G+ bacilli & Anaerobes & Branching filaments
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
87 Terms
G+ bacilli
Corynebacteria characteristics
Appearance: Club-shaped G+ bacilli with irregularly stained segments
Appear in V/Y/Chinese letters configurations
Staining: Cells contain metachromatic granules that can be visualized with methylene blue stain (Albert Stain)
Corynebacteria genus
We got:
→ Corynebacterium diphtheriae (pathogen)
→ Diphteroids: commensals of throat/ nasopharynx/ skin/ UT/ Conjunctiva
What’s another name for C. diphtheriae. What does Diphtheros mean?
Klebs-Loeffler bacillus
Leather (for tough leathery pseudomembrane)
How is C. diphtheriae spread?
Respiratory droplets of asymptomatic/ convalescent carriers
What infecctions other than RTIs can C. diphtheriae cause
It can cause cutaneous infections - more common in tropics
Diphtheria toxin mechanism
Classic AB toxin.
It causes inhibition of protein synthesis by ADP-ribosyoation of the Elongation Factor EF2 in the presence of NAD → No chain elongation
→ Necrosis in pharyngeal, cardiac, and CNS tissues
Explain general diphtheria pathogenesis
C. diphtheriae gets into RT
C. diphtheriae multiplies in superficial layers and causes necrosis
Inflammatory response → Pseudomembrane formation on tonsils/Posterior pharynx (Made of dead cells, immune cells, RBCs, and bacteria)
Pseudomembrane spreads either up towards the nasopharynx, and down towards the larynx → Mechanical suffocation
Note: Inflammation and antigen drainage cause polylymphadenopathy. And at any point, toxin can become systemic by entering through bloodstream/lymphatics → Major complications
Lab diagnosis C. diphtheriae (Non-culture)
Take swab from lesions and look for G+ bacilli in chinese letter/V/Y arrangements, and use Albert stain that can tell us if there are metachromatic granules
C. diphtheriae culturing
Loeffler serum slope
Tellurite blood agar: Tellurite reduced to tellurium → Gray/black color
C. diphtheriae virulence test
Elek’s gel precipitation test → Leads to toxin precipitation if present
C. diphtheriae treatment
Must suppress toxin production and kill bacteria:
→ Penicillin + Erythromycin
→ Early administration of antitoxin
C. diphtheriae Prophylaxis
Toxoid vaccine , given IM
DTaP
TD (10 Times smaller dose of toxoid)
Antitoxins vs B fragment
Listeria monocytogenes general characteristics
Note, motility is just like Yersinia (but yersinia not tumbling)

Where can Listeria monocytogenes be found in nature
Unpasteurized dairy products (soft cheese), unwashed vegetables, raw or undercooked fish and meat products (hot dogs and luncheon meats)
What property of Listeria monocytogenes, makes it something you gotta always be careful about
It’s a psychrophile, and can grow on refrigerated foods.
Also, it can spread from person to person (hands/food prep)
