01.20 BIO How Scientists Work (ALL)
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

24 Terms
Scientific Method
A step by step method used to explain the natural world.
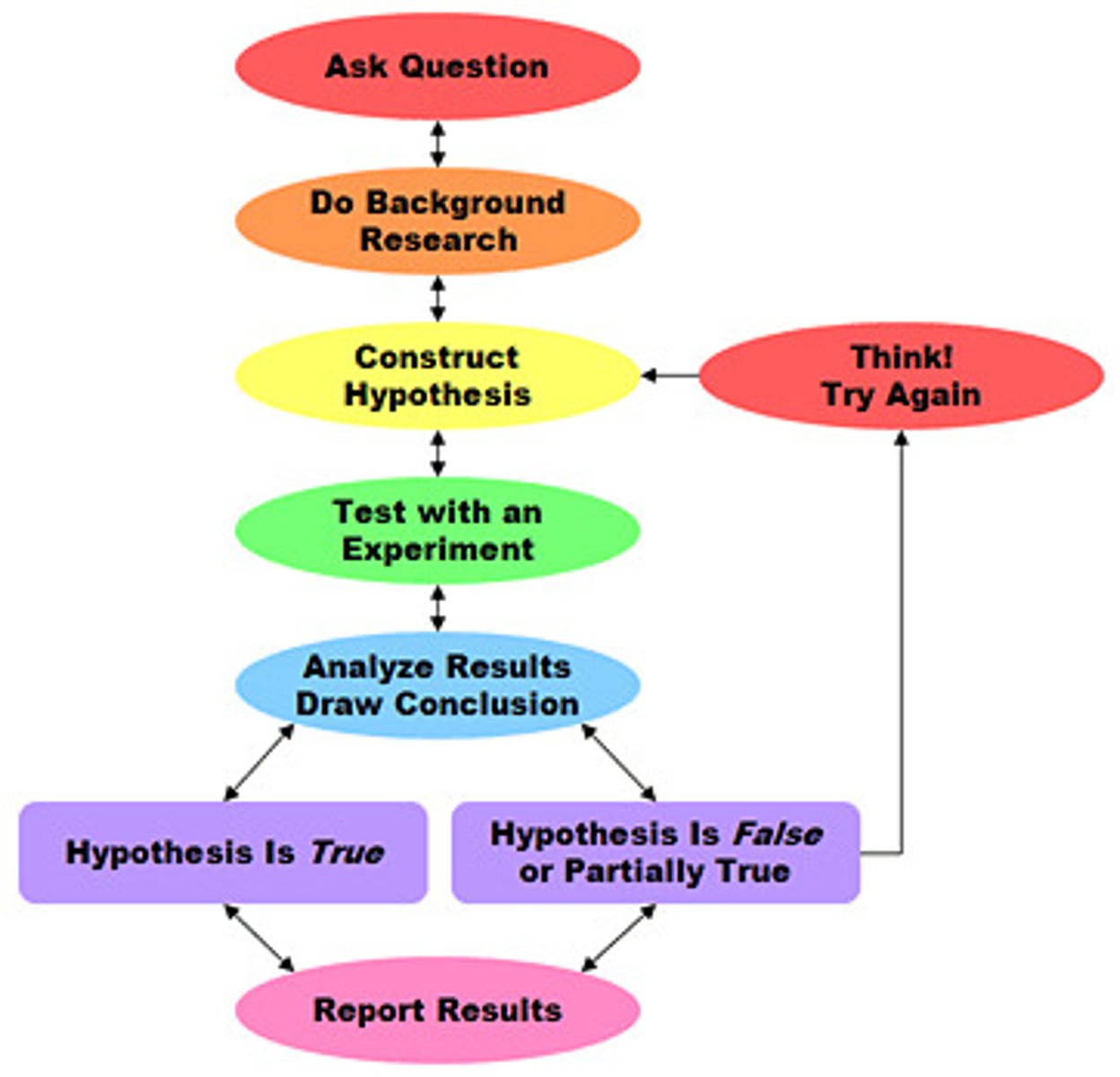
Make an Observation/Ask a Question (Scientific Method)
Make an observation and then ask a question about that observation. The first step of the scientific method. The first step of the scientific method.
