Chapter 4: Forces in action
1/34
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Mass
Is a property and is measured in kg
Resists change in motion
Greater the mass of a body, the smaller the change produced by an applied force
Definition of mass
Measure of an amount of matter in an object
Weight
As it is a force on an object due to the pull on gravity,
its measured in Newtons (N)
The weight is equal to:
w = mg
g: changes depending on the planet
Definition of weight
Effect of a gravitational field on mass
Free fall
- it is solely falling under the influence of gravity
- on Earth every object accelerates at 9.81 ms-2
- in the absence of air resistance - all bodies near the
Earth fall with the same acceleration- regardless of their
mass
Force and acceleration
according to newtons second law, objects will accelerate if
there is a resultant force exerted on them
this acceleration is in the same direction as the
resultant force
F = ma
RESULTANT FORCE
force is directly proportional to acceleration (when mass is
constant)
Geometric centre
The middle of an object
Centre of mass and geometric centre
Objects with uniform density - the centre of mass is
the geometric centre of the object
A force being applied at the objects centre of mass will
produce a straight line motion without rotation.
Weight (centre of gravity)
W = mg
Weight (W) - the resultant gravitational force, will act
through the point - centre of gravity (which coincides with
the objects centre of mass)
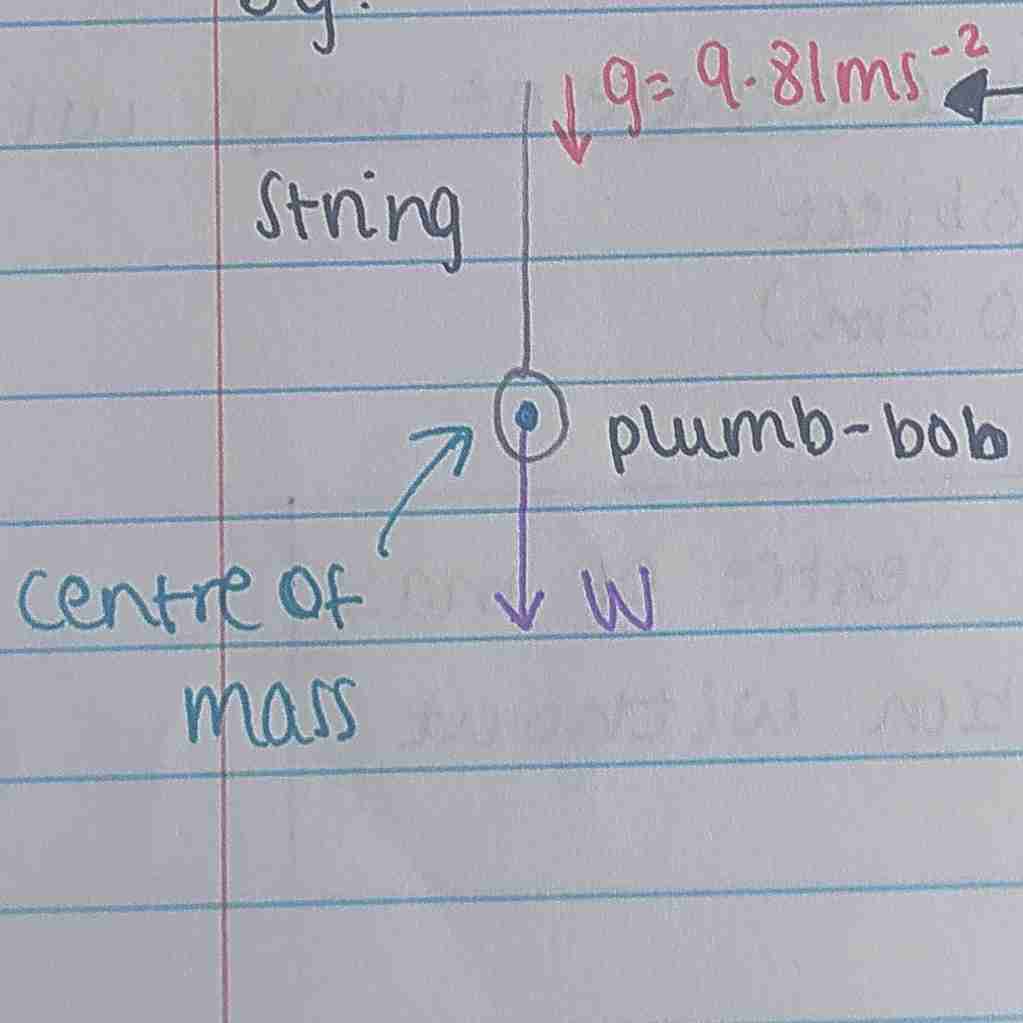
Finding the centre of gravity
A freely suspended object will come
to rest with its centre of gravity
below the the point the object is
suspended by.
