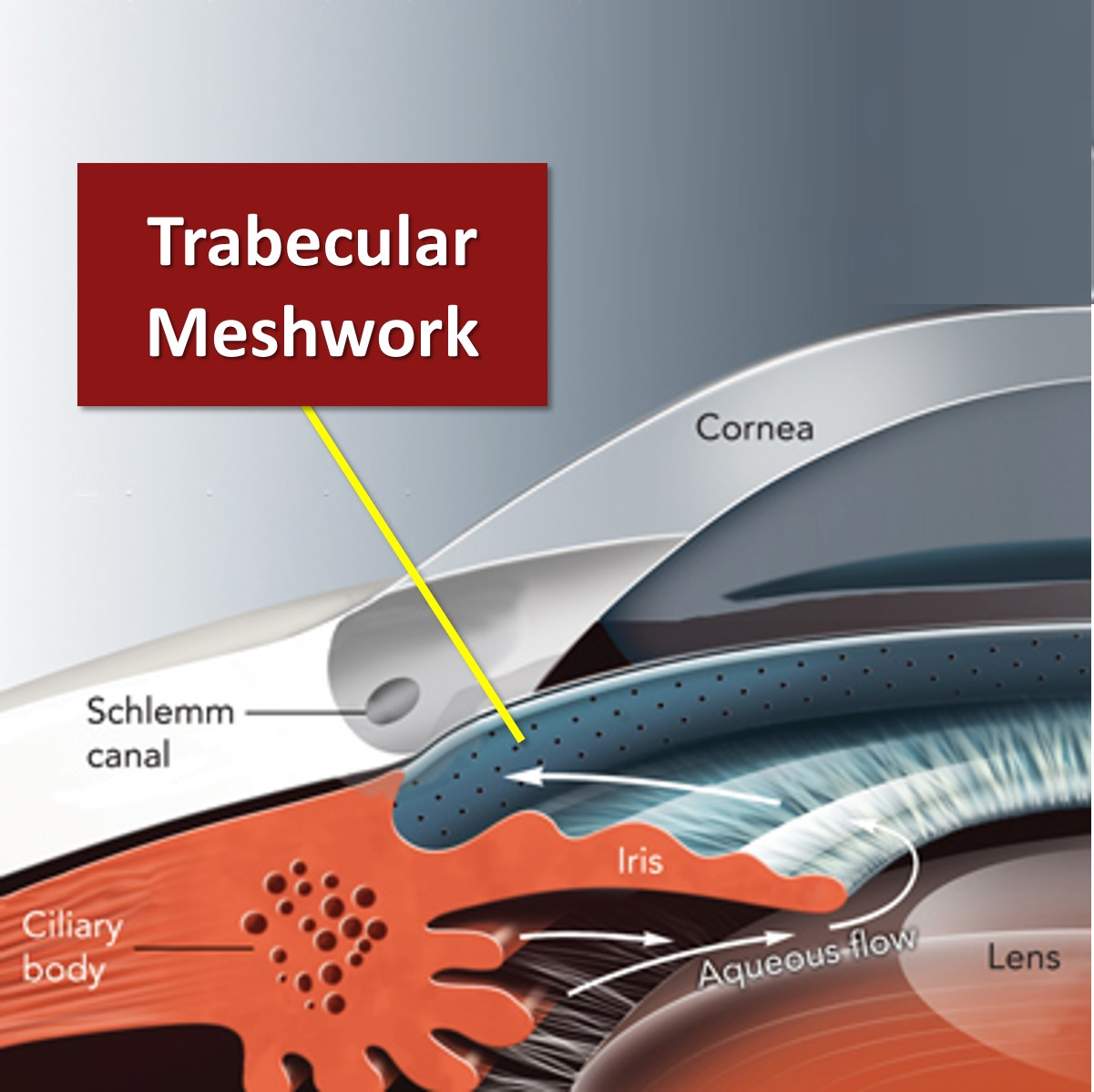
what is the major role of the TM
aqueous humor filtration
shape and positioning of TM
lines the AC circumferentially
triangular: base abuts scleral spur and apex points towards cornea and Schwalbe’s line
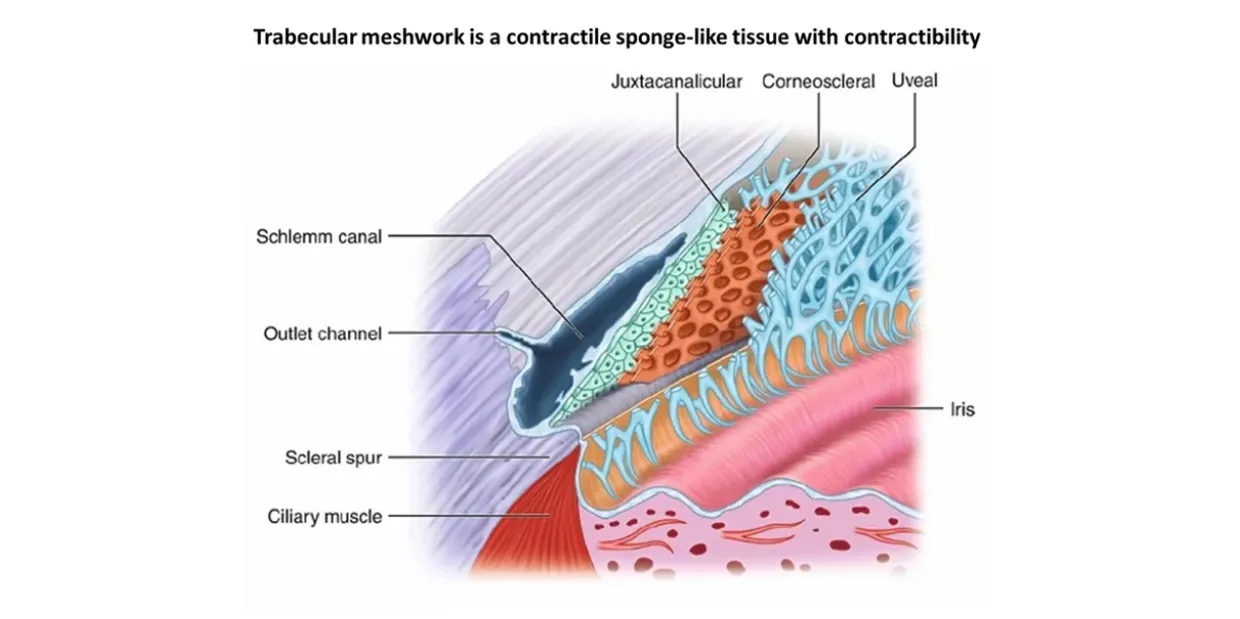
what lines the external border of TM
juxtacanalicular tissue
where is the greatest amount of pigment in the TM
inferior part of angle
where is the best place to start gonio and why
inferiorly
TM has most pigmentation there
layers of TM (inner to outer)
uveoscleral meshwork > corneoscleral meshwork > juxtacanalicular tissue
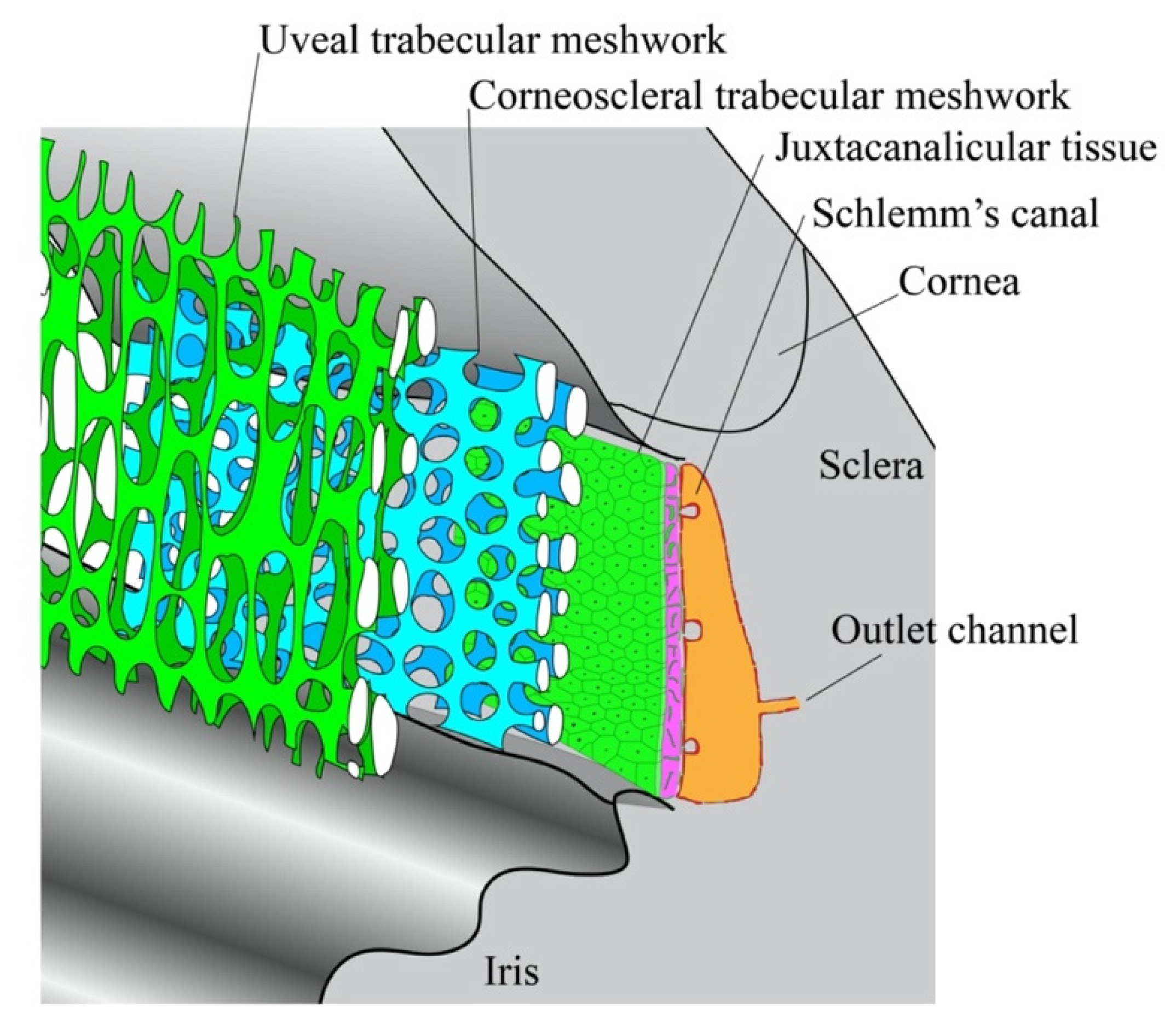
2 divisions of TM
uveoscleral meshwork
corneoscleral meshwork
the uveoscleral meshwork is the (innermost/outermost) layer of the _____, consisting of (large/small) pores and ___ number of layers
the uveoscleral meshwork is the innermost layer of the TM, consisting of large pores and 1-5 layers
layer of TM inward to the scleral spur and adjacent to the AC
uveoscleral
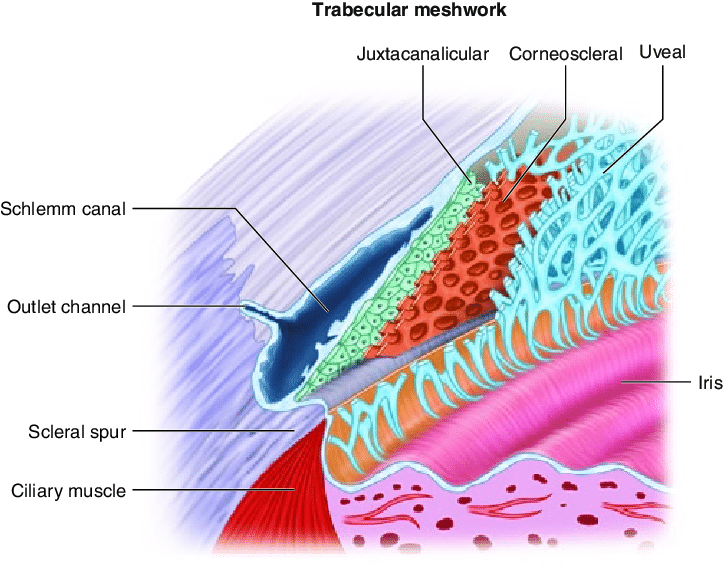
composition of uveoscleral meshwork
large pores in a network of cords
inner core of collagen, elastin, and ground substance
surrounded by endothelium and BM
role of endothelial cells in uveoscleral meshwork
protein synthesis