Transplacental transmission OR vaginal transmission during birth
Listeria monocytogenes clinical manifestations in different demographics
Healthy: Asymptomatic carriage or gastroenteritis
Pregneant: Amnionitis & Spontaneous abortion
Neonates and IC individuals: Meningitis and septicemia
*LISTERIOSIS, is the form of the disease in pregnant/neonates/IC, gastroenteritis isn’t “Listeroisis”
Listeria monocytogenes pathogenesis
In the mucosa, Listeria monocytogenes can enter enterocytes (Directly unlike shigella), and once inside, it can manipulate actin filaments to propel it laterally from cell to cell (like shigella - no exposure to complements and antibodies)
Immune evasion: Listeriolysin → Generates pores in phagosome that allow its escape into the cytoplasm
Listeria monocytogenes specimens

Listeria monocytogenes culture
Blood agar → Small zones of hemolysis
Enrichment with: NA/ Cold (4 C)/ Bile salts
NOTE: Negative culture should not rule out infection if there is strong clinical evidene
Listeria monocytogenes serology
Unreliable
Uses anti-LLO antibodies, however, common Ags with Strep species and E. feacalis
Listeria monocytogenes treatment
Ampicillin/Erythromycin IV
If pregnant → Give antibiotics immediatly
Anthrax spread in nature
Bacillus anthracis forms spores in soil → Grazers get infected → Shed large amounts in feces (and mouth and nose) → Back to soil
Classify anthrax manifestations according to fatality
Cutaneous: ~10-20% - Most common (95%)
Gastroenteritis: ~25-60% (Even with treatment) - Rare
Pulmonary: ~80-90% (Untreated) / 40-50% if treated
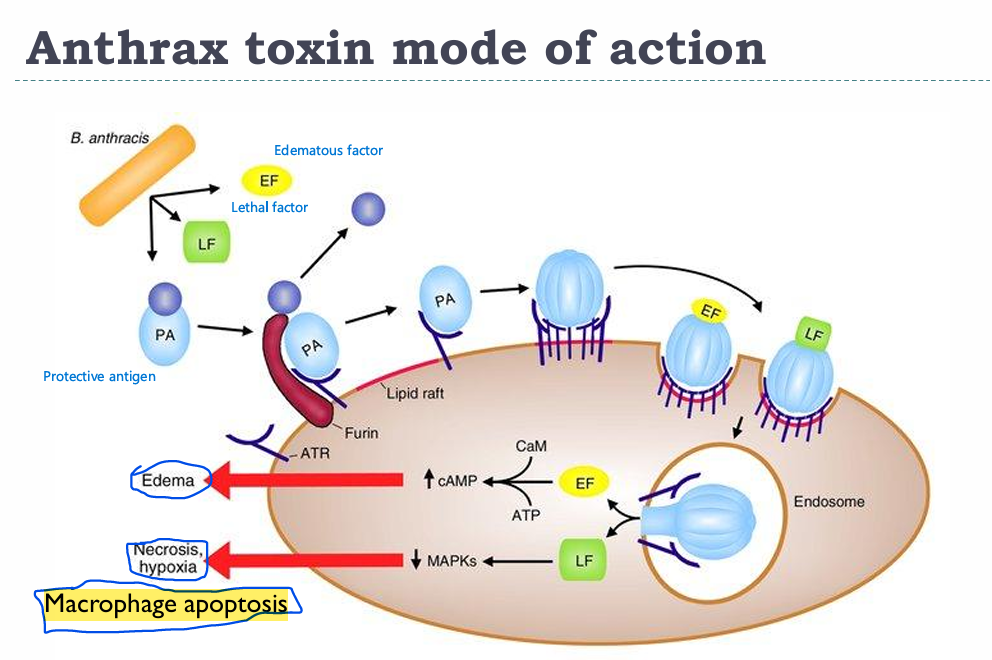
Anthrax pathogenesis
PA gets cleaved by the receptor Furin and bound by ATR in lipid rafts → PA can now bind LF/EF and get them RMEed along with it
EF → Increase in cAMP → Edema
LF → Inhibits MAPK pathway → Necrosis and hypoxia (Macrophage apoptosis)
Describe cutaneous anthrax symptoms
Papule → Vesicle → Malignant pustule around a painless necrotic lesion covered by a black Eschar - Hide Porter’s disease
Involved: Face, neck, hands, arms, back
Pulmonary anthra symptoms - Woolsorter’s disease
Life-threatening hemorrhagic pneumonia caused by spore inhalation.
Flu-like symptoms that rapidly progress to fever, pulmonary hemorrhage and mediastinitis (Enlarged mediastinum on X Ray) and Shock
Anthrax serology
Ascoli’s thermoprecipitation → Demonstrates presence of anthrax in tissues
Bacillus anthracis morphological characteristics
Solo, duo, or chains → The entire chain is surrounded by one capsule (Bamboo stick appearance) and spores that are centrally-located within the bacteria
Note: PROTEIN CAPSULE (Poly D-Glu)
How should we culture Bacillus anthracis
Grow on BA or NA at 37 C
Medusa head appearance, Non or weakly hemolytic
Anthrax vaccine
Sterne vaccine: Live-attenuated strains, rendered avirulent by the loss of the plasmid which encodes anthrax toxins.
