ALDEHYDES & KETONES
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Definition of Aldehydes and Ketones
Compounds containing a carbonyl group (C=O).
Aldehydes: RCHO.
Ketones: R1COR2.
Carbonyl Group Characteristics
Composed of a sigma (σ\sigma) and pi (π\pi) bond. Polar due to oxygen's electronegativity.
Naming Aldehydes
Replace "-e" of parent alkane with "-al" (e.g., methanal).
Naming Ketones
Replace "-e" of parent alkane with "-one" (e.g., propanone).
Physical Properties of Carbonyl Compounds (Aldehyde & Ketone)
Higher boiling points than alkanes, lower than alcohols.
Soluble in water up to 2–3 carbons due to hydrogen bonding.
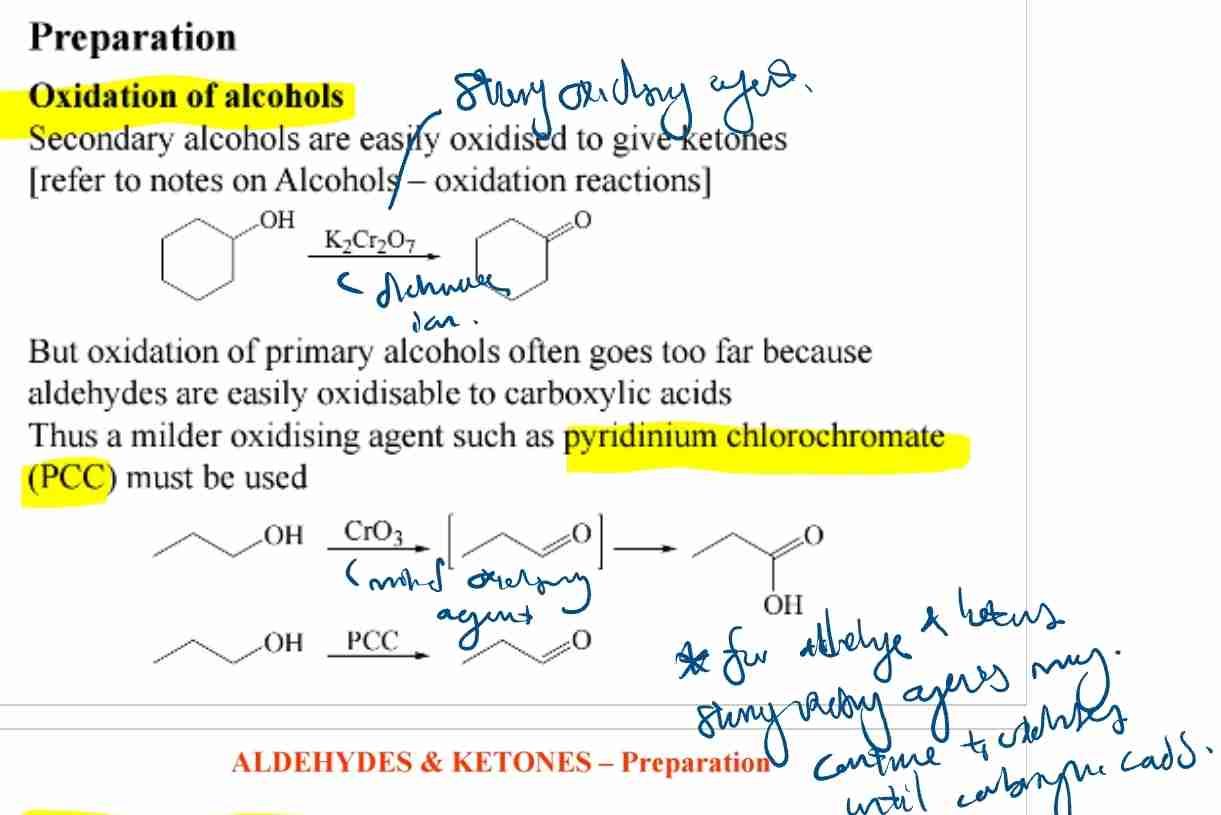
Preparation of Carbonyl Compounds: Alcohol Oxidation
Primary alcohols → Aldehydes (mild oxidants like PCC).
