The Ideal Gas Law
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
T
Temperature in Kelvin
P
Pressure with a value of 1 atm (SI unit)
V
volume with the SI unit of m3
n
Amount of gas/number of moles
An ideal gas
PV = nRT
R
molar gas constant
The characteristics of an ideal gas
The volume of an ideal gas is negligible compared to the volume of its container
The particles have zero intermolecular force of attraction
Ideal Gas
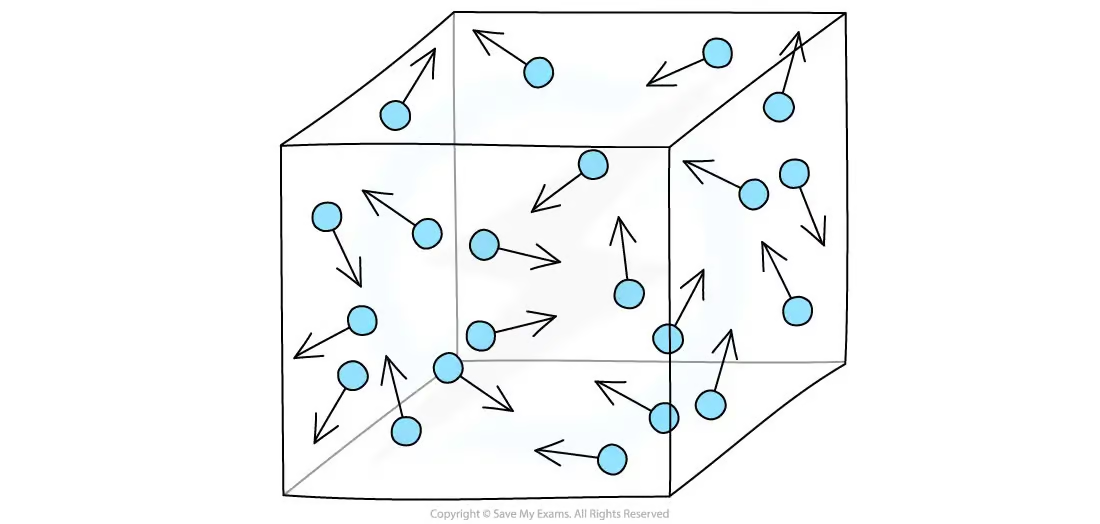
Gas particles exert pressure by constant collision with the walls of their container
The SI unit of atmospheric pressure is
Pascal (Pa)
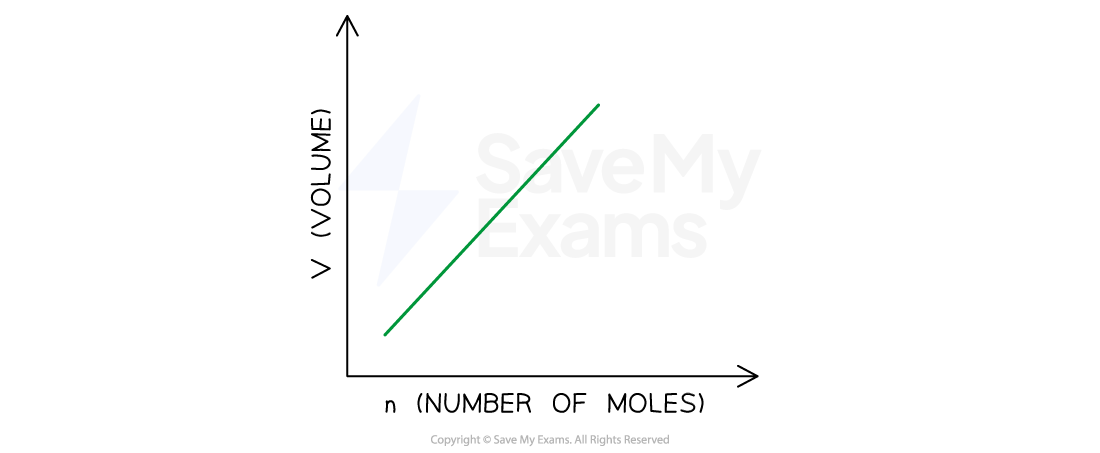
Quantity-Volume Relationship: Avogadro’s Law
Equal volumes of gases at the same temperature and pressure contain equal numbers of molecules
Quantity-Volume Relationship
V1/n1 = V2/n2
Lowest possible temperature
absolute zero
0 K is equivalent to
-273.15 ℃
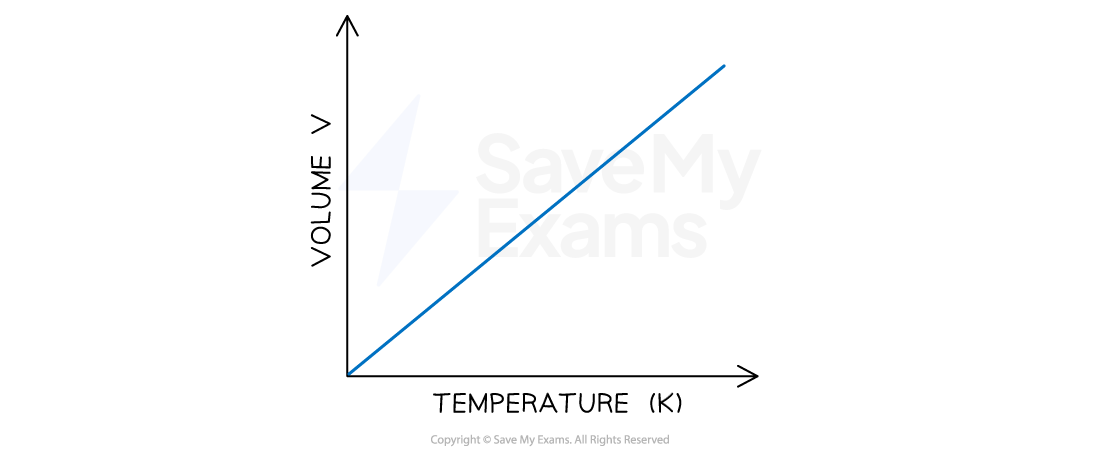
Temperature-volume relationship
the volume of a fixed amount of gas maintained at constant pressure is directly proportional to its absolute temperature:
V1/T1 = V2/T2
A plot of volume against temperature gives
a straight line which intercepts the volume and temperature axis at zero