Mazucchi vaccine: Contains spores of an attenuated strain
*Note: Bacillus anthracis, cereus, talasomething are all genetically identical, they differ in the presence or absence of plasmids
Where is Bacillus cereus commonly found
In soil: Vegetables and also milk/ cereals/ spies/ poultry/ meat
What phenomenon in Bacillus cereus associated with
Reheated rice syndrome (if there were spores on the rice to begin with
What clinical manifestations are associated with Bacillus cereus
2 forms of food poisoning:
Diarrheal form: Incubation more than 6 hours, longer convalescence (20-36 hours) * Caused by spore ingestion and germination in gut
→ Secretion of LT-like toxin
→ Watery diarrhea & GI pain
→ Associated with meatsEmetic form: Incubation less than 6 hours, shorter convalescence (8-10 hours) * Caused by ingetion of preformed cereulide toxin
→ Ingestion of preformed toxin: cereulide
→ Severe vomiting
→ Associated with reheated rice (rice is commonly contaminated with emetic strains)
Rarely, we can also have a systemic infection with bacteremia
*Note: The rice vs meat thing isn’t always guaranteed, and the vice-versa can occur in both cases
Bacillus cereus diagnosis
Depends Primarily on clinical picture and patient history (foods eaten)
But we can do labs on stools/ vomit/ food.
Culture stools and test for toxins to differentiate from staphylococcal food poisoning
Bacillus cereus treatment
Food poisoning: Supportive - Rehydration
Systemic infection: Cipro/ Aminoglycosides/ Vanco/ Clindamycin
What are the main features of anaerobes and their infections
They lack either superoxide dismutase or catalse, or both
Anaerobe infections are often polymicrobial
% of C. diff carriers
Normally present in the gut of 3% of healthy adults, and 66% of infants (<1 yo)
Where can C. diff be found in the environment
Soil
Water
What clinical manifestations are associated with C. diff
Pseudomembranous colitis - PMC
Antibiotic-associated diarrhea - AAD
Antibiotic-associated colitis - AAC
Why does PMC occur
Complication of oral antbiotic therapy with PPI, especially:
Fluoroquinolones, Ampicillin, clindamycin, cephalosporins - FACC
→ C diff overgrowth 4-9 days after starting antibiotics and up to 6 weeks after discontinuation
PMC symptoms and complications
Symptoms: Watery diarrhea, Abdominal cramps, Fever, Nausea ± vomiting, Mucus in stool
Complications: Ileus, and toxic megacolon → Perforation and death
C. diff virulence factors
Toxin A - Enterotoxin (Gastroenteritis symptoms)
Toxin B - Cytotoxin (PMC)
C. diff risk factors

C. diff diagnosis
PCR or ELISA using antitoxin A monoclonal antibodies or Antitoxin A/B polyclonal antibodies
Colonoscopy
C. diff treatment
Oral vancomycin or fidaxomycin (severe cases)
Probiotics, FMT
Relapse is common cause spore kinda unkillable
Describe the appearance of C. perfringes and C. tetani
C perfringes: Srtandard rod (Subterminal spores)
C. tetanii: Drumstick (Terminal spores with larger diameter)
What are the tetanus toxins
Tetanospamin (toxoidable) and Tetanolysin
Tetanus pathogenesis
Deep anaerobic wound → Germination of spores → Tetanospamin produced → Toxin absorption by peripheral nerve endings → Retrograde transport to CNS → Fixation to gangliosides of inhibitory neurons → Block inhibitory NT release (Glycine and GABA) → Muscle regidity and spasm → Respiratory failure
What are the clinical manifestations of tetanus
Ophisthotonus (Spasms of spinal cord)
Trismus
Risus sardonicus
C. tetanii culture
Gram-postive bacilli with drumstick appearance, capsulated, motile, peritrichous flagella
Rarely isolated in the lab cuz their culture requires trict anaerobiosis
What should be noted about old C. tetanii cultures
They may appear Gram-negative
What antibiotics are used vs C. tetanii
Beta-lactams
Chloramphenicol
Clindamycin
Vancomycin
Nitroimidazoles
BCC VN
Tetanus prophylaxis and treatment
Passive: TIG (tetagam shot)
Active: Tetanus toxoid (TT), DPT
Compined
Diazepam for muscle spasms and wound debridement
Clostridium botulinum habitat
Environment and intestines of humans & animals
Different types of botulism?