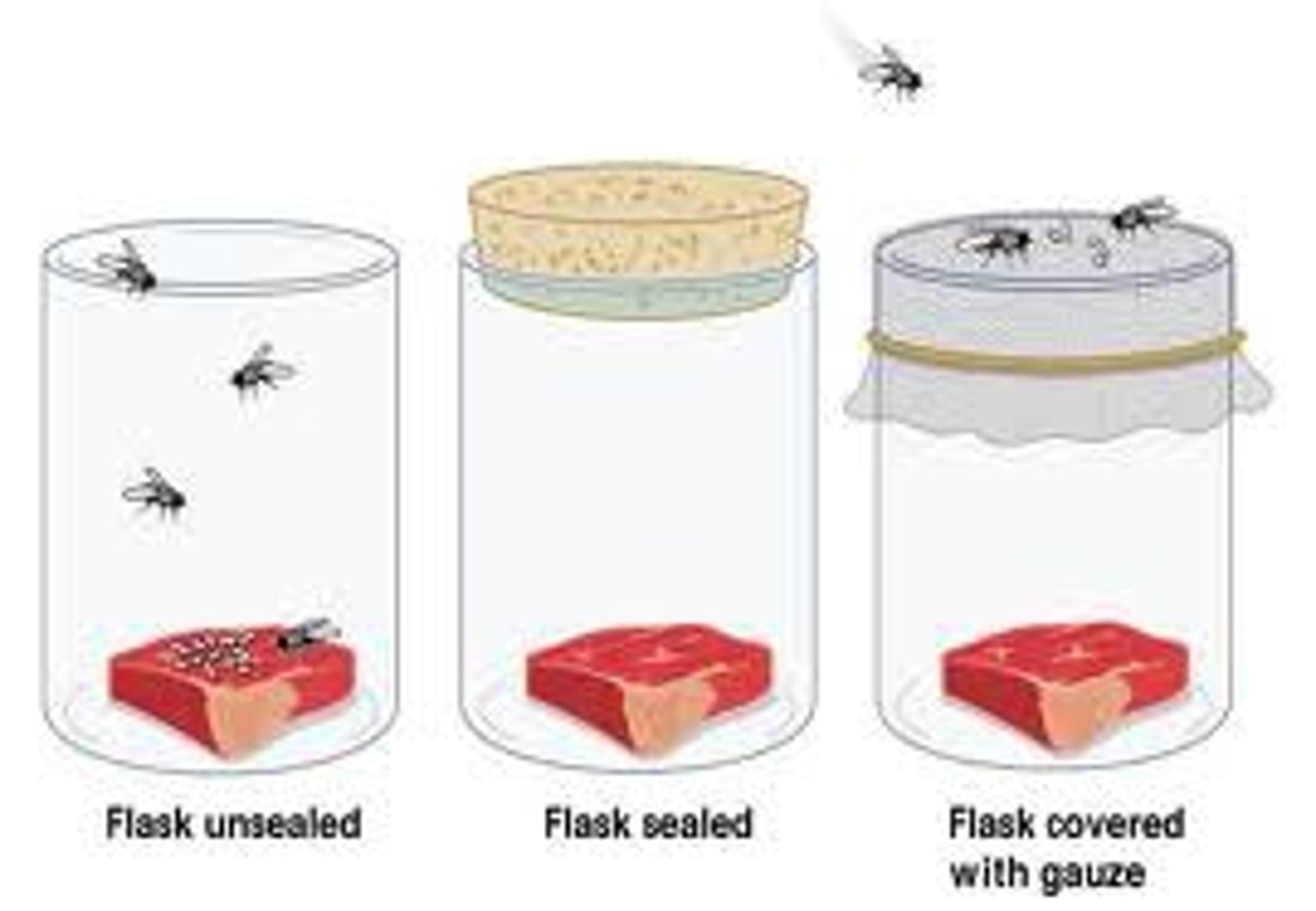
Controlled experiment
A scientific investigation in which both the control group and experimental group(s) are kept under the same variables EXCEPT for the ONE factor being studied so that the effect of that factor can be identified or determined
Do Background Research (Scientific Method)
Gather information about the topic that is being studied. The second step of the scientific method.