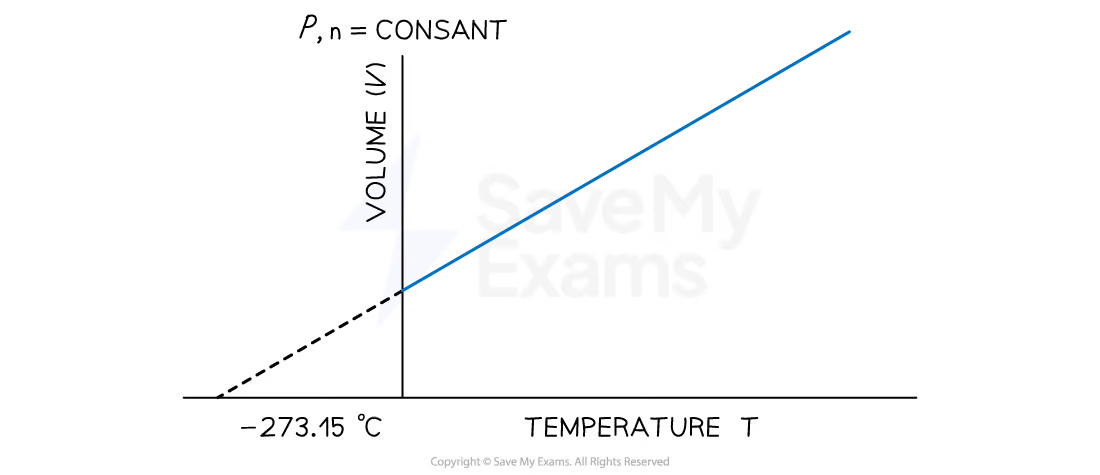
Temperature-Volume Relationship: Charles’s Law
at constant pressure
the volume of a gas sample expands when heated and contracts when cooled
volume of gas decreased as the pressure increased
the pressure increased
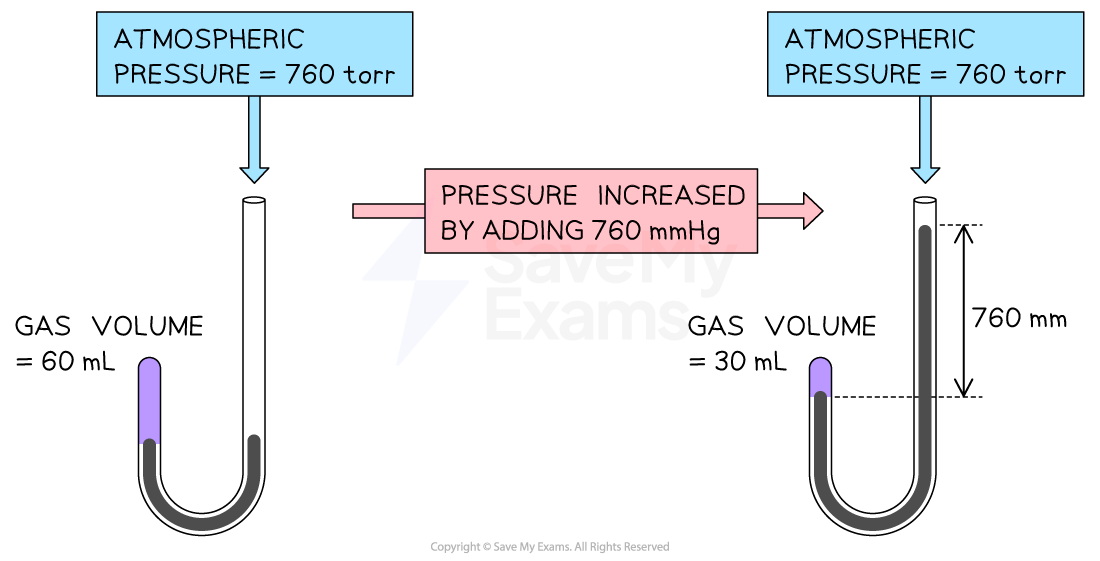
Pressure-Volume Relationship
V ∝ P ; PV = constant
P1V1 = P2V2
Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressure
the total pressure of a mixture of gases equals the sum of the pressures that each would exert if it were present alone
PT = PA + PB + PC
partial pressures of the gases A, B and C
XA known as the mole fraction of gas
mole fraction of gas A
XA
= nA/(nA + nB + nC)
Dalton
The total pressure of a mixture of gases is equal to the sum of the pressures of each of the individual gases in the container
Boyle
The volume of a fixed amount of gas varies inversely with the pressure at constant temperature.
Charles
The temperature and volume of a gas at constant pressure are directly proportional.
Avogadro
The volume of two different gases at the same temperature and pressure is the same, and each sample contains the same number of gas molecules.