unit 5 & 6 economics
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
12th grade ap microeconomics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
product market
helps determine the demand market
demand and supply changes
changes price -> changes employment decisions
derived demand
- demand for a factor of production
- derived from the demand for the goods and services the factor of production is used to produce
- ex: if demand for cars increases, then the price increases, which leads to an increase in demand for iron ore (resources)
shifters of labor demand
- anything besides wage will shift
- product market changes: rise in consumer demand, product price changes
- productivity of workers: labor becomes more cost efficient than capital
- price/ productivity of other resources changes: substitutes, complements
shifters of labor supply
- anything besides wage will shift
- number of workers
- changes in working conditions
- changes in worker's requirements: unions, licenses
- change in cultural preferences: leisure time
marginal physical product (MPP)/ marginal productivity (MP)
measure of efficiency in finished products, per unit of resource used
marginal revenue product (MRP)
- change in revenue that results from the addition of one extra input (resource) when all other resources are kept equal/ additional revenue generated by an additional worker (resource)
- add employments to the point additional labor won't bring in enough revenue to cover the additional costs
- curve = demand for labor
- ∆ total revenue/ ∆ total product OR marginal product(price)
marginal cost of labor (MCL)
- additional cost of an additional worker
- ∆ total labor cost/ ∆ total labor OR marginal labor(wage)
MRP = MRC rule
- continue to hire until MRP = MRC/MCL
- revenue > cost
perfectly competitive labor market
- many small firms are hiring workers
- many workers with identical skills
- wage is constant: firms are wage takers and can hire as many workers as they want at the wage set by the industry
monopsony (imperfect labor market)
- single buyer of labor
- few large firms are hiring
- optimizes resource use at MRP = MCL
- current quantity of labor at MCL > wage
- pays lower wage and employs fewer than competitive resource market
- wage makers: increase workers by increasing wage to all workers
nondiscriminating monopsony (imperfect labor market)
employer who must increase the wage offered to all workers in order to attract more workers (MCL > wage)
imperfect labor market
- monopsonists max profits by hiring a less than competitive wage
- less than socially optimal resource employment levels and cost
discriminating monopsony (imperfect labor market)
- pays the higher wage only to the extra worker (MCL = wage)
- illegal if based on gender, age, religion, or race
- tends to be cheaper
economies of scale
when change of factors of production lead to a change in the average output cost
return of scale
short run concept that explains the relationship between the rate of output with changing inputs of production
least cost rule
hire the one with the highest MP/P
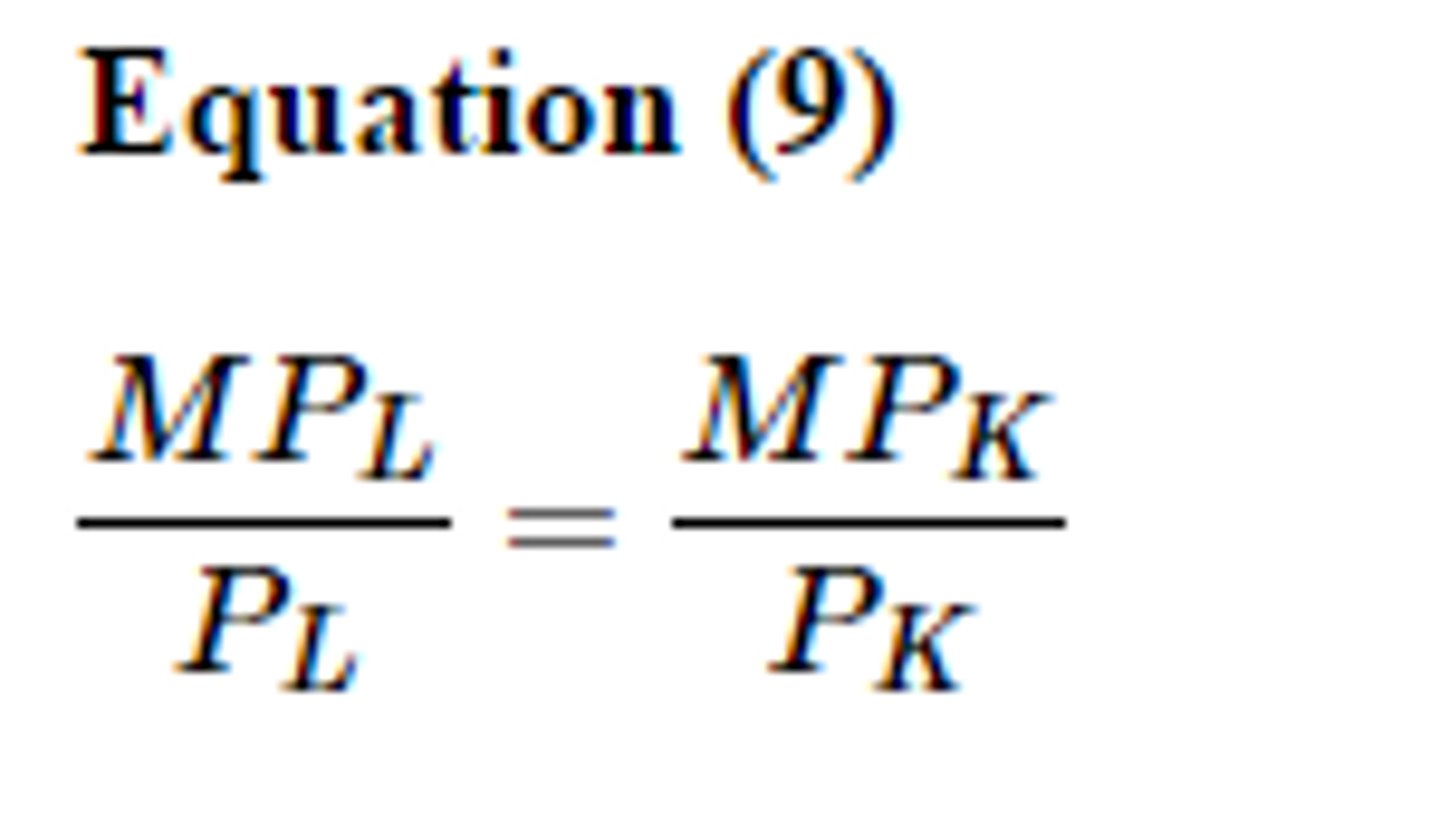
problem with higher minimum wage
discourages employers from demanding labor
graphing the labor market
- availability of labor: shift in supply
- price: shift in demand
- shifting demand = double shift in firm
- double shift even = don't know new Q
public goods
- not provided by the private market
- must be nonexcludable and nonrivalrous
