Symmetric Cryptography
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
What is Symmetric Cryptography?
both encryption and decryption operations use the same key
secret-key systems have been around for many hundreds of years
What are the Types of Symmetric Cryptography?
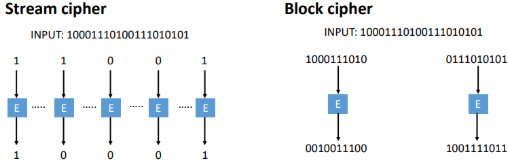
What is a Stream Cipher?
a method that encrypts data one bit or byte at a time by combining it with a pseudorandom keystream, typically using the XOR operation
require sender and receiver synchronicity
What is the Method for a Stream Cipher?
take as input a (short) key
key is often combined with an initialisation vector (IV)
key is converted into a continuous keystream
working with one bit at a time, the plaintext is mixed with the keystream
What are the Advantages of Stream Cipher?
no error propagation
on-the-fly-encryption - good choice for real-time services
fast and easy to implement, especially in hardware
How does Stream Cipher Work?
keystream generation - a small secret key and initialisation vector (IV) feed a PseudoRandom number generator (PRNG) to produce a long, seemingly random keystream
encryption - each bit/byte of the plaintext is XORed with the corresponding bit/byte of the keystream to produce ciphertext
decryption - the same keystream is XORed with the ciphertext to recover the plaintext
What is a Block Cipher?
a method to transform fixed-length blocks of data (e.g., 128 bits) into ciphertext using a secret key
What is the Method for a Block Cipher?
take as input a key and a block of plaintext and outputs a block of ciphertext
a good block cipher should be designed to provide confusion and diffusion
confusion hides the relationship between the plaintext and ciphertext
diffusion spreads the statistics of the plaintext through the ciphertext
usually obtain protection from chosen plaintext attacks if the block cipher behaves like a pseudorandom permutation
block length should be chosen to ensure a balance of efficiency and security
What are the Block Cipher Modes of Operation?
Electronic Code Books (ECB)
Counter Block Chaining (CBC)
Cipher Feedback (CFB)
Counter (CTR)
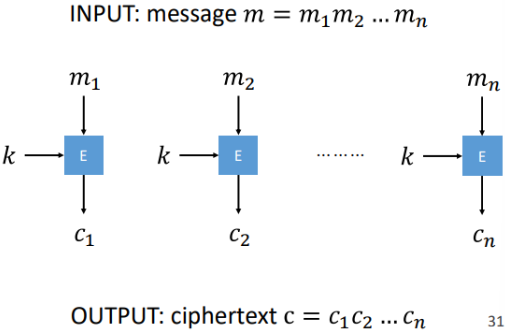
What is Electronic Code Books (ECB)?
the simplest mode of operation where each plaintext block is encrypted independently using the same key, resulting in identical ciphertext blocks for identical plaintext
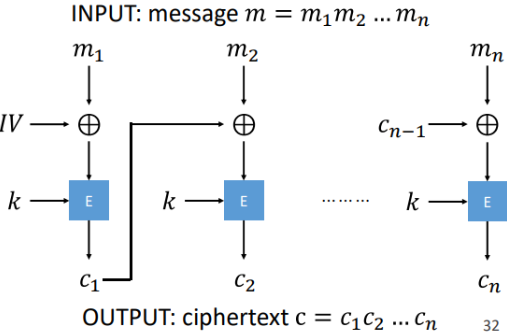
What is Counter Block Chaining (CBC)?
a mode by XORing each plaintext block with the previous ciphertext block before encryption, breaking up patterns
requires an initialisation vector (IV) for the first block to ensure uniqueness
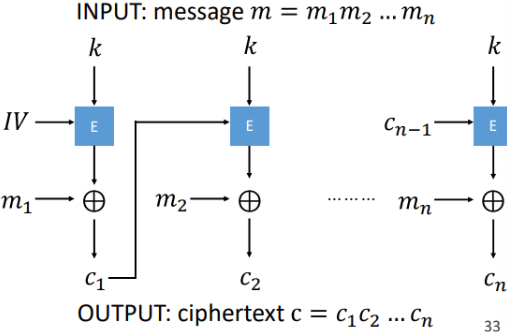
What is Cipher Feedback (CFB)?
works by encrypting the previous ciphertext block (or IV for the first block) using the block cipher algorithm, and XORing the result with the current plaintext to produce the ciphertext
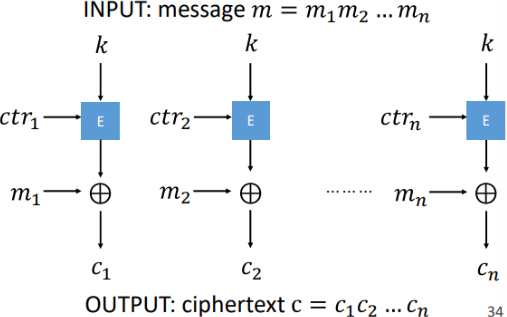
What is Counter (CTR)?
works by encrypting successive values of a counter to generate a keystream, which is then XORed with plaintext to produce ciphertext
What is Padding?
extending a plaintext message to multiple of the block size, needed when data doesn’t fit the exact block size