Organic Theory Questions
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
What are ambident nucleophiles?
Nucleophiles that can attack through two different sites are called ambident nucleophile.
Ex: :CN- (nitrites) and :NC- (iso cyanide or iso nitrites)
Difference between SN1 and SN2
CW
Optical Isomers and Enantiomers
Two compounds with same molecular formula but differ in the direction of plane polarised light are called optical isomers
Dextro Rotatory (+) and Laevo Rotatory (-)
Two optically active compounds which can form non-super imposable mirror images to each other are collectively called enantiomers
Haloalkanes react with KCN to form alkyl cyanides as main product while AgCN forms isocyanides as the chief product. Explain.
KCN is predominantly ionic and provides cyanide ions in the solution.
Although both carbon and nitrogen can donate electron pairs, the attack takes place through the carbon atom since the C-C bond is more stable than the C-N bond.
However AgCN is mainly covalent in nature and nitrogen is free to donate electron pair forming isocyanide as the main product
n-Butyl bromide has higher boiling point than t-butyl bromide.
N-Butyl bromide is a straight chain molecule with strong intermolecular forces whereas t-butyl bromide is a branched chain molecule with weak intermolecular forces due to smaller surface area. Hence n-Butyl bromide has higher boiling point than t-butyl bromide.
Alkyl halides, though polar, are immiscible with water.
This is due to less energy being released by interaction of alkyl halides and water which is not enough to break the hydrogen bonding in water
Why does p-dichlorobenzene have a higher melting/boiling point than its o- and m-isomers?
This is because the para isomer has a symmetrical structure and therefore, can fit crystal lattices better than the ortho and meta isomers. Hence, it has strong intermolecular forces of attraction than o and m isomers and requires higher energy to break. Therefore, it shows a higher melting/boiling point.
The dipole moment of chlorobenzene is lower than that of cyclohexyl chloride.
This partial double bond character in the C–Cl bond due to resonance reduces the polarity and thus the dipole moment.
The carbon in chlorobenzene is sp2 hybridised having greater S-character, making it more electronegative. Hence, sp2 hybrid carbon of C - Cl bond in chlorobenzene is less polar than cyclohexyl chloride having sp3 hybridised carbon.
Therefore, dipole moment of chlorobenzene is lower than that of cyclohexyl chloride.
(±)-butan-2-ol is optically inactive.
or
Racemic mixture is optically inactive.
(±)-butan-2-ol is a racemic mixture, which contains equal amounts of both enantiomers dextro-rotatory and levo-rotatory
When equal amounts of the two enantiomers are present, their optical activities cancel each other out.
Therefore, the overall rotation of the mixture is zero.
Since the overall optical rotation of the (±)-butan-2-ol mixture is zero, it is considered optically inactive.
Grignard’s reagents should be prepared under anhydrous conditions.
Grignard reagents are very reactive. In the presence of moisture, they react to give alkanes. Therefore, Grignard reagents should be prepared under anhydrous conditions.
R-MgX + H2O → [Dry ether] R−H+Mg(OH)X
Chloroform is stored in closed dark coloured bottles completely filled so that air is kept out.
Chloroform is slowly oxidised by air in the presence of light to an extremely poisonous gas phosgene. Therefore it is stored in dark bottles completely filled so that air is kept out.
2CHCl3( Chloroform) + O2 → 2HCl + 2COCl2 (Phosgene)
C-Cl bond length in chlorobenzene is shorter than C-Cl bond length in CH3Cl.
sp² hybridisation of C-Cl bond in chlorobenzene has more s-character compared to sp³ hybridised C-Cl bond in CH3Cl pulling electrons closer to the nucleus.
Also, because of resonance in chlorobenzene, C-Cl bond in chlorobenzene has double bond character, which makes it shorter in length.
Although chlorine is an electron withdrawing group, yet it is ortho-, para-directing in electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions.
Although chlorine is an electron-withdrawing group due to its -I (inductive) effect, which pulls electron density away from the benzene ring, it also exhibits a +R (resonance) effect. Through resonance, chlorine can donate its lone pair of electrons to the benzene ring, increasing the electron density at the ortho and para positions.
butan-1-ol is optically inactive but butan-2-ol is optically active.
Butan-1-ol is an achiral compound. Therefore it is optically inactive. Butan-2-ol is a chiral molecule. Therefore it is optically active.
The presence of nitro group (—NO2) at o/p positions increases the reactivity of haloarenes towards nucleophilic substitution reactions.