Secondary alcohols → Ketones.
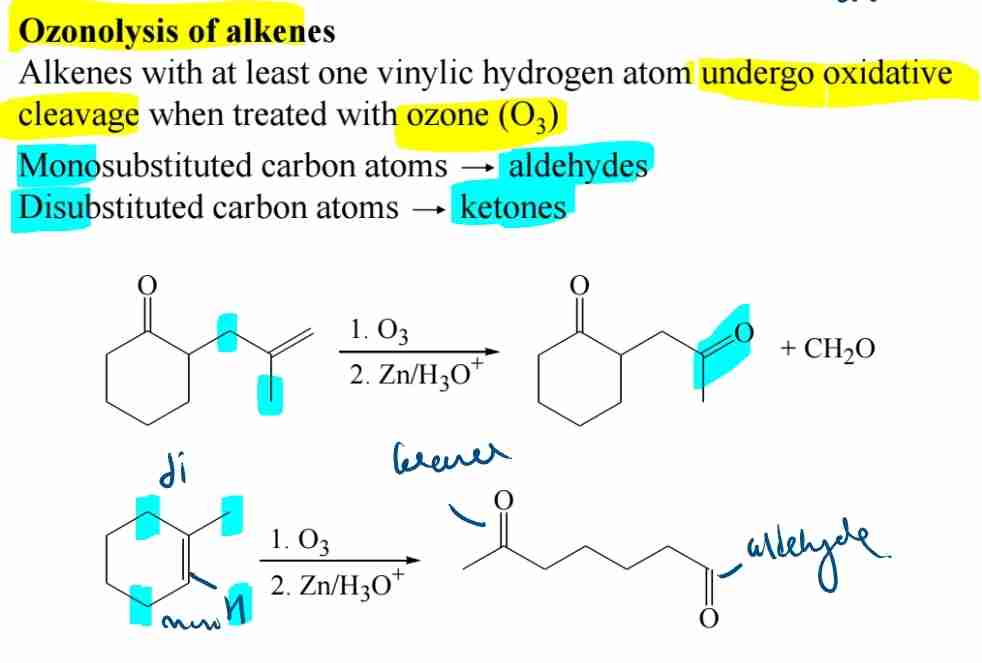
Preparation of Carbonyl Compounds: Ozonolysis of Alkenes
Cleavage forms aldehydes and ketones depending on substitution.
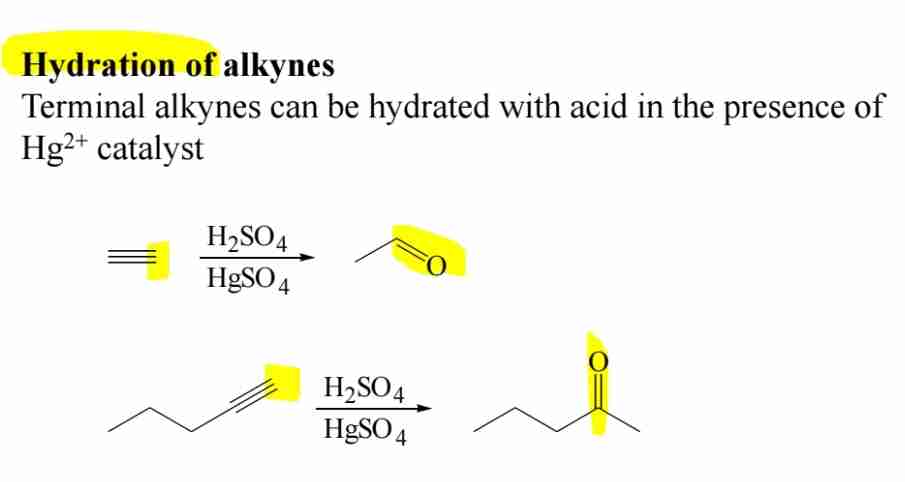
Preparation of Carbonyl Compounds: Hydration of Alkynes
Terminal alkynes react with water (Hg2+^{2+}, acid catalyst) to form ketones.
