Bio 150 DCCC - Lab Practical 1
1/282
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
283 Terms
Glass waste container

sharp object waste container

specimen waste container

chemical waste container

Beakers

Graduated
cylinders

test tubes and test tube rack

Test Tube & Holder
in Action
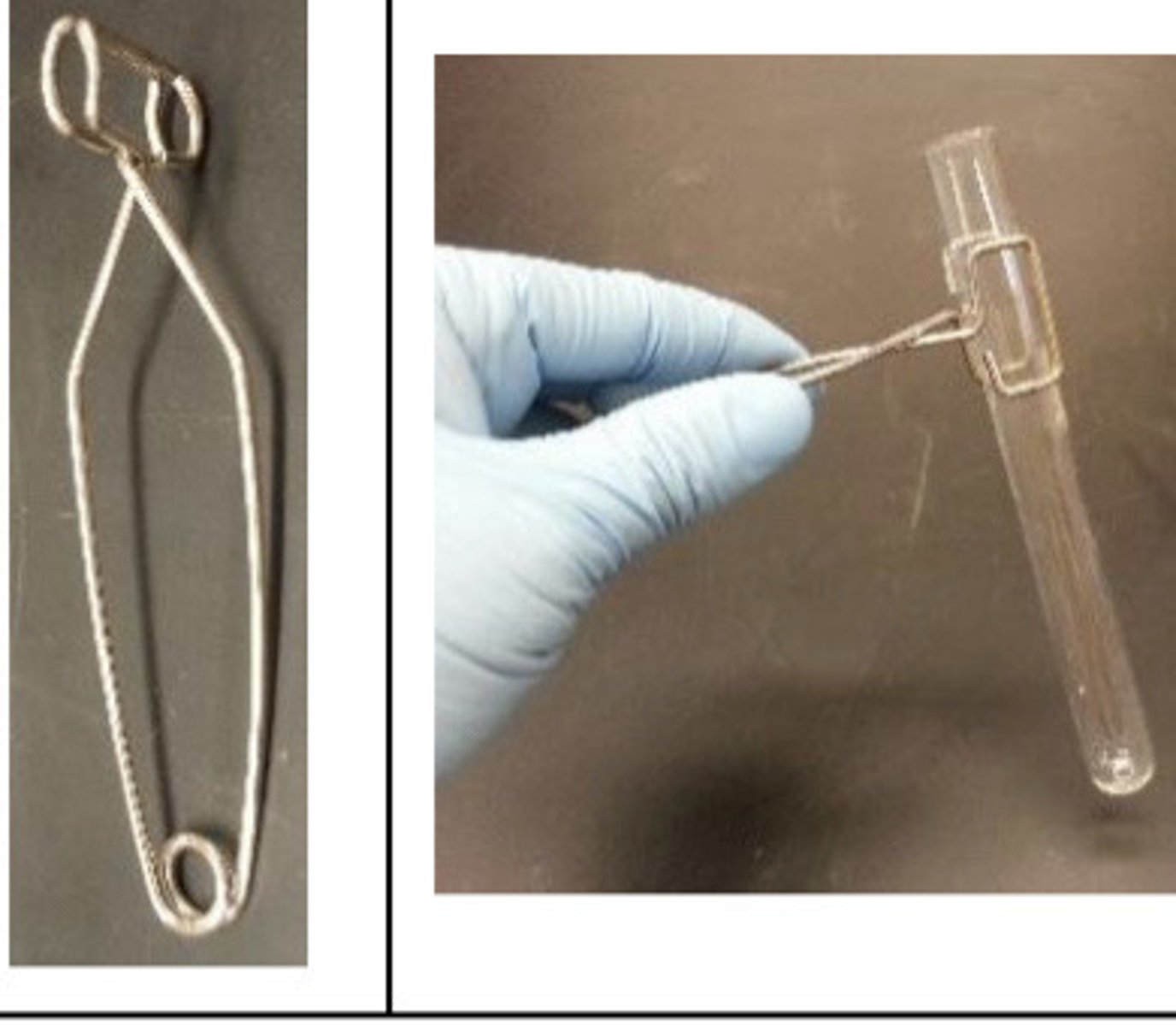
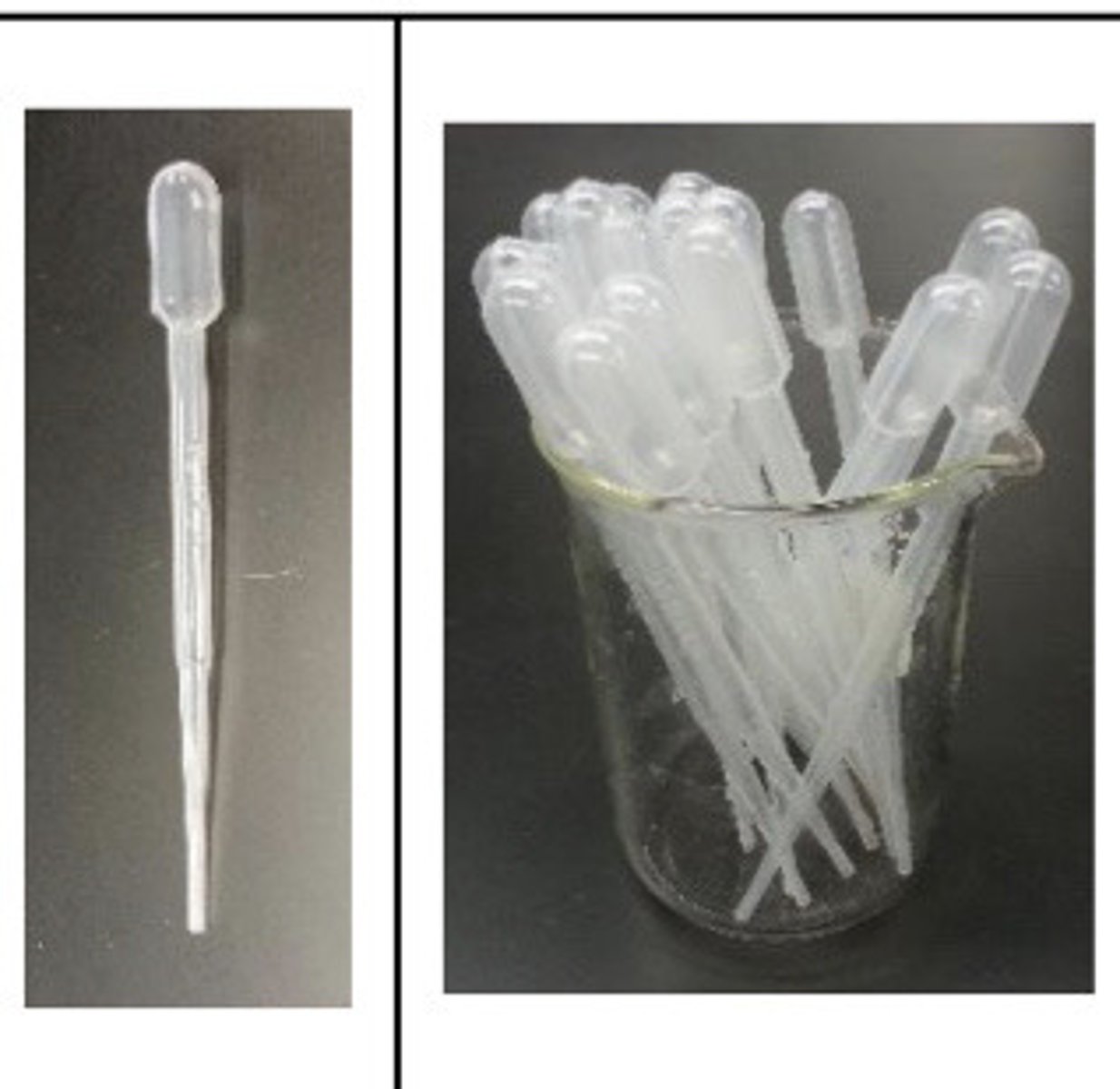
Disposable pipette

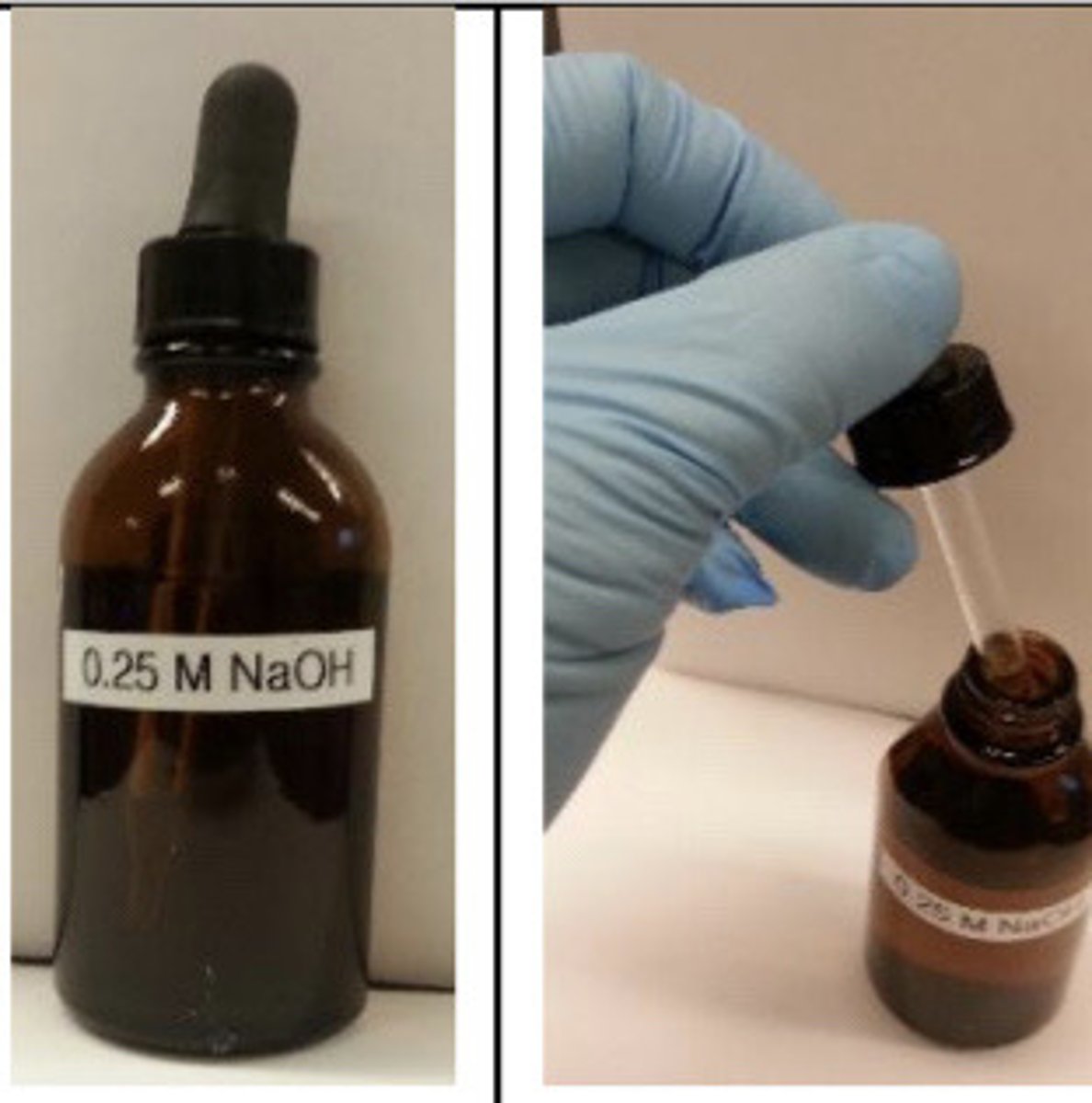
Chemical reagent and
attached dropper
in action

