Physiology Exam Questions
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/171
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 8:07 PM on 12/11/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
172 Terms
1
New cards
central dogma of molecular biology
DNA
transcription
mRNA transcript
translation
protein
transcription
mRNA transcript
translation
protein
2
New cards
amino acid derivatives
binding to its receptor sometimes produces a slow response and sometimes a fast response
3
New cards
steroids
binding to its receptor almost always produces a slow response
4
New cards
peptides
binding to its receptor produces a fast response
5
New cards
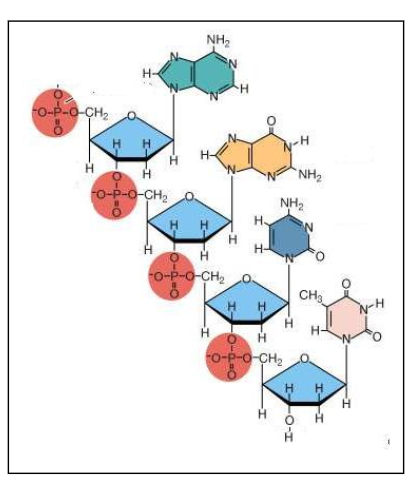
Which of the four organic biomolecules is pictured here?
nucleic acid
6
New cards
Which of the following hormones would bind with a receptor inside the cell?
steriods
7
New cards
paracrine signals
Paracrine signals communicate with adjacent cells.
Autocrine signals are often also paracrine signals.
Autocrine signals are often also paracrine signals.
8
New cards
The role of oxygen in cells is to?
act as an electron acceptor
9
New cards
enzymes
metabolic catalysts
lower activation energy
proteins
lower activation energy
proteins
10
New cards
What is the extracellular matrix of blood called?
Plasma
11
New cards
Which of the four major classes of organic biomolecules has up to three different folded structures?
proteins
12
New cards
When a catecholamine or peptide hormone binds to receptors on the surface of a cell...
second messengers are activated
13
New cards
What catabolic pathways in the body produce ATP?
glycolysis (2 ATP), citric acid cycle (2 ATP), and the electron transport chain (26-28 ATP)
14
New cards
Which of the following glial cells is found in the peripheral nervous system?
Schwann cells
15
New cards
The conduction of an action potential along an axon...
is not faster for a strong stimulus than a weak stimulus
is not faster along unmyelinated nerve fibers
does not decrease in amplitude as it is propagated along the axon
is not faster along unmyelinated nerve fibers
does not decrease in amplitude as it is propagated along the axon
16
New cards
If GABA binds receptors on a post-synaptic cell body, what will likely happen to the membrane potential?
hyperpolarization
17
New cards
Where are synapses primarily located?
in grey matter
18
New cards
Which is least likely to diffuse across the blood brain barrier?
lipophobic molecule
19
New cards
If fluid taken from a lumbar puncture is not clear and colorless, this could indicate:
either an infection or a brain hemorrhage depending on the color
20
New cards
Which component(s) of the central nervous system is/are responsible for the basic functions of life (e.g., involuntary breathing and heart rate, relaying of sensory and motor signals)?
brain stem
spinal cord
spinal cord
21
New cards
dorsal root and horns
receive afferent signals
22
New cards
ventral root and horns
project efferent signals
23
New cards
parasympathetic division
dominates during the "resting and digesting" time and its ganglia are on or near the target organs
24
New cards
"dual innervation"
organ receiving both sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves
25
New cards
Imagine a scenario where a presynaptic neuron's voltage-gated Ca+ channels failed to open in response to the neuron's depolarization. Which of the following would result from this situation?
neurotransmitter would not bind to the receptors on the the postsynaptic neuron
26
New cards
protection of the brain
cranium
dura matter
subarachnoid space
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
dura matter
subarachnoid space
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
27
New cards
During the rising phase of the action potential...
Na+ moves down both a concentration and electrical gradient.
