Carboxylic Acid
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
In Progress (remaining: prep of formic acid, acetic acid)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
What is the general name of carboxylic acids?
Alkanoic Acid
What is the general formula of carboxylic acids?
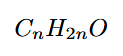
What are the two names of HCOOH?
Formic Acid
Methanoic Acid
What are the two names of CH3COOH?
Acetic Acid
Ethanoic Acid
What sort of compounds can you oxidise to get carboxylic acids? (name 5)
Alcohols
Aldehydes
Ketones
Alkenes
Alkyl benzene
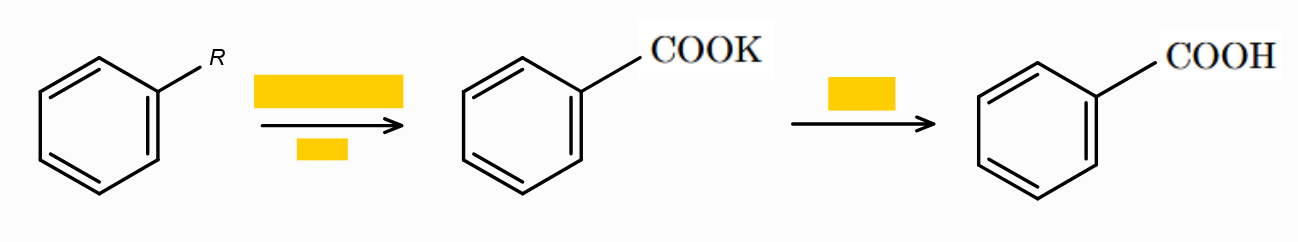
Fill in the blanks
Why can’t K2Cr2O7 be used in the preparation of benzoic acid from alkyl benzene?
K2Cr2O7 is not as strong as KMnO4, and the oxidation of alkyl benzene to form carboxylic acid needs the strongest oxidising agent.
What sort of alkenes do you need to oxidise to make carboxylic acid?
Unbranched alkenes
What are the reagents you can use to make carboxylic acid from alkenes?
Concentrated KMnO4 or H2SO4 / OH- / heat followed by H3O+
This is Vigorous Oxidation in acidic medium
O3 / H2O / H2O2
This is Oxidative Ozonolysis
What is the general mechanism when oxidising alkenes to form carboxylic acid?
The double bond between the carbons is broken, O and OH are added to those carbons. Two molecules of carboxylic acid are formed from one molecule of unbranched alkene.
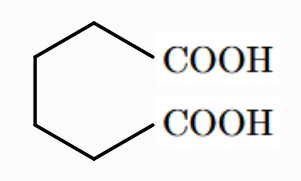
What is the IUPAC and general name of this acid?
Hexan -1,6 - dioic Acid
Adipic Acid
What do you react a 1 degree alcohol with to get carboxylic acid?
a strong oxidising agent
What do you react aldehydes with to get carboxylic acid?
an oxidising agent, and Tollen’s Reagent.
By hydrolysis of which compounds can we get carboxylic acid?
Alkyl nitriles / cyanides
1,1,1 - trihalo alkanes
Acid Derivatives
What is the mechanism behind the acidic hydrolysis of alkyl nitrile to make carboxylic acid?
H+ Attacks the negative centre N (from CN), resulting in positive charge on N, who then takes one of the bonds between C and N, leaving positive charge on C.
A lone pair from O (from OH-) attacks the positive centre C (from CN). THe C-OH bond and C=NH bond undergo tautomerism to form CONH2.
Another water molecule attacks, OH- goes to positive centre C and H+ goes to negative centre N, to give NH3 + R-COOH.