- subject to tragedy of the commons
nonexcludable
- good that is available for everyone to enjoy
- ex: digital goods
nonrivalrous (shared consumption)
- consumption by a person does not prevent others from enjoying it
- ex: fireworks, sun
free rider problem
- everyone waits until someone pays for the public good, then they can use it freely
- good would never be paid for, this gov provides the good
tragedy of the commons
- when many people have access to a shared resource, they will overuse it and eventually destroy its value
- public goods must be regulated by the gov
- ex: water, fishing grounds, public transport
monopolies
gov will enforce social optimal or fair return pricing to correct monopoly/oligopoly behavior
externalities
- unintended consequences of the free market
- gov corrections: taxes, regulations, fines, subsidies, public goods
positive externalities
- spill over benefits
- other people are benefitted
- underallocation of resources in market
negative externalities
- spill over costs
- harmful effects to society
- overallocation of resources in market
marginal private benefit (MPB)
extra benefit to a firm/person from producing/consuming an extra unit of product
marginal private cost (MPC)
extra cost to the firm/person of producing/consuming an extra unit of output
MPC = MPB
what the private market is only concerned about
marginal social benefit (MSB)
extra benefit to society from the firm making an extra unit of output
marginal social cost (MSC)
cost to society of a firm making an extra unit of output
MSC = MSB
what the societal market should be concerned about
graphing positive externality
- DWL points to the right
- MSB > MSC
- per unit subsidy
graphing negative externality
- DWL points to the left
- MSB < MSC
- per unit tax
production externality
2 supply curves
consumption externality
2 demand curves
income inequality
government intervention to lessen the gap between income groups
lorenz curve
- income distribution of an area
- more bowed curve = more income inequality
gini coefficient
- measure of equality
- 0: equal distribution of wealth (good)
- 1: unequal distribution of wealth (bad)
benefits received principle
- those who receive benefits should pay taxes
- problem: many projects would be underfunded
ability to pay principle
- those with the ability to pay should pay more of the tax
- problem: discourages the incentive to earn more money and penalizes those whose hard work have helped them earn higher incomes
taxation or welfare
how to fix income
progressive/ income tax
- those who make more, pay more
- targets higher income earners
regressive/ sales tax
- takes a larger percentage of income from people whose income is low
- targets lower income earners
proportional/flat tax
charges the same percentage of income, regardless of income state
laffer curve
shows the relationship between tax rates and tax revenue
changes in productivity
affects MRP and MCL
MRP curve
- slope will be greater the less competitive the product market is
- ex: nondiscriminating monopolies will have a more downward slope than perfect competition
changes in product demand
- shifts demand for a resource/labor bc MRP for resource/labor also shifts
- so, any change to revenue or resource productivity will change labor
income inequality
- benefit: provides incentives for individuals to innovate and grow the economy as a means of increasing personal income
- issue: redistribution of income will result in increased total utility in society