Unit 1 AP Psychology
1/144
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Ap Psychology
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
145 Terms
The study of behavior and mental processes
Psychology
Debate between whether your characteristics are more influenced by nature (biologicial + genetic factors) or nurturing (environmental factors+ learning from your surroundings)
Nature vs. Nurture
The study of the evolution of behavior and the mind using principles of natural selection
Evolutionary Psychology
Organisms better adapted to their environment tend to survive and produce more offspring
Natural Selection
The study of the relative power and limits of genetic and environmental influences on behavior
Behavior genetics
Modification of an organism that makes it more fit for existence under the conditions of its environment
Adaptation
Random errors in gene replication
Mutation
The genetic transfer of characteristics from parents to offspring
Heredity
The complete set of DNA found in an organism
Genome
The biochemical units of heredity
Genes
Also known as identical twins, they are developed from a single fertilized egg that splits. They are genetically identical
Monozygotic twins
Also known as fraternal twins, they form from two separatley fertilized eggs. No more similar than ordinary siblings
Dizygotic twins
They use these studies to see how genetics and the environment one grows up in affects your behaviors/personality.
Why are twin and adoption studies used in psychology?
The study of the molecular mechanisms by which environments can influence genetic expression without DNA change
Epigenetics
The body system made up of neurons that communicate via neurotransmitters
Nervous system
Made up of the brain and spinal cord
Central nervous system
Responsible for gathering information and transmitting CNS decisions to other body parts. Made up of sensory and motor neurons that connect the CNS to the rest of the body
Peripheral nervous system
Controls the glands and internal organ muscles. Responsible for all the muscles we do not voluntarily think about moving
Autonomic nervous system
Enables voluntary control of our skeletal muscles, ie: turning your head in response to something
Somatic nervous system
Arouses the body, mobilizing its energy. Accelerates heart rate, races blood pressure, cools you with sweat, “fight or flight”
Sympathetic nervous system
Conserves energy and calms you. “Rest and digest”. It essentially tries to return/keep your body at homeostasis
Parasympathetic nervous system
Takes information inwards from body tissues and sensory receptors (sensory neurons) to the CNS
Affarent neurons
Carry instructions from the CNS outwards to the body’s muscles and glands (motor neurons)
Efferent neurons
A nerve cell, the basic building block of the nervous system
Neuron
Contains the nucleus, the cell’s life support center
Cell body/ Soma
The branching fibers of a cell body, they receive messages from other cells
Dendrite
Carry impulses away from the cell body to other neurons, muscles, or glands
Axon
Form junctions with other cells
Axon terminals
A layer of fatty tissue that insulates axons and speeds their impulses
Myelin Sheath
The glial cells that form the myelin sheath on axons
Schwann Cells
Support, nourish, and protect neurons
Glial cells
Dendrites
Cell body
Axon
Axon terminal
How does information pass through the neuron?
The level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse
Threshold
A brief electrical charge that occurs when a nerve cell or muscle fiber is activated by a stimulus
Action potential
The difference in electrical charge between the inside and outside of a neuron’s cell membrane
Resting potential
A brief resting pause that occurs after a neuron has been fired; subsequent action potentials cannot occur until the axon returns to resting state
Refractory period
A neuron’s reaction of either firing with a full strength response or not firing
All-or-none response
Chemical messengers that cross the synaptic gap between neurons
Neurotransmitters
The junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of a receiving neuron
Synapse/Synaptic cleft
A neurotransmitter’s reabsorption by the sending neuron
Reuptake
Enables muscle action, learning, and memory
Acetylcholine
Influences movement, learning, attention, and emotion; rewarding sensation
Dopamine
Affects mood, hunger, sleep, and arousal
Serotonin
Helps control alertness and arousal
Norepinephrine
A major inhibitory neurotransmitter
GABA
A major excitatory neurotransmitter involved in memory
Glutamate
Neurotransmitters that influence the perception of pain or pleasure
Endorphins
Involved in pain perception and immune response
Substance P
Drugs affect brain chemistry by exciting or inhibiting neurons’ firing
How do drugs and other chemicals alter neurotransmitters?
A molecule that increases a neurotransmitter’s action, ie: Morphine
Agonist
A molecule that inhibits or blocks a neurotransmitter’s action, ie: Botox
Antagonists
The endocrine system transmits information via hormones which travel through the bloodstream and interact with the brain
How does the endocrine system transmit information and interact with the nervous system?