ruler

Balance

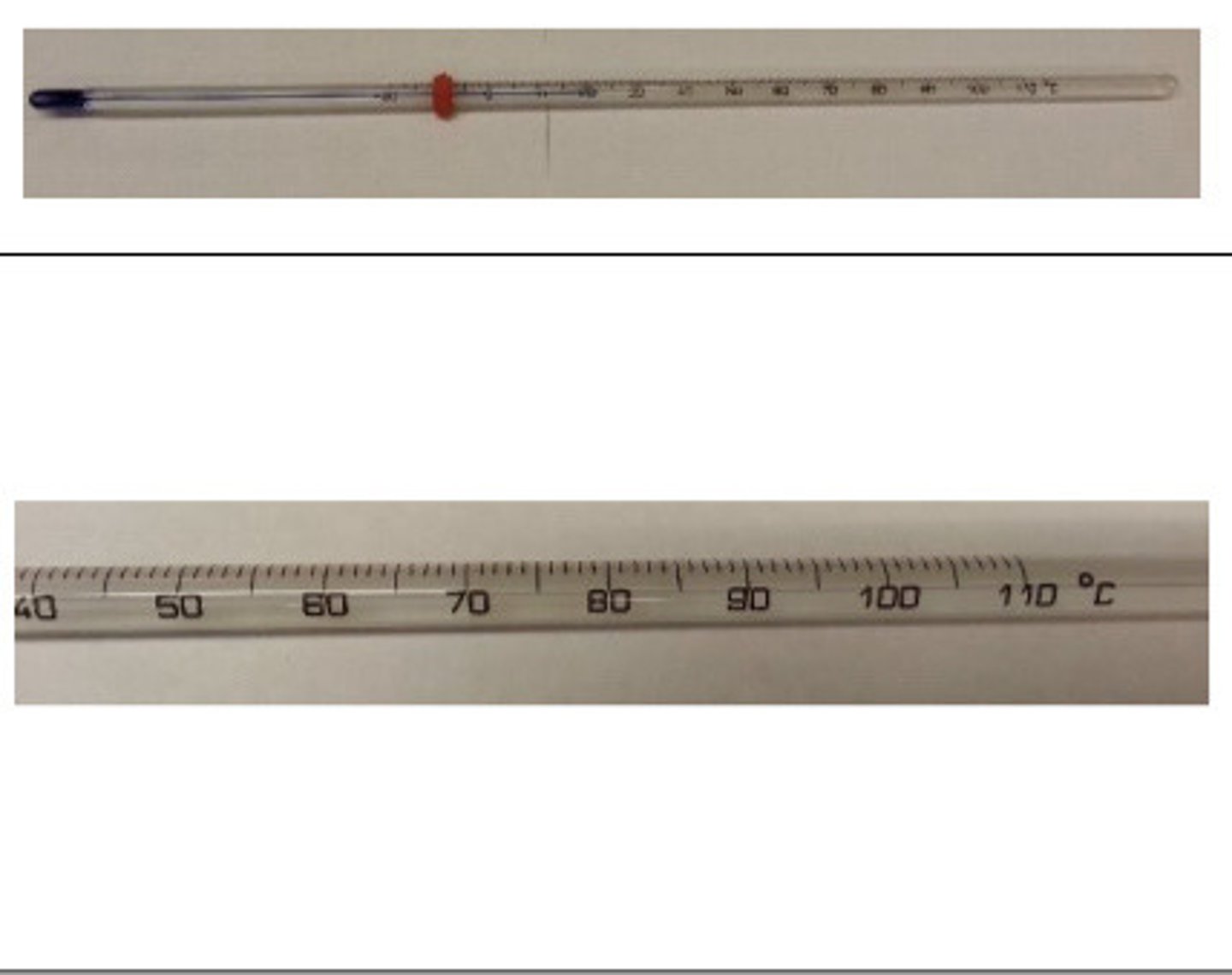
thermometer

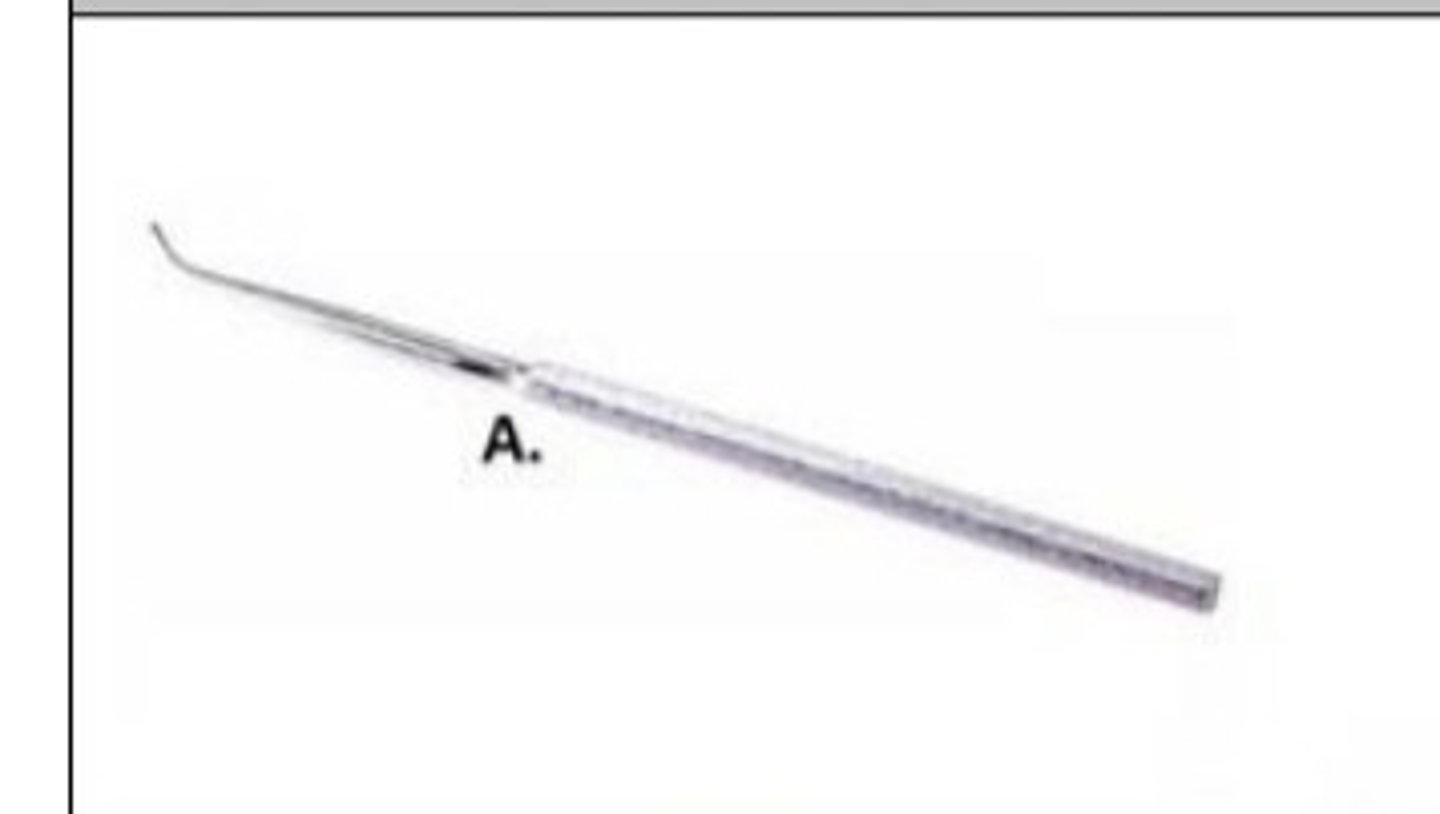
blunt point dissecting probe

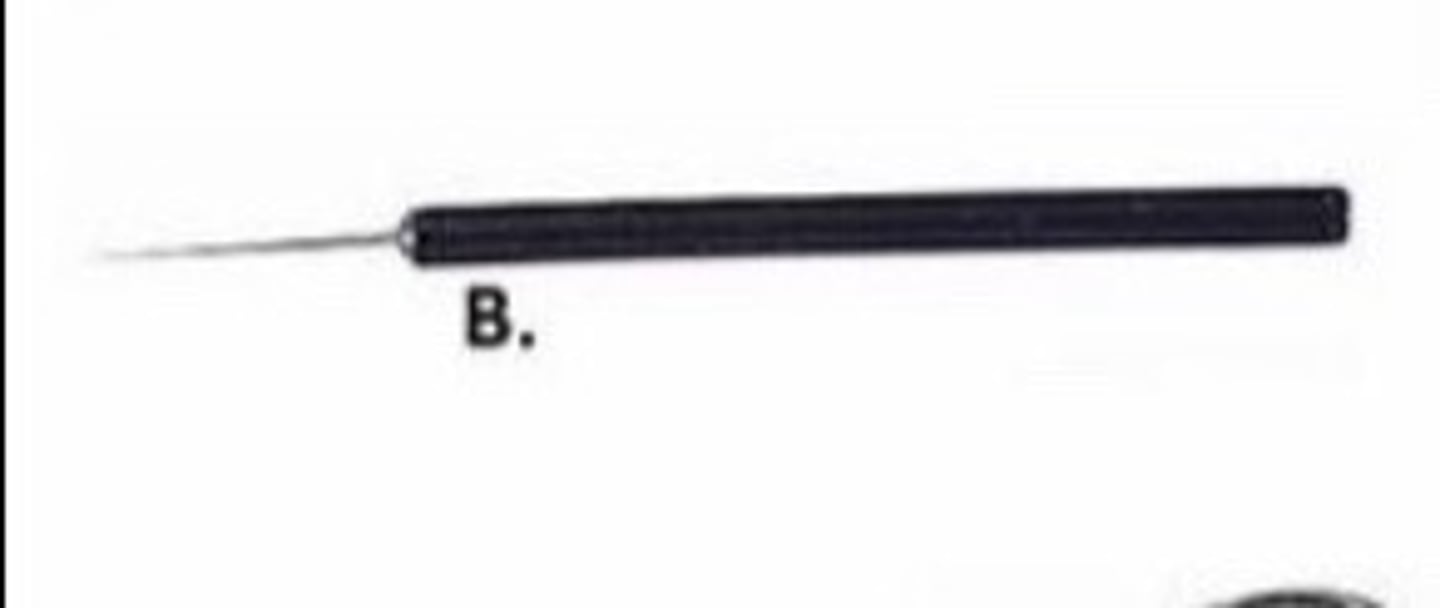
sharp point dissecting probe

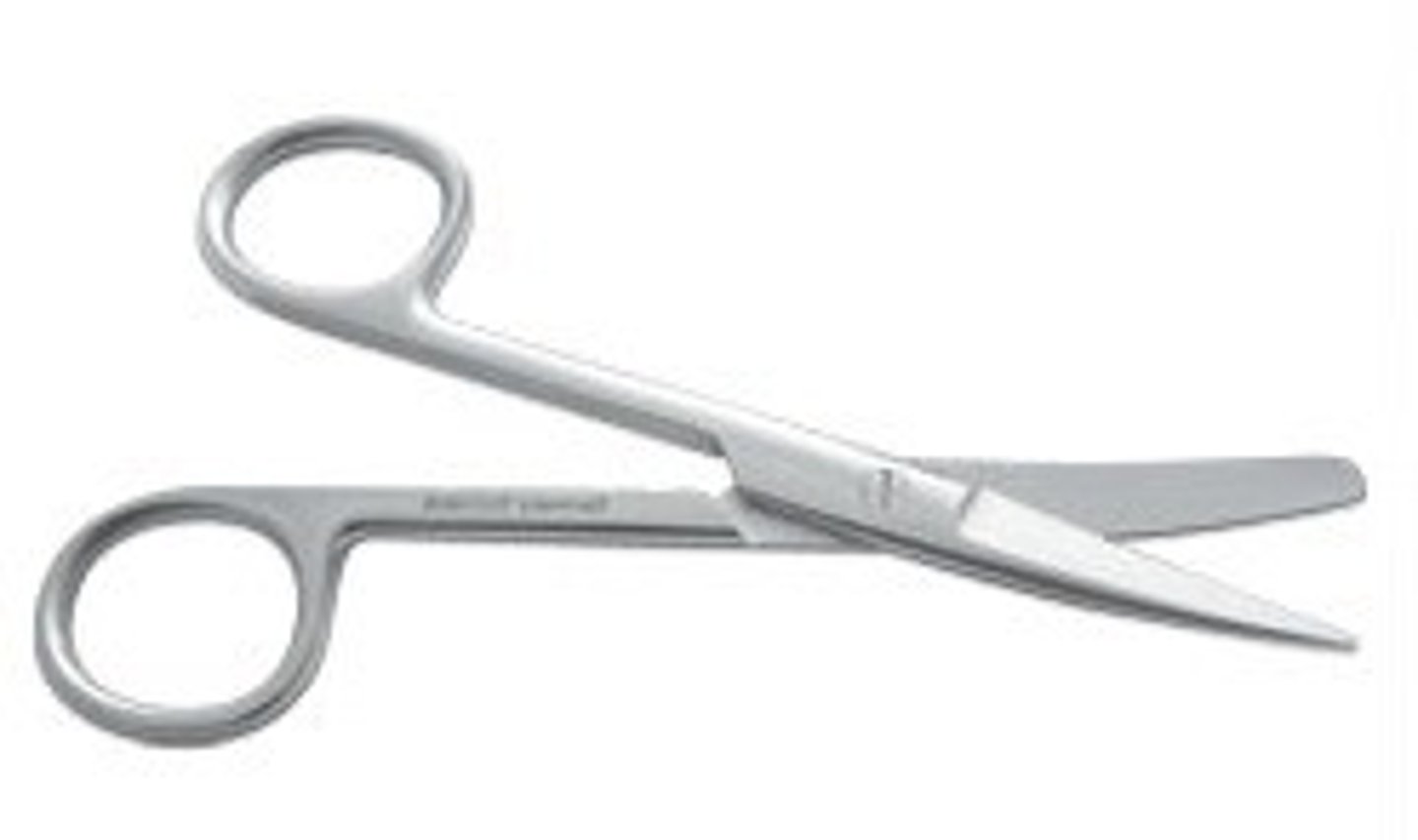
blunt/sharp dressing scissors

dissecting forceps

Scalpel Handle
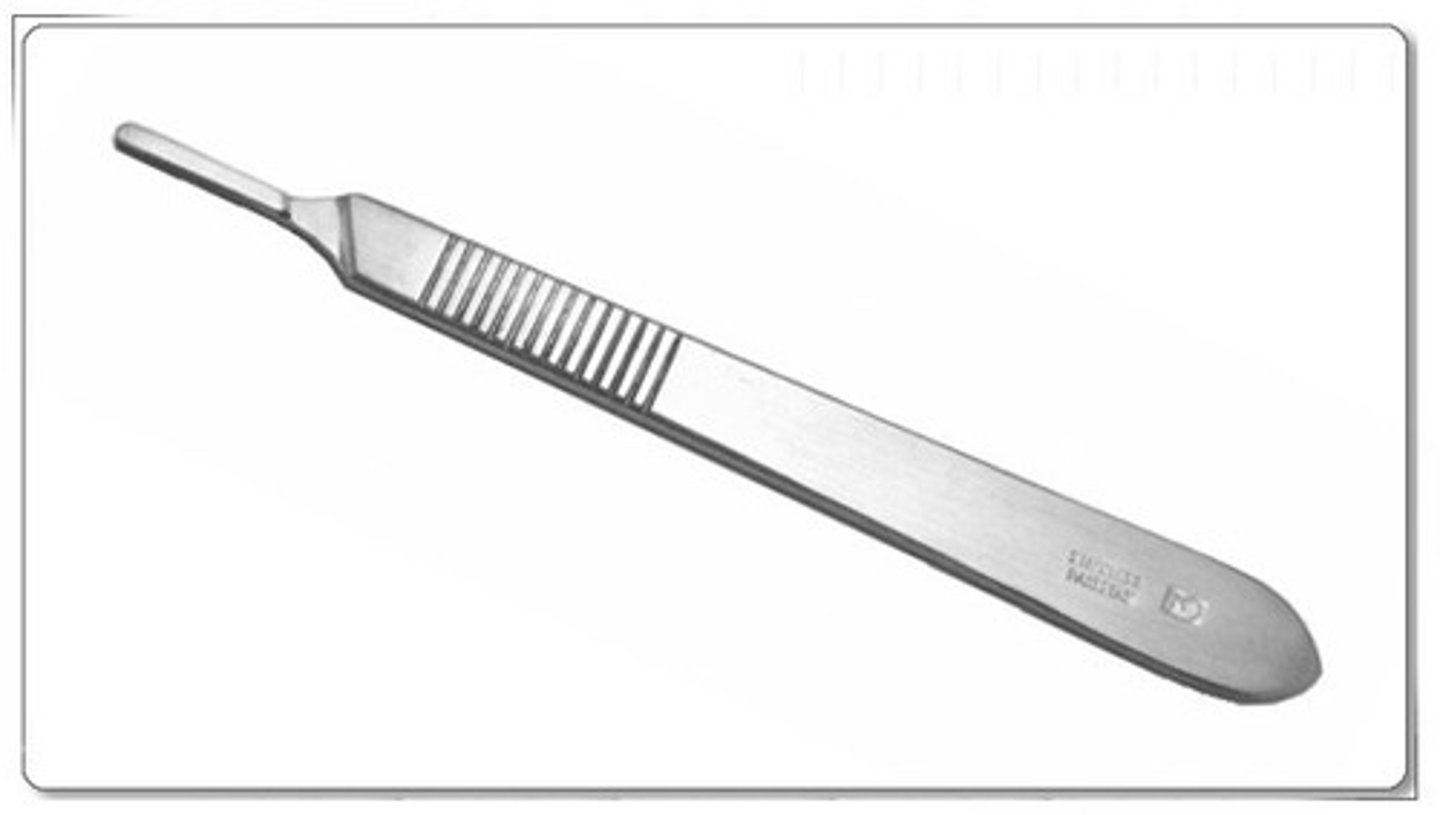

disposable scalpel blade

i) to protect yourself and others from harmful chemicals (do not contaminate your work area)
ii) to prevent contamination of the chemicals
There are two reasons to wear gloves:
-Emergency phone number
-Emergency kit
-Eyewash-Safety shower
-Fire extinguisher
-Fire alarms
-Evacuation route
Lab Safety Resources
-Name of the chemical
-Supplier contact info
-Spill cleanup info
-Hazard info
MSDS (MATERIAL SAFETY DATA SHEETS)
-Each MSDS includes:
-gloves
-goggles
-aprons
Preserved specimens require:
to understand how the natural world works.
what's the purpose of the Scientific Method?
1. Observation.
2.Gather Information.
3.Propose a Hypothesis.
4.Test the Hypothesis.
5.Present and Analyze Results.
6.Conclusion.
Six steps of the scientific method
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4.Discussion
5. Conclusion
Sections of a Scientific Lab Report
Gram (g)
Mass is measured in
Liter (L)
Volume is measured in
Meter (m)
Linear measurement measures in
Seconds (s)
time measures in
1,000,000,000 G
Giga
1,000,000 M
Mega
1,000 k
Kilo
100 h
Hecto
10 dk or da
Deca
Gram (g)
Meter (m)
Liter (L)
Second (s)
base units
0.1 d
deci
0.01 c
Centi
0.001 m
mili
0.000,001 μ
micro
a. All non-zero numbers are significant. Example: 145 has 3 significant figures
b. All zeros between non-zero numbers are significant. Example: 1001 has 4 significant figures