28
New cards
A presynaptic neuron releases excitatory neurotransmitter into the synaptic cleft twice in a span of milliseconds. The resulting graded potential in the postsynaptic neuron reaches threshold and fires an action potential. This is an example of?
temporal summation
29
New cards
During a dissection, you observe a motor neuron that exits the spinal column at the level of thoracic vertebrae #3. It reaches its autonomic ganglion almost immediately upon exiting the spinal column. This must be a:
sympathetic pathway
30
New cards
central nervous system
brain and spinal cord
31
New cards
myelin sheath
does not cover the entirety of the axon
increases the speed of an action potential
composed of neuroglial cells
increases the speed of an action potential
composed of neuroglial cells
32
New cards
A neuron releases acetylcholine into the synaptic cleft at its target tissue. The acetylcholine binds muscarinic receptors initiating a response in the target tissue. Which autonomic pathway is this?
parasympathetic
33
New cards
secondary endocrine disorder
too much or too little hormone form the anterior pituitary
34
New cards
Considering a neuron with excitatory post-synaptic potential, you would predict that a drug binding and inactivating the breakdown enzyme for its neurotransmitter would result in...
more post-synaptic action potentials
35
New cards
Which statement accurately describes why a graded potential loses amplitude as it moves away from its stimulus?
Charged ions leak out of the membrane before reaching the trigger zone.
36
New cards
The nervous system's ability to communicate is primarily dependent on the movement of…
charged particles
37
New cards
blood-brain barrier
can be comprised of tight junctions between endothelial cells
permeable to small, nonpolar, or lipophilic molecules
helps protect the brain from pathogens
permeable to small, nonpolar, or lipophilic molecules
helps protect the brain from pathogens
38
New cards
Successful recovery from a brain injury, like that seen in the case of Phineas Gage, likely requires the re-wiring of neuronal connections and possibly even the formation of new neurons. This type of reorganization is called...
neural plasticity
39
New cards
In a complex endocrine pathway, long-loop negative feedback inhibits...
the hypothalamus and/or the pituitary
40
New cards
During sexual intercourse, secretion and lubrication of the vagina is accomplished via parasympathetic innervation to the uterus, while contraction of the uterus (and/or vagina) is accomplished via sympathetic innervation. Similar to the male orgasm, these are best described as _________.
synergistic (or cooperative) effects
41
New cards
If the white matter of the spinal cord is damaged, what symptoms would you expect?
impaired sensory relay
impaired movement
impaired movement
42
New cards
How does electroencephalography (EEG) detect brain activity?
free electrons in the metal electrodes respond to the flow of ions in and out of neurons
43
New cards
The brain is mostly composed of…
44
New cards
Which is used for rapid signaling over long distances?
action potentials
45
New cards
neurotransmitters that hyperpolarizes the cell will...
decrease the probability that the cell will produce an action potential
makes the cell body more negative
makes the cell body more negative
46
New cards
In order for an action potential to be propagated, the threshold membrane potential in the cell body must be reached…
once, at the axon hillock
47
New cards
somatosensory cortex
processes general sensory information and the size of the area dedicated to each part of the body is correlated with receptor concentraction
48
New cards
sodium-potassium (NaK) pump
uses active transport
binding of potassium (K+) triggers the pump to change shape
when the pump is open to the intracellular fluid its shape proves binding sites for sodium (Na+)
binding of potassium (K+) triggers the pump to change shape
when the pump is open to the intracellular fluid its shape proves binding sites for sodium (Na+)
49
New cards
A neuronal pathway emerging from the cranial region that slows the heart rate must be a...
parasympathetic pathway
50
New cards
Neurotransmitter is stored and released from...
axon terminals
51
New cards
agonistic effects on the primary endocrine gland will...
increase production of the primary hormone
decrease production of releasing hormone from the hypothalamus
decrease production of tropic hormone from the anterior pituitary
decrease production of releasing hormone from the hypothalamus
decrease production of tropic hormone from the anterior pituitary
52
New cards
afferent neurons
transmits information coming into the central nervous system
53
New cards
Both the cell body and the axon have Na+ channels. Are these channels the same or different? If so, how?