lysozymes for phagocytosis of melanin and debris
uveoscleral meshwork (DOES/DOES NOT) use schlemm’s canal for outflow
does not
the uveoscleral meshwork is pressure (dependent/independent)
independent
2 possible paths of aqueous humor drainage in uveoscleral outflow
AH flows between the ciliary muscle fibers, into the suprachoroidal space, and through the sclera
AH drains through the anterior ciliary veins or vortex veins
what % of aqueous outflow is the uveoscleral meshwork responsible for
5-35%
how do prostaglandins increase uveoscleral outflow
decrease resistance in uveoscleral meshwork by relaxing the ciliary muscle and changing the ECM to increase uveoscleral outflow
the corneoscleral meshwork is located (closer/further) from Schlemm’s canal than the uveoscleral meshwork
closer
what 2 structures does the corneoscleral meshwork extend between
scleral spur and cornea
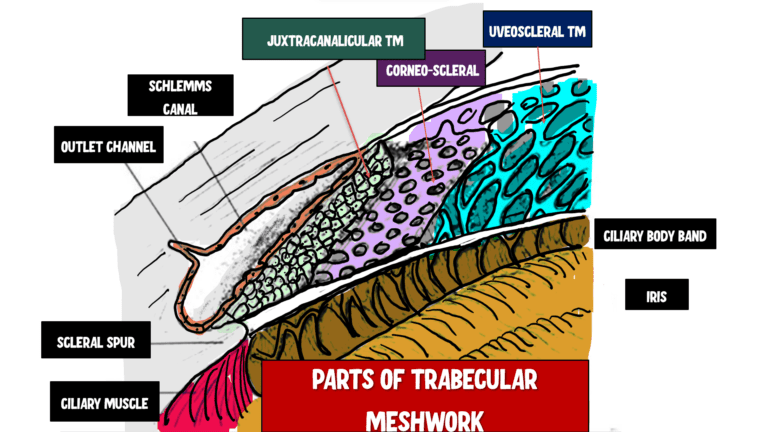
the corneoscleral meshwork consists of the (inner/outer) ____ (number) layers of the TM
outer 8-15 layers
composition of the corneoscleral meshwork
small pores within a network of sheet-like fibers similar to the uveoscleral cords
where are the smallest pores in the TM located
closest to Schlemm’s canal and within the juxtacanalicular tissue
other name for juxtacanalicular tissue
cribriform layer
