Topic 2
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
What is current?
Current is the flow of electric charge around a circuit
What is potential difference?
The driving force that pushes the charge around
Measured in volts V
What is resistance?
Anything in the circuit that slows the flow down.
Measured in ohms
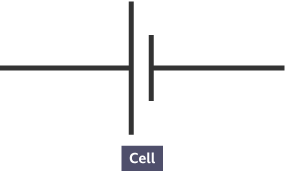
What is this symbol?
A cell
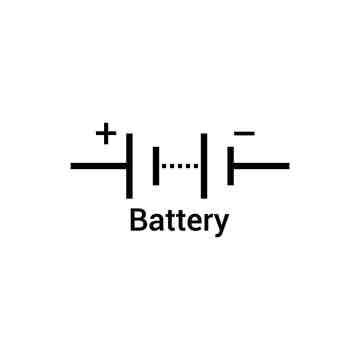
What is this symbol?
A battery
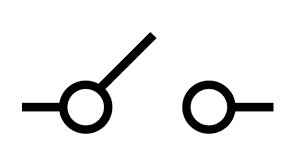
What is this symbol?
An open switch
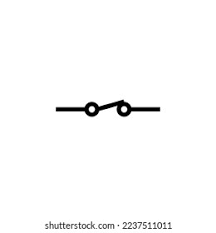
What is this symbol?
A closed switch

What is this symbol?
A bulb or filament lamp
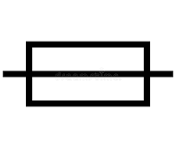
What is this symbol?
A fuse
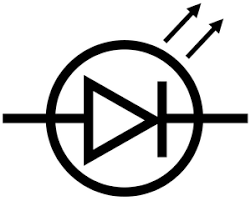
What is this symbol?
A LED (light emitting diode)