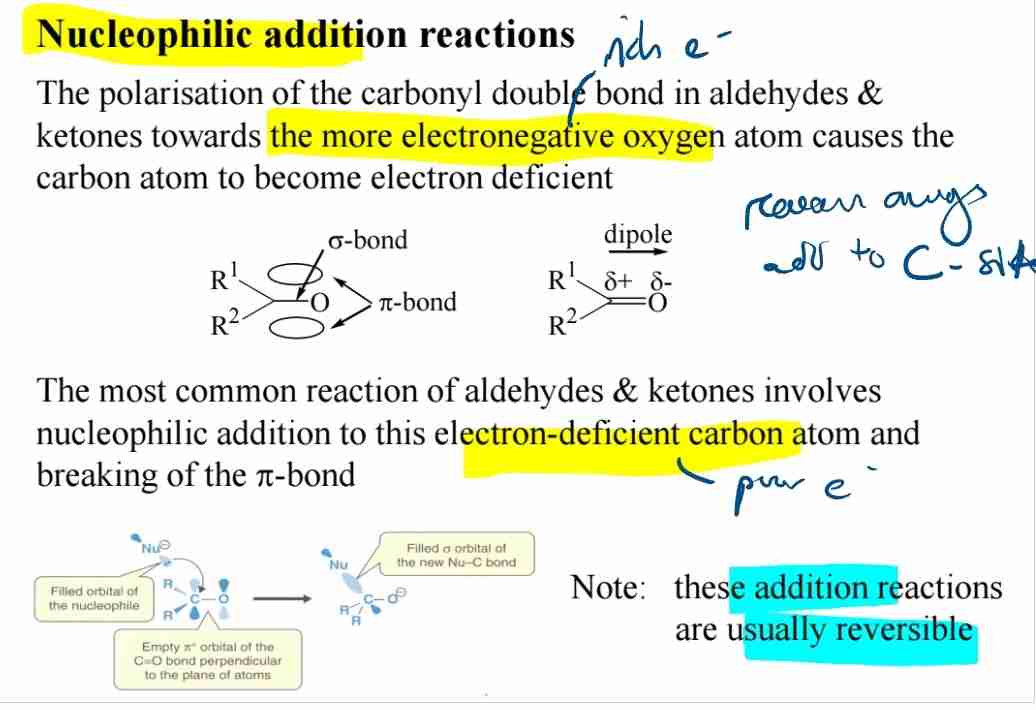
Nucleophilic Addition Reactions
Carbonyl carbon (δ+) attracts nucleophiles, breaking the π bond.
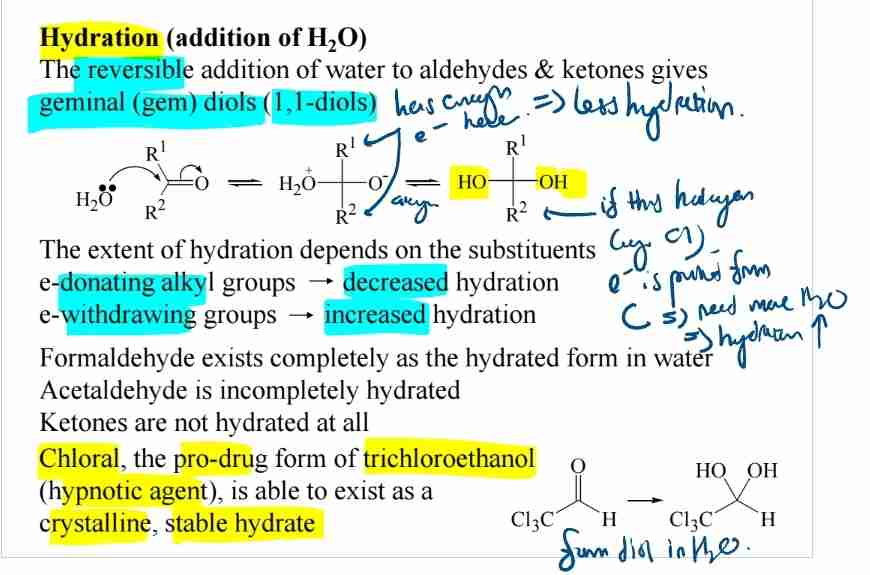
Hydration of Aldehydes and Ketones
Forms geminal diols (e.g., chloral hydrate, a hypnotic).
