Reservoir Characterization & Geological Modeling (QCB4043)
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A compilation of key terms and definitions related to reservoir heterogeneities and geological modeling for petroleum geoscience.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
Reservoir Heterogeneity
Variations in reservoir properties as a function of space impacting production and fluid flow.
•Small to large scale geologic features
•from static reservoir characterization (significant and
non significant)
•from dynamic reservoir characterization (significant)
Micro Heterogeneity
Heterogeneities at the grain level affecting pore and pore throat.
•Produced by deposition of sediments and subsequent compaction, cementation and dissolution phenomena
•Identified from laboratory measurements → variations in pore and pore throat size, grain shape and size, throat opening, minerals, pore roughness, etc.
•Create preferential paths for displacing fluids while residual or trapped hydrocarbon is left behind
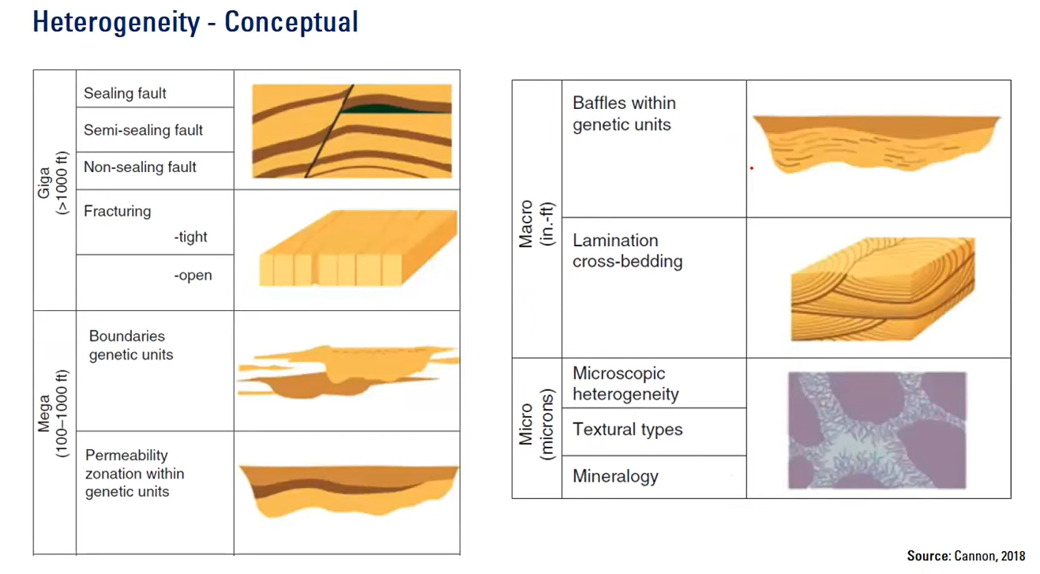
Macro Heterogeneity
Heterogeneities at the core level affecting porosity and permeability.
•Identified from laboratory measurements → variations in porosity, permeability, fluid saturation, capillary pressure, wettability, etc.
•Used to calibrate logs, well tests, to provide inputs to flow simulators
•Influence the shape of the front of the displacing fluids (hence determine the amount of bypassed hydrocarbon)
Mega Heterogeneity
Heterogeneities between wells impacting lateral continuity.
Identified from transient pressure well test analysis, log correlations, high resolution seismic, investigated using reservoir simulation → lateral discontinuities of individual strata, pinchouts, fluid contacts, trends, reservoir compartmentalization…
Same impact as macroscopic heterogeneities, but on a larger scale
Giga Heterogeneity
Heterogeneities at the basin level influenced by original depositional setting or subsequent structural deformations and modifications due to tectonic activities.
Sealing Fault
A fault that prevents fluid movement between reservoir units.
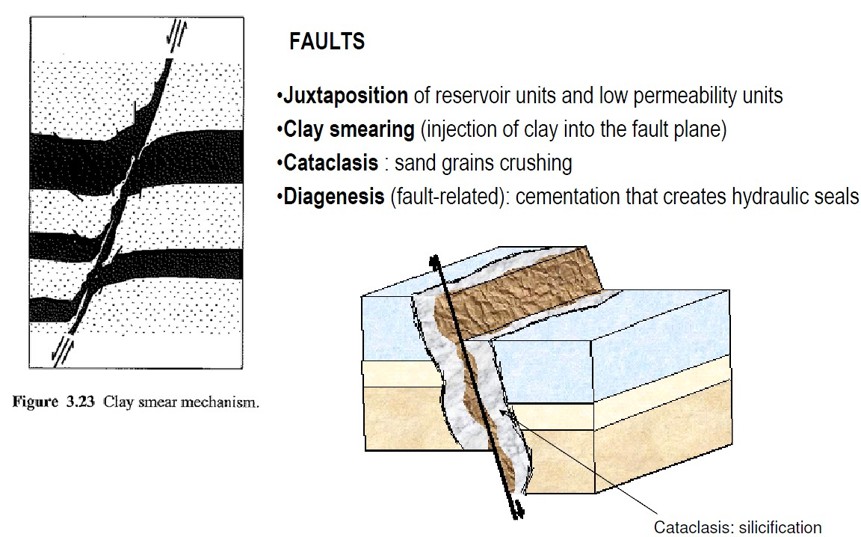
Semi-Sealing Fault
A fault that restricts but does not fully block fluid movement.
Non-Sealing Fault
A fault that allows free flow of fluids across the fault plane.
Permeability Zonation
Variation in permeability within genetic units affecting fluid flow.
Clay Smearing
Injection of clay into the fault plane causing low permeability zones.
Diagenesis
The physical and chemical changes occurring in sediments as they become rock.
Fractures in Reservoirs
Cracks within rocks that can enhance or hinder fluid flow depending on their nature.
Genetic Unit Boundaries
Stratigraphic discontinuities representing variations in deposition.
Baffles
Geological features that impede fluid flow, often associated with shale.
Lamination
Thin layers of sedimentary deposits resulting from deposition processes.
Cross-Bedding
Sedimentary structures formed by the movement of sediment in flows.