The presence of nitro group at ortho or para position increases the reactivity of haloarenes towards nucleophilic substitution because − N O 2 group, being an electron-withdrawing group decreases the electron density over the benzene ring
Chlorobenzene is extremely less reactive towards a nucleophilic substitution reaction.
he C-Cl bond acquires partial double bond character due to resonance which is more difficult to break
Cl attached to sp2 hybrid carbon which is a stronger bond (more s character), so harder to break
Instability of phenyl cation
Benzene ring is always electron rich so it will repel the electron rich nucleophile
Ethyl iodide undergoes SN2 reaction faster than ethyl bromide.
Iodide (I⁻) is a better leaving group than bromide (Br⁻). This is due to the larger size and lower electronegativity of iodine compared to bromine, which makes it more stable when it leaves as an ion.
The order of reactivity of haloalkanes is RI > RCl > RBr.
As the size of the halogen atom increases, the attraction between the carbon and the halogen decreases. This is because larger halogen atoms (like iodine) have their outer electrons further from the nucleus, resulting in weaker bond strength with carbon.
The C–I bond is the longest and weakest due to the large size of iodine, making it easier to break during reactions.
The C–Br bond is shorter and stronger than C–I but weaker than C–Cl.
The C–Cl bond is the shortest and strongest, making it the hardest to break.
As the bond length increases, it becomes easier for the halogen to dissociate from the carbon, making the compound more reactive. Hence, reactivity increases with the size of the halogen atom.
Thionyl chloride is preferentially used to convert alcohols to chloro alkanes
In this reaction alkyl halides are formed with byproducts SO2 and HCl which are gases escape into the atmosphere. So pure alkyl halide is obtained.
2ROH +SOCl2 → RCl +SO2(g)+HCl(g)
Why is sulphuric acid not used during the reaction of alcohols with KI in the conversion of an alcohol to the alkyl iodide?
In the presence of sulphuric acid (H₂SO₄), KI produces HI:
2KI + H₂SO₄ → 2KHSO₄ + 2HI
Since H₂SO₄ is an oxidizing agent, it oxidizes HI (produced in the reaction) to I₂
2HI + H₂SO₄ → I₂ + SO₂ + H₂O
As a result, the reaction between alcohol and HI to produce alkyl iodide cannot occur.
Therefore, sulphuric acid is not used during the reaction of alcohols with KI.
Instead, a non-oxidizing acid such as H₃PO₄ is used.
Why is CH3CHFCH2COOH is stronger acid than FCH2CH2CH2COOH?
The inductive effect decreases with distance, so −I effect of F is stronger in 3-fluorobutanoic acid than in 4-fluorobutanoic acid. Hence, CH3CHFCH2COOH is stronger acid than FCH2CH2CH2COOH.
Phenol is more acidic than ethanol.
Phenol is more acidic than ethanol because after losing a proton (H+), phenol forms phenoxide ion which is stabilised by resonance whereas ethoxide ion is not.
The C-O bond is much shorter in phenol than in ethanol.
Due to resonance in phenol, the C-O bond requires partial double bond character which is hard to break
In phenol oxygen is attached to sp2 hybridised carbon atom while in methanol it is attached to sp3 hybridised carbon atom. The bond formed between oxygen and sp2 hybridised carbon is more stable i.e. shorter than that formed between oxygen and sp3 hybridised carbon
Ortho-nitrophenol has lower boiling point than p-nitrophenol.
P-nitrophenol shows intermolecular hydrogen bonding. So it has higher bonding point. Whereas o-nitrophenol shows intra molecular H-bonding hence lower boiling point.
Ortho-nitrophenol is more acidic than orthomethoxyphenol.
Ortho nitrophenol is more acidic than ortho methoxyphenol because nitro group is an electron withdrawing and it will increase +ve charge on the oxygen atom to make it more acidic whereas OCH3 group is an electron releasing group and it will decrease +ve charge on the oxygen atom, thus making it less acidic and hence the O-H bond will not break easily
Propanol has higher boiling point than that of the hydrocarbon butane.
The boiling point is directly proportional to the intermolecular forces existing in a compound.
In propanol, there is an intermolecular hydrogen bonding and Van der Waal's forces.
Whereas in butane weak van der Waal's force of attraction is the only forces between the molecules. Therefore, propanol has highest boiling point as compared to that of butane
Alcohols are more soluble in water than the hydrocarbons of comparable molecular masses.
As alcohol is a polar solvent, it forms Hydrogen Bond with water molecules while other hydrocarbons of comparable molecular masses does not form Hydrogen Bond due to being non - polar. Hence Alcohol is more soluble in water.
The boiling point of ethanol is higher than that of methanol.
As the number of carbons increases, boiling point of alcohol increases. For alcohols, boiling point depends on van-der Waals dispersion forces also. This force increases as the length of the hydrocarbon chain increases. Hence ethanol possesses a higher boiling point than methanol.