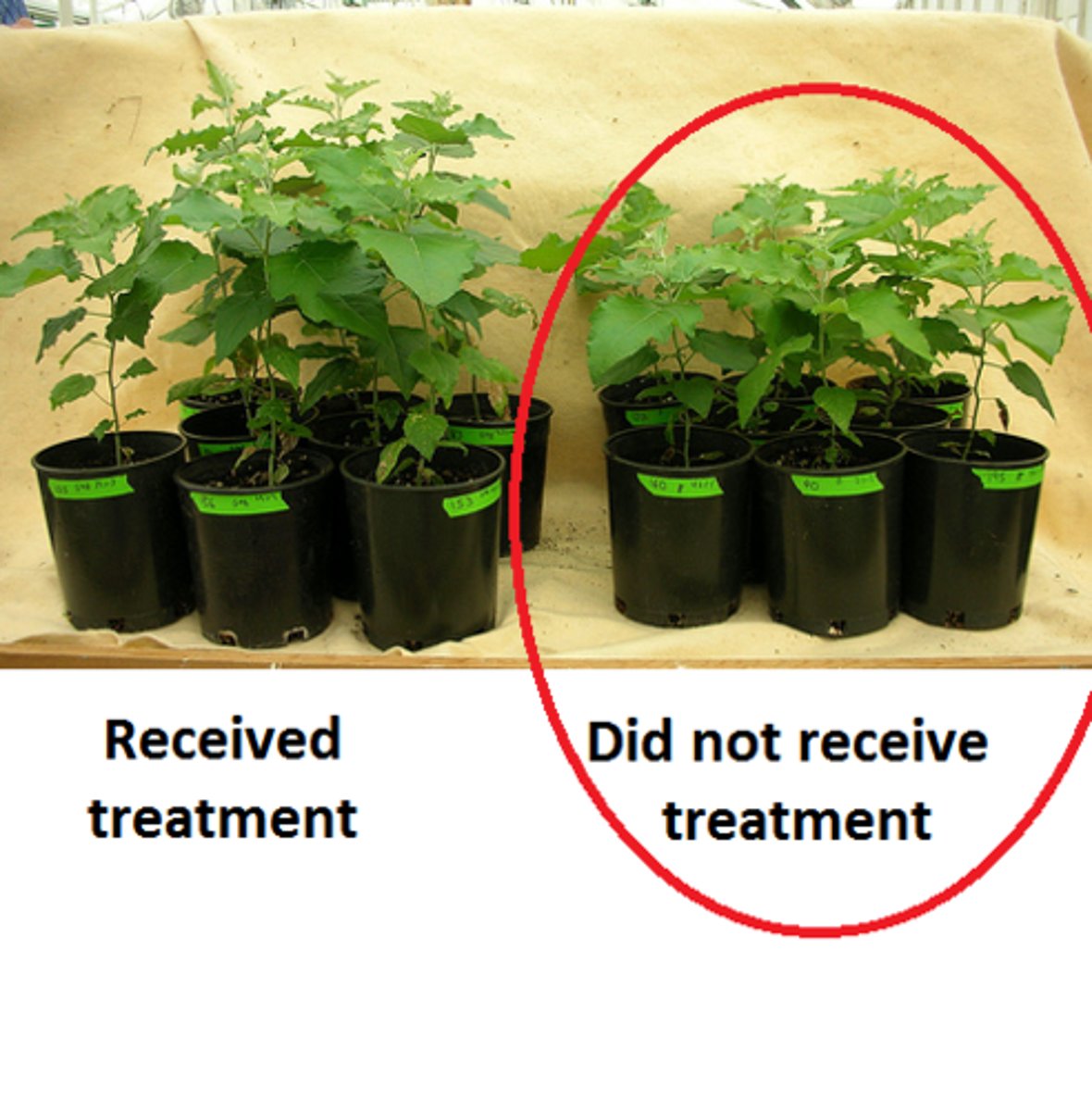
Control group
The group that does not receive the experimental treatment.

Construct a Hypothesis (Scientific Method)
An educated guess or prediction to a question that can be tested. The third step of the scientific method.