what separates Schlemm’s canal from TM
juxtacanalicular tissue
what is juxtacanalicular tissue composed of
endothelial cells and ECM
what is the site to most resistance to outflow in the TM and why
juxtacanalicular tissue
has the fewest and smallest pores
why is the outflow of the corneoscleral meshwork pressure dependent
to penetrate the endothelial tight junctions that line Schlemm’s canal and the endothelial cells that fill the lumen, the IOP has to be higher than the episcleral venous pressure
AH must use high to low pressure gradient
biggest difference between uveoscleral and corneoscleral meshwork
UM is pressure independent
CM is pressure dependent
what % of AH drains through Schlemm’s canal
up to 90%
what is Schlemm’s canal
circular venous channel lined by endothelial cells where most AH drains
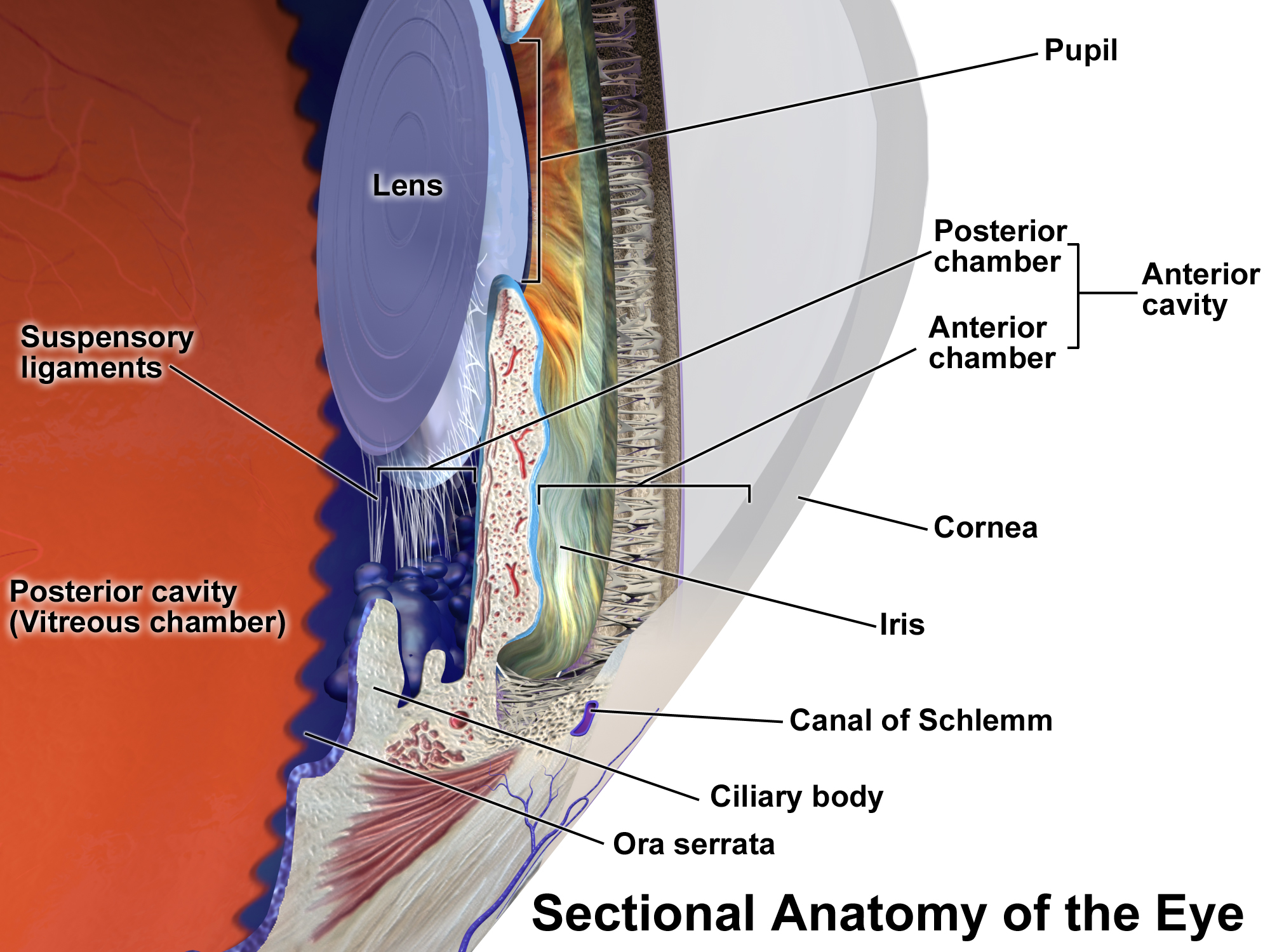
what structures are adjacent to the inner and outer border of Schlemm’s canal
inner border: (closest to AC, deeper in the eye) against scleral spur and TM (juxtacanalicular tissue)
outer border: against the sclera near the limbus
what are the walls of Schlemm’s canal lined with
endothelial cells
what is the difference between the linings of the inner and outer walls of Schlemm’s canal
endothelial cells of inner wall contain giant vacuoles that transport AH across the JXT into the canal