The proportion of variation among individuals in a group that we can attribute to genes
Heritability
Released by adrenal glands on top of kidneys; it increases heart rate, blood pressure, and blood sugar. Provides a surge of energy to power fight or flight response
Adrenaline
Released by pituitary gland; it enables orgasm, labor contractions, and milk flow
Oxytocin
Released by adrenal glands; it is a stress hormone that increases blood sugar
Cortisol
Chemicals that alter the brain by producing changes in perceptions and mood
Psychoactive drugs
A disorder characterized by continued substance use despite resulting life disruption
Substance Use Disorder
Depressant; slows brain activity that controls judgement and inhibitions, effects memory
Alcohol
Depressant; Drugs that mimic the effects of alcohol- depress CNS activity and can lead to impaired memory and judgement
Barbiturates
Depressant; Opium and its derivatives (morphine and heroin) depress neural activity, temporarily lessening pain and anxiety
Opiates
Depressant; provides a short-lived feeling of blissful pleasure, followed by craving for another fix
Heroin
Often used when trying to combat a heroin addiction; enough to reduce intense physical cravings but you can still become addicted to this
Methadone
Drugs that reduce neural activity and slow body functions; lowers inhibitions; decrease sympathetic nervous system activation
Depressants
Drugs that excite neural activity and speed up body functions, increase sympathetic nervous system activation; increases pulse, energy, and breathing rates
Stimulants
Stimulant; causes mind-wandering cravings and withdrawal symptoms (cravings, insomnia, anxiety, crankiness)
Nictotine
Stimulant; increases attentiveness and improves mood; it is physically addictive
Caffeine
Stimulant; pills prescribed for people with adhd and previously used for weight loss
Amphetamines