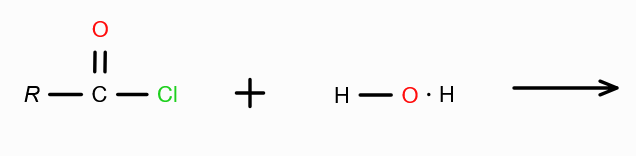
in presence of dilute acid
in presence of dilute acid
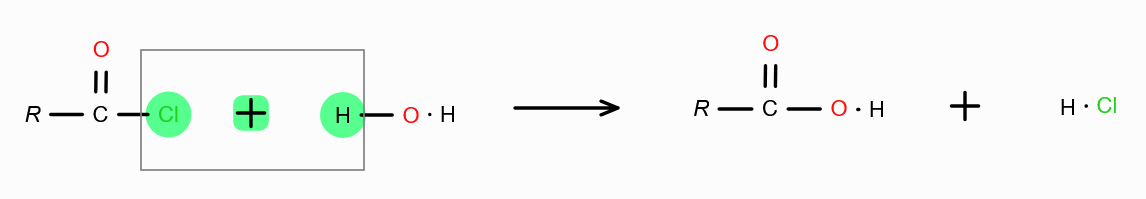
in presence of dilute acid
in presence of dilute acid
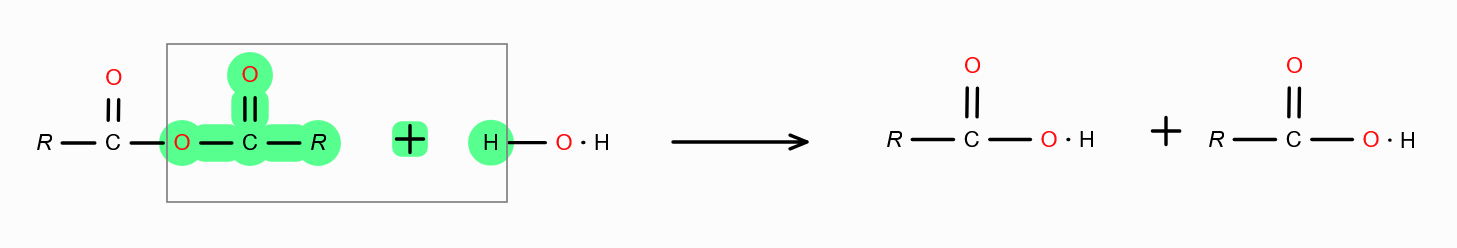
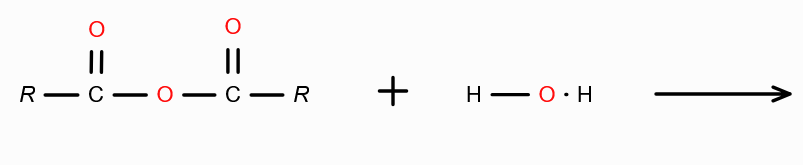
What is the mechanism behind forming carboxylic acid from carboxylic acid derivatives?
Hydrolysis — Addition of water.
Combine H from water with the group attached with RC=O, and remove. Join RC=O with OH.
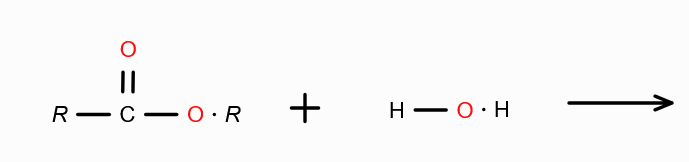
in presence of dilute acid
in presence of dilute acid
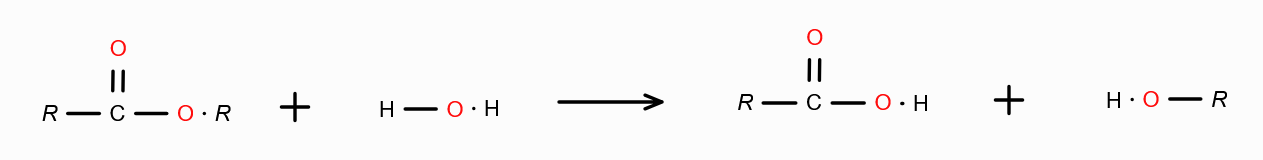
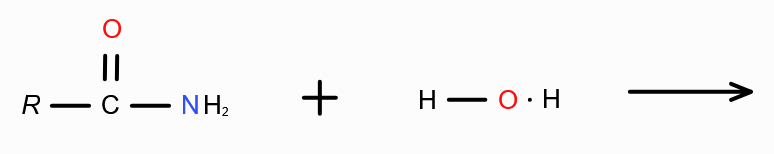
in presence of dilute acid
in presence of dilute acid
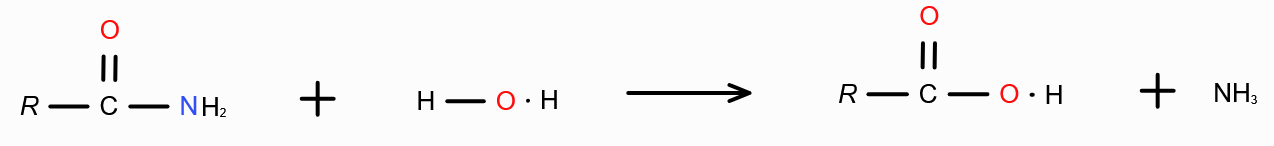
What is the order of reactivity of hydrolysis of these compounds?