endothelial cells of outer wall do not have vacuoles, but the outer wall has a thin CT covering and efferent vessels that drain the AH out of the eye
what is the purpose of CT septae in Schlemm’s canal
form multiple channels that increase the surface area for AH filtration
internal collector channels
channels formed by CT septae that increase the surface area in Schlemm’s canal for AH filtration
what ultimately drains AH out of the eye
episcleral venous plexus
2 routes AH can drain out of Schlemm’s canal
external collector channels (efferent vessels) > deep scleral venous plexus > intrascleral venous plexus > episcleral venous plexus
aqueous veins of ascher > episcleral venous plexus
path of episcleral venous plexus drainage to heart
episcleral venous plexus > anterior ciliary veins > muscular veins > superior/inferior ophthalmic veins > cavernous sinus > superior/inferior petrosal sinus > internal jugular vein > brachiocephalic vein > superior vena cava > right atrium of heart
where does episcleral venous plexus directly drain to
anterior ciliary veins
Schwalbe’s line represents termination of _________
descemet’s membrane
what is Schwalbe’s line
area of collagenous CT that represents termination of Descemet’s membrane and delineates outer area of the limbus
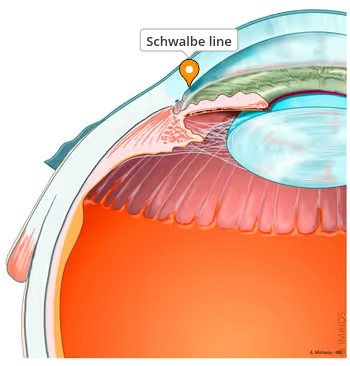
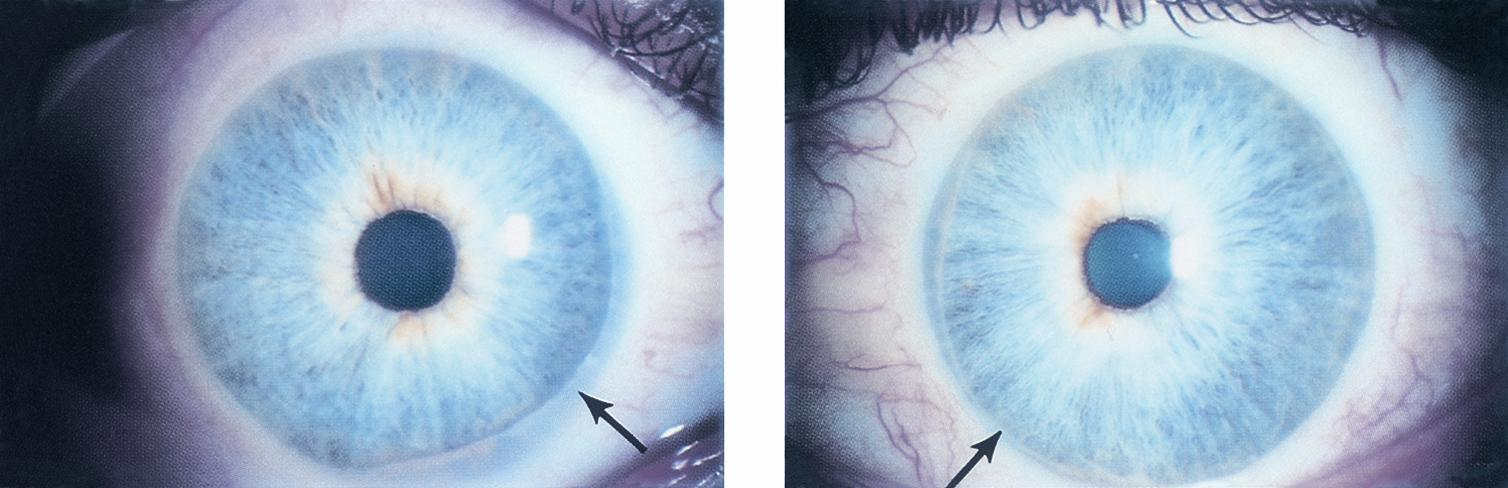
posterior embryotoxon
anteriorly displaced Schwalbe’s line
iris
circular structure dividing anterior and posterior chambers
pupil location
opening in iris slightly nasal and inferior to center
pupil diameter under normal illumination
3-4 mm
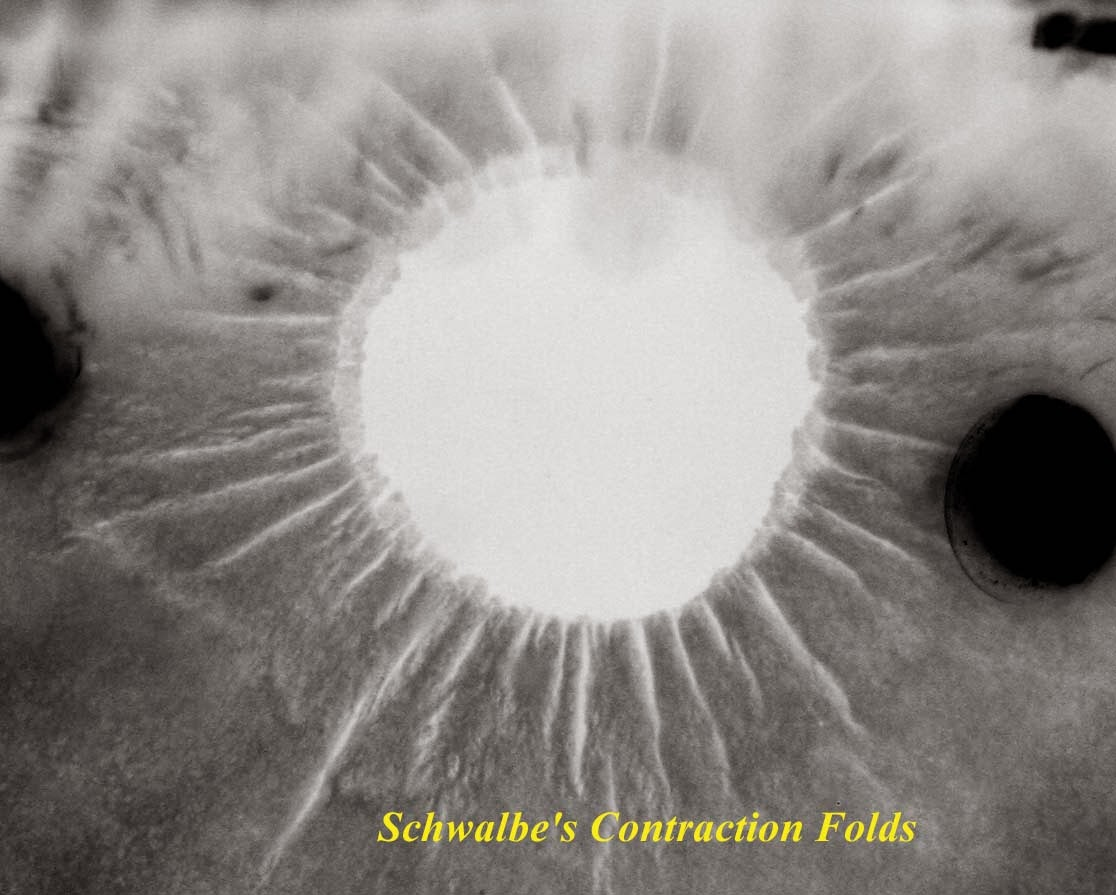
Schwalbe’s contraction furrows
located at pupillary margin of iris
variations in thickness of posterior pigmented iris epithelium

average iris width
12 mm
where is the iris thickest
collarette region
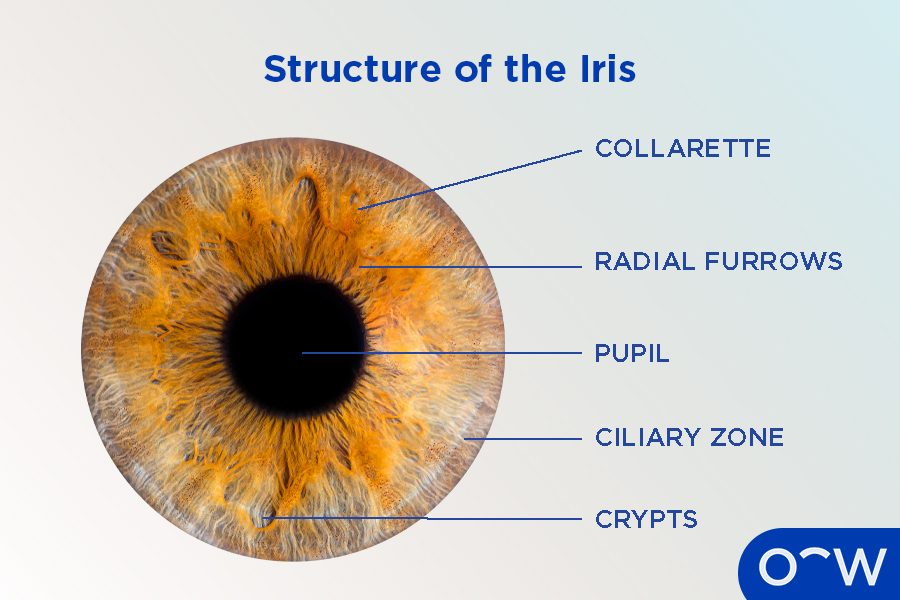
where is iris thinnest
iris root (0.5 mm)
collarette
circular ridge 1.5 mm from pupillary margin that is site of attachment for fetal pupillary membrane during embryogenic development
has active iris vessels and remnants of old fetal vessels
what divides the iris into pupillary and ciliary zones
collarettes

2 zones of the iris
pupillary zone, ciliary zone
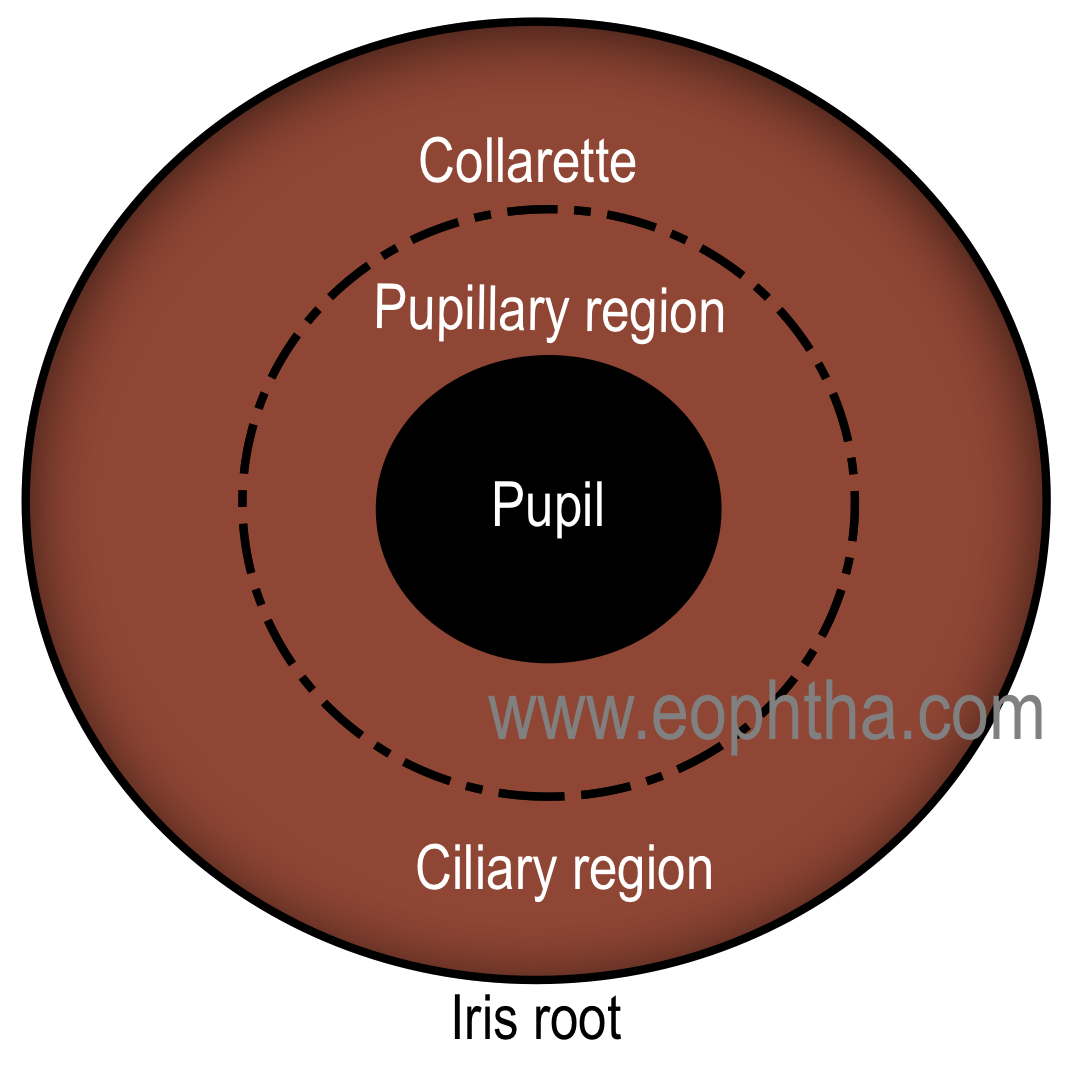
ciliary zone of iris
has iris furrows that allow iris tissue to bunch towards periphery during dilation
has radial streaks that are white and represent collagen in the iris vessels
radial streaks of iris
in ciliary zone, collagen in the iris vessels
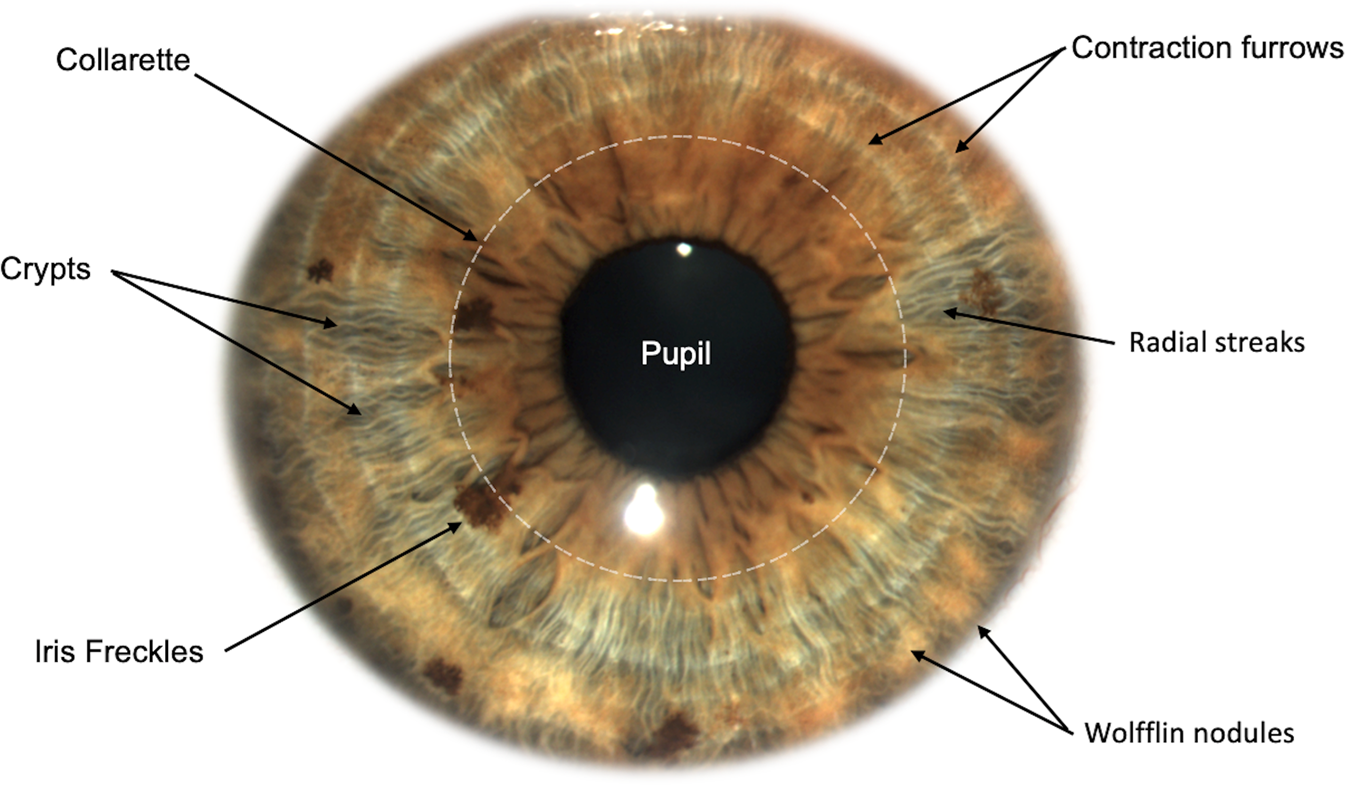