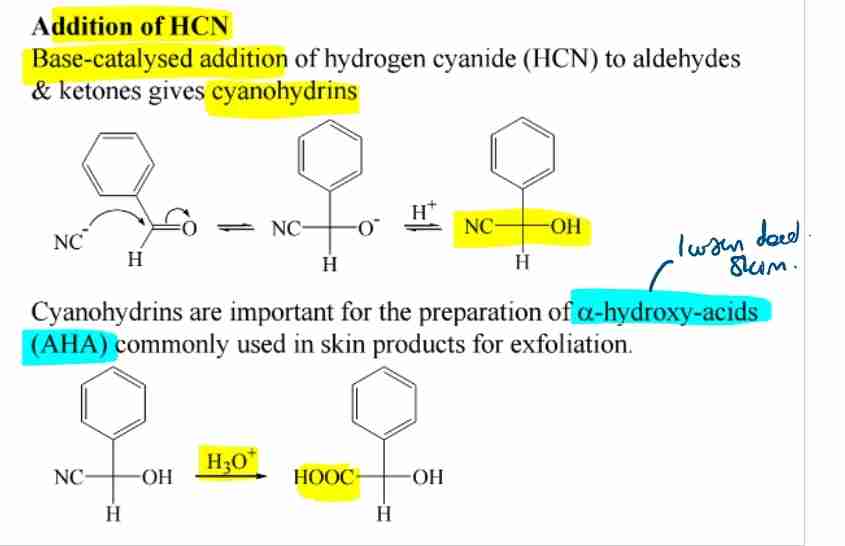
Cyanohydrin Formation
Reaction with HCN produces cyanohydrins, used in synthesizing α-hydroxy acids.
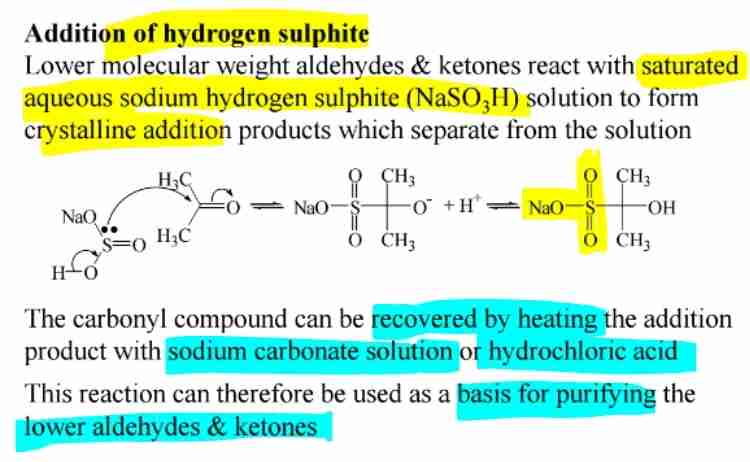
Sodium Hydrogen Sulfite Addition
Forms crystalline addition products for purification of lower aldehydes and ketones.
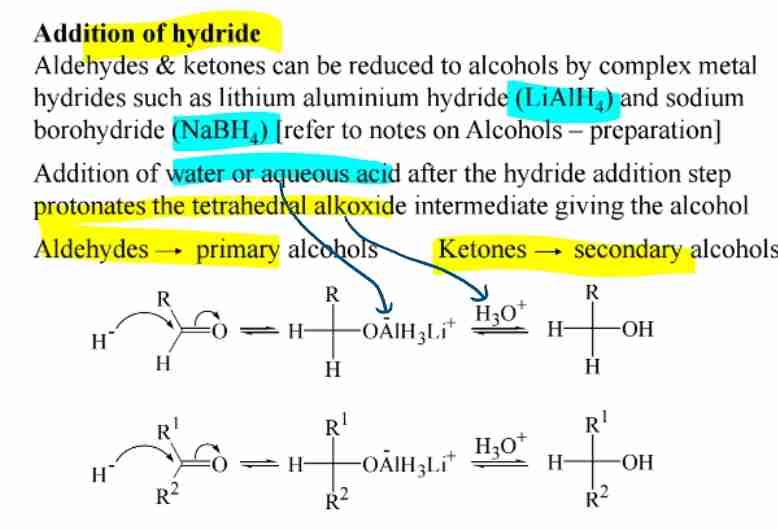
Reduction of Carbonyls//Addition of hydride
Aldehydes → Primary alcohols, Ketones → Secondary alcohols (reagents: NaBH4,LiAlH4).