Acid Halide
Amide
Ester
Acid Anhydride
Acid halide > Acid Anhydride > Ester > Amide
What other substances do you need in order to form carboxylic acid from Grignard’s Reagent?
CO2 in acidic medium (with H+).
What is the mechanism of forming carboxylic acid from Grignard’s Reagent and carbon dioxide?
R- attacks the positive centre C in CO2 and one of the double bonds goes to one of the oxygens, giving it a negative charge. Since it is in acidic medium, H+ attacks the negative O- to form RC(=O)OH
What is the byproduct when making carboxylic acid from Grignard’s reagent in acidic medium?
Mg(OH)X
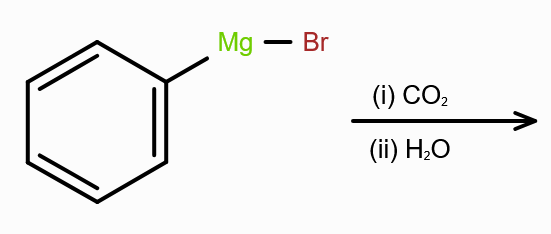
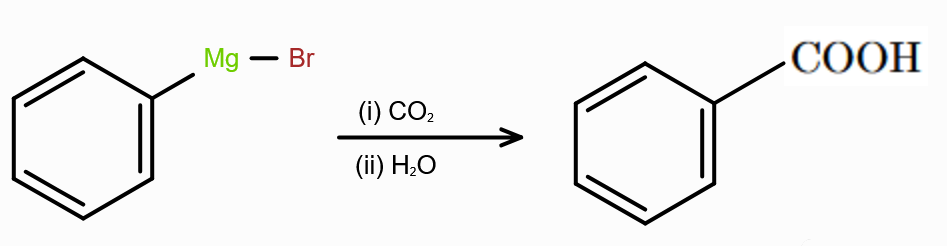
What should you react with CO2 to make carboxylic acid?
Grignard’s reagent
What should you react with CO to make carboxylic acid?
Sodium Alkoxide in acidic medium.
What should you react with Sodium Alcoxide to get carboxylic acid?
CO, at high temperature and pressure in acidic medium.
What is formed when grignard’s reagent reacts with CO2 in absence of acidic medium?
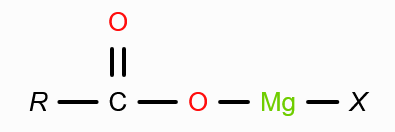
What form of CO2 is reacted with grignard’s reagent to form carboxylic acid?
