4. organic chemistry
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
Hydrocarbon
A chemical compound composed of carbon and hydrogen ONLY.
how to calculate tangent
rise/run
As the chain of a hydrocarbon gets longer what happens to intermolecular forces, viscosity and boiling point?
As the hydrocarbon chain gets longer the intermolecular forces increase
As the hydrocarbon chain gets longer the viscosity increases
As the hydrocarbon chain gets longer the boiling point increases
Fractional Distillation
A separation technique used to separate a mixture of liquids into different fractions by their boiling point.
Order of Fractions in Fractionating Column
From top to bottom: Refinery gases, gasoline, kerosene, diesel oil, fuel oil, bitumen.
Trend in Boiling Point and Hydrocarbon Chain Length
Boiling points get HIGHER and hydrocarbon chain length gets LONGER as you go down the column.
Boiling Point
The temperature at which a liquid turns into a gas.
Volatility
How easily something evaporates.
Viscosity
How easily something flows.
Flammability
How easily something burns.
Alkane
A group of saturated hydrocarbons.
General Formula for an Alkane
CnH2n+2.
Mnemonic for Naming Order of First 4 Alkanes
Many Elderly Problems (?) Build Pension Houses (methane, ethane, propane, butane, pentane, hexane
Isomer
Molecules that have the same molecular formula but different structural arrangement of atoms.
Displayed Formula
Illustrates the arrangement of atoms for each element in space and includes the bonds between atoms.
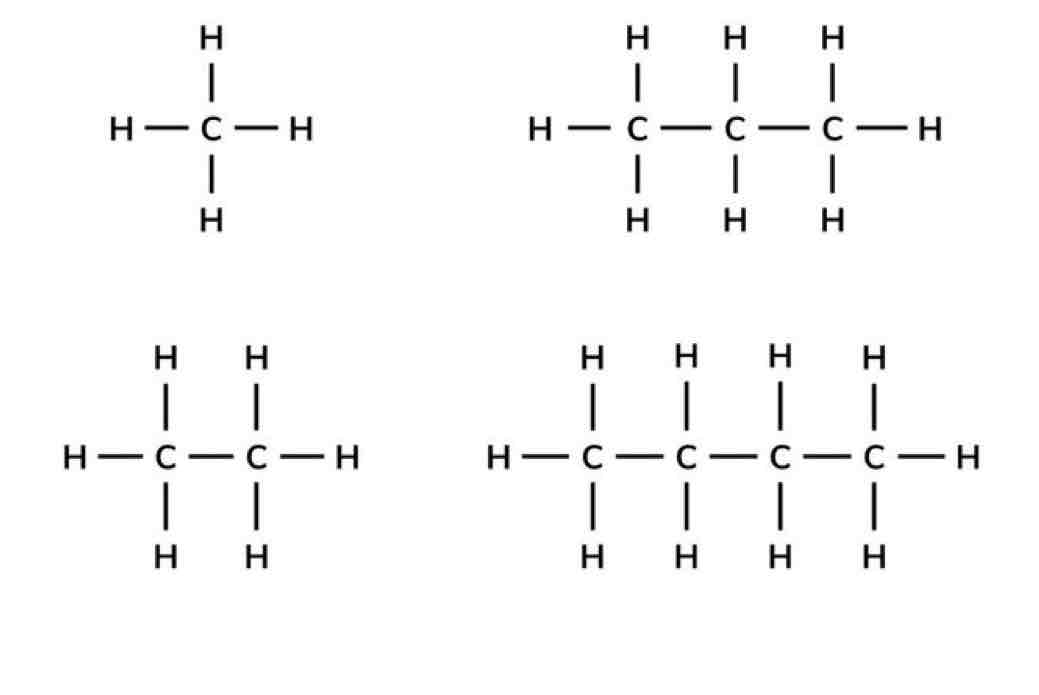
Molecular Formula
A formula that shows the actual number of atoms for each element in a compound.
Homologous Series
A family of hydrocarbons with similar chemical properties who share the same general formula.
Features of a Homologous Series
They have the same general formula and the same chemical properties.
Combustion
When a fuel (hydrocarbon) reacts with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water.
Products of Complete Combustion
Carbon dioxide and water.
Substitution Reaction
When an atom in a compound is replaced by another atom.
Halogenation Reaction of Methane
Methane + bromine -> Bromomethane + hydrogen bromide (CH4 + Br2 -> CH3Br + HBr).
Condition for Halogenation
Requires UV light.
Colour Change in Halogenation of Methane
The mixture turns from orange to colourless.
Cracking
The thermal decomposition of a long chain hydrocarbon into small chain molecules.
Catalyst and Temperature for Cracking
Alumina and around 600-700 °C.
Why Crack Long Chain Hydrocarbons
Small chain hydrocarbons are more useful and we have a surplus of long chain hydrocarbons from crude oil.
Thermal Decomposition
When heat is used to break down a compound.
Saturated Hydrocarbon
A hydrocarbon that only contains single carbon bonds.
General Formula for an Alkene
CnH2n.
Why Alkenes Are Unsaturated
They contain a double bond between two carbon atoms.
Test for Alkane or Alkene
Add bromine water: yellow stays for alkane, turns colourless for alkene.
Incomplete Combustion
Occurs when a fuel burns in insufficient oxygen, producing carbon monoxide.
Toxicity of Carbon Monoxide
It stops blood cells from transporting oxygen efficiently.
Polymer
A long chain molecule made from monomers joined end to end.
Monomer
A small molecule that can be joined to another monomer to make a polymer.