different, cell body has chemically-gated channels and axon has voltage-gated channels
54
New cards
action potential sequence
1. Na-K pump establishes resting membrane potential
2. stimulus causes a graded potential
3. graded potential reaches threshold at the axon hillock
4. voltage gated Na channels open near the axon hillock
5. additional voltage-gated Na channels open along the axon
6. Na-K pump re-establishes resting membrane potential
2. stimulus causes a graded potential
3. graded potential reaches threshold at the axon hillock
4. voltage gated Na channels open near the axon hillock
5. additional voltage-gated Na channels open along the axon
6. Na-K pump re-establishes resting membrane potential
55
New cards
Which of the following is secreted by neurons AND acts via diffusion across a synapse?
neurotransmitters
56
New cards
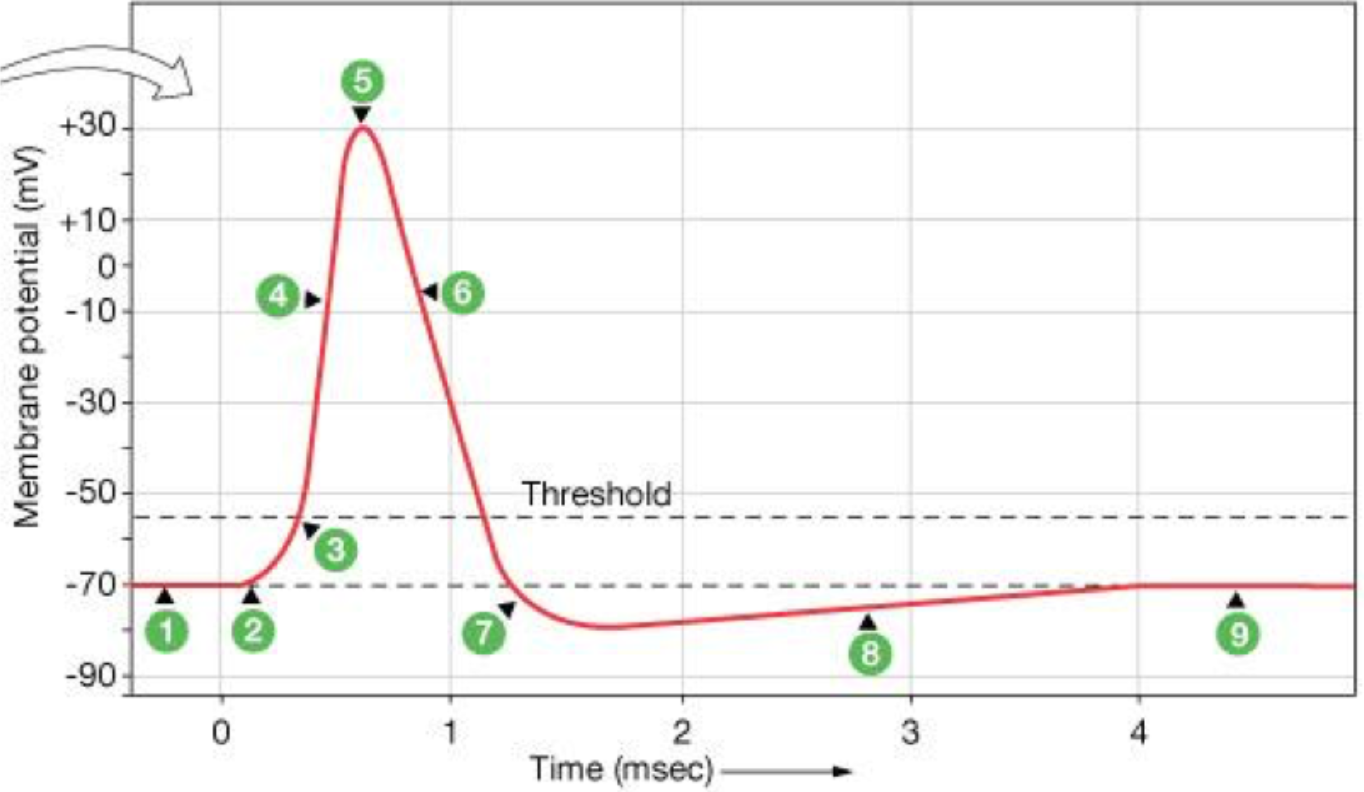
What is the primary event causing the voltage change indicated by #4 on this image?