Acid catalysed dehydration of t-butanol is faster than that of n-butanol.
The dehydration reaction is an elimination reaction that goes via carbocation formation. Since tertiary carbocations are most stable due to + Inductive effect of alkyl groups, then is the secondary and least stable is primary.
Therefore the reactivity of alcohol is governed by the stability of carbocation that follows the order as
Tertiary > secondary > primary
Hence, acid catalysed dehydration of t-butanol is faster than that of n-butanol because tertiary carbocation formed by t-butanol is more stable than primary carbocation formed by n-butanol.
Preparation of ethers by acid dehydration of secondary or tertiary alcohols is not a suitable method.
In secondary and tertiary alcohols, the alkyl groups create steric hindrance and the nucleophillic attack becomes difficult. Hence, elimination to form alkene is favored over substitution to form ether. Hence, preparation of ethers by acid dehydration of secondary or tertiary alcohols is not a suitable method.
The treatment of alkyl chlorides with aqueous KOH leads to the formation of alcohols but in the presence of alcoholic KOH, alkenes are major products. Explain.
In an aqueous solution, OH- ion (obtained from KOH) acts as a strong nucleophile and causes nucleophilic substitution of alkyl chloride to give alcohol.
In an alcoholic medium, an alkoxide ion (RO-) is formed, acting as a strong base to cause an elimination reaction, thereby producing alkene as the major product.
The boiling points of ethers are lower than isomeric alcohols.
or
Boiling point of ethanol is higher in comparison to methoxymethane.
Hydrogen bonding in alcohols that is absent in ethers due to low polarity
Phenylmethyl ether reacts with HI to give phenol and methyl iodide and not iodobenzene and methyl alcohol.
Phenyl methyl ether (anisole) CH3OC6H5 reacts with HI to give phenol and methyl iodide and not iodobenzene and methyl alcohol because the lone pair of O are involved in resonace (+ mesomeric effect) with the benzene ring and imparts it a double bond character and increases the C-O bond strength with the benzene ring. Moreover, the reaction goes via SN2 mechanism which prefers the attack of nucleophile I− from least hindered side of the molecule. Thus it prefers to attack the methyl group.
Tertiary alcohols are less acidic than primary alcohols.
More the number of CH3 groups on-chain, less will be the stability of alkoxide ion and so will be the acidic character of alcohol.
Formaldehyde does not take part in aldol condensation
Due to the absence of α-hydrogen
Propanal is more reactive than propanone towards nucleophilic reagents / HCN
Propanone is sterically more hindered than propanal due to presence of alkyl group on both sides of carbonyl carbon making them less reactive towards nucleophilic attack
Both methyl groups have electron releasing tendency due to -I effect. These alkyl groups makes ketone less reactive towards nucleophiles by increasing electron density in the carbonyl group.
Hence propanal is more reactive than propanone towards nucleophilic reagents
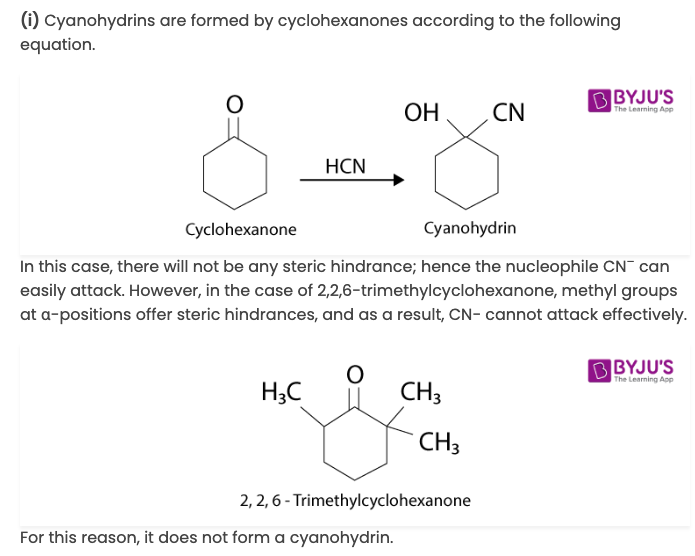
Cyclohexanone forms cyanohydrin in good yield but 2,2,6-trimethylcyclohexanone does not
There are two −NH2 groups in semicarbazide. However, only one is involved in the formation of semicarbazones.
Semicarbazide undergoes resonance involving only one of the two −NH2 groups, which is attached directly to the carbonyl-carbon atom.
Therefore, the electron density on the −NH2 group involved in the resonance also decreases. As a result, it cannot act as a nucleophile.