c. All zeros to right of the decimal point AND at the end of the number are significant. Example: 0.1100 has 4 significant figures
d. All zeros before a non-zero digit are NOT significant -they are placeholders only. Example: 0.00034 has 2 significant figures
e. Zeros after a non-zero number with no decimal point are NOT significant. Example: 5000 has 1 significant figure
f. Exact numbers have an unlimited number of significant digits. Exact numbers are counted numbers or ones that are created by definition. They have no uncertainty. Examples: 10 heart beats, 12 inches in a foot
significant figures rules
round off the answer to the same number of decimal places as the lowest in the calculation.
Example: 4.3 + 2.456 = 6.8 (you must round the answer off to 1 decimal place)
addition and subtraction sig figs
round off the answer to the lowest number of significant digits in the calculation.
Example: 4.3 x 2.456 = 11 (you must round off answer to 2 significant figures)
Multiplication and Division sig figs
5
How many sig figs in 10045
2
How many sig figs in 0.0010
1
How many sig figs in 1000
110
Round the following numbers to 2 significant digits. 113
0.46
round the following numbers to 2 significant digits. 0.457
0.0032
round the following numbers to 2 significant digits. 0.003246
3.4
Perform the calculation and use the rounding rules to use the correct number of significant figures. 1.4 + 2.005
302.1
Perform the calculation and use the rounding rules to use the correct number of significant figures 3.006 x 100.5
4
Perform the calculation and use the rounding rules to use the correct number of significant figures. 5.67-2
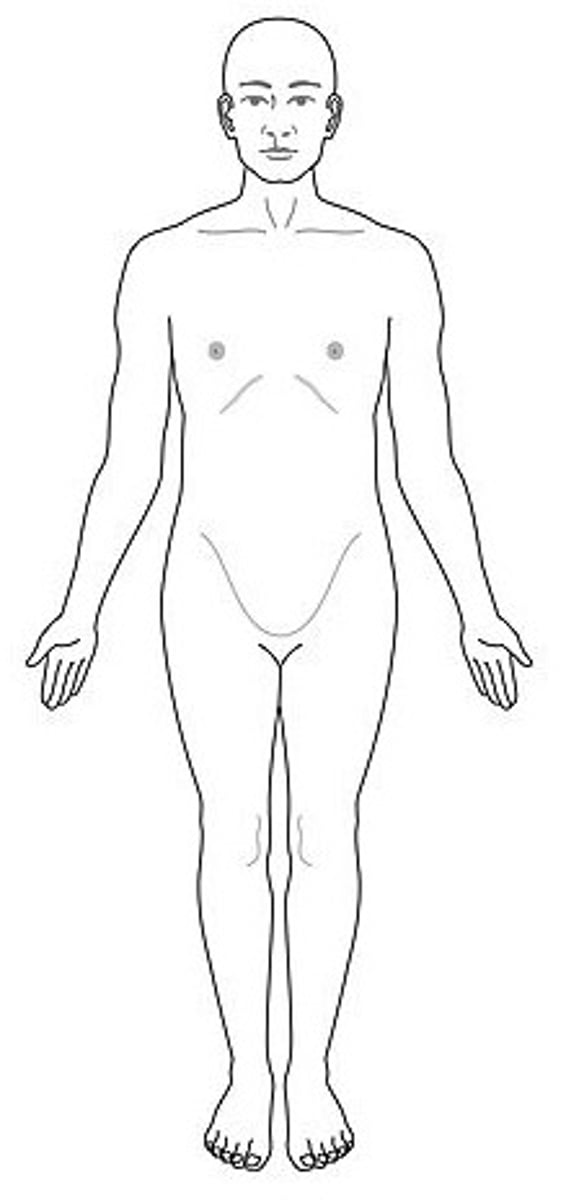
Anatomical Position
a. Standing upright in front of the observer