difference between ciliary zone and pupillary zone of iris
pupillary zone has smaller radial streaks because iris BVs are smaller towards the pupillary margins
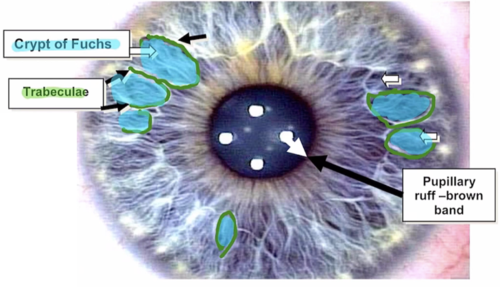
location of crypts of Fuchs
anterior border layer of iris
span the collarettes into pupillary and ciliary iris zones
aniridia
bilateral condition with complete or partial absence of iris
patients have poor vision (foveal hypoplasia), subsequent nystagmus
can also have microcornea, lens subluxation, and ON hypoplasia
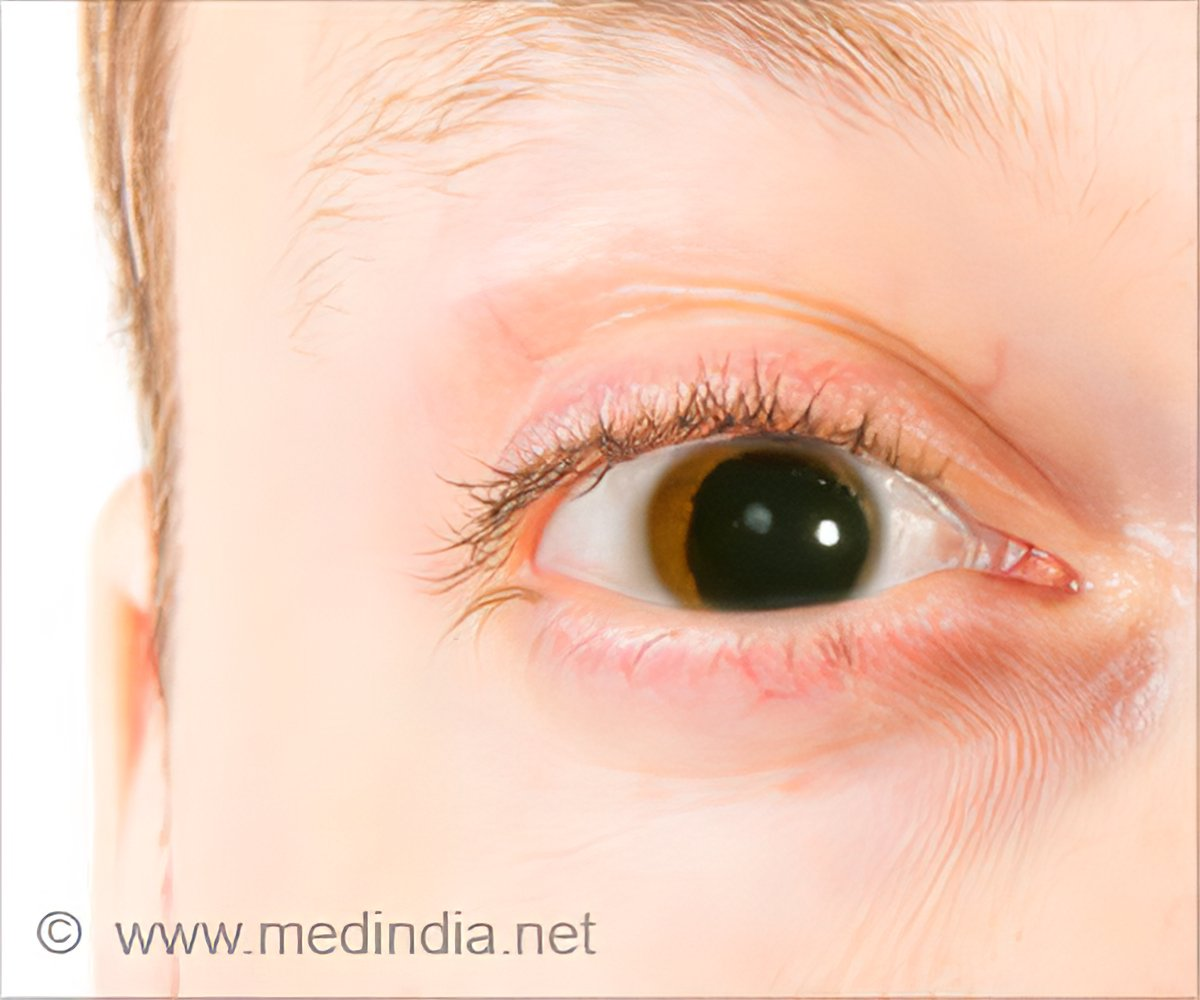
disease highly associated with aniridia and why
glaucoma
PAS can cause angle closure
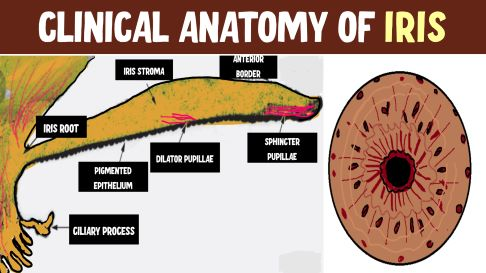
layers of iris front to back
anterior border layer, iris stroma, anterior epithelium & dilator muscle, posterior pigmented epithelium
anterior layer of iris
anterior border layer
contents of anterior border layer of iris
fibroblasts, melanocytes, collagen fibrils
function of anterior border layer of iris
provides colors to iris
what determines iris color
amount of melanin in iris melanocytes
not the number of melanocytes
in a blue iris, anterior border is (thick/thin) and melanocytes have ___________
anterior border is thin
melanocytes have a small amount of melanin