Stimulant; stimulates the release of dopamine; causes a crash of fatigue, deep sleep, mental depression, and decreased appetite
Methamphetamines
Stimulant; when inhaled/snorted it reaches the brain in minutes- producing intense euphoria, mental alertness and self confidence; results in a crash
Cocaine
Stimulant and mild hallucinogen; makes a person feel calm or relaxed while seeming to have an endless energy supply; popular club drug that causes severe dehydration
Ecstasy
Psychedelic drugs that distort perceptions and evoke sensory images
Hallucinogens
Hallucinogen; “Acid”, one of the most powerful drugs known, trips can last from 6-14 hours
LSD
Hallucinogen; produces feeling of elation, promotes relaxation, relieves inhibitions; chronic use associated with loss of motivation and general apathy
Marijuana
A border of blood vessels in the brain that don’t allow the blood of the peripheral nervous system to have an impact on the central nervous system
Blood-brain barrier
Repeated exposure to a psychoactive drug produces tolerance; the drug’s effects lessen as exposure is repeated
Tolerance
The adaption of the body to the repeated use of a drug (meaning it no longer produces the naturally existing neurotransmitter that is being replaced by the drug)
Drug dependence
Physical conditions caused by chronic use of a tolerance-forming drug in which abrupt or gradual drug withdrawal causes unpleasant physical symptoms
Physical dependence
A state that involves emotional-motivational withdrawal symptoms upon cessation of drug use
Psychological Dependence
Focus their research on the scientific study of the links between biological (genetic, neural, hormonal) and psychological processes
Biological psychologists
The process of creating new neurons in the brain
Neurogenesis
The brain’s ability to change, especially during childhood, by reorganizing after damage or by building new pathways based on experiences