b. Head level with eyes forward
c. Legs straight, feet flat, pointed forward
d. Arms at sides, straight, palms facing forward, thumbs to the side
e. Right and left refers to subject, not observer
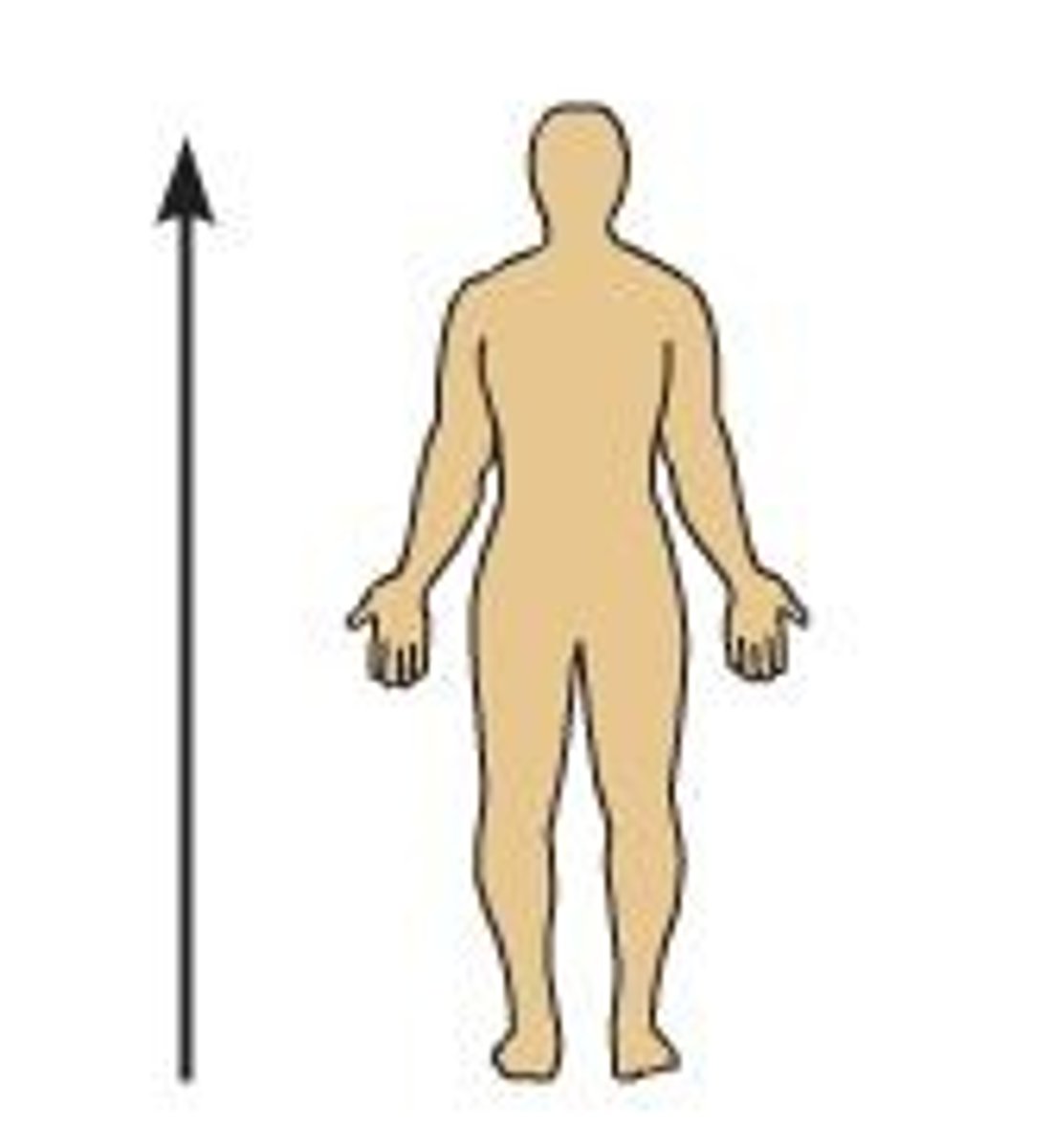
superior / cranial
above or toward the head
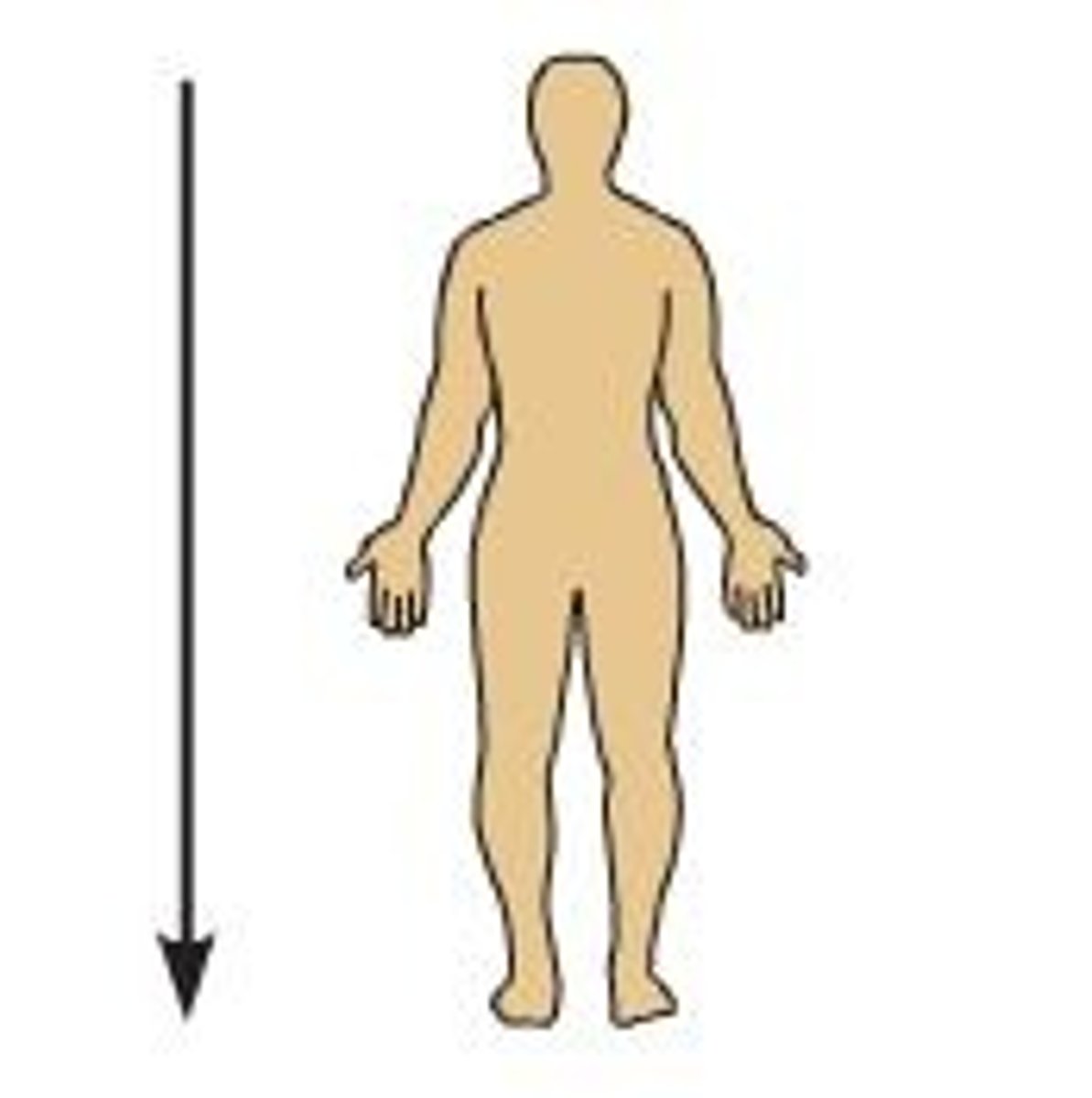
inferior (caudal)
Below or away from the head
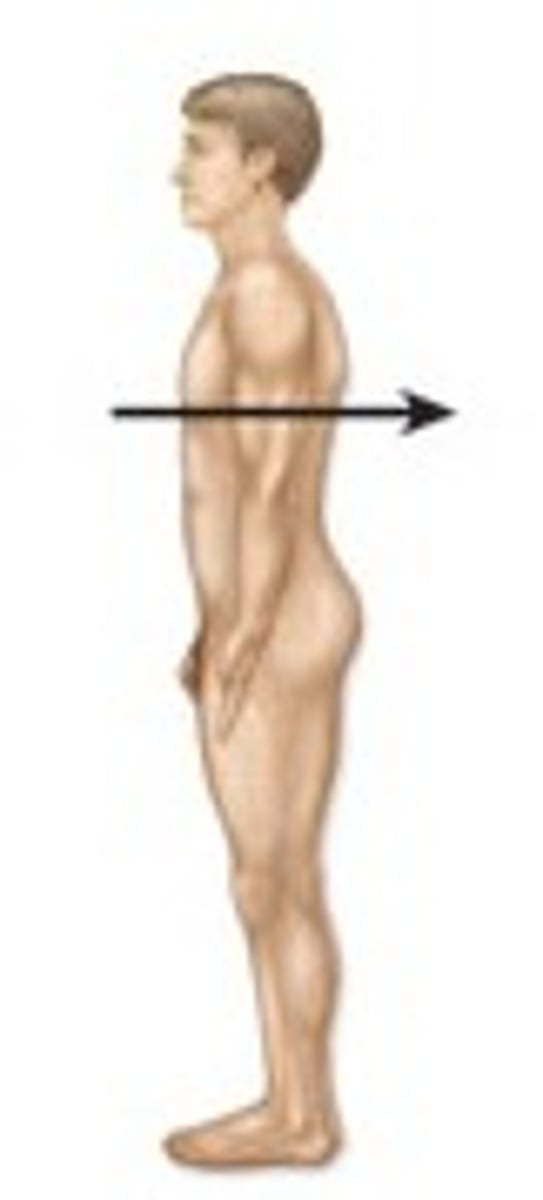
anterior / ventral
closer to the front of the body
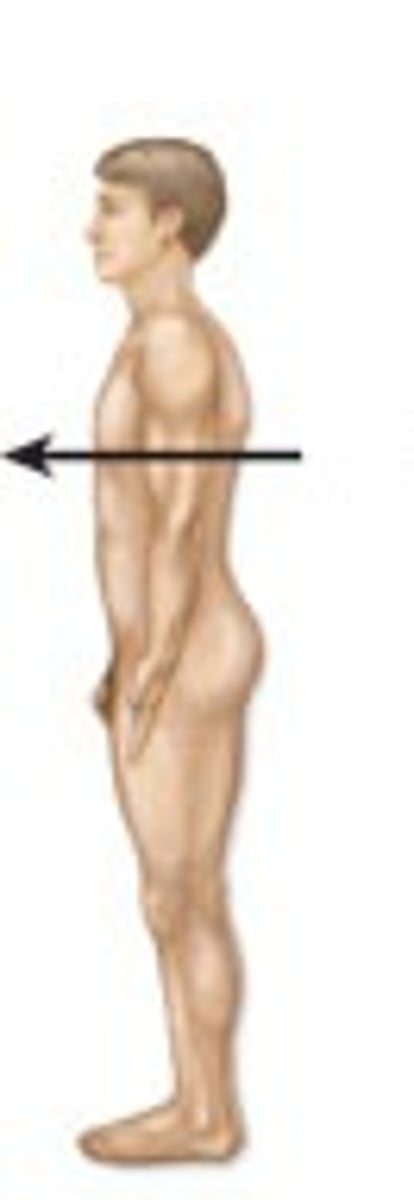
posterior / dorsal
loser to the back of the body
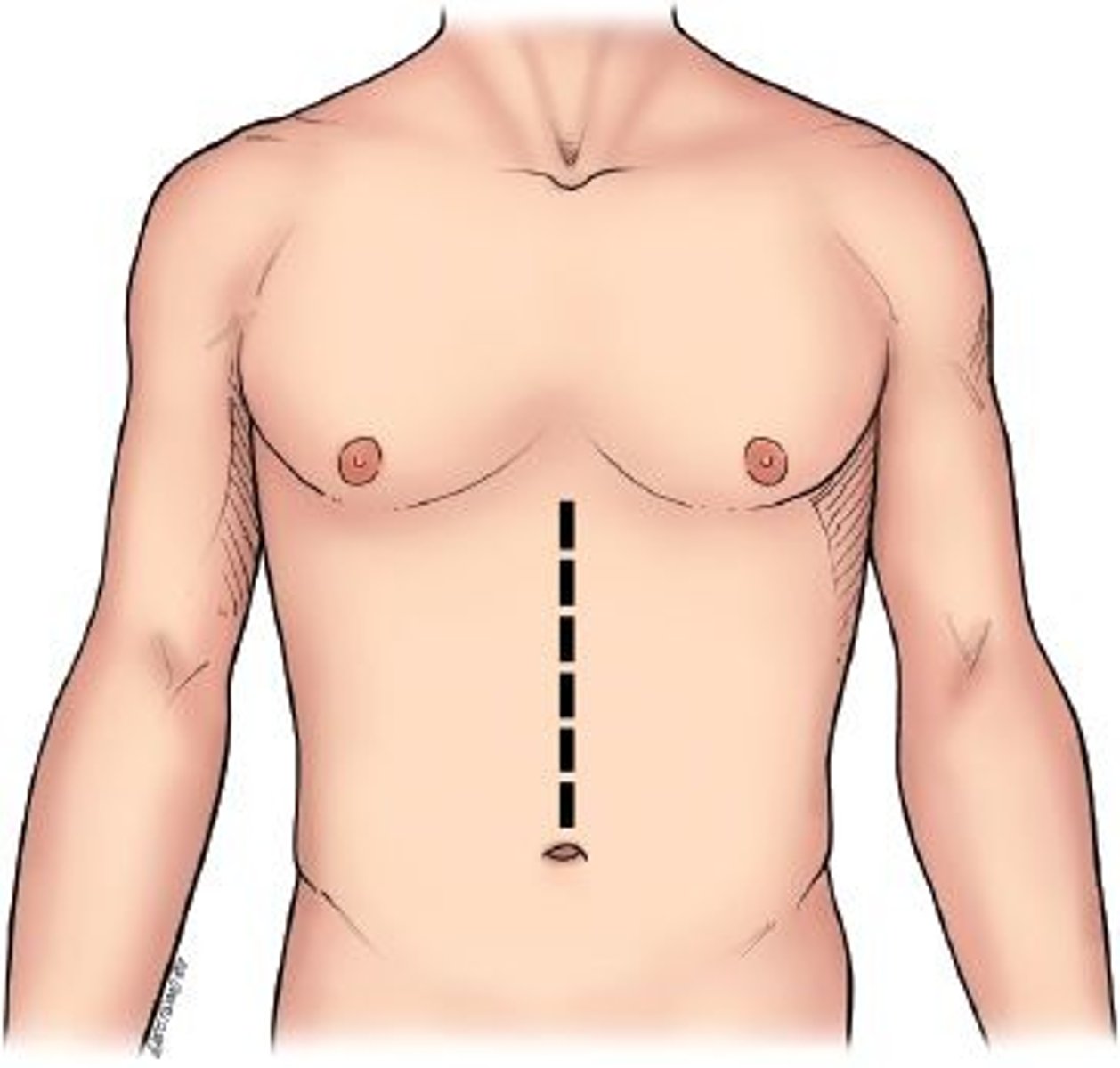
midline
an imaginary line down the center of the body dividing it into matching halves
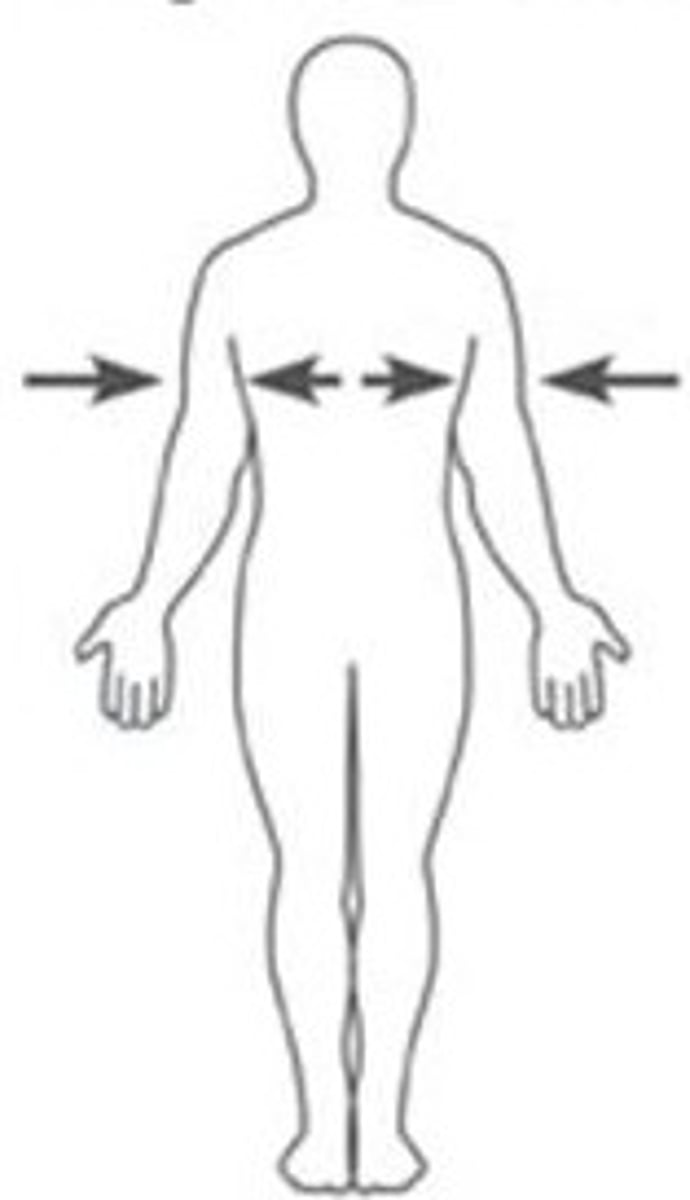
medial
closer to midline of the body
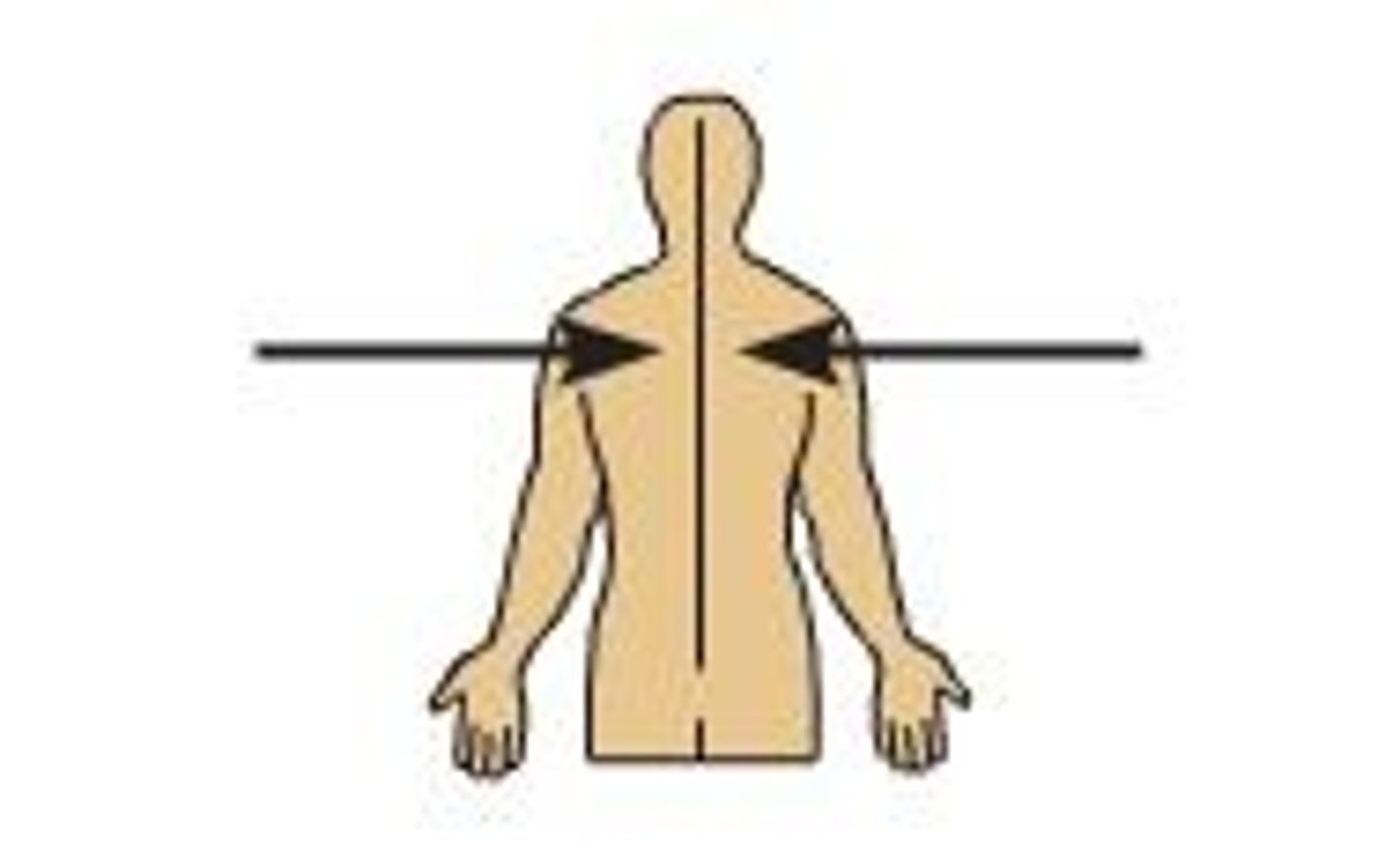
lateral
farther from the midline of the body
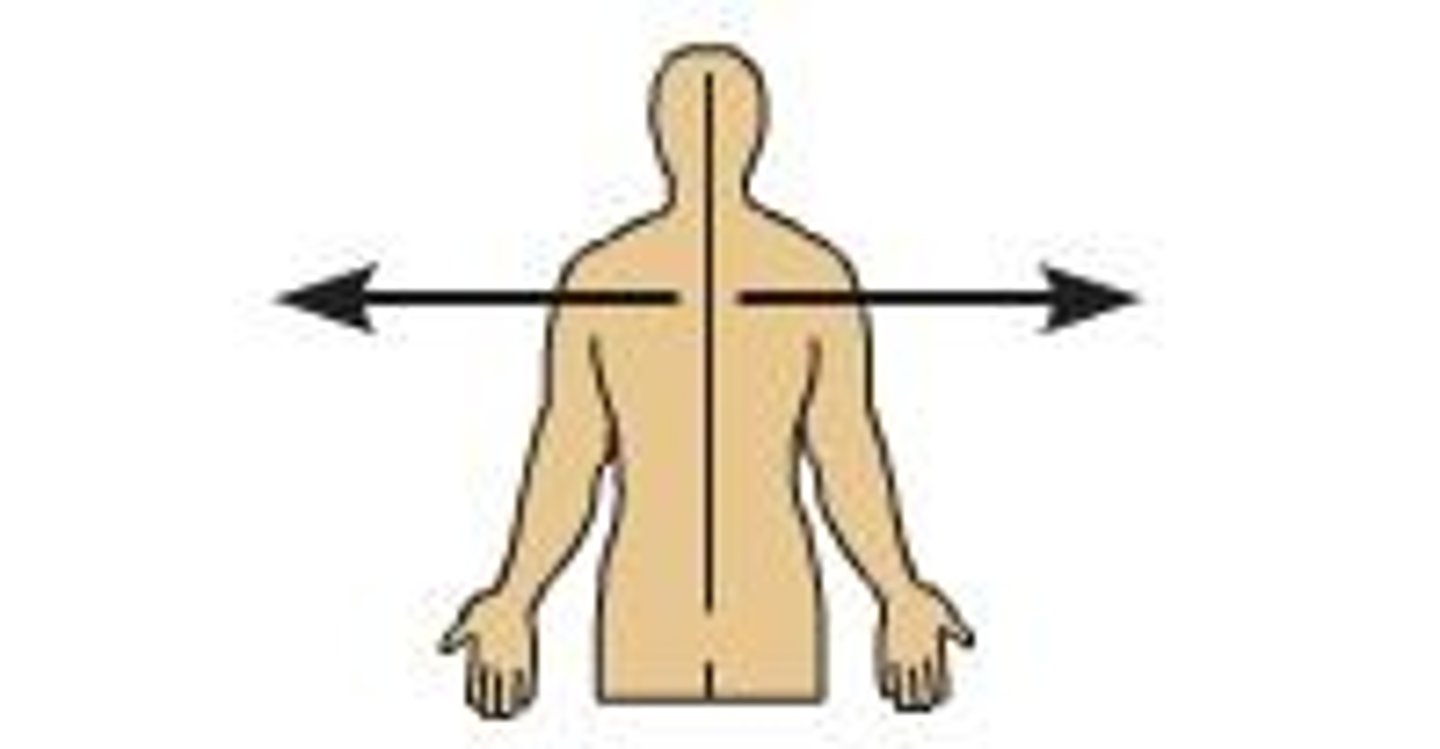
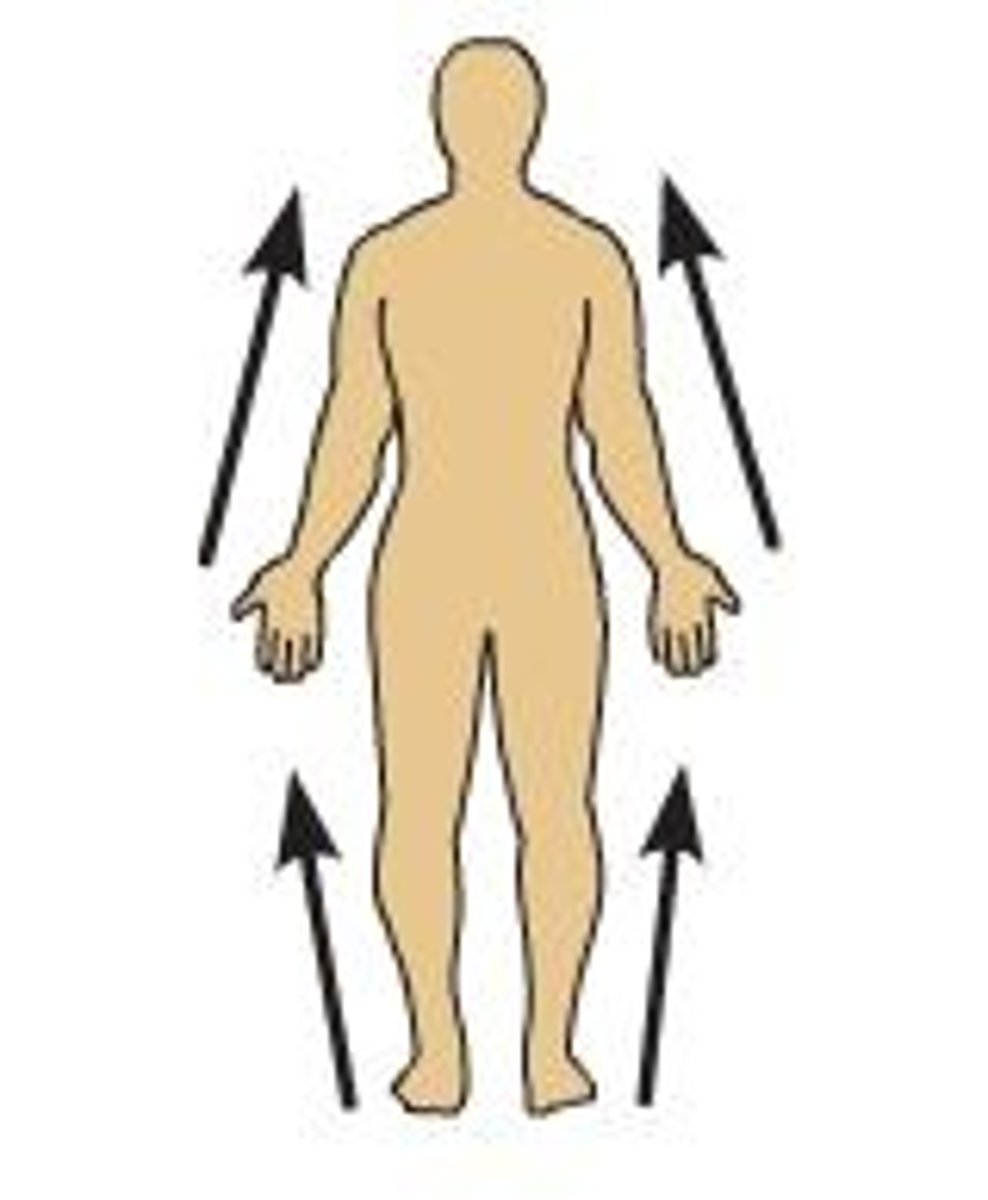
Proximal
closer to the point of attachment
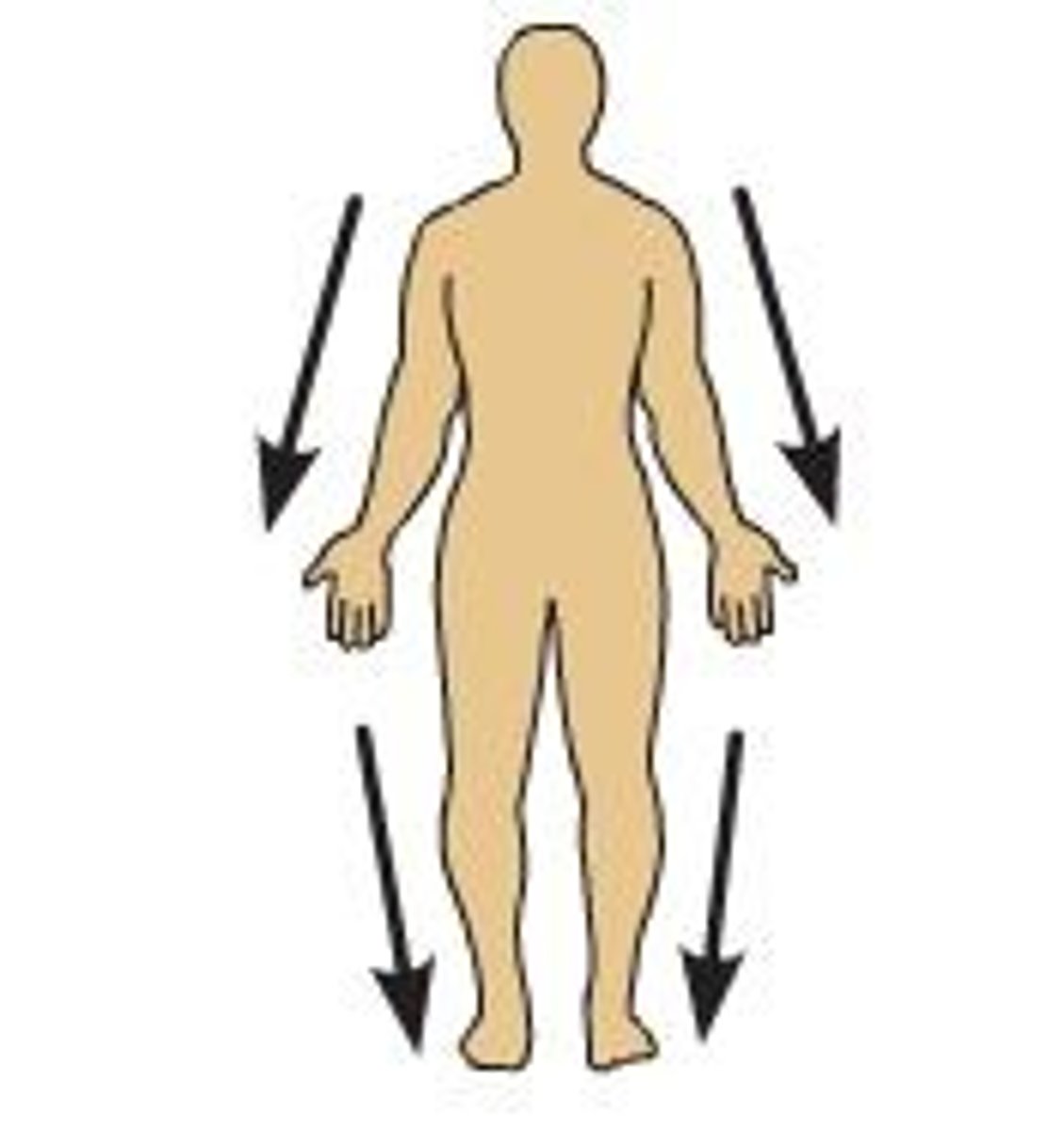
distal
farther from the point of attachment
superficial
toward the surface of the body
deep
toward the interior of the body
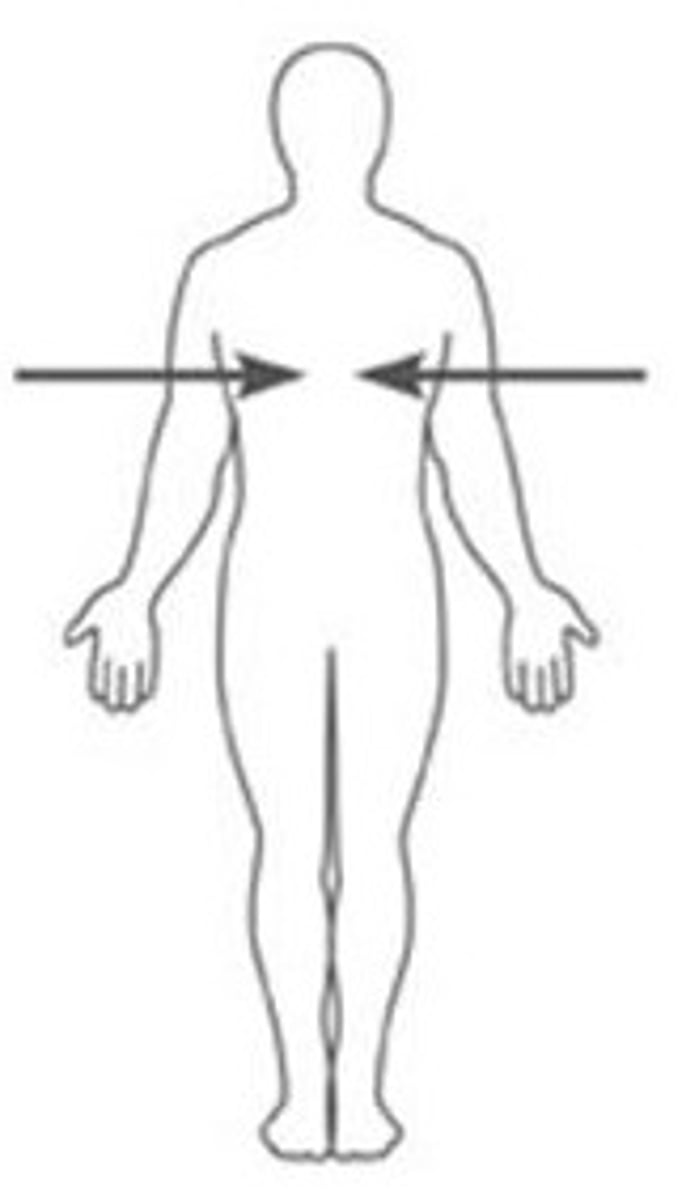
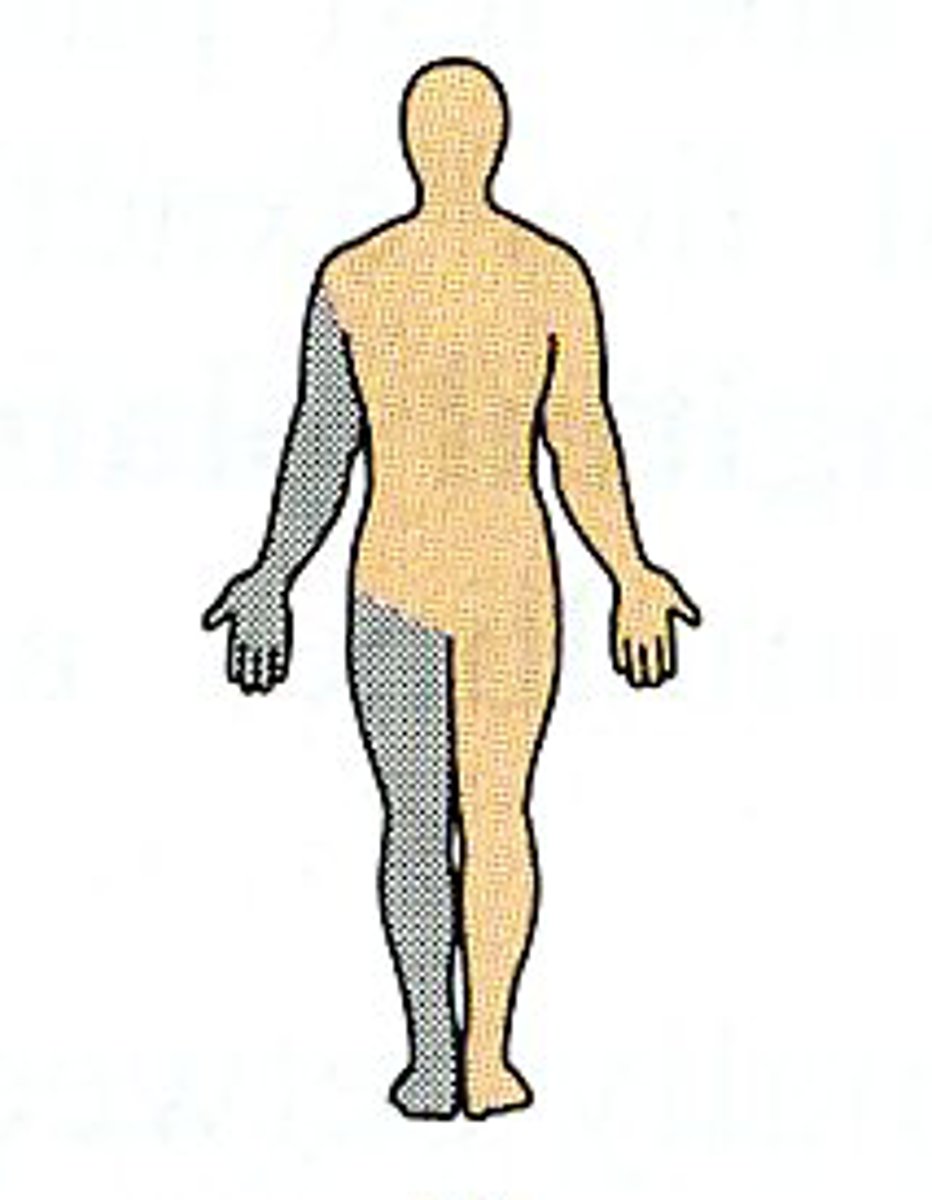
Ipsilateral
on the same side of the body
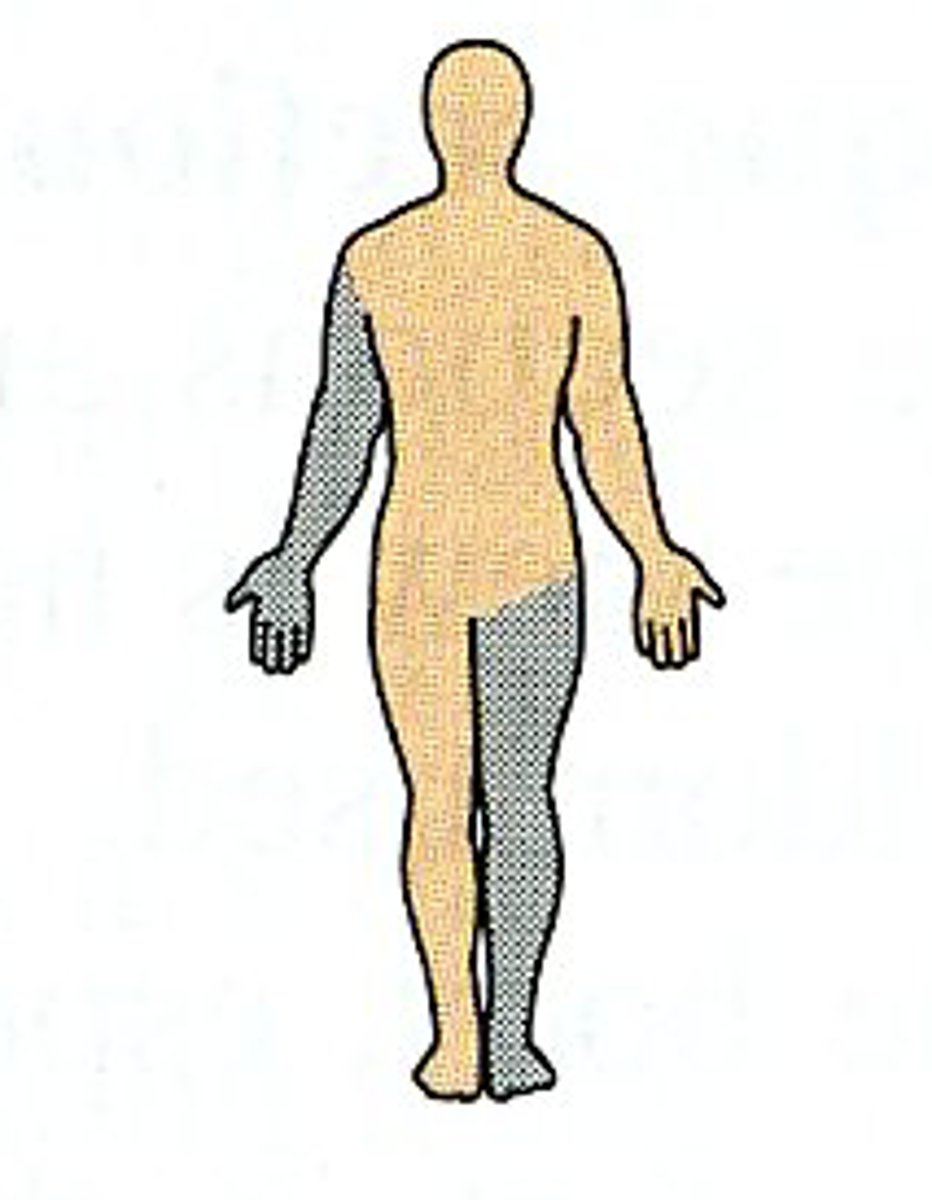
Contralateral
on opposite sides of the body
visceral
pertaining to organs (viscera)
Parietal
pertaining to cavity linings
afferent
to carry toward
_______ neurons carry impulses 'toward' the CNS
efferent
to carry away
_______ neurons carry impulses ' away from' the CNS
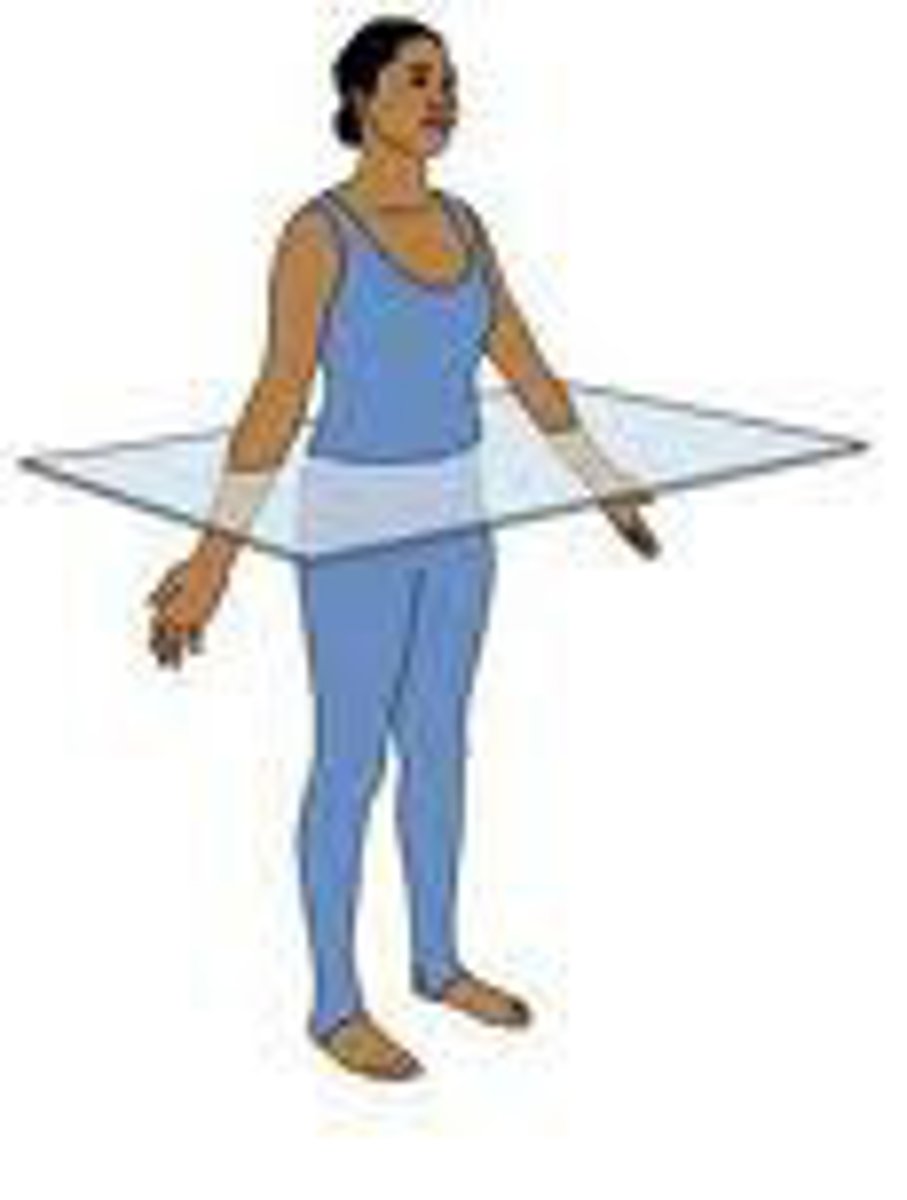
midsagittal plane
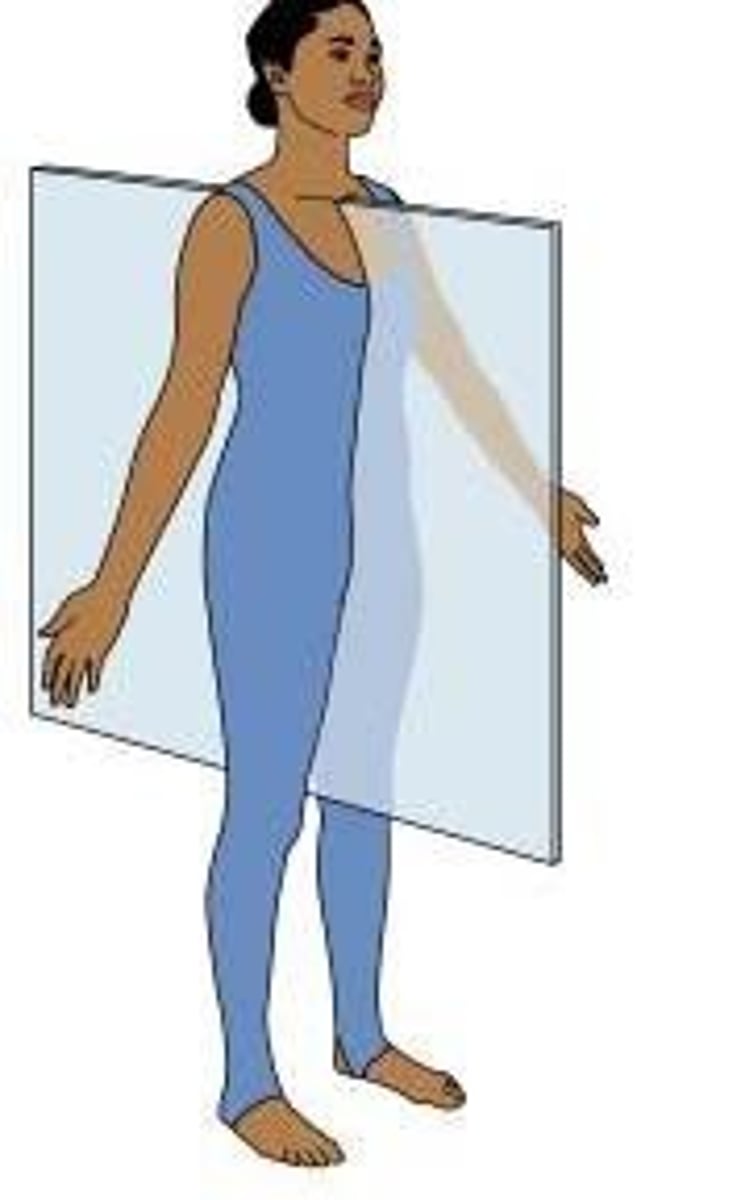
parasagittal plane
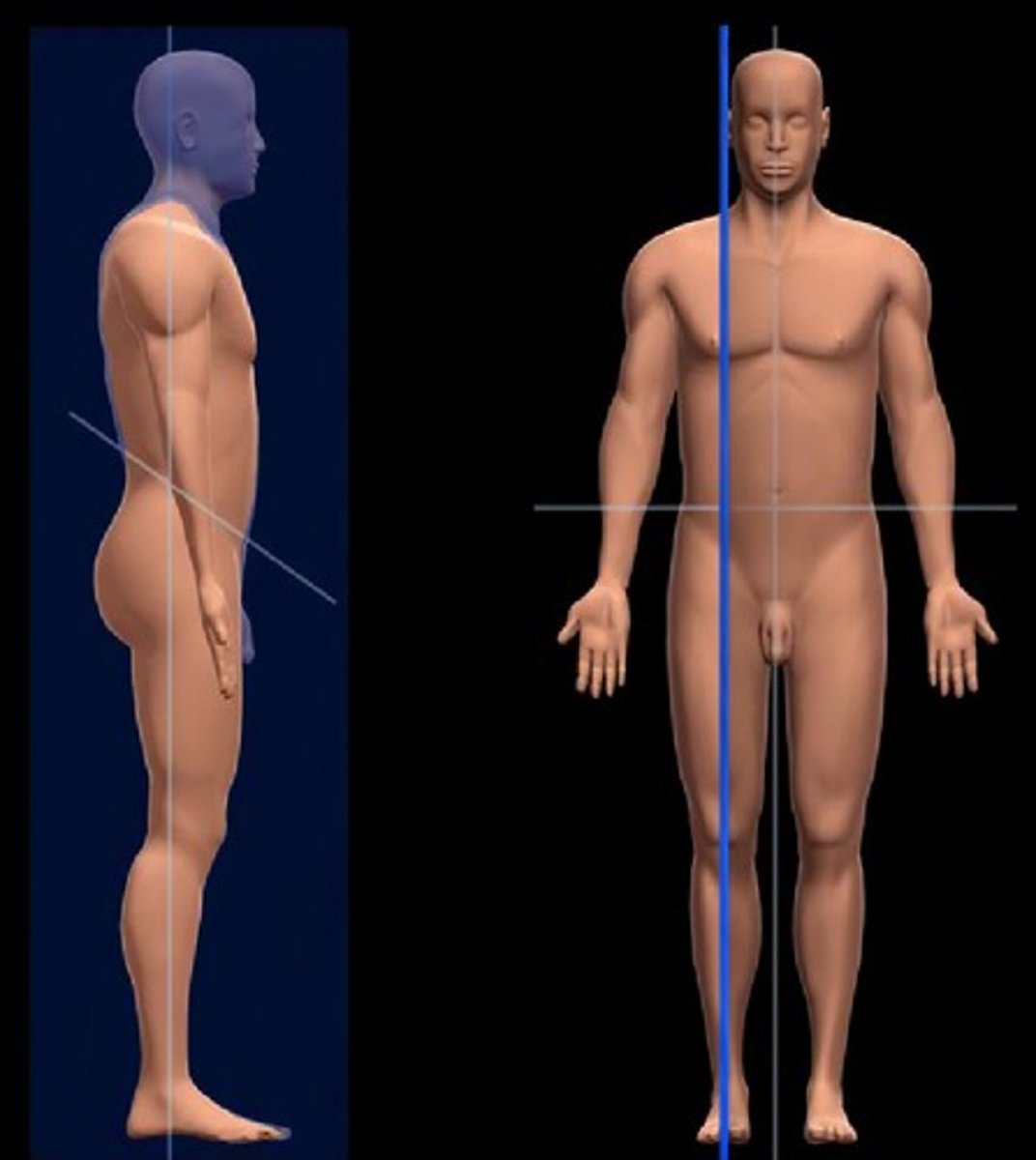
Frontal (coronal) plane