What is this symbol?
A resistor

What is this symbol?
An ammeter
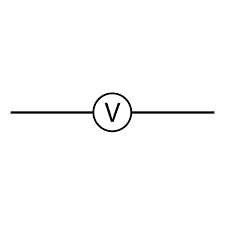
What is this symbol?
A voltmeter
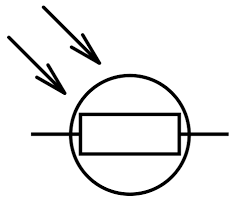
What is this symbol?
A LDR(light dependant resistor)
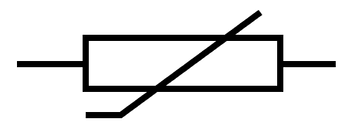
What is this symbol?
A thermistor
How to investigate the factors affecting resistance?
Attach a crocodile clip to the wire level with the 0cm on the ruler
Attach the second crocodile clip to the wire, eg 10cm away. Make sure to measure this distance.
Close the switch then measure the current and p.d through the wire.
Open the switch, then remove the second crocodile clip, eg add another 10cm to the wire, then record the new length, current and p.d
Repeat this for a number of different lengths of the test wire.
Use your measurements of current and p.d to calculate the resistance for each length of wire using R = V÷I (from V =IR)
Plot a graph of resistance against wire length and draw a line of best fit. It should be a straight line. If your graph doesn’t go through the origin it may be because you didn’t put the crocodile clip at exactly 0cm which is a systematic error.
How to test I-V characteristics?
Set up a test circuit with an ammeter, a variable resistor, a voltmeter and your component.
Alter your variable resistor to alter the current and p.d across the component.
Take several pairs of readings from the voltmeter and ammeter to see how the p.d across the component varies as the current changes. Repeat each reading twice to take an average p.d at each current.
Swap over the wires connected to the battery so the direction of current is reversed.
Plot a graph of current against voltage for your component.
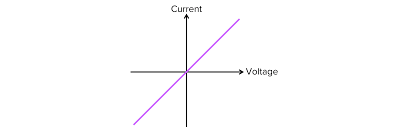
What component does this IV characteristics graph belong to? And interpret it
An ohmic conductor.
The current through an ohmic conductor is directly proportional to potential difference.
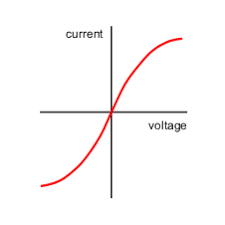
What component does this IV characteristics graph belong to? And interpret it
A filament lamp.
As the current increases the temperature of the filament lamp increases, so the resistance increases. This means less current can flow per unit pd, so the graph gets shallower.
What is a LDR? Uses and resistance
A resistor that is dependant on the intensity of light.
Resistance decreases as light level increases.
Used in street lamps or headlights.
What is a thermistor? Uses and resistance
Resistors that vary based on temperature.
Used in electronic thermostats.
Resistance goes down as temperature goes up.
How are sensing circuits used?
This is using a fan as an example.
the fixed resistor and fan are connected in parallel so they have the same p.d
The p.d is shared between the thermistor and the loop with the fixed resistor and fan according to the their resistances. (The bigger a components resistance the more p.d it takes.)
As the room gets hotter the thermistor’s resistance decreases and it takes less p.d. Makeing the p.d against the fixed resistor and fan rise so the fan spins faster.
Describe a series circuit. Include cell p.d, total p.d , current and resistance.
The different components are connected in a line end to end. Except for voltmeters as they are always connected parallel but they don’t count.
Cell potential differences add up.
Total potential difference is shared.
Current is the same everywhere.
Resistance adds up.
Describe a parallel circuit, including p.d, current and the effect of adding a resistor.
Each component is separately connected to the supply. Except ammeters which are always connected in series.
Potential difference is shared across all components.
Current is shared between branches
Adding a resistor reduces the total resistance.
Explain why adding resistors in parallel decreases total resistance
Multiple paths for electrons to flow so total current is greater
How to investigate adding resistors in series? (And parallel)
Find 4 identical resistors.
Then build a circuit with an ammeter and a resistor. Make note of the potential difference of the battery.
Measure of the current through the circuit using the ammeter. use this to calculate the resistance of the circuit R = V÷I.
Add another resistor in series with the first.
Again, measure the current through the circuit and use this on the potential difference of the battery to calculate the overall resistance of the circuit.
Repeats step form five until you’ve added all four resistors
Plot graph of the number of resistance against the total resistance of the circuit.
To do this in a parallel circuit, do the same steps but connect the resistors in parallel.
What type of current is mains supply? Including Hz and volts
Alternating current 230V and 50Hz
What is the difference between direct and alternating potential difference.
In ac supplies the current is constantly changing direction however in dc it is always flowing in the same direction.
In ac supplies alternating currents are produced by alternating potential difference (positive and negative ends keep changing) however in direct current it is produced by a direct potential difference.
What colour is the live wire and what does it do?
Brown
Provides the alternating potential difference from the mains supply.
What colour is the neutral wire and what does it do?
Blue
Completes the circuit.
What colour is the earth wire and what does it do?
Green and yellow
Stops the appliance casing from becoming live
Why does touching the live wire give you a shock?
Your body like the earth is at 0V this means that if you touch the live wire a large p.d is produced across your body and current flows through you.
Why is connection between live wire and earth wire dangerous?
If the link creates a Lowe resistance path to earth a huge current will flow which can result in a fire
What are electrical appliances meant to do?
Transfer energy to components in a circuit when energy flows
What do appliances power ratings tell you? What does it not tell you?
The maximum amount of energy transferred between stores per second when the appliance is in use. It doesn’t mean that it transfers energy more usefully an applience can be more powerful but less useful.
What is the national grid?
A system of cables and transformers that link power stations to consumers
What’s the problem with using a high current to transmit large amounts of power?
You loose lots of energy to the surroundings as the wires heat up
What are step up transformers used for?
To increase the potential difference for the national grid
What are step down transformers used for?
To decrease the potential difference of the electricity taken in from the national grid to make it safe for domestic use.
How is static caused?
Friction
When two insulating materials are rubbed together negatively charged electrons are scraped off one and dumped on another. One will be negatively charged the other will have an equally positive charge.
How can static cause sparks?
an electric charge builds on object(due to static), the p.d between the object and earth increases. If the potential difference is large enough electrons can jump across the gap between the charged object and the earth. They can also jump to any earthed conductor nearby.
What is electrostatic attraction and what type of force is it?
Opposite charges attracting and negative charges repelling.
Non-contact forces
Where are electric fields created?
Around any electrically charged object
How to draw an electric field?
field lines go from positive to negative
At a right angle from the surface
The closer the lines are the stronger the field
What happens when a charged object is placed in the electric field of another object?
It feels a force which causes attraction/repulsion. The force is linked to the strength of the electric field.
How can sparking be explained by electric fields?
Sparks are caused when there is a high enough potential difference between a charge object and the earth.
A high potential difference causes a strong electric field between the charged and earthed object. The strong electric field causes loss of electrons in the air particles.
When air is ionised it is very conductive, so current can flow. Which causes a spark.