It produces a vertical line which
is inline with g and the centre of mass
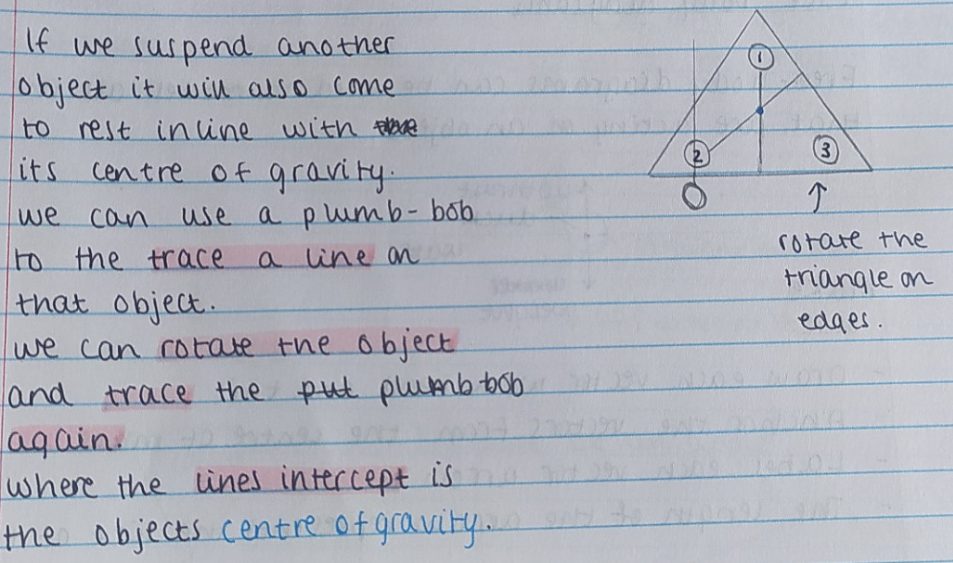
Centre of gravity of another object
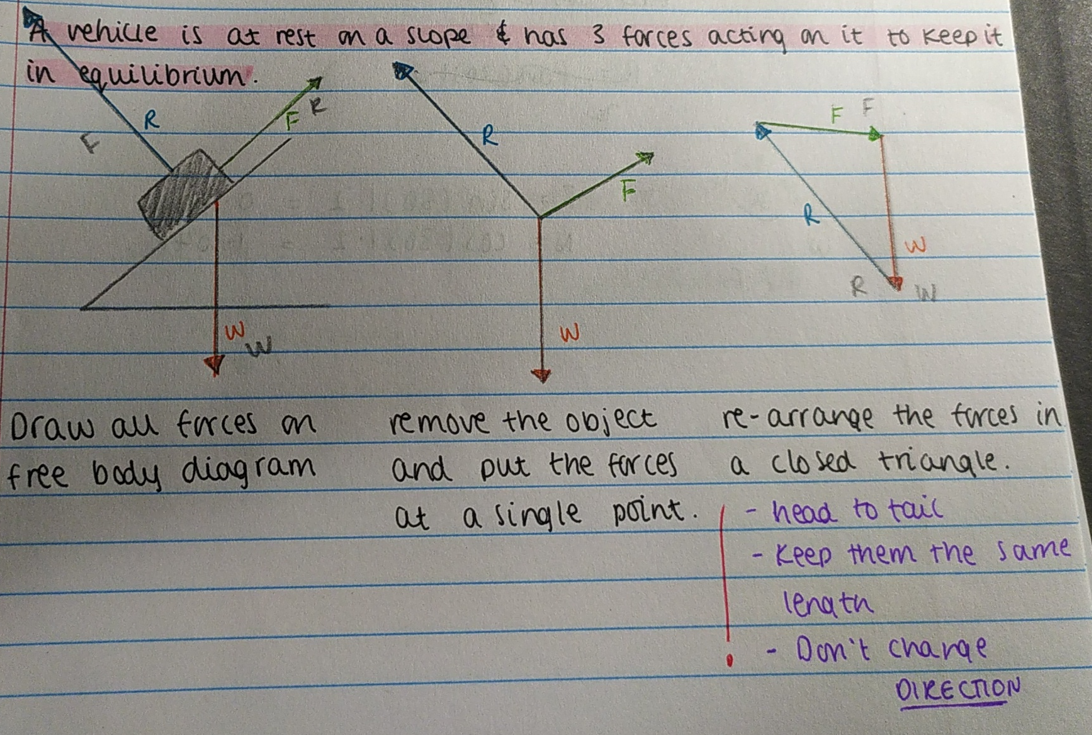
Free-body diagram rules
draw each vector head to tail
anchor the vectors from the centre of mass
label each vector arrow
the length of the arrow represents the size of the force
Different forces
weight
friction
drag
upthrust
thrust
tension
normal contact force !!