Transverse plane
Oblique plane
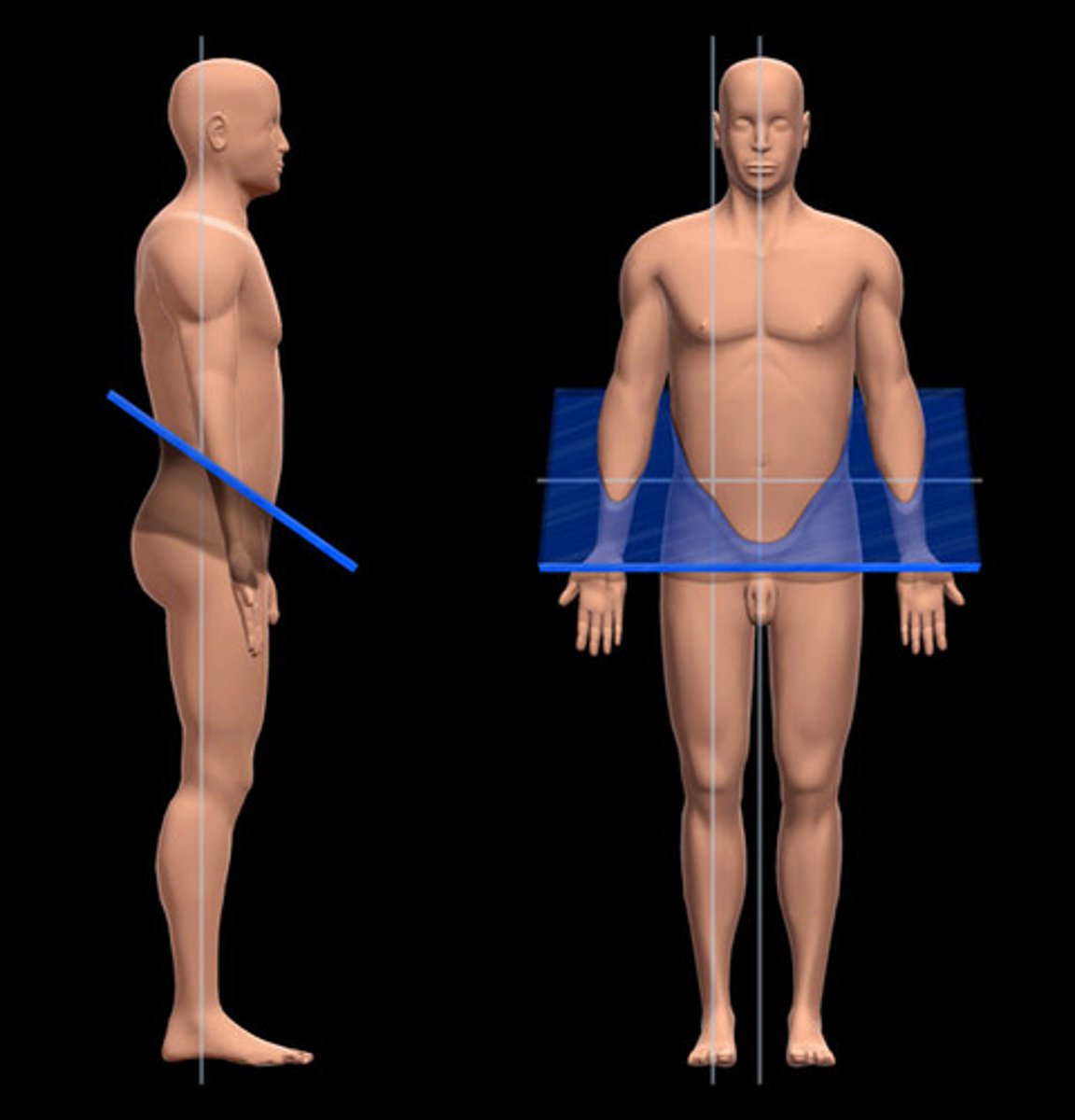
a. Cranial Cavity
b. Vertebral Cavity
Dorsal Body Cavity
a. Thoracic Cavity
i. Pleural Cavity
ii. Pericardial Cavity:
b. Abdominopelvic Cavity
i. Abdominal Cavity
ii. Pelvic Cavity
Ventral Body Cavity
diaphragm
Which structure separates the ventral body cavity into a superior and inferior portion?
LUQ
The majority of the stomach - quadrant
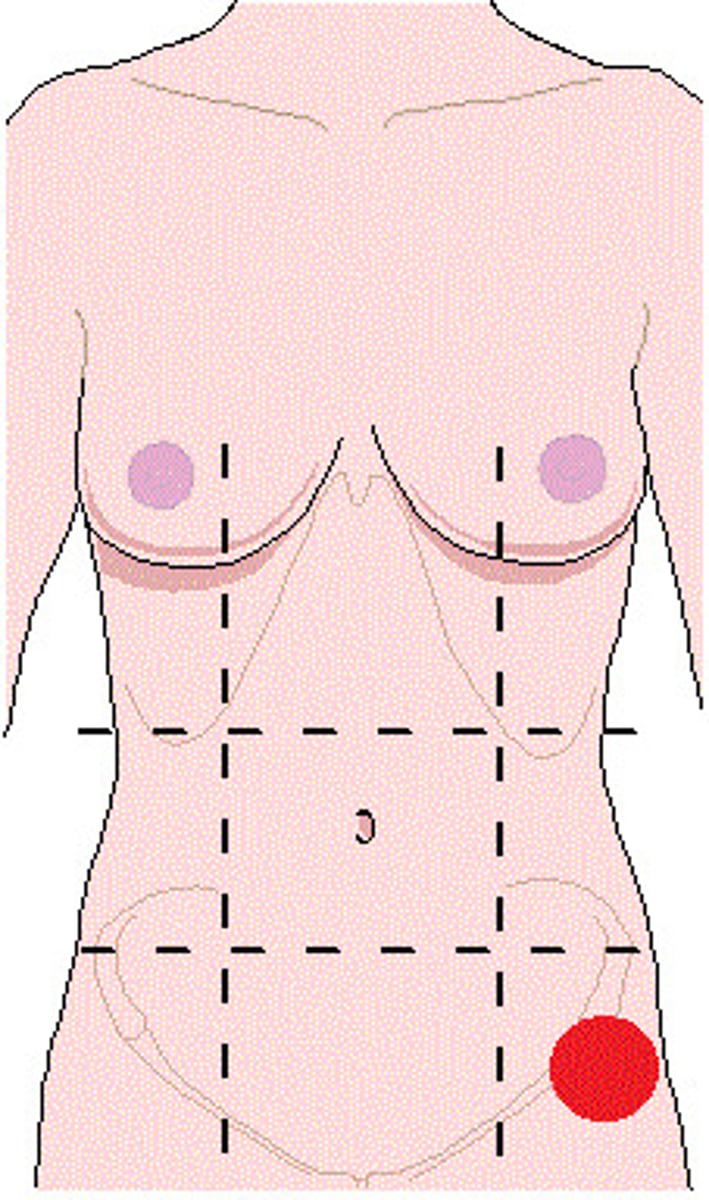
RLQ and LLQ
The uterus(two answers) - quadrant
RUQ
The majority of the liver - quadrant
left hypochondriac region
spleen - region
right inguinal or iliac region
right hip - region
umbilical region
The center region named for the 'belly button'
epigastric region
upper right portion of the liver
Right Upper Quadrant (RUQ)
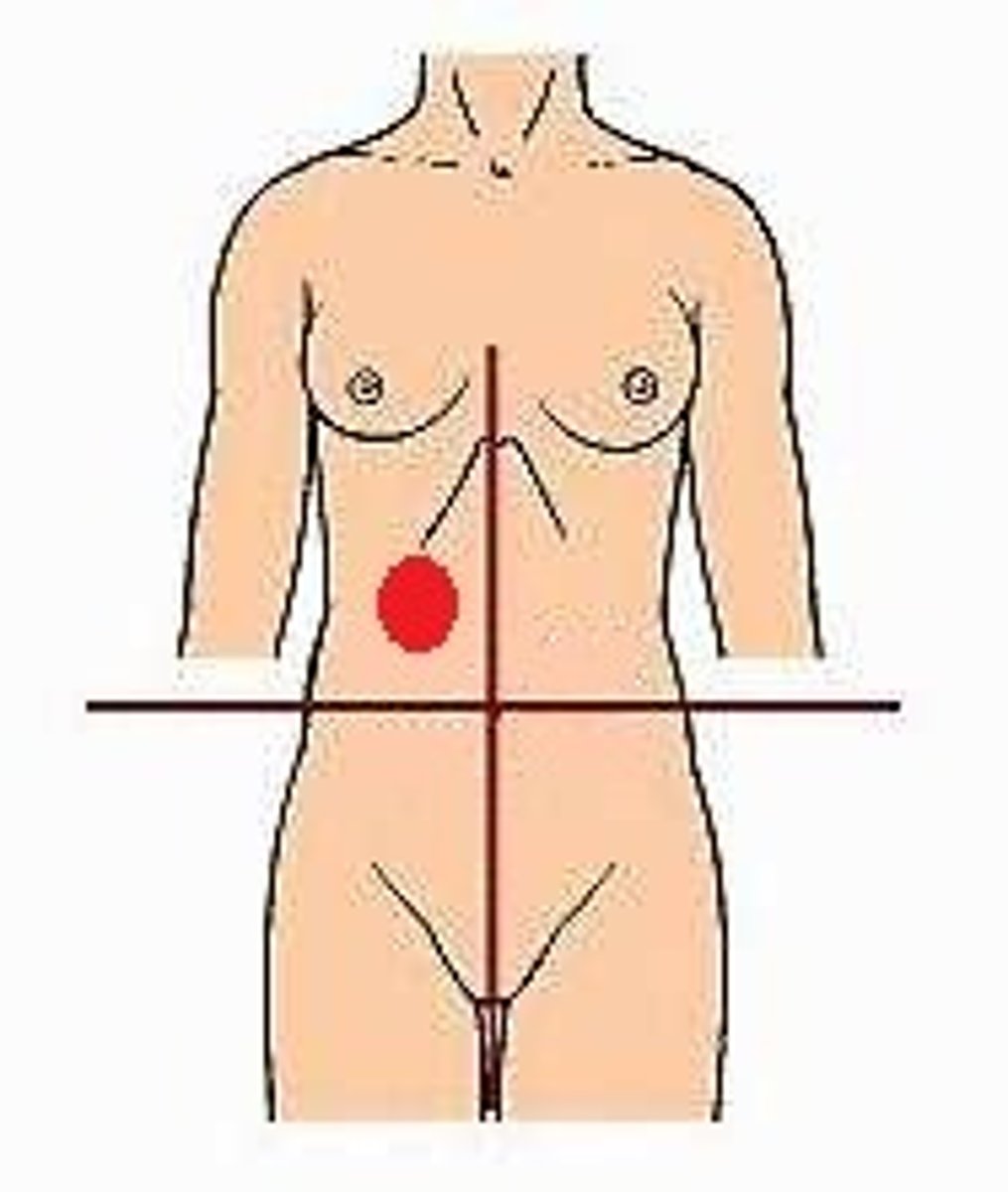
left upper quadrant (LUQ)