Grignard Reagents
React with aldehydes and ketones to produce alcohols.

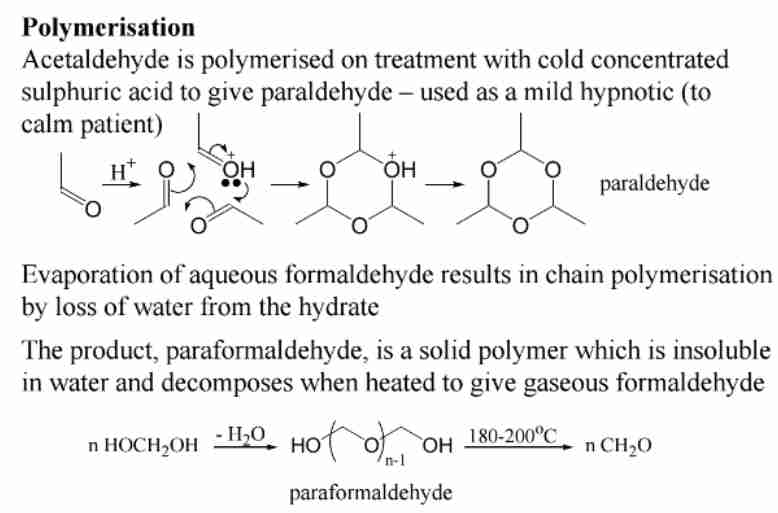
Polymerization of Formaldehyde
Forms paraformaldehyde (solid) and paraldehyde (liquid hypnotic).
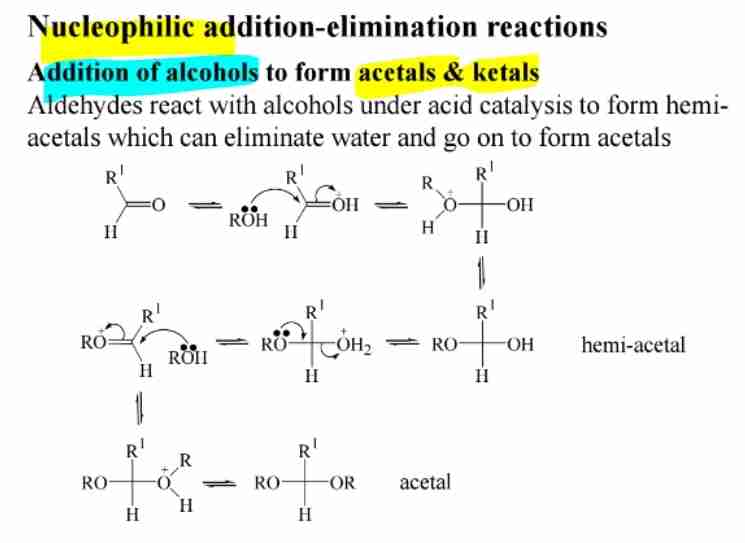
Hemiacetal and Acetal Formation
Aldehydes react with alcohols to form hemiacetals; further reaction produces acetals.