8 types depending on the toxin produced
→ A, B, C1, C2, D, 3, F, G
→ All identical in their activity except C2, which is a CYTOTOXIN
Describe the botulinum toxin
Mechanism: It blocks acetlycholine release → Inhibits muscle cell contraction
Extremely potent
Heat-labile
The bacterium needs to autolyse to release the cells
Slow acting
Botulism clinical pictures
Infant botulism: Floppy baby syndrome (Honey)
Wound botulism
Foodborne botulism: AB/EF (E → Fish products)
*Cans are inflated and show bubbles
→ 5Ds: Diplopia/ Dysarthia/ Dysphagia/ Dyspnea/ Descending flaccid paralysis
→ Death due to respiratory paralysis
Botulism treatment
Alll Beta-lactams
Stomach wash
Botulinum Ig IM
Botulinum toxoid
C. perfringes toxins
Alpha (Lecithinase)
Beta
Epslion
Iota
What strains of C. perfringes cause most diseases
Type A
C. perfringes food poisoning
Spores in spore-contaminated food germinates if left for too long <60 C → Production of heat-labile enterotoxin → Produces late-onset → Resolution in 24 hours
Necrotizing enteritis *Type C”
List some things that can cause gangrene
Follows Trauma: burns, crush injuries, battle wounds, open fractures, surgeries, clinical abortion & Caesarian section, IM injections
Gangrene
Edema
Necrosis
Crepticus (Gas production - H2/ CO2/ N2/ O2)
→ Can rapidly progress to septicemia/shock/death
C. perfringes llab and culture
Very very important to note the Double Zone of Hemolysis on BA
Nagler reaction → Look for alpha-toxin

C. perfringes wound treatment
Supportive/ debridement/ Antibiotics (They don’t work alone cuz can’t penetrate the necrotic tissue)
Number of anaerobes in different anatomical sites compared to aerobes

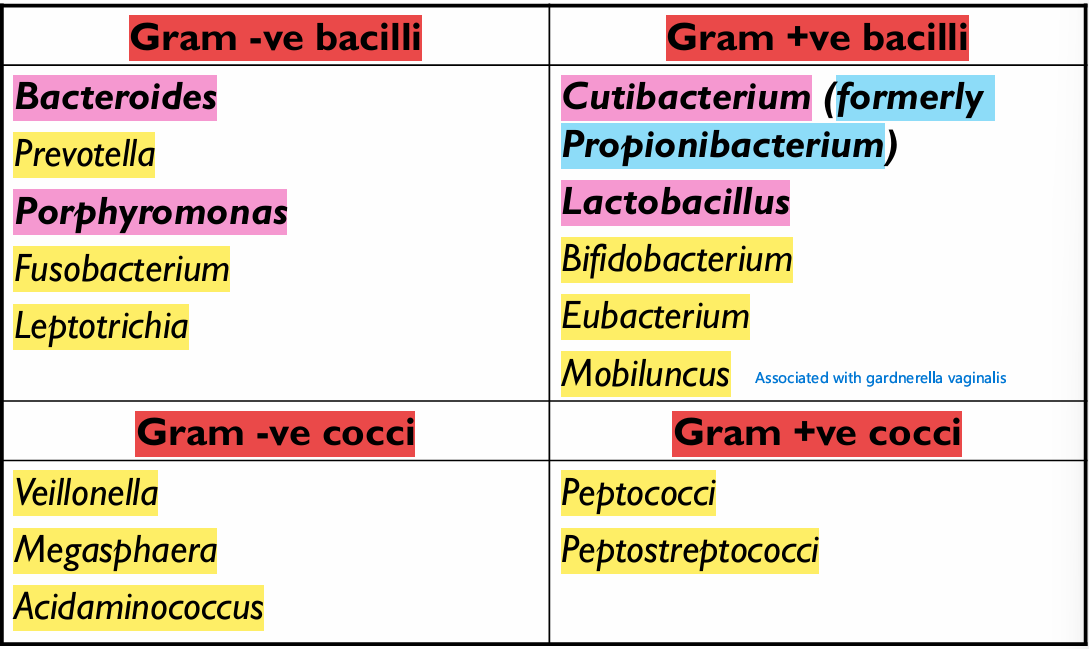
List the anaerobes
BLAME MPPP CLAMP VF
What are the risk-factors for anerobe-infections
Trauma/Tissue necrosis
Impaired circulaton - Seen in: Diabetes, malnutrition, malignancy, hematoma
Presence of foreign bodies in the body
Prolonged treatment with aminoglycosides
What does bacteroides fragilis cause
Brain abcess/ intra-abbdominal abcess/ Genital tract infections in females
Prevotella melaninogenica
