bio unit 3 pt 2 (cell membrane transport and nervous system)
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
fluid mosaic model
the parts that make up the cell membrane, can move around
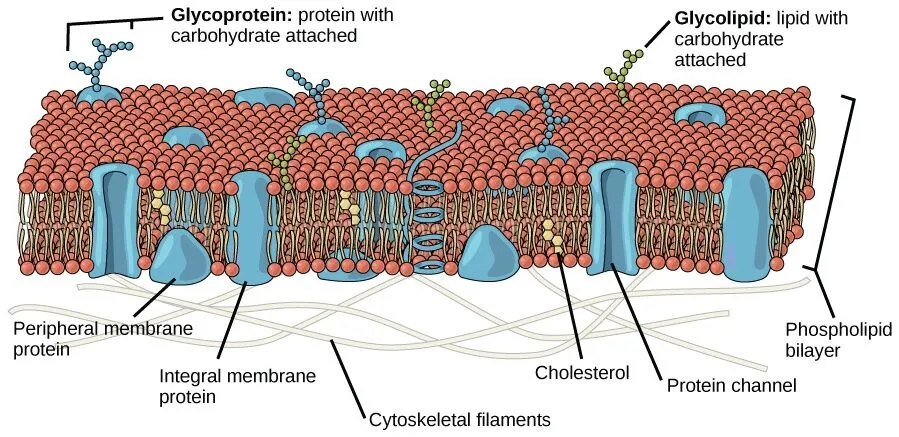
head of phospholipid
tail of phospholipid
hydrophillic, polar
hydrophobic, non-polar
amphiphilic
head likes water because it is also POLAR WOW
semi-permeable
lets some materials through but not others
aplicable to cell membrane
cholesterol in the phospholipid bilayer
acts as spacers between phospholipids in cold temps
acts as connecters in warm temps
integral proteins
go through membrane - involved in transport, lets things in / keeps things in
transport (channel) proteins
allow only certain molecules to pass through
exclusively involved in passive transport, also known as facilitated diffusion
receptor proteins
receive info from outside the cell and trigger a response inside
marker proteins (glycoproteins)
have carbohydrate chains that act as identifiers to identify cells
passive transport
no energy
moves molecules along (DOWN) concentration gradient
moves small nonpolar and polar molecules
uses: water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, glucose
examples: simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, osmosis
active transport
uses energy
uses: large and charged particles
moves molecules against (UP) concentration gradient
always involves channel proteins
ions line Na+ and K+
examples: pumps, exocytosis (pinocytosis and phogocytosis), exocytosis
simple diffusion
movement of molecules from high to low concentration (down gradient)
molecules pass between phospholipids
moves small polar and nonpolar molecules
ex: oxygen and carbon
facilitated diffusion
movement from high to low concentration (down gradient)
always involving transport proteins/channel (membrane spanning) proteins
moves small polar and nonpolar molecules
ex: water and glucose
osmosis
the diffusion of water across a membrane though channels called aquaporins
hypotonic
outside has lower solute than inside
water moves into cell
cell swells
hypertonic
outside has higher solute than inside
water moves out of cell
cell shivels
isotonic
solute concentrations are equal
no net movement
what is active transport
movement of molecules from low to high concentration
required energy in the form of ATP
uses transport proteins (often pumps)
proteins pumps
use energy to push molecules against their concentration gradient
uses energy released within cells to force substances through the plasma membrane
endocytosis
cell taking materials in
phagocytosis and pinocytosis
phagocytosis
cell eating (large particles)
Movement of large food particles across the membrane with the use of pseudopods
pinocytosis
cell drinking (small dissolved molecules)
exocytosis
cell gets rid of particles by fusing a vesicle with the cell membrane
how are the bubbles similar to cell membranes
hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tail
how are the bubbles different from cell membranes
the surrounding medium (air) is non polar so the tails of the bilayer face outward and the heads form the inside with a thin layer of film of water
what is the function of the cell membrane
separates the contents of the cell from the surroundings, serves as a barrier for which substances can enter and exit a cell, recognizes chemical signals which will trigger the cell to react in a particular way
peripheral proteins
more loosly attached, act as enzymes, help with cell shape
glycoproteins
proteins and carb bound
identifies cell as part of the organism
glycolipids
carbs and phospholipids
communcation
ion channel
protein that acts as a pore to ions - allows them to pass freely through plasma membrane in either direction
aquaporin
pores made of protein, allows for water molecules to pass easily through cells plasma membrane
oxygen
concentration of oxygen in the cell is lower than the outside
passes from high to low - into the cell (diffusion)
carbon dioxide
higher concentration of carbon dioxide in the cell
passes from high to low - out of the cell (diffusion)
sodium
protein pumps
water
can pass through lipid bilayer (slower) OR with aquaporins (faster)
enzymes
exported through exocytosis process (surrounds enzyme and releases it out of the cell)
potassium and sodium
passive (facilitated diffusion) and active (pumps out of cell)
hypotonic vs hypertonic
hypotonic = the solution has less solute than the cell, so water will flow from the solution into the cell (down the gradient, high to low), causing it to swell hypertonic = the solution has more solute than the cell, so water will flow from the cell into the solution, causing it to shrink