in a brown iris, anterior border is (thick/thin) and melanocytes have ___________
anterior border is thick
melanocytes have a large amount of melanin
what color of irises have heavily pigmented two iris epithelial layers
both brown and blue irises
condition characterized by a lack of pigment in the iris epithelial layers
oculocutaneous albinism
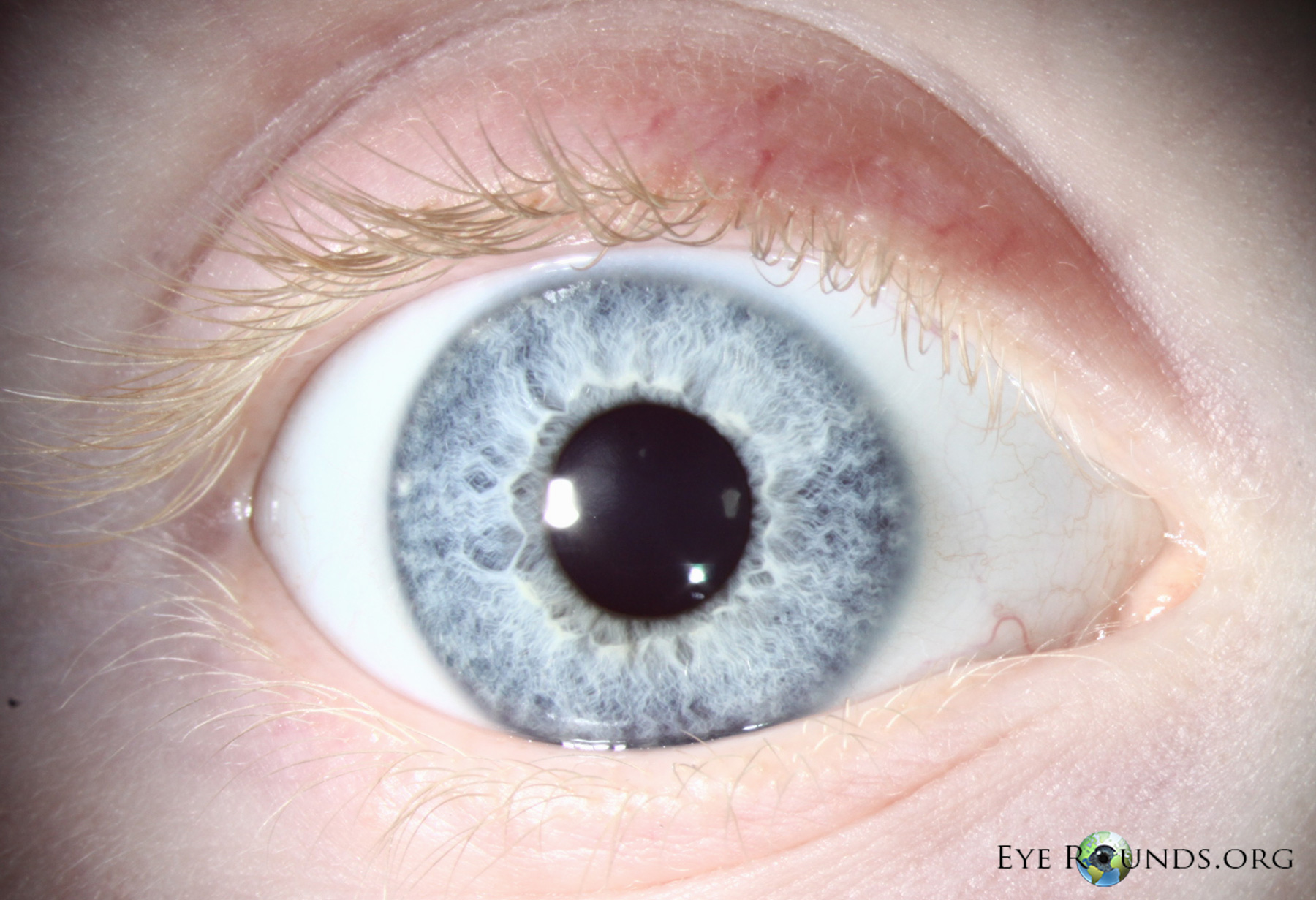
what are iris crypts
collagenous columns in the anterior border layer that serve as passageways for AH to enter the iris stromah
heterochromia
difference in eye color between eyes
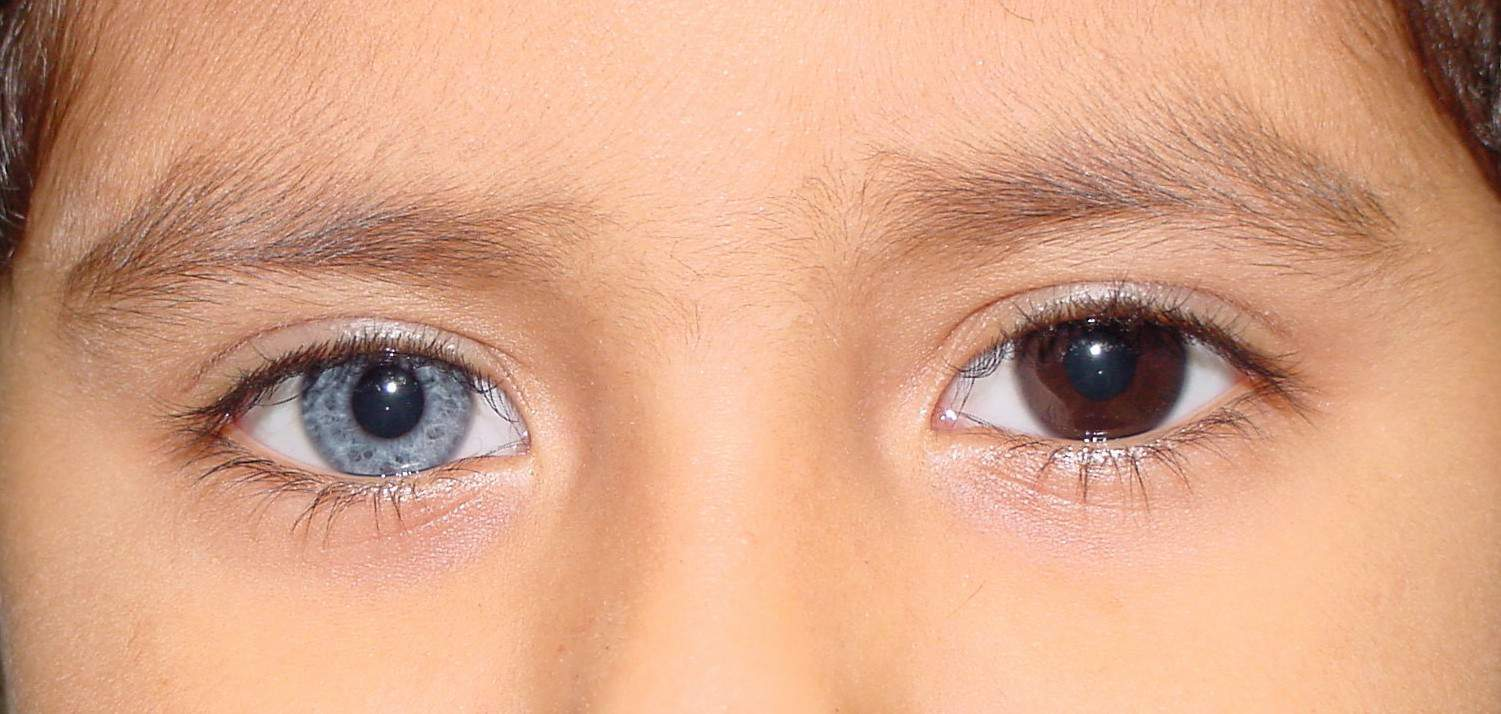
what can cause heterochromia
congenital
topical prostaglandins
chronic inflammation (uveitis)
what is the iris stroma composition
vascularized loose collagen network
iris stroma has (more/less) cells than the anterior border layer
less
iris stroma is continuous with the stroma of the ____________
ciliary body
what is contained in the iris stroma
cells, nerves, blood vessels, sphincter muscle
nerves in the iris stroma
LPCNs and SPCNs
sensory fibers and sympathetic fibers of the LPCNs and SPCNs
parasympathetic fibers of the SPCNs
what kind of blood vessels are in the iris stroma (and their junctions) and what do they form
non-fenestrated BVs with zonula occludens junctions
form part of the blood-aqueous barrier