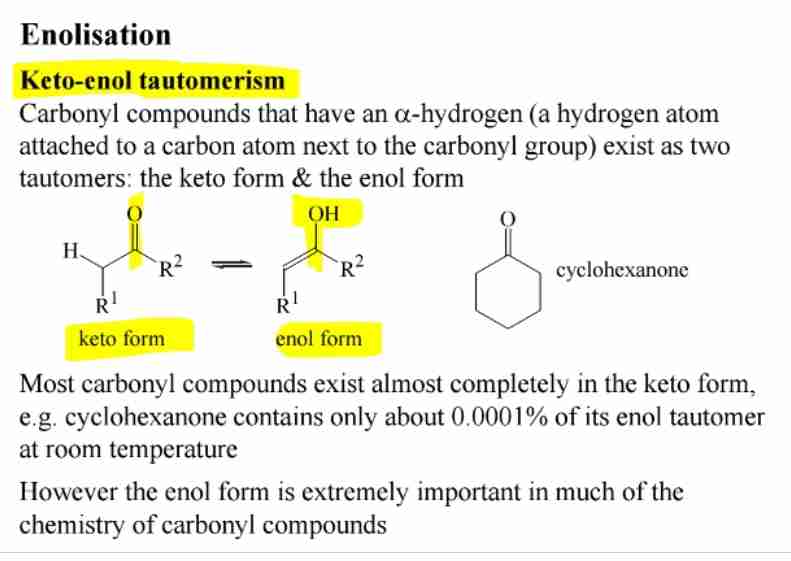
Keto-Enol Tautomerism
Carbonyl compounds exist in equilibrium with their enol form.
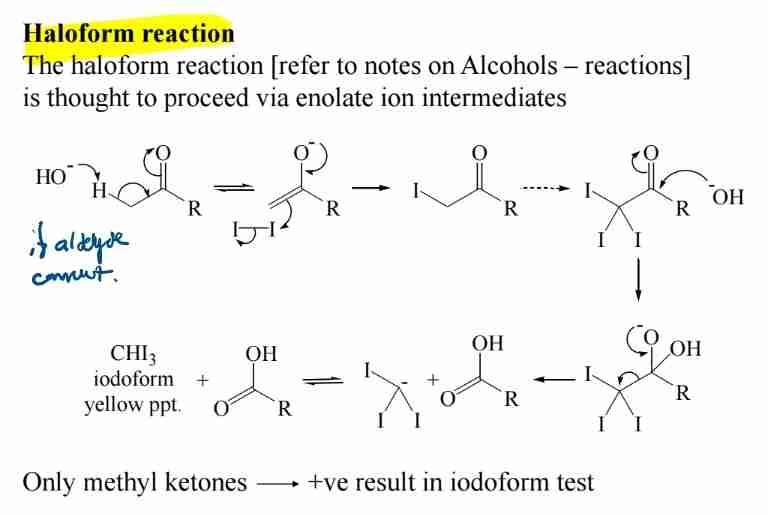
Haloform Reaction
Methyl ketones react with halogens (e.g., iodine) to form haloforms (positive iodoform test).
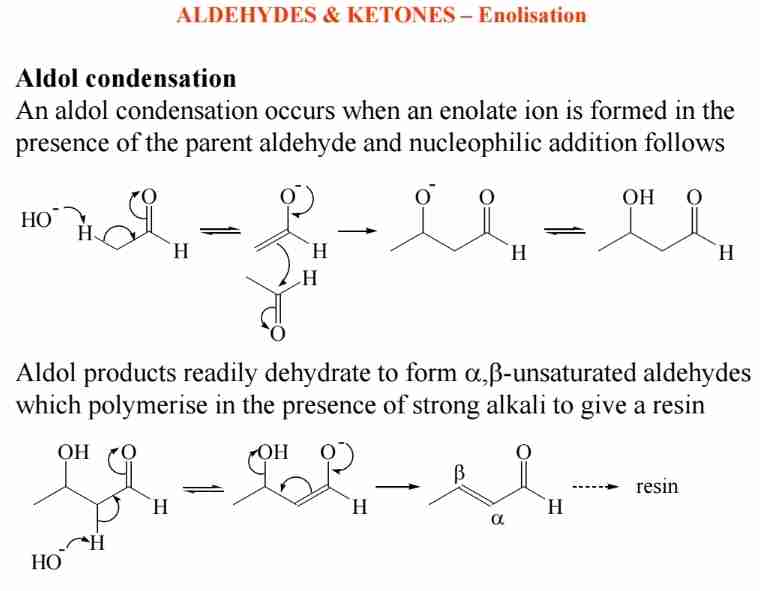
Aldol Condensation
Enolate ions react with aldehydes to form β-hydroxy aldehydes, which dehydrate to α,β-unsaturated compounds.
