Cellular respiration
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Aerobic cellular respiration
uses oxygen to harvest energy from organic compounds
energy is used to synthesize ATP from ADP and PI
4 stages of aerobic respiration
pyruvate oxidation
citric acid/ kreb’s cycle
electron transport
oxidative phosphorylation
Anaerobic pathways
energy extracted from food molecules
occurs in areas with no oxygen
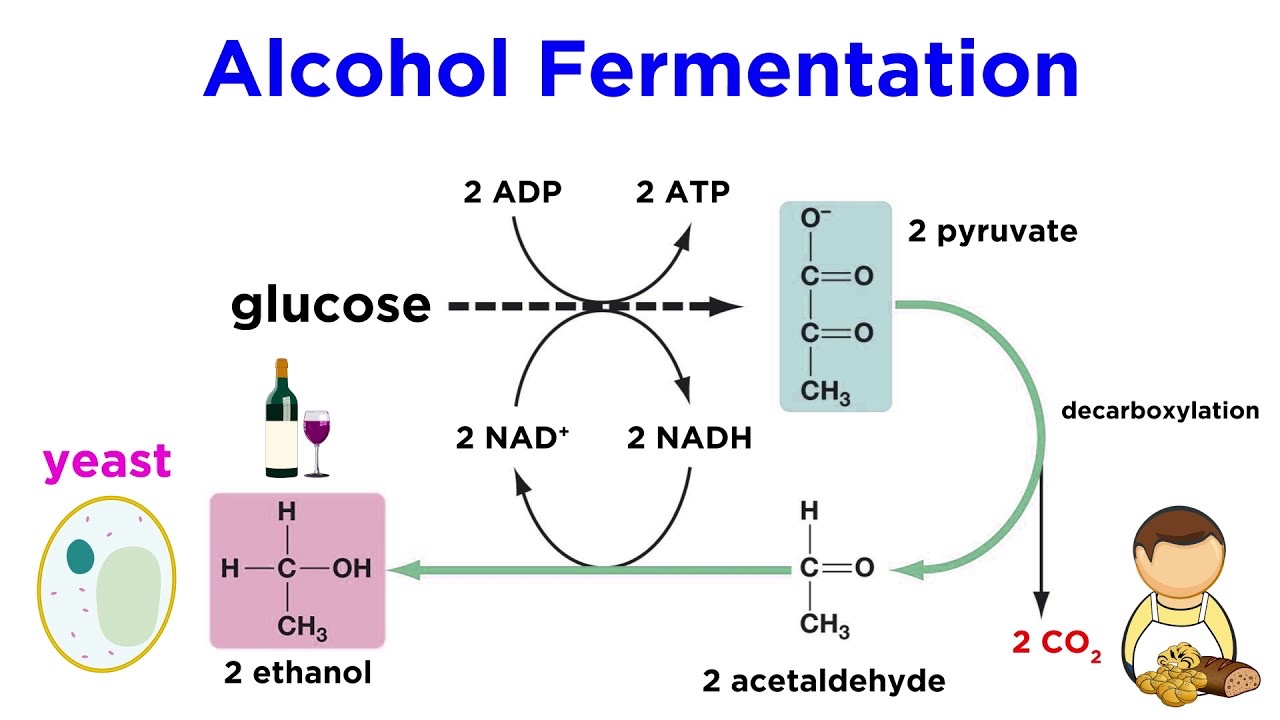
Fermentation
uses an organic compound as the final oxidizing agent to produce energy
Glycolysis
source of ATP
production of 10 enzymatic reactions in cytosol
Products of glycolysis
2 G3P
4 ATP
2 NADH
Energy investment phase
conversion of glucose into 2 3-C sugars
Energy payoff phase
2 G3P created
Pyruvate oxidation
pyruvate created in glycolysis must pass through both the inner and outer membranes through large pores
Process of pyruvate oxidation
in-between step of glycolysis and kreb’s cycle
pyruvate is converted into an acetyl group and temporarily bonded to sulfur at the end of CoA
results in Acetyl-CoA complex
Steps of pyruvate oxidation
COOH group of pyruvate removed and produces Co2
remaining C molecules are oxidated
dehydrogenation reaction transfers 2 electrons and a proton to NAD+, forming NADH
Citric acid/ kreb’s cycle
8 enzyme-catalzyed reactions
results in oxidation of acetyl groups to Co2
for every 1 ATP produced, 1 FADH2, 3 NADH and 1 acetyl-CoA are produced
Steps of citric acid cycle
2 Acetyl-CoA enter from glycolysis
step 1: acetyl group enters and reacts with oxaloacetate to from citrate
step 3,4,5,6,8: some relased energy is captured to form NADH, ATP and FADH2
steps 3,4,8: NAD+ reduced to form NADH
step 5: ATP from ADP + Pi
Products of the Kreb cycle
each glucose molecule= 2 pyruvate molecules = 2 turns of citric acid cycle
Electron transport chain
occurs on inner mitochondrial membrane in eukaryotes
facilitates transfer of electrons from NADH → FADH2
Electron transport chain protein complexes
NADH hydrogenase
succinate hydrogenase
cytochrome complex
cytochrome complex
Electron shuttles in ETC
ubiquinone (UQ): hydrophobic, found in core
shuttles electrons from complex 1→ 3
Cytochrome C (Cyt. C): located on inter membrane
space slide of membrane and transfers electrons from complex 3 → 4
electronegativity of ETC
increasing electronegativity along chain
have cofactors that alternate between reduced and oxidized states
O2 has strongest pull
NADH has weakest pull
Beta-oxidation
process by which fatty acids (saturated) are broken down for use in energy production
occurs in mitochondrial matrix