Weight (force)
gravitational force produced when a mass in a
gravitational field (g)
acts through the objects centre of mass
ALWAYS DRAWN STRAIGHT DOWN
Friction
opposes motion of an object
Drag
opposes motion when an object is travelling through a fluid
(gas / liquid)
because the object collides with particles in the fluid
Upthrust
an upward buoyancy force acting on an object when it is a
fluid. this is due to the pressure difference between the top
and bottom of a submerged object
Tension
the force within a stretched cable / rope
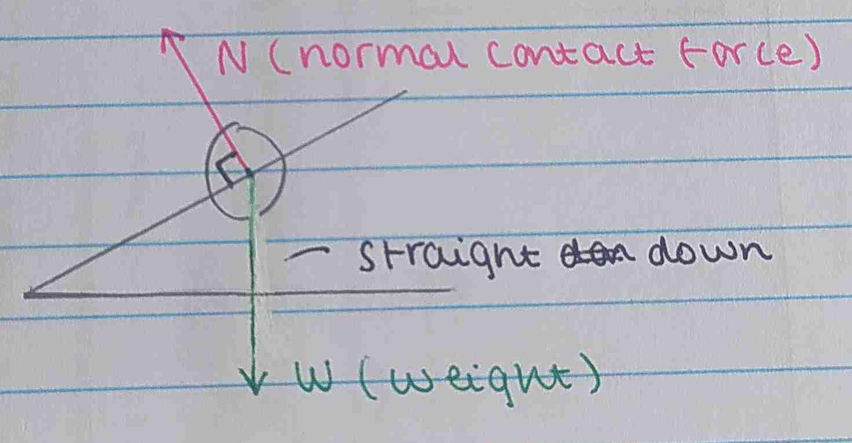
Normal contact force
when an object rests
against another (is
stationary).
the normal is at 90 degrees where the objects touch
Compare the force drag and the force friction
- both forces oppose the motion of an object
- drag is when an objects motion is opposed by a fluid (liquid or
gas)
- while friction is when an objects motion is opposed by its
surface being in contact with another object
Factors affecting drag
- ↑ cross-sectional area ↑ drag
- ↑ speed ↑ drag
Relationship between drag and speed
drag ∝ speed2
Terminal velocity
As the speed of an object increases, the drag does.
This continues until the drag force balances the weight of the
object.
It has now reached terminal velocity.