Neuroplasticity
Tissue destruction
Lesion
Measures subtle changes in the brain’s electrical activity through electrodes placed on the head
EEG
A brain-imaging technique that measures magnetic fields from the brain’s natural electrical activity
MEG
Scan a visual display of brain activity that detects where a radioactive form of glucose goes while the brain performs a given task
PET
Uses extremely powerful electromagnets and radio waves to get structural information from the brain. Shows brain anatomy and structures
MRI
A technique for revealing blood flow and therefore brain activity
Functional MRI
Cross-sectional images of the brain using a series of x-ray pictures taken from different angles
CT Scans
Contains brainstem structures that direct essential survival functions such as breathing, sleeping, arousal, coordination, and balance
Hindbrain
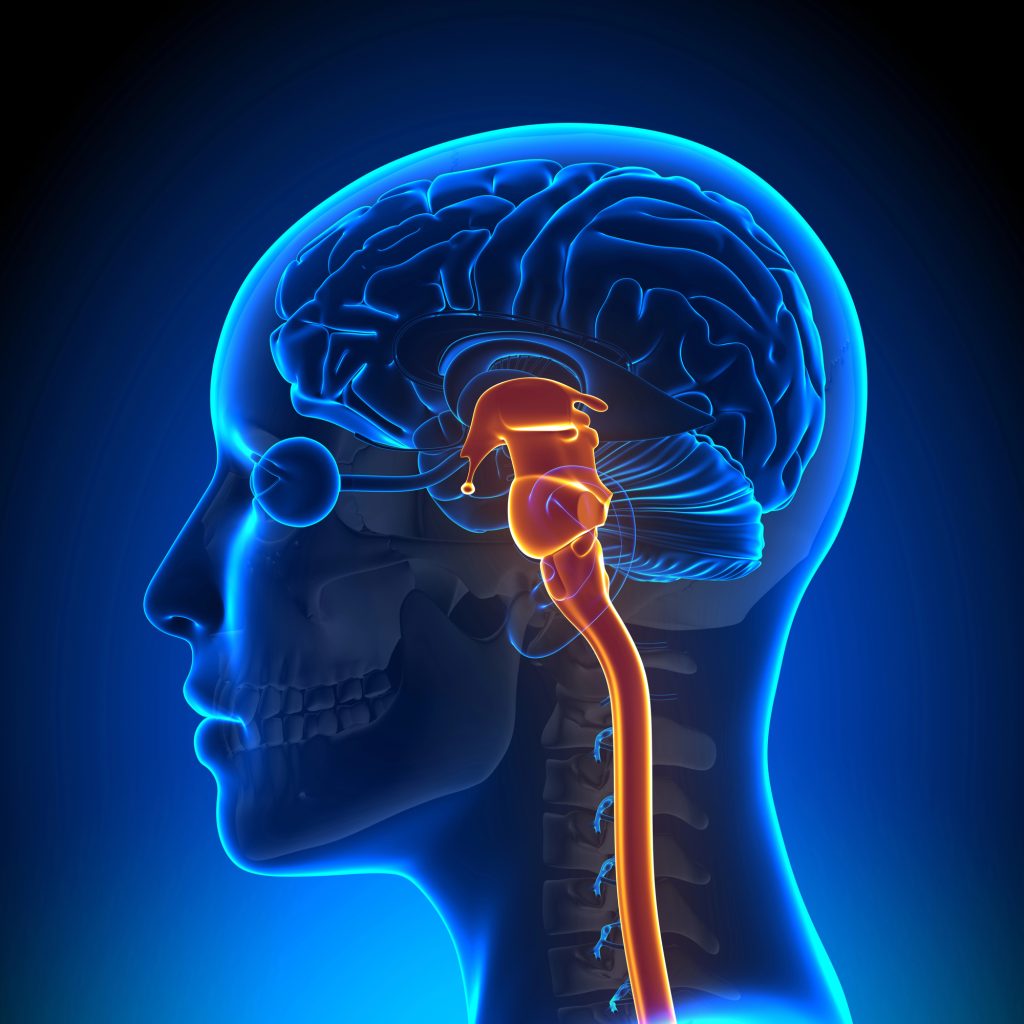
Connects the hindbrain with the forebrain; controls some movement and transmits information that enables our seeing and hearing
Midbrain
Manages complex cognitive activities, sensory and associative functions, and voluntary motor activities
Forebrain
Responsible for automatic survival functions such as heartbeat, breathing, etc
Brainstem
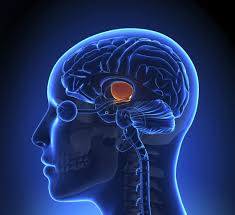
Relay station for all sensory info except smell
Thalamus
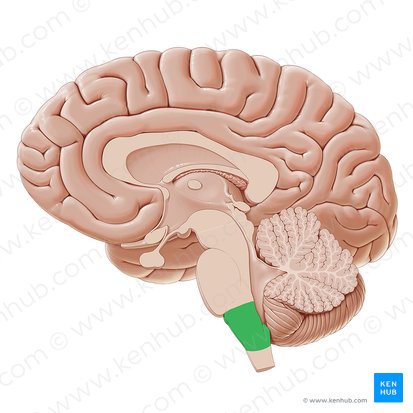
Responsible for general level of arousal, or attention
Reticular Formation
Controls heart rate, breathing, and blood pressure
Medulla
Bridge between midbrain and stem; responsible for sleep and arousal
Pons
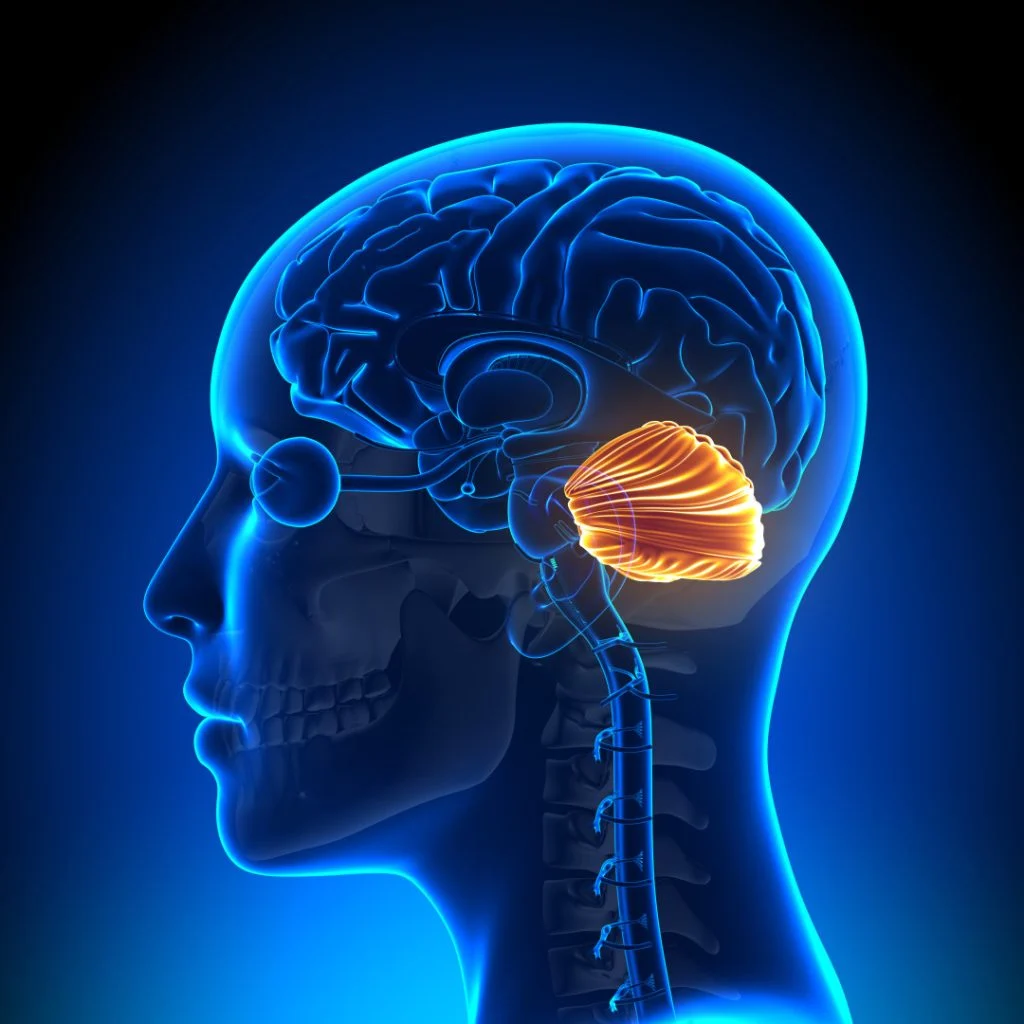
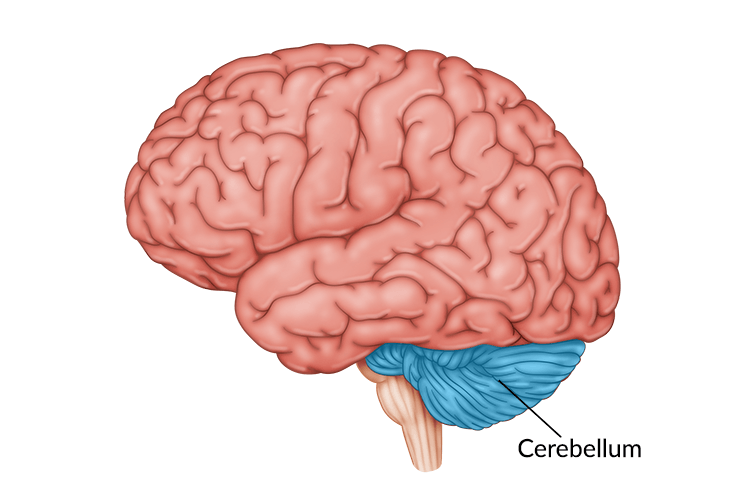
Controls basic movements, balance, and coordination; learning new skills
Cerebellum
Regulates hunger, thirst, body temperature, and sexual arousal
Hypothalamus
Master gland of the endocrine system
Pituitary Gland