what are the blood vessels in the iris
major arterial circle
minor arterial circle
radial veins and radial arteries
location of major arterial circle of iris
located in the ciliary body
extends radially through the iris stroma up to the pupil marginwh
what forms the major arterial circle of the iris
anastomoses between the ACAs and LPCAs
location of the minor arterial circle of the iris
located in the iris stroma near the pupil margin, inferior to the collarette
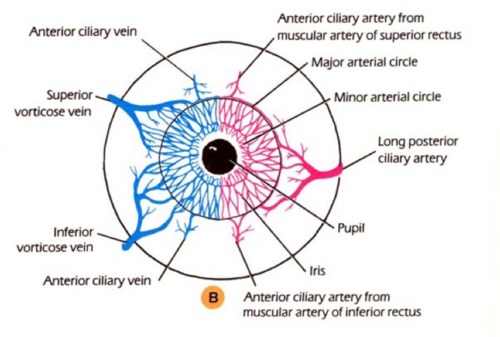
what forms the minor arterial circle of the iris
anastomoses of the radial arteries branching off the major arterial circle of the iris
what veins drain blood from the iris
radial veins
path of blood draining through radial veins
radial veins (blood from iris) > ciliary body veins > choroidal veins > vortex veins > superior/inferior ophthalmic veins
the minor arterial circle of the iris is (fenestrated/non-fenestrated) and makes up part of the ______________
non-fenestrated (doesn’t leak)
makes up part of the blood-aqueous barrier
what layer of the iris is the sphincter muscle in
stroma
what forms the iris sphincter muscle
anterior iris epithelial cells that detach and migrate into the stroma and become smooth muscle cells
what kind of muscle is the iris sphincter
circular smooth muscle