Solid CO2 (Dry Ice)

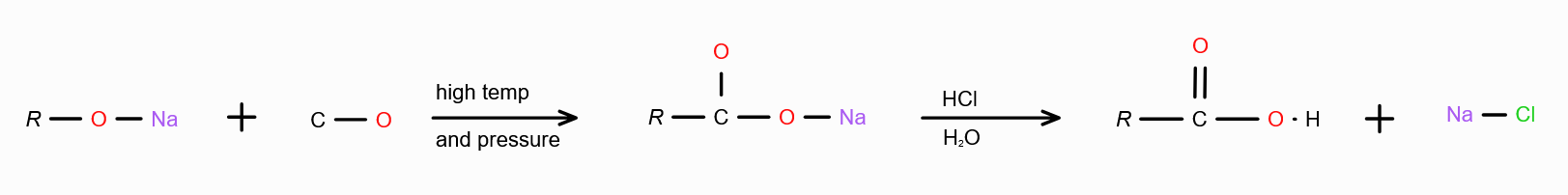

sorry for bad quality
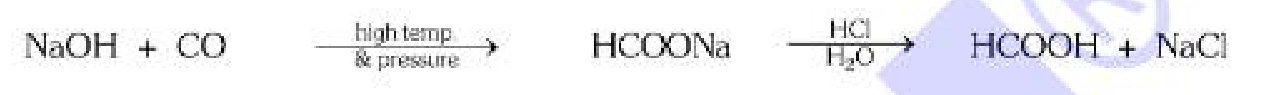
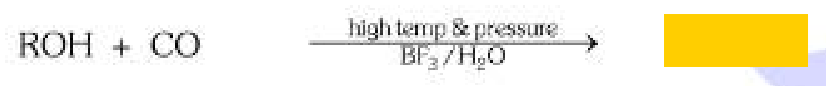
sorry for bad quality
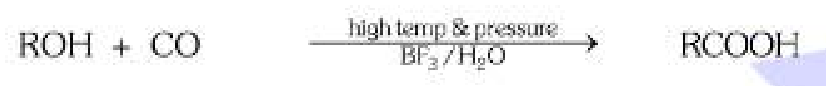
If we want to make carboxylic acid from CO and R-OH, what else should we use?
High temperature, high pressure, BF3 and H2O
What is the general mechanism of making carboxylic acid from dicarboxylic acid? What should the reaction take place in the presence of?
Decarboxylation, in the presence of glycerol and heat (110°C).
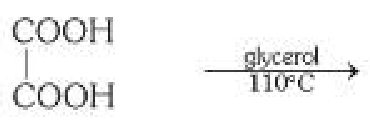
sorry for bad quality

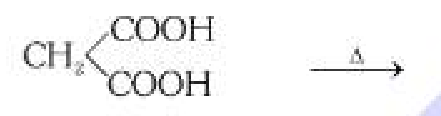
Sorry for bad quality
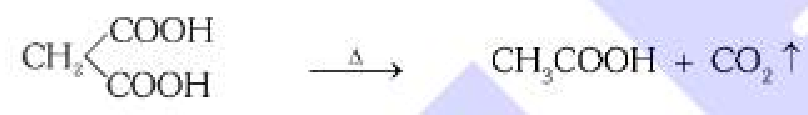
What is Koch’s reaction?
Also known as Modern Method,
Reaction of alkenes with CO and H2O in presence of H3PO4 and high temperature+pressure to form carboxylic acid.
What is the byproduct in the decarboxylation of dicarboxylic acid?
CO2 gas.
What is the relation between the number of C atoms in the product and reactant in Koch’s Reaction?
The product (carboxylic acid) has one more carbon atom than the reactant (alkene).
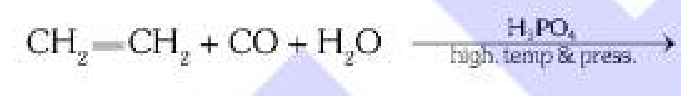
sorry for bad quality


sorry for bad quality

What is the ratio of the products (acids) in Koch’s reaction?
they are formed in equal amounts.
What is the general mechanism of formation of carboxylic acid from AAE (Aceto Acetic Ether)?
Acidic Hydrolysis, in the presence of KOH.
What is the full form of AAE?
Aceto Acetic Ether
What happens when you react AAE with dilute KOH?
You get a ketone.
What happens when you react AAE with concentrated KOH?
You get carboxylic acid.

sorry for bad quality
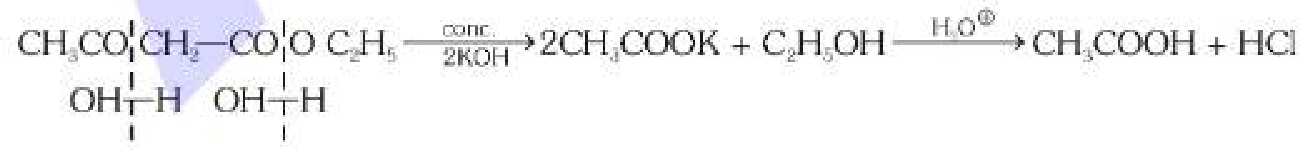
What are the byproducts in the acidic hydrolysis of AAE? carboxylic acid is the main product.
C2H5OH + HCl (not sure how that last one got there tbh)