Since the other −NH2 group is not involved in resonance, it can act as a nucleophile and attack carbonyl-carbon atoms of aldehydes and ketones to produce semicarbazones
During the preparation of esters from a carboxylic acid and an alcohol in the presence of an acid catalyst, the water or the ester should be removed as soon as it is formed.
The formation of esters from carboxylic acids and an alcohol in the presence of an acid catalyst is a reversible reaction
RCOOH + R’OH → RCOOR’ + H2O
Therefore to shift the equilibrium in the forward direction, the water or ester formed should be removed as soon as it is formed
Although phenoxide ion has more number of resonating structures than carboxylate ion, carboxylic acid is a stronger acid than on phenol. Why?
There are two electronegative oxygen atoms in carboxylate ion as compared to only one oxygen atom in phenate ion
Therefore, the electron charge in carboxylate ion is more dispersed in comparison to phenate ion
Consequently, carboxylate ion is relatively more stable as compared to phenate ion
Thus the release of H+ ion from carboxylic acid is comparatively easier and therefore it behaves as stronger acid than phenol
Acetophenone reacts faster than benzophenone with HCN. Give reason.
Electronic reason.
The carbonyl carbon of acetophenone is more positive than the carbonyl carbon of benzophenone due to the +I effect of the methyl group.
Steric reason.
Benzophenone has two bulky benzene rings on either side of the carbonyl group making it less difficult for the nucleophile to attack. Acetophenone one side is a methyl group, comparatively easy to attack.
Sodium bisulphite is used for the purification of aldehydes and ketones. Explain.
Aldehydes and ketones form water-soluble sodium bisulphite addition products, which separate them from organic impurities. On hydrolysis of this addition product, we will get the aldehydes and ketones back
Carboxylic carbon is less electrophilic than carbonyl carbon
or
Carboxylic acids do not take part in nucleophilic addition
In carboxylic acid, presence of lone pairs of electrons on oxygen which are involved in resonance. Due to this, the electrophilic character of carbon in carboxylic acid decreases.
Whereas aldehydes and ketones lack this resonance stabilization, making their carbonyl carbons more electrophilic
Carboxylic acids do not take part in nucleophilic addition
Because the carboxylic carbon is less electrophilic than the carbonyl carbon
Carboxylic acids are stronger acids than phenol
Due to resonance stabilization of the carboxylate ion (–COO⁻)
Aromatic carboxylic acids do not undergo Friedel-Crafts reaction
Because –COOH group present in aromatic carboxylic acids is an electron withdrawing group causing deactivation of benzene ring. This results in the bonding of anhydrous AlCl3 with carboxyl group. Hence electrophillic substitution i.e. Friedel-Crafts reaction does not occur in aromatic carboxylic acids.
In aqueous solution 2° amines are more basic than 3° amines
Because 2° amines are more soluble than 3° amines
Aliphatic amines are stronger bases than aryl amines
or
pkb value of methylamine is less than that of aniline
Due to more +I effect in aliphatic amines, the electron density of nitrogen increases and due resonance stabilization of aniline, electron density on the nitrogen decreases
1° Amines have a higher boiling point than 3° amines
Because 1° amines are engaged in greater intermolecular hydrogen bonding
Amines are less acidic than alcohols
Loss of proton from amines gives amide ion whereas loss of proton from alcohol gives an alkoxide ion. Since O is more electronegative than N, RO can accommodate the negative charge more easily than RNH-. Thus alcohols are more acidic than amines.
Ammonolysis is not a preferred method for the preparation of 1° amine
Because the reaction yields a mixture of 1°, 2°, 3° and quaternary ammonium salts
During the reduction of nitro compounds to prepare amines iron scrap and HCl are preferred
FeCl2 formed due to the reaction between iron and HCl gets hydrolysed to release HCl acid. Thus only a small amount of hydrochloric acid is required to initiate the reaction.
Aromatic amines cannot be prepared using Gabriel Phthalimide Synthesis
Because aryl halides do not undergo nucleophilic substitution with the anion of phthalimide
Aniline does not take part in Friedel-Crafts reaction
Aniline reacts with AlCl₃ (Lewis acid catalyst) to form a salt
Nitration of aniline give subsequent amount of meta product. Explain.
In the strongly acidic medium, aniline is protonated to form the anilinium ion which is deactivating and meta-directing.
Aromatic diazonium salts are more stable than aliphatic diazonium salts.
In aromatic diazonium salts, due to resonance, there is dispersal of positive charge on benzene ring.
But in aliphatic diazonium salts, resonance is not possible, so aliphatic diazonium salts are less stable than aromatic diazonium salt.