opening of voltage-gated sodium channels
57
New cards
What is located in the medulla oblongata?
centers for respiratory control (breathing)
pyramids, where tracts cross to the opposite side of the body
centers for vomiting control
pyramids, where tracts cross to the opposite side of the body
centers for vomiting control
58
New cards
Which neurocrine behaves as a neurohormone in the PNS and as a neurotransmitter in the CNS?
epinephrine
59
New cards
peripheral nervous system (PNS)
consists of all sensory and motor neurons outside of the CNS
contains components of the autonomic and somatic nervous system
contains components of the autonomic and somatic nervous system
60
New cards
limbic system
center for emotions
61
New cards
spatial summation
can be excitatory or inhibitory
62
New cards
The total amount of neurotransmitter released at the axon terminal is directly related to the…
total number of action potentials
63
New cards
charge distribution across a neuron's membrane
extracellular fluid = positive
intraceullar fluid = negative
intraceullar fluid = negative
64
New cards
Which of the following is true about efferent information in the central nervous system?
can be carried from the CNS by motor neurons
65
New cards
A person with defective rods will have trouble...
distinguishing shapes at the periphery of the visual field
seeing well in the dark
seeing well in the dark
66
New cards
A blind spot in the retina occurs where...
the optic nerve leaves the eye
67
New cards
iris
controls diameter of the pupil
68
New cards
rhodopsin
light receptor
69
New cards
tectorial membrane
stimulates hair cells
70
New cards
cristae in ampullae
senses rotational movement
71
New cards
otoliths in maculae
senses lateral movement
72
New cards
The primary purpose of the middle ear bony structures (maleus, incus and stapes) is to...
amplify the vibration as it conducts to cochlea
73
New cards
You work at the Tabasco factory in Louisiana. You spend your workday blending barrels of fermented chili peppers with vinegar and bottling hot sauce. The smells do not bother you, because...
Olfactory receptors are phasic, they quickly adapt to constant stimulus.
74
New cards
skeletal muscle contraction
starts when the muscle fiber depolarizes due to the release of calcium into the cytoplasm
75
New cards
Why does rigor mortis occur after death?
myosin is tightly bound to actin
there is no ATP available to bind to myosin
there is no ATP available to bind to myosin
76
New cards
Which is a potential energy source for an athlete sprinting the 40-yard dash?
phosphocreatine
77
New cards
smooth muscle contraction
Ca2+ initiates the contraction
uses actin-myosin crossbridges to create force
contraction can occur without a change in membrane potential
uses actin-myosin crossbridges to create force
contraction can occur without a change in membrane potential
78
New cards
As a protective mechanism, stretching a skeletal muscle fiber causes sensory neurons (i.e. proprioceptors) to ______ their rate of firing.
increase
79
New cards
troponin and tropomyosin in skeletal muscle contraction
they inhibit the bindings necessary for contraction
80
New cards
Most reflex movements are integrated by…
the spinal cord
81
New cards
Which is a characteristic of slow-twitch oxidative skeletal muscle fibers?
long contraction duration AND many mitochondria
82
New cards
Stretching a muscle spindle causes…
reflex contraction of that muscle.
