plate tectonics and isostasy
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
what are plate tectonics?
can be oceanic, continental, or both depending on location of boundary
“slabs” of the earths crust and mantle, they move over the asthenosphere
continental plates
plates are much thicker, but less dense, made of granitic rock
oceanic plate
on the bottom of the ocean, thinner and much more dense, made of basalt
types of plate boundaries
convergent
divergent
transform
convergent plate boundary
two plates coming together →←
form either subduction zones, or create mountain ranges
continental plates + continental plates
continental plates + oceanic plates
oceanic + oceanic
continental plates + continental plates =
mountain ranges, no subduction
continental + oceanic =
subduction zones, denser oceanic dives beneath continental, volcanic arcs/stratovolcanoes
oceanic + oceanic =
older, more dense oceanic plate subducts underneath the younger, less dense one
divergent plate boundary
two tectonic plates spreading apart ← →
can happen in ocean or on land
divergent plate boundaries in the ocean
new crust is created, magma rises and creates new oceanic crust
divergent plate boundary on land
continental rift valley, two tectonic plates stretch the crust and thin it out, example east african rift system
transform plate boundaries
tectonic plates “slip” past one another (in opposite directions), instead of directly converging or diverging
hot spots
plumes of magma rise from the mantle of the earth, melt the overlying crust, and create shield volcanoes
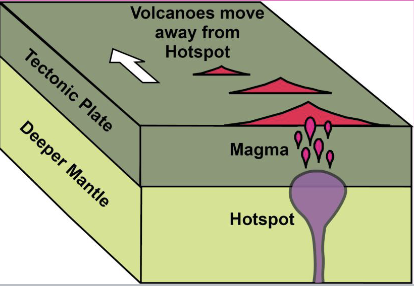
seamount
created from hot spots
as hotpsot creates volcanoes, the crust that volcano sits on is always moving but the mantle plume is stationary
the movement of the ground makes a seqeunce of volcanoes (seamount) that are moving away from the hotspot/mantle plume
isostasy
gravity-controlled equilibrium between lithosphere and asthenosphere
isostasy equilibrium: how do tectonic plates sit on top of the mantle?
lithospheric plate floats above the asthenosphere because the floating depends on the thickness and density of the lithosphere. asthenosphere is thick and hard but still maleable. the heat from mantle helps the asthenosphere act as a solid to hold up the lithosphere
lithosphere is transformed by plate tectonics surface is constantly being modified)
lithosphere weight and thickness changes through geologic time, triggering isostatic adjustments