right lower quadrant (RLQ)
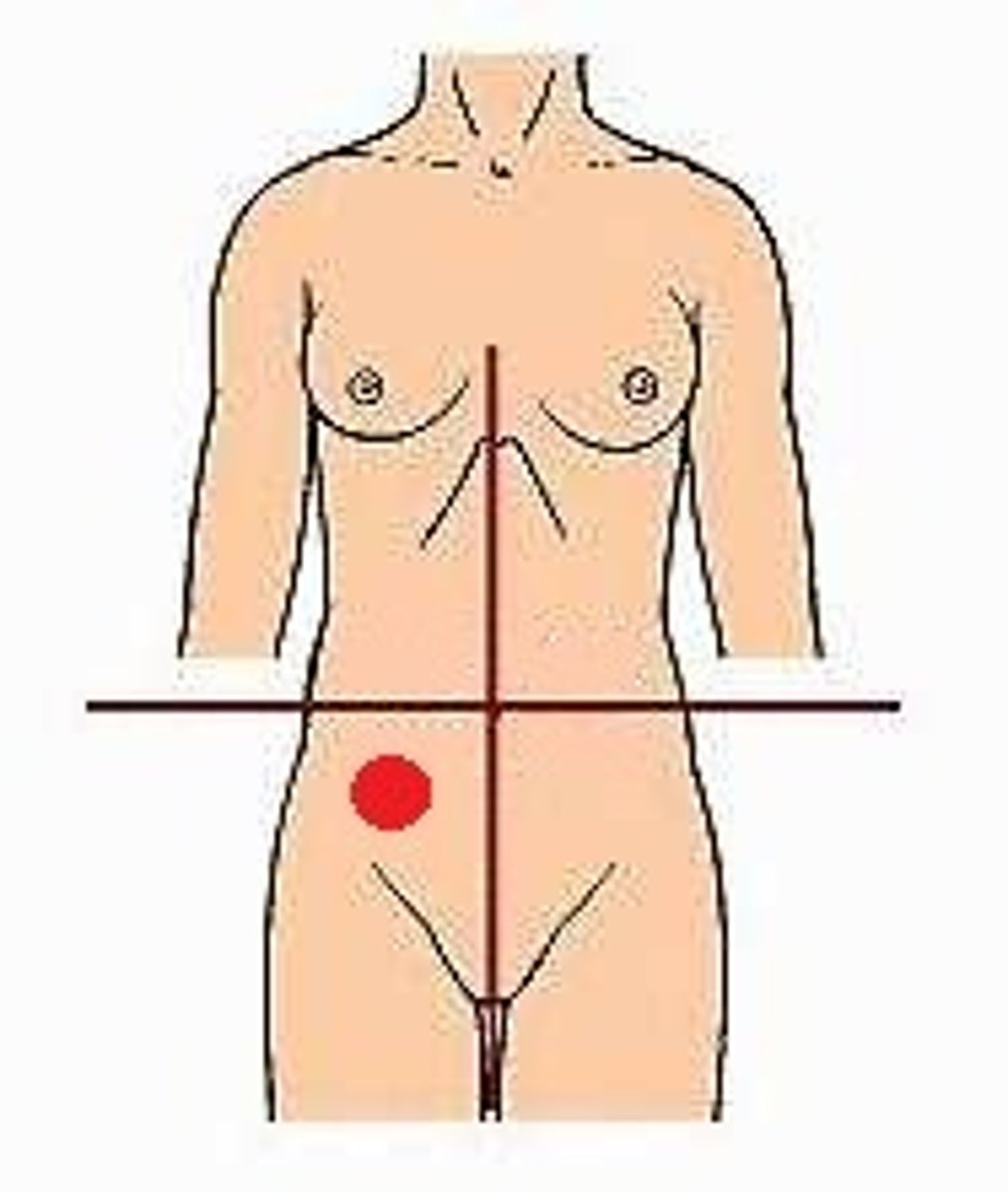
left lower quadrant (LLQ)
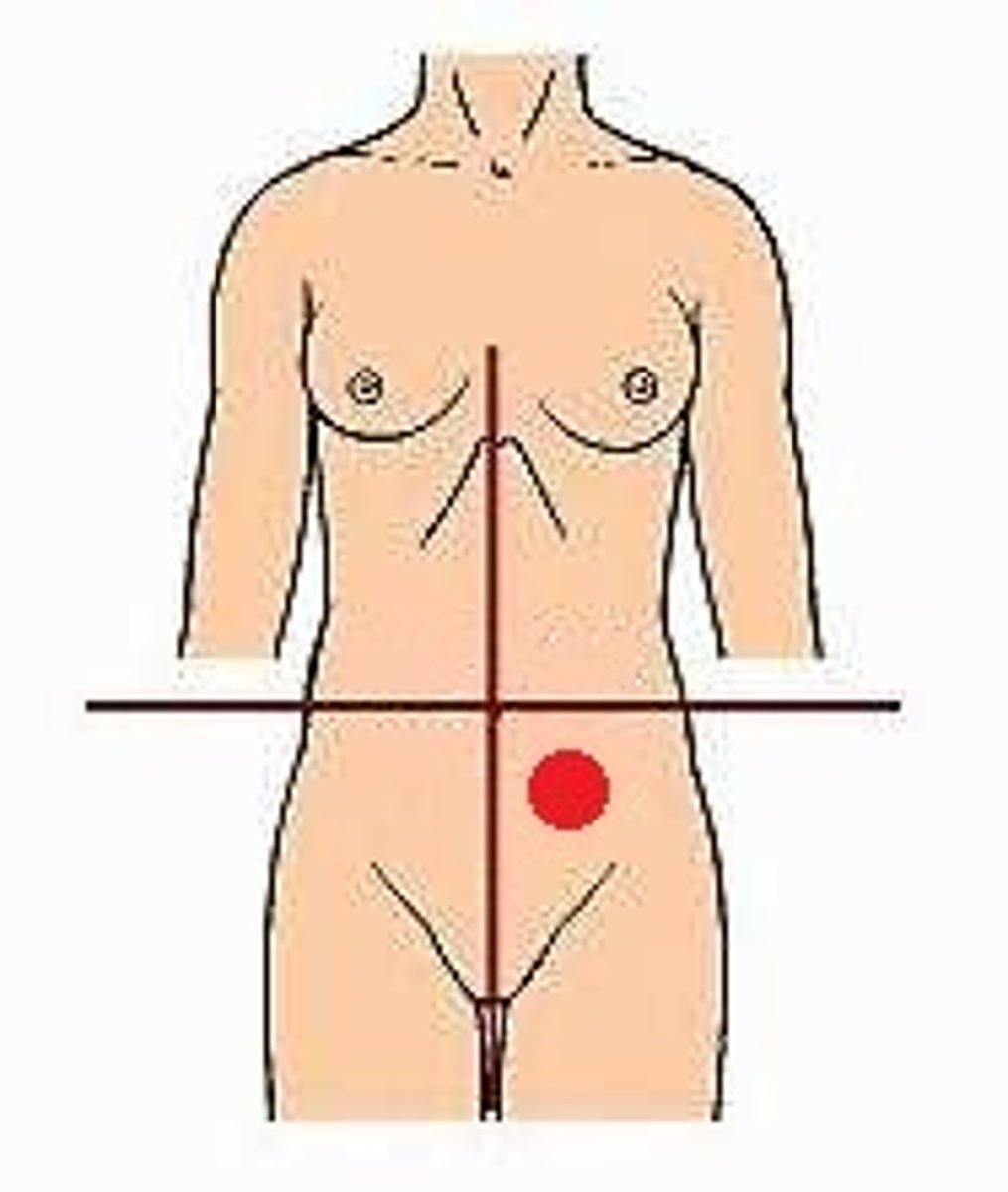
umbilical region

