Motion & Forces
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
What is a uniform velocity?
An object moving with uniform velocity has a constant speed and a constant direction. This means its velocity is not changing.
What is the definition of acceleration?
Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity.
What is uniform acceleration?
An object undergoing uniform acceleration has a velocity that changes by the same amount in equal time intervals.
On a velocity-time graph, what does the gradient and the area under the graph represent?
The gradient represents the acceleration, and the area under the graph represents the displacement.
What are the three kinematic equations for uniformly accelerated motion?
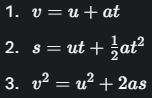
What is Newton's First Law of Motion?
An object will remain in its state of rest or uniform motion unless a resultant force acts on it.
What is the formula for Newton's Second Law of Motion?
Fnet=ma, where Fnet is the resultant force, m is the mass, and a is the acceleration.
What is the relationship between force and acceleration based on Newton's Second Law?
The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the resultant force acting on it and inversely proportional to its mass.
What is Newton's Third Law of Motion?
For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. The action and reaction forces are equal in magnitude, opposite in direction, and act on different bodies.
What is the difference between mass and weight?
Mass is the amount of matter in an object, while weight is the gravitational force acting on that object.
When an object is in free fall, what is the only force acting on it?
The only force acting on the object is gravity (its weight).
What does the velocity-time graph for an object in free fall look like?
It's a straight line with a constant negative slope of −9.81m/s2 (or −10m/s2 if the value of g is approximated to 10), representing the constant acceleration due to gravity.