83
New cards
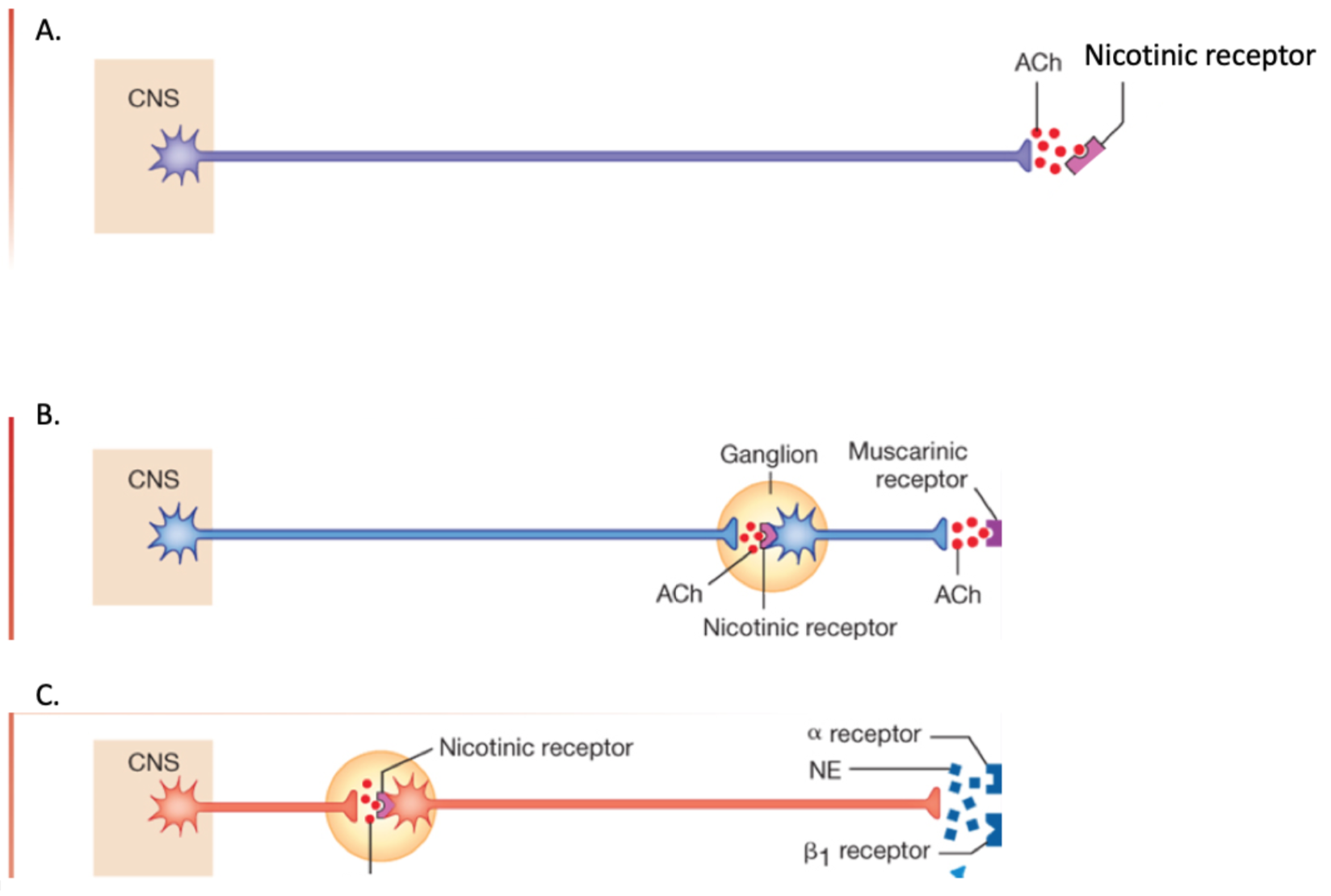
Which of the following represents a somatic motor pathway?
Figure A
84
New cards
In the human eye, if the ________ focuses the light anywhere but the ________ then vision is imperfect.
lens, fovea
85
New cards
Bob fell off a ladder trying to clean out his gutters. His wife rushed him to the emergency room. The doctor tested his knee-jerk reflex and found it was normal. These results suggest that?
Bob has no damage to his spinal cord.