right lumbar (flank) region
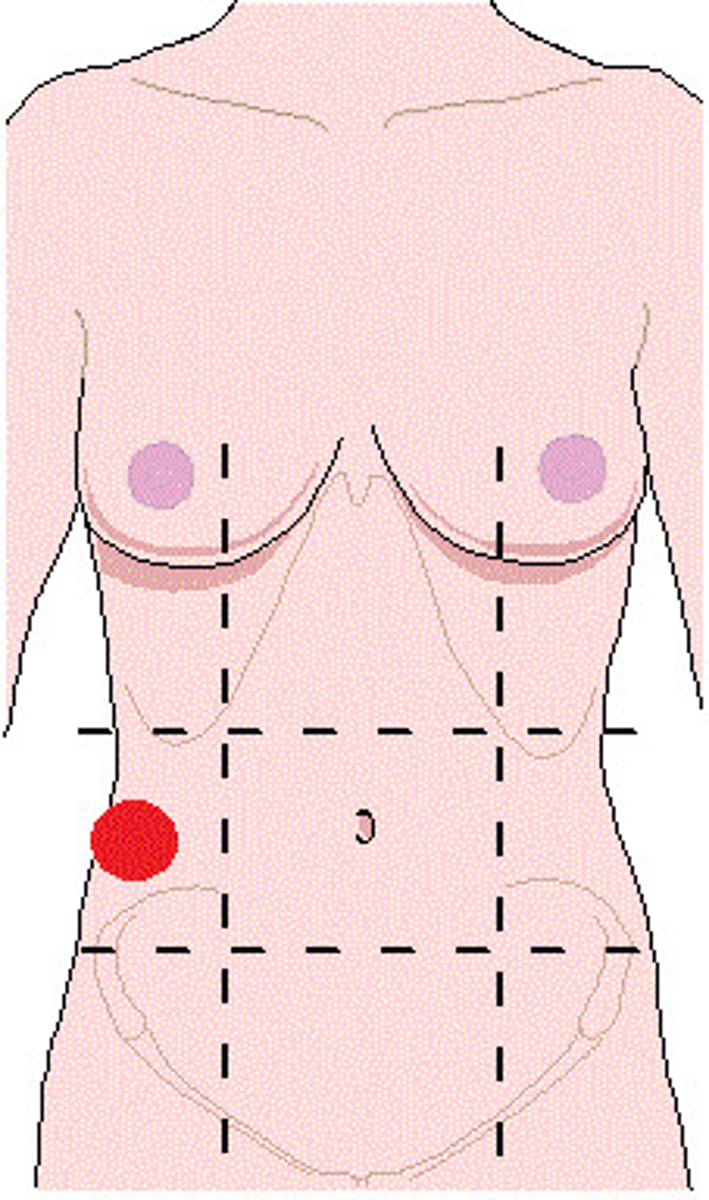
left lumbar (flank) region