Turning moments
the turning effect of a force and can be
clockwise / anti-clockwise
can occur when forces cause objects to rotate at a point
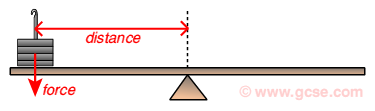
Moment definition and formula (Nm)
force x perpendicular distance of the line of action of force from
the axis / point of rotation
= Fx
Force (N)
Perpendicular distance (m)
Force applied at an angle (Moments)
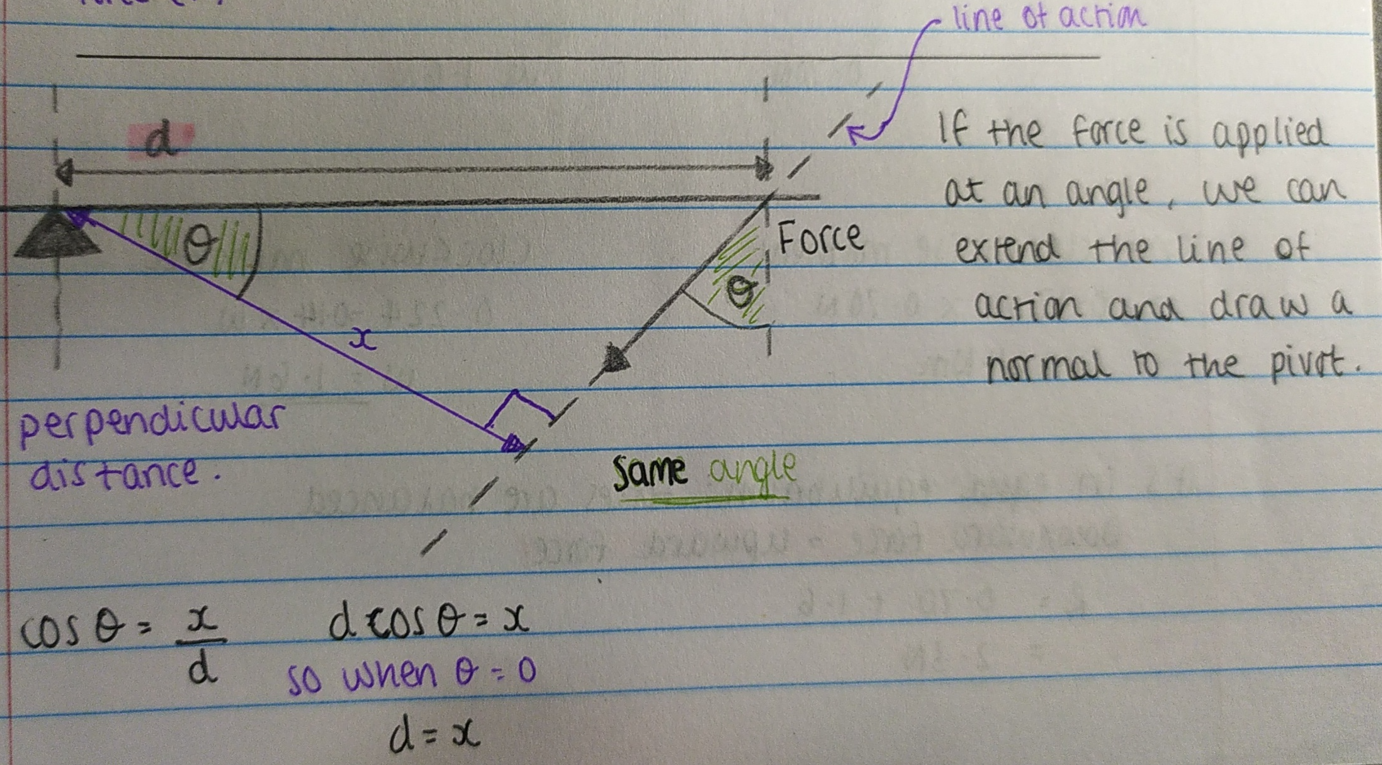
Equilibrium: principle of moments
When a body is in equilibrium, the net forces and the net moments on an object is zero.
the object is not accelerating - no net forces
the object is not rotating - no net moment
no net moment means clockwise moment = anti-clockwise moment
Translational motion
object moving through space
Making an object move with no translational motion
Apply equal and opposite forces
Couples
Forces that produce rotational motion and no translational
motion
the moment of a couple doesn’t depend on a povot, only the
perpendicular distance between the two forces
A couple consists of two forces that are..
equal in magnitude
opposite in direction
perpendicular to the distance between them
couples produce a zero resultant force - the object doesn’t accelerate
the size of the turning effect is given by the torque
Torque of a couple (Nm)
one of the forces (N) x perpendicular sperating between the forces (m)
Equilibrium
A system is in equilibrium when all the forces are balanced:
no resultant force
no resultant torque
An object as equilibrium will therefore remain at rest / constant
velocity - DOESN’T ROTATE
Coplanar forces in equilibrium
can be represented by vector triangles.
In equilibrium - they’re closed triangles - form a closed path
Triangular forces in equilibrium