86
New cards
A person with defective rods will have trouble...
distinguishing shapes at the periphery of the visual field
seeing well in the dark
seeing well in the dark
87
New cards
If you were floating in outer space experiencing zero gravity, the weightlessness would cause the otoliths in your macula to lose their reference point. Which of these sensations might you expect to have difficulty perceiving?
head position
linear acceleration
linear acceleration
88
New cards
The neurons of the special senses each carry information to cortexes in the brain that are specific to each sense. However, general sensation information is all carried to the…
somatosensory cortex
89
New cards
In smooth muscle, the Ca2+ necessary for contraction can come from…
the sarcoplasmic reticulum
the extracellular fluid
the extracellular fluid
90
New cards
feedforward control
allows the body to anticipate a stimulus and begin a movement
91
New cards
negative feedback
generally result in the cessation of that movement
92
New cards
If glutamate is normally an excitatory neurotransmitter, why are some bipolar cells turned ON by light and some OFF by light?
different receptors
93
New cards
chemoreceptor
surcrose solution
94
New cards
mechanoreceptor
muscle tension
95
New cards
thermoreceptor
temperature
96
New cards
Sweet, bitter, and umami signals are communicated through a G-protein coupled ______ which can amplify the signal sent to the primary sensory neuron.
second-messenger system
97
New cards
After an injury, Jodie has difficulty recognizing and interpreting certain sounds. These symptoms imply damage to the…
auditory cortex
98
New cards
During crossbridge cycling, the binding of ATP to the myosin head…
releases the myosin head from actin
99
New cards
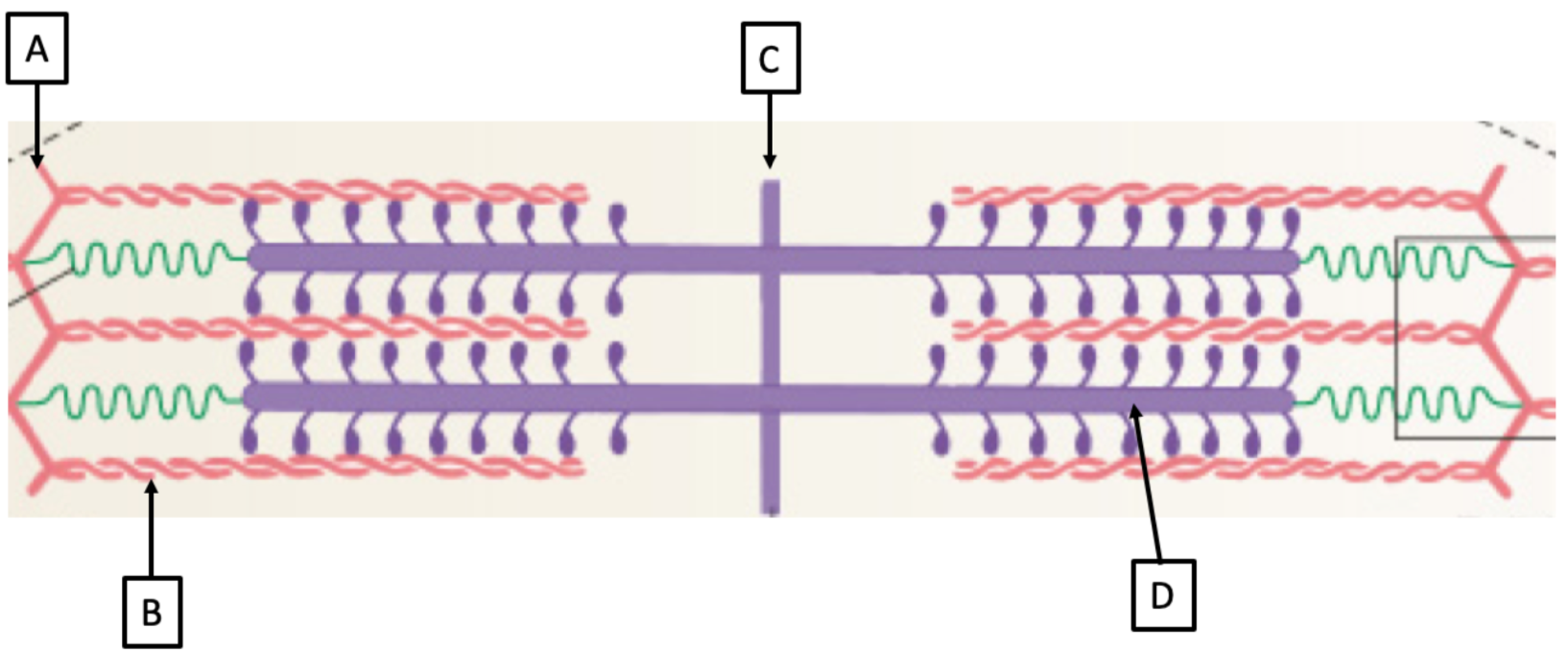
M line
C
100
New cards
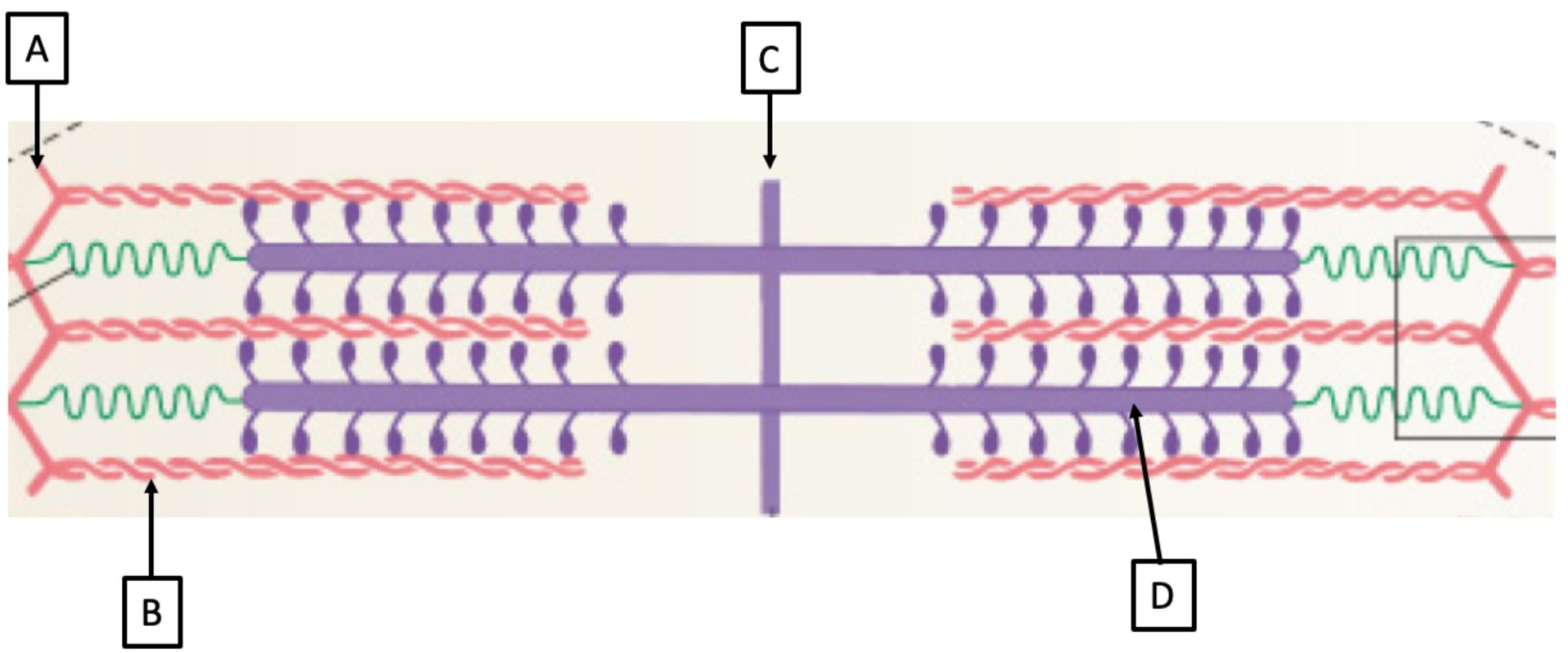
Z line
A