epigastric region
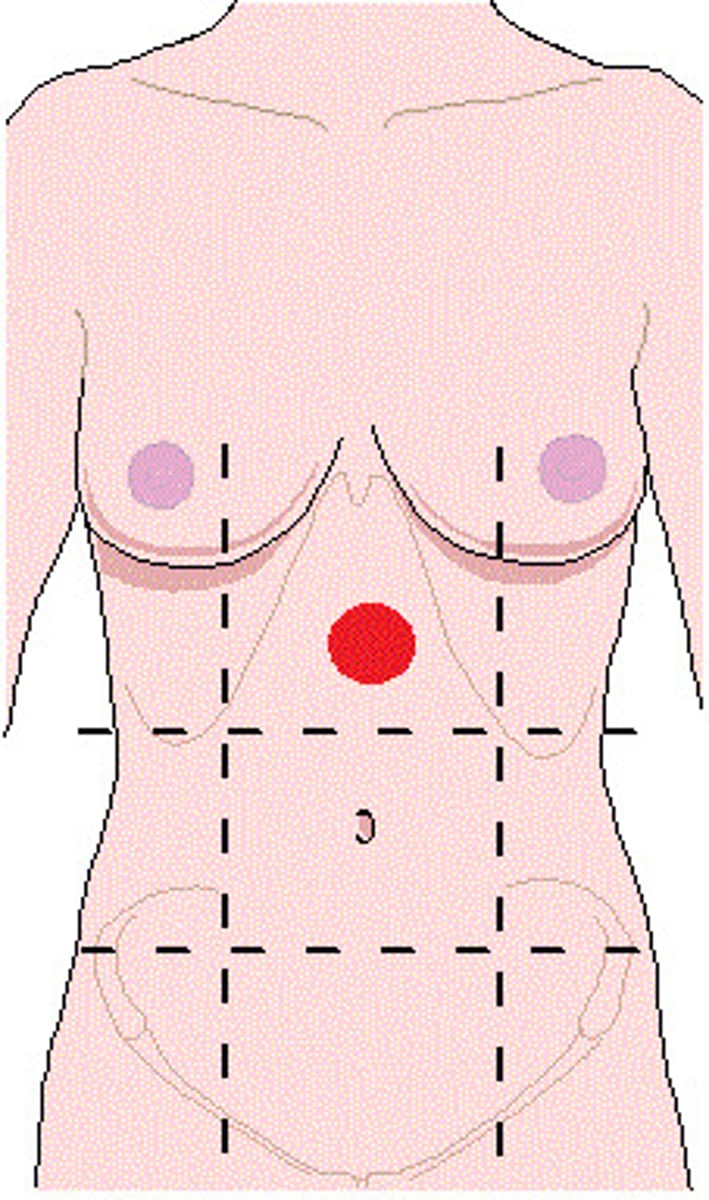
right hypochondriac region
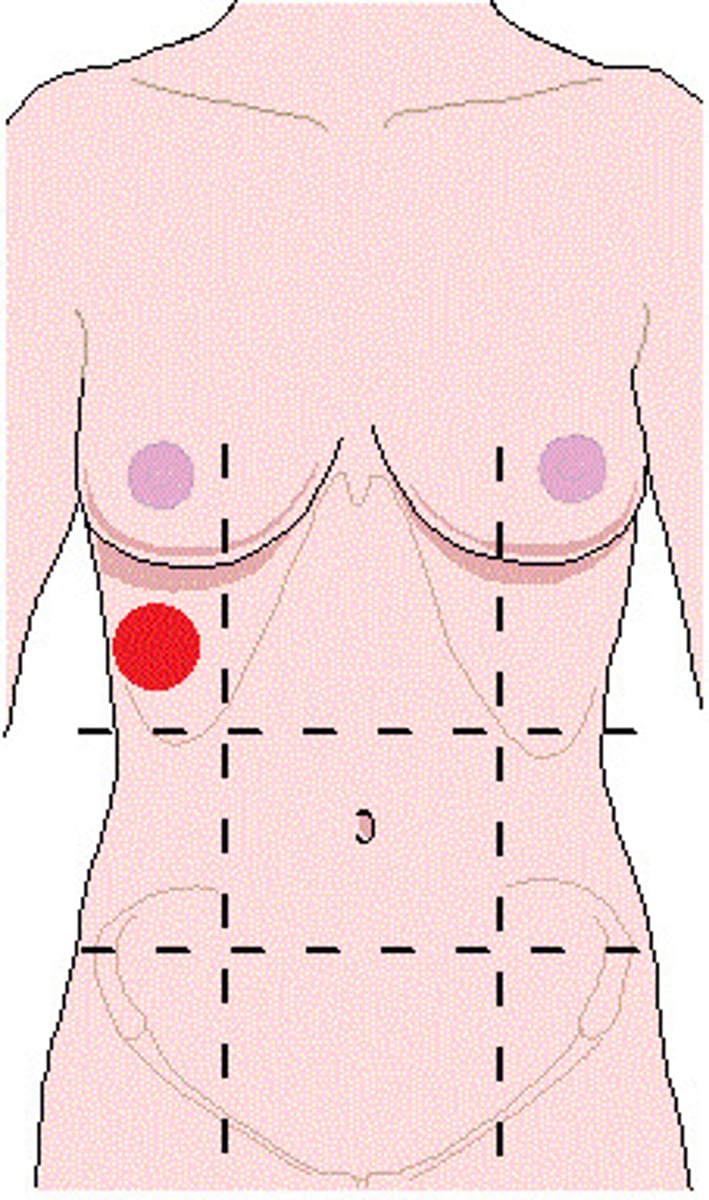
left hypochondriac region
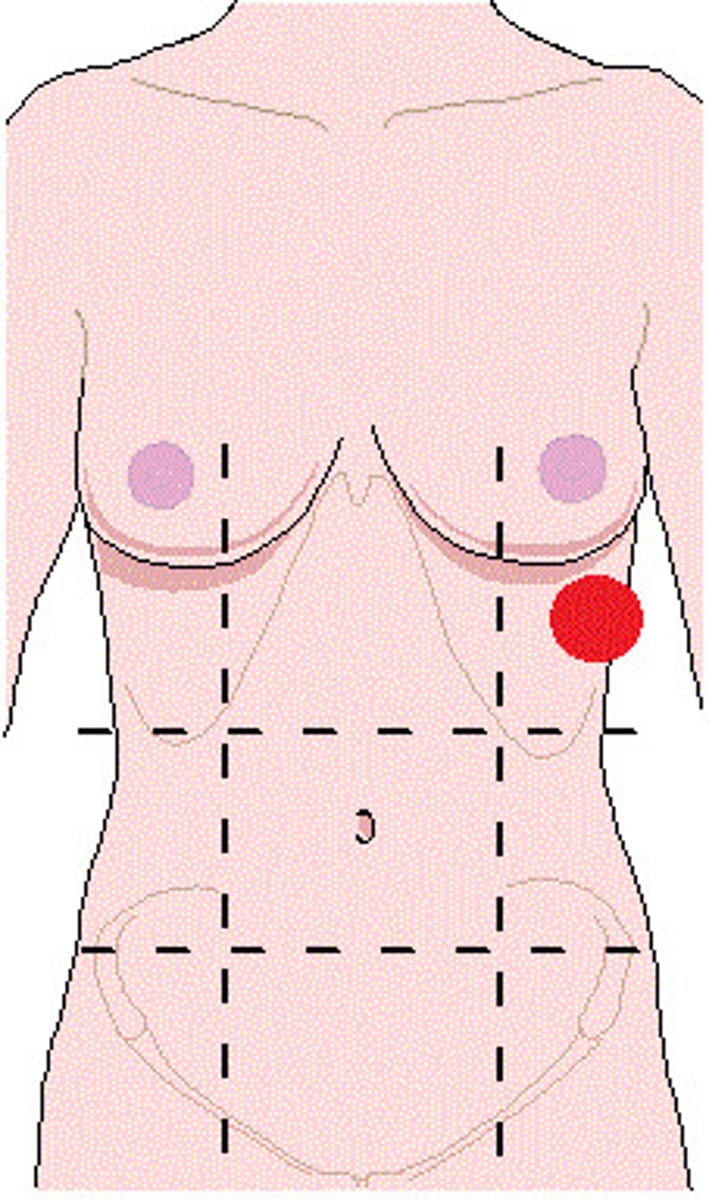
hypogastric (pubic) region
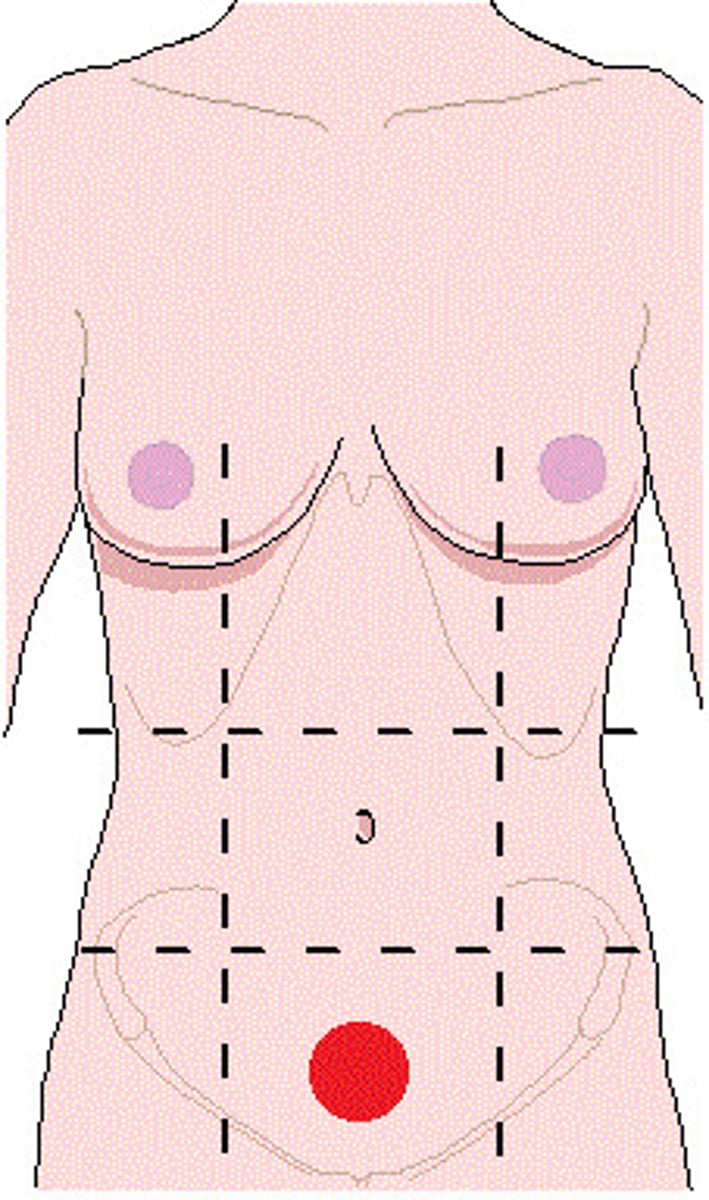
right iliac (inguinal) region
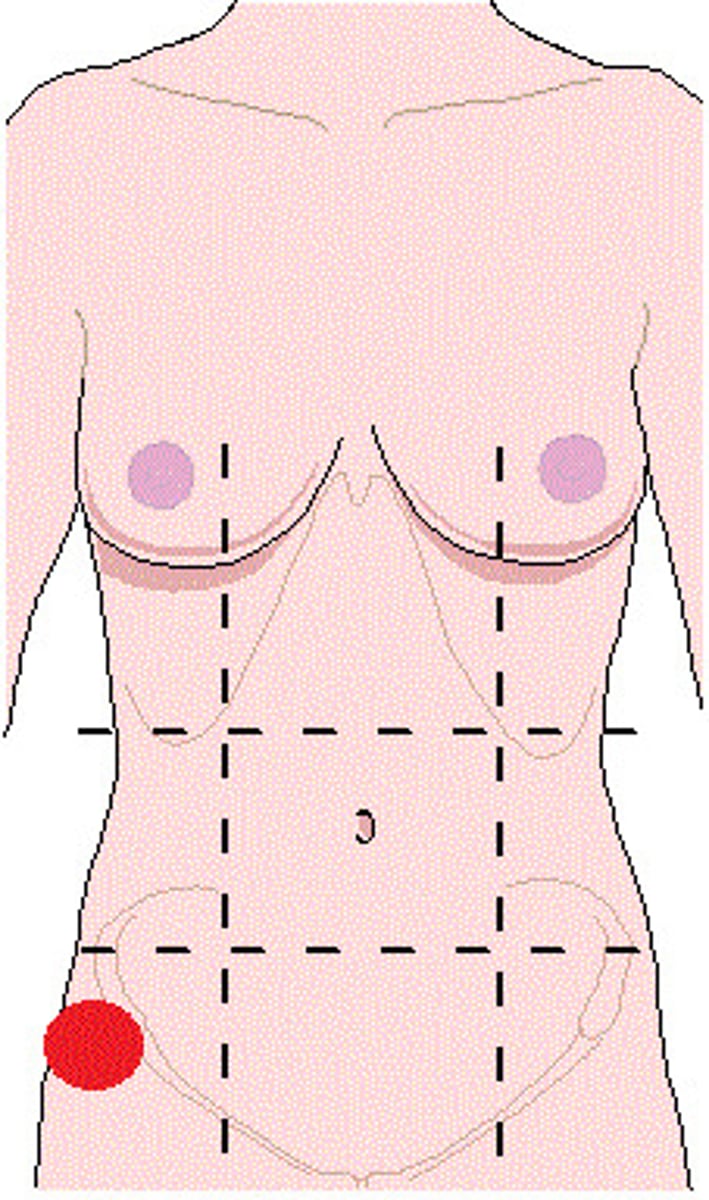
left iliac (inguinal) region
acid
a substance that produces hydrogen ions in a solution; a proton donor
base
a substance that increases the hydroxide (OH)ions in a solution; proton acceptor (check this)