Aldehyde Oxidation
Oxidized to carboxylic acids by mild oxidants (e.g., KMnO4).
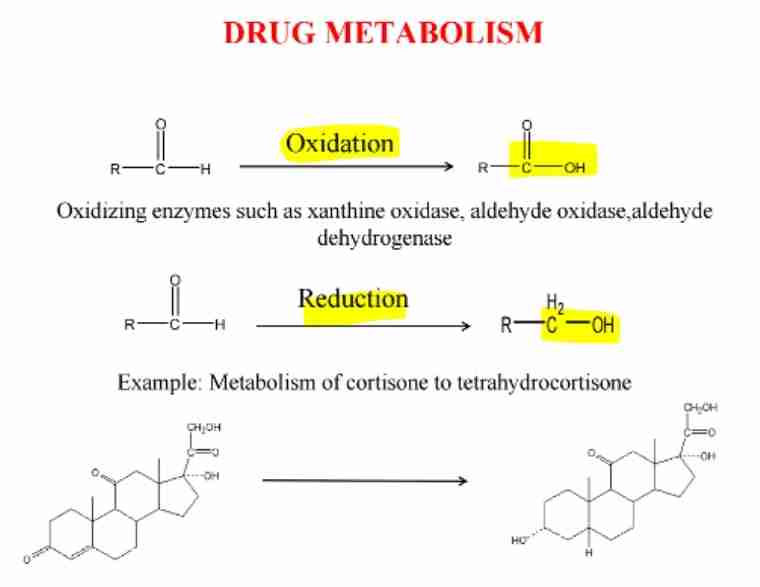
Drug Metabolism of Aldehydes
Catalyzed by enzymes like aldehyde dehydrogenase.
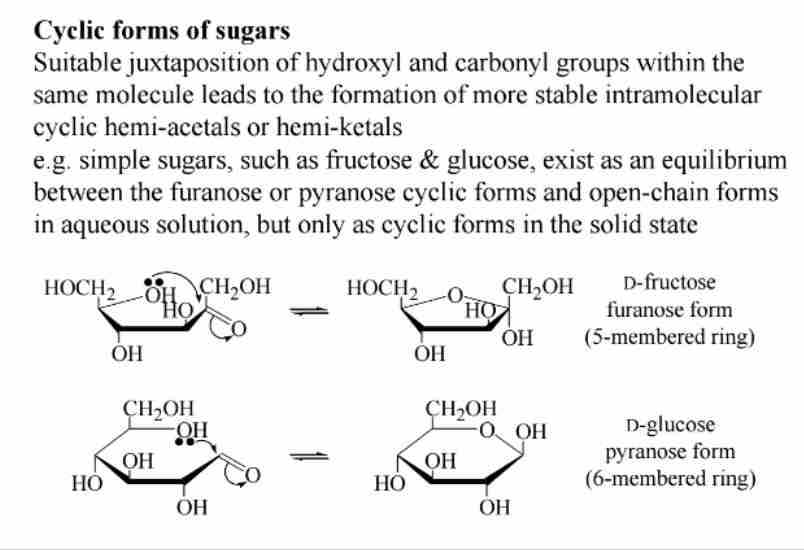
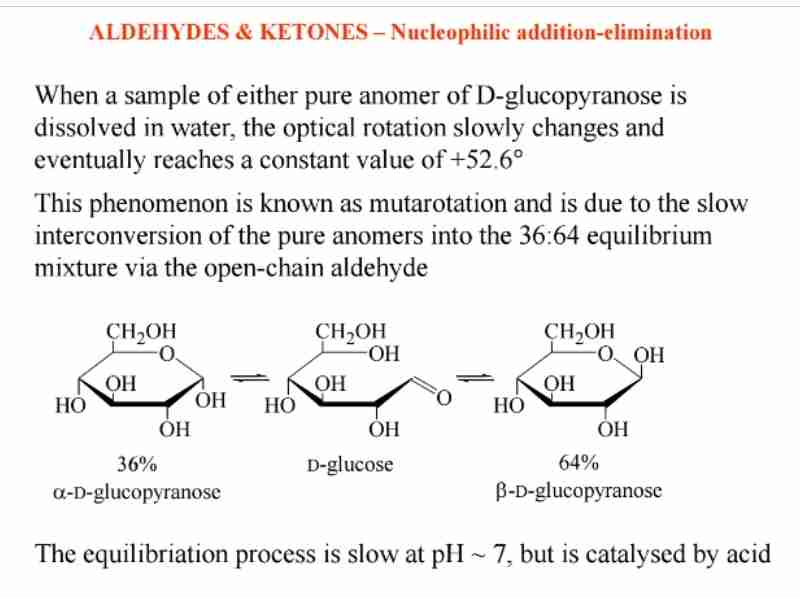
Sugar Cyclization
Intramolecular hemiacetals form stable cyclic structures (e.g., glucose as pyranose).