Lung or liver abcess
Pelvic inflammation and breast abcess in females
Wound infection
Porphyromonas infections
Dental root canal infections - Periodontal diseases
Fusobacterium necrophorum & nucleatum
Aspiration pneumonia → Lung/liver abcess (Especially in unconscious patients)
Oral infection/ chronic sinusitis/ abdominal infetions
Decribe bifidobacteria morphology
Pleomorphic bacilli with true and false branching
What is the clinical significance of peptococcus and peptostreptococcus
Involved in mixxed anaerobic infections:
→ Puerperal sepsis & genital infections
→ Wound infection
→ Gangrenous appendicitis
→ Osteomyelitis
→ UTI
→ Brain and lung abcesses
General treatment for anaerobic infections
Pus drainage from abcesses
Wound debridement and removal of necrotic tissue
Antibiotics:
→ Metronidazole
→ Penicillin (Cocci)
→ Clindamycin
→ Cephamycins
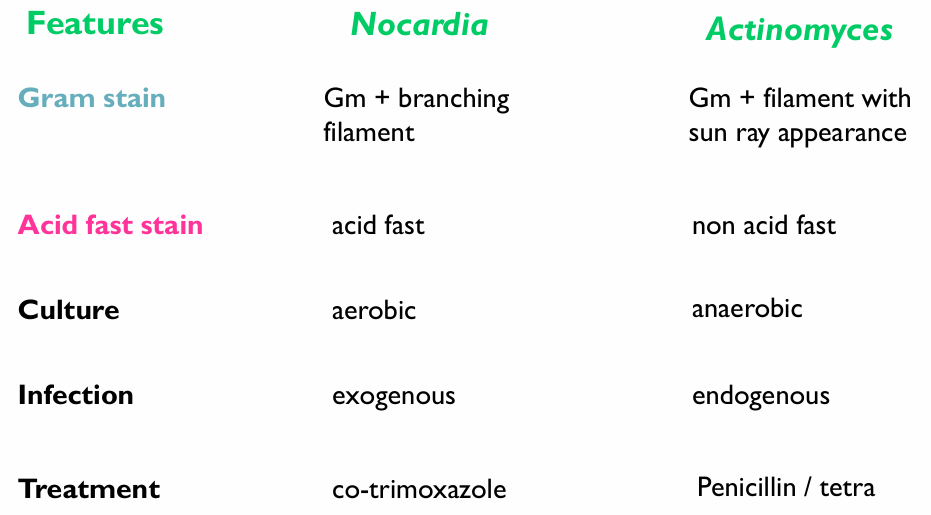
What is Atinomyces israelii, and what is it associated with
Anaerobic, endogenous microbiota of the oral and reproductive cavities and GIT
It causes Actinomycosis → Multiple abscesses and granuloma formation
Describe actinomycosis
Mostly
Cervico-facial lesions
Endogenous infections,
But can also cause:
Thoracic actinomycosis (aspiration)
Pelvic Actinomycosis → PID with intrauterine devices
Actinomycosis treatment
Surgery and Long-term penicillin
Actinomycosis diagnosis
Take specimen from open aspiration material and look for yellow-ish sulfur granules
Culture: Molar tooth appearance on agar (Teeth are Oral → Actinomyces)
Describe Nocardia asteroides
Saprophytic, aerobic, rare opportunistic pulmonary pathogen
Nocardia asteroides clinical manifestation
TB-like pneumonitis (- PPD)
Can cause ectopic foci that can help spread the infection to any other organ (Brain/spleen/kidney/liver/heart)
What is Nocardia Brasiliensis associated with
Madura foot
Lympho-cutaneous disease
How can we diagnose nocardia in the lab
Exudates from samples contain sulfur granules
Acid-fast branching filament into rods and cocci
Culture will reveal bread crumb appearance
Nocardia treatment
TMP-SMX
Compare Nocardia and actinomyes