Radioactivity - CCEA
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Atomic Number letter
Z
Mass number letter
A
Radioactivity definition
the spontaneous disintegration of an unstable nucleus by alpha, beta, gamma decay
What is an Alpha Particle
a particle emitted in radioactive decay consisting of 2 neutrons and 2 protons,
alpha particle is a helium nucleus
positively charged
alpha particles are big and move slowly

Why does alpha decay happen
when nuclei have too much mass to remain stable
Alpha Particle penetration
blocked by thick paper/ cardboard
Alpha Particles range in air
2-3 cm, as scattered by air particles
What is ionisation
the addition or removal of an electron from an atom
Ionisation ability of alpha
Highest as alpha particles are big they easilly dislodge electrons from nearby atoms, producing ions
What happens if atoms in humans are ionised
this disrupts their DNA structure, cause mutated cell.
What is a Beta Particle
A fast moving electron
negatively charged

What does beta decay happen
when a nuclei has too many neutrons to remain stable
Beta particle penetrate
5mm Aluminum
Beta range in air
several meters
why does beta have medium ionisation ability
beta particles are very small and move very fast, therefore they interact less with matter and have a lower ionisation ability
What is gamma ray
High energy electromagnetic wave emitted in radioactive decay from an unstable nucleus
no mass no charge
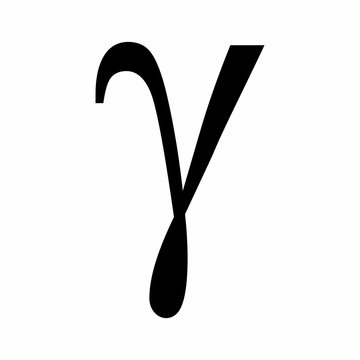
Gamma penetration
thick layered concrete
Gamma range in air
manny km
Background radiation definition
Background Radiation or Background Activity is the radioactive count rate still detected when no radioactive sources are present
Sources of background radiation
cosmic rays from the sun
leakage from radiotherapy and x-ray department
radioactivity from rocks e.g granite
radioactivty from smoke alarms
radioactive waste from power stations
How to deal with background activity in an experiment
Before source is present record the background activity in the room e.g 15 counts per second
Introduce the source and record the countrate
Calculate corrected countrate = experimental value - background activity
How to prevent background radiation
Make homes well ventilated to prevent radon gas
How to minimise risk while using it
wear protective clothing
handle the source with long tong, especially for alpha
minimise exposure time to source
store source in led lined box
What is half life
Time taken for activity (number of decays in one second) to fall to half of its initial value
Nucleur Fission process
Large Uranium Nucleus absorbs the slow moving neutron
The Uranium Nucleus divides into smaller nuclei
Extra fission neutrons are produced
Each of these neutrons divides another uranium nucleus
This sets up a chain reaction which all fuel available is use up
Positives Fission
Jobs available in nuclear sector
no CO2 produced
large global reserves of Uranium are available
fission produces 1 million times more energy than fossil fuels per kg of fuel
Negatives Fission
Produces highly toxic radioactive waste with a long half-life, which is difficult, dangerous and expensive to store safely
Nuclear accidents (Ukraine/ Japan) could destroy the planet for future generations
Although Fission does not produce CO2 directly the mining and transport of uranium does
Nuclear Fusion occurs naturally where
stars e.g sun
Process of Nuclear Fusion
Two low mass hydrogen nuclei combine to form a more massive high mass ( and more stable nucleus)
Nucleur Fusion reaction
Deuterium + Tritium = Helium + neutron + energy
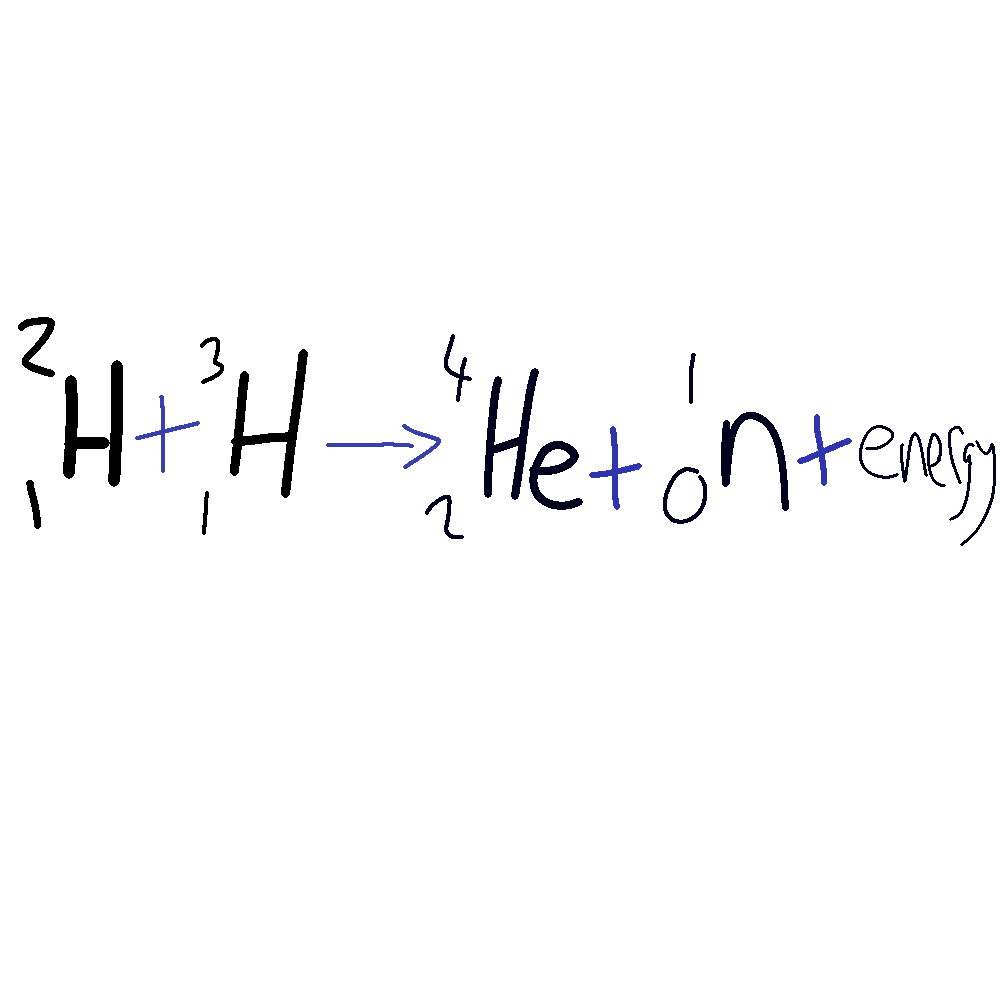
Advantages to Nuclear Fusion
has potential to solve worlds energy crisis as it releases 4 million time more energy that fossil fuels and 4 times more energy than fusion per kg of fuel
the fuel Deuterium and Tritum is abundant and available from sea water
fusion does not produce any greenhouse gas, only helium which is non toxic
fusion does not produce highly toxic radioactive waste
Difficulties to overcome with performing
The hydrogen nuclei are both positive and repel each other, huge temperatures are required to provide the kinetic energy to overcome the repulsive force so that they can combine
it is expensive and technically difficult to heat and contain the fuel for long enough for fusion to occur
fusion reactors are very expensive and could spend money on hospitals or food