Mutarotation of Sugars
Interconversion between anomers (α and β) in solution, changing optical rotation.
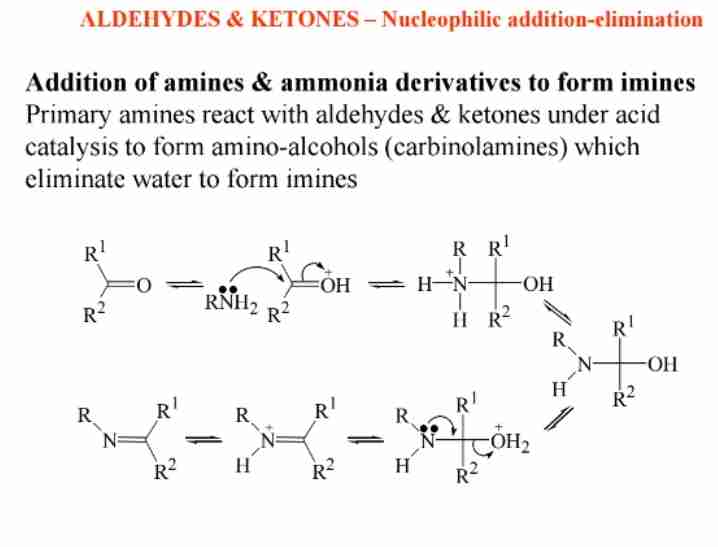
Addition of Amines
Primary amines react with aldehydes to form imines, intermediates in organic synthesis.
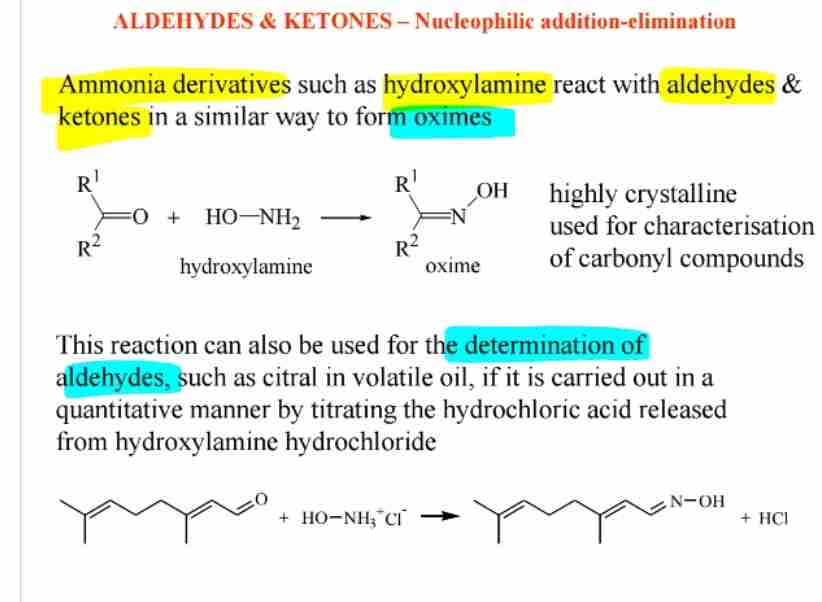
Oxime Formation
Aldehydes react with hydroxylamine to form oximes, useful for characterization.