Experimental group
The group in which one variable is changed. The variable which is changed is called the independent variable. This groups' data is compared to the controls' group data
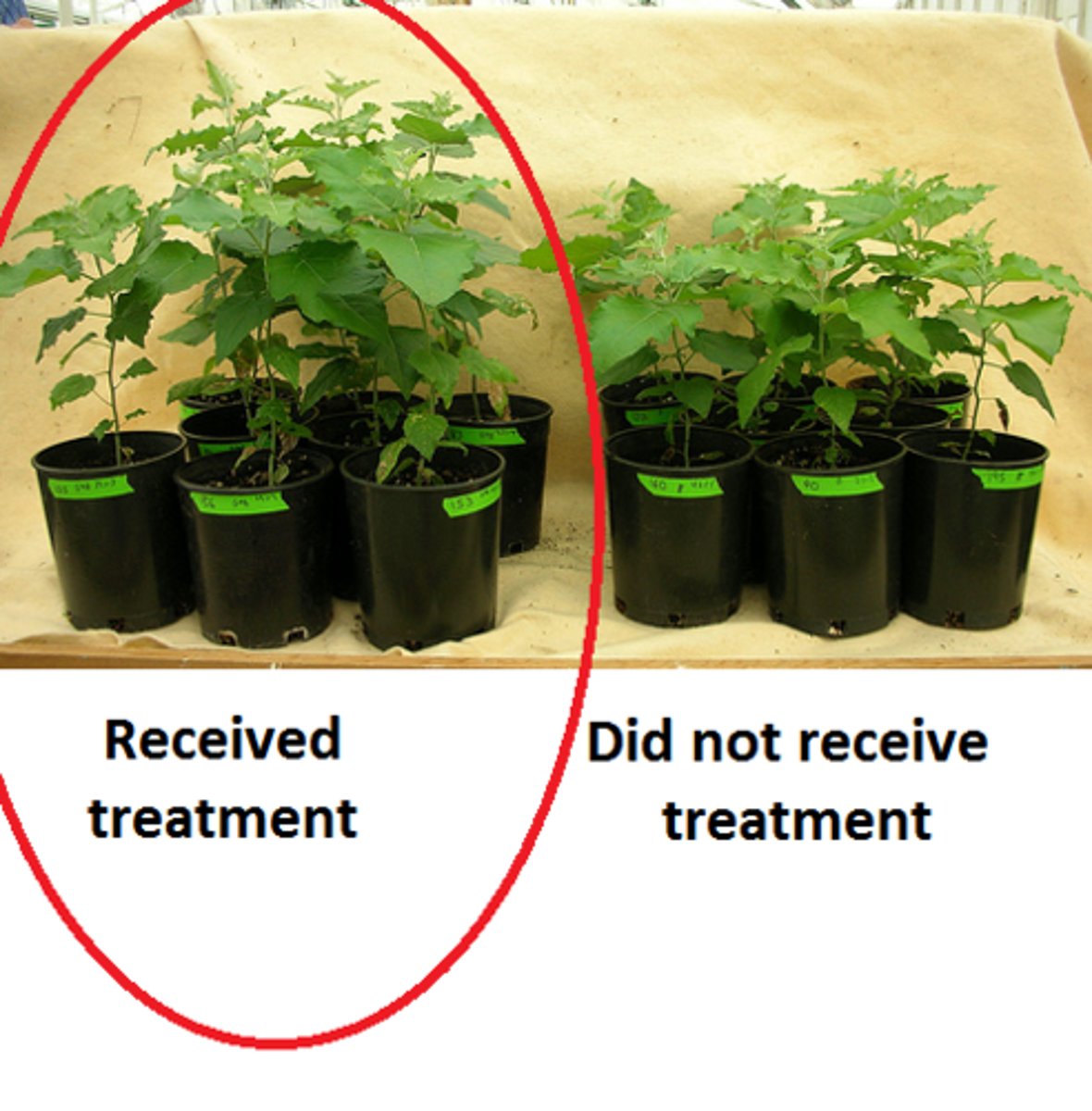

Test with a Controlled Experiment (Scientific Method)
A controlled way to test the hypothesis. The fourth step of the scientific method.
Analyze Data (Scientific Method)
Analyze the evidence gathered during an experiment that will help you decide if your hypothesis is supported or not. The fifth step of the scientific method.
Draw Conclusions (Scientific Method)
State whether your hypothesis is supported or not. If it is supported, repeat the experiment. If it is not supported, make a new hypothesis and test that with a new experiment. The fourth step of the scientific method.
Communicate Results (Scientific Method)
Share the results of the experiment with other scientists.
Variable
Anything in an experiment that can affect the outcome of the experiment.
Controlled variables
Factors that stay the same during the experiment
Independent variable /Manipulated variable
The variable the scientist changes or manipulates so that it can be tested. Expressed after the word IF in your hypothesis. Can be referred to as the manipulated variable
Dependent variable / Responding variable
The variable that is measured and expressed after the word THEN in your hypothesis. This is the data you collect. Think "D" for dependent = data
Hypothesis (Description)
An educated guess about a possible solution to a problem that is expressed in an IF , THEN ... BECASUSE statement. i.e. If (insert independent variable), then (insert dependent variable) BECAUSE. . ..

Inference
A conclusion based on the observations using reasoning skills, previous experiences, and opinions.
Theory
A well-tested hypothesis that explains observations. and lets scientists make predictions. It allows you to explain other natural phenomena.
Quantitative data
Data that is measured and expressed in numbers that include records or time, temperature, mass, distance, and volume

Qualitative data
Data that is collected using your senses.

Sample size
The number of times data is collected in an experiment.
Table
A chart to organize and record measurements that you make
Bar graph
A graph that uses thick bars to compare the frequency of data (how often something occurs) or to show comparisons among data that does NOT continuously change.
Line graph
A graph that shows relationships between variables that change over time