Globalisation
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/97
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
98 Terms
1
New cards
Gloablization
is the process by which people, their cultures, money, good and information are transferred between countries which few or no barriers
2
New cards
Global flows
new degrees of connectedness between and within economies
3
New cards
examples of global flows
social- tourism
cultural- religion
political- international organisations (eg- UN)
economic- remittances
environmental- paris climate agreement
technology- instagram
cultural- religion
political- international organisations (eg- UN)
economic- remittances
environmental- paris climate agreement
technology- instagram
4
New cards
Shrinking world effect (time-space compression)
when the relative distance between places becomes smaller due to things such as outsourcing and instant communication
5
New cards
Containerization
The transporting of goods in standard-sized shipping containers.
6
New cards
Glocalisation
The modification of global products and ideas to suit local cultures.
7
New cards
Infaltion
rise in the general level of prices of products
8
New cards
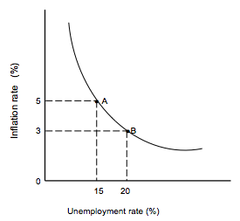
Phillips Curve
a curve that shows the relationship between inflation and unemployment
9
New cards
Stagflation
a period of slow economic growth and high unemployment (stagnation) while prices rise (inflation).
10
New cards
an example of stagflation
in 1970's (challenged ideas of Keynesianism)
11
New cards
Keynesianism
Belief in aggressive government intervention to combat recession & promote economic growth by creating a multiplier effect
12
New cards
multiplyer effect
the idea that an initial amount of spending (usually by the government) leads to increased consumption & spending resulting in an increase in national income greater
13
New cards
Neoliberalism
a view tending to favour free-market capitalism and deregulation. the belief that government spending increases inflation
14
New cards
intergovernmental organisations
to create a system so that the world's inhabitants can work more successfully together resulting in peace and security, and also to deal with the economy.
15
New cards
examples of intergovernmental organisations
IMF (international monetary fund)
WB (world bank)
WTO (world trade organisations)
WB (world bank)
WTO (world trade organisations)
16
New cards
IMF (International Monetary Fund)
organization which gives loans to poor countries
17
New cards
World Bank
An agency of the United Nations that makes loans to countries for economic development, trade development, and debt consolidation.
18
New cards
WTO (World Trade Organization)
the only global international organization dealing with the rules of trade between nations
19
New cards
trade blocs
Voluntary international organisations that exist for trading purposes, bringing greater economic security to the nations that join due to reduced tariffs and trade barriers
20
New cards
Tarrifs
Taxes on imported goods
21
New cards
example of a trade bloc
NAFTA
22
New cards
tax breaks and subsidies
a giveaway of cash or public resources that is intended to encourage a particular activity or lower the price of a product
23
New cards
example of subsidy (UK)
Nissan was given money in order for it to invest in the uk
24
New cards
example of tax breaks (UK)
Canary Wharf
25
New cards
examples of china's efforts to increase globalisation
- open door policy in 1978
- set up export processing zones
- set up export processing zones
26
New cards
Export processing zone
areas where governments create favourable investment and trading conditions to attract export-oriented industries
27
New cards
TNCs (Trans-national corporations)
Companies that are located in or produce and sell products in more than one country
Factories tend to be located in poorer countries where labour is cheaper so they make more profit
Factories tend to be located in poorer countries where labour is cheaper so they make more profit
28
New cards
TNCs +ives and -ives
Advantages:
+They create jobs
+They spend money to improve local infrastructure
+New technology and skills are brought to poorer countries
Disadvantages:
-Employees in poorer countries may be paid less than employees in richer countries
-Employees often have to work long hours in poor conditions
- Profits go back to richer countries and are not reinvested in the poorer countries
+They create jobs
+They spend money to improve local infrastructure
+New technology and skills are brought to poorer countries
Disadvantages:
-Employees in poorer countries may be paid less than employees in richer countries
-Employees often have to work long hours in poor conditions
- Profits go back to richer countries and are not reinvested in the poorer countries
29
New cards
Ltd. (Limited)
to show that it is a limited company (a company whose owners only have to pay part of its debts if it fails)
30
New cards
Switched on countries
very open and globalised countries (eg USA)
31
New cards
Switched off countries
closed off and not globalised countries (eg north korea)
32
New cards
two speed economy
economies whose industries experience unevenly distributed rates of growth
33
New cards
KOF Index
measures the progress of globalization, combines economic, political, and social factors.
34
New cards
AT Kearney Index
Measures the globalisation level of countries.
Has 4 criteria;
- personal (eg remittances)
- political (eg. treaties)
- technological (eg. number of internet users)
-economical (eg. international trade)
Has 4 criteria;
- personal (eg remittances)
- political (eg. treaties)
- technological (eg. number of internet users)
-economical (eg. international trade)
35
New cards
3 main factors causing counteis to become more globalised
- open door policies for trade
- TNCs outsourcing
- FDI
- TNCs outsourcing
- FDI
36
New cards
Open Door Policy
A policy proposed by the US, under which ALL nations would have equal opportunities to trade in China.
37
New cards
Outsourcing
obtaining key products from alternative, cheaper locations - often abroad
38
New cards
FDI
Foreign Direct Investment - Investment made by a foreign company in the economy of another country
39
New cards
Green GDP
Gross domestic product which takes into account environmental destruction and/or health consequences of environmental problems.
40
New cards
economic growth +ives
- more money invested in healthcare and education
- transport is developed
- safer housing
- transport is developed
- safer housing
41
New cards
economic growth -ives
- exploitation of employee
- uneven benefit throughout population
- environmental damage
- uneven benefit throughout population
- environmental damage
42
New cards
Rural-urban migration
the movement of people from the countryside to the city
43
New cards
Reasons for Rural to Urban Migration
people looking for jobs, education and conveniences
44
New cards
BRICS
Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa
45
New cards
MINT
Mexico, Indonesia, Nigeria, Turkey
46
New cards
Megacity
City with more than 10 million people
47
New cards
factors that increase urbanisation
- rural to urban migration
- natural increase
- natural increase
48
New cards
international migrants
people that move between countries
49
New cards
Internal Migrants
People moving within a country.
50
New cards
economic migrants
people who move for economic purposes
51
New cards
Elite migrants
Migrants who are able to move easily due to the valuable skills and or wealth
52
New cards
Low-wage migrants
people who move and become cheap labour workers in another country
53
New cards
global hubs
are 'cores' that demonstrate high connectivity to the rest of the world.
they are very globalised and diverse, have high natural and human resources, and have good education and healthcare due to governments investment.
they are very globalised and diverse, have high natural and human resources, and have good education and healthcare due to governments investment.
54
New cards
cultrural diffusion
The spread of different beliefs, governments, and religions from a culture to another.
55
New cards
cultural imperialism/ westernisation
The dominance of one culture over another, this is mainly the influence of western countries
56
New cards
ethnic enclave
a small area occupied by a distinctive minority culture
57
New cards
development
social and economic development of a country that leads to a stronger economy and better quality of life. it is often a result of political advancement which over all makes a HIC become a LIC
58
New cards
sectors of development
demographic, political, social, environmental, cultural
59
New cards
example of demographic development
life expectancy increasing
60
New cards
example of political development
freedom of speech
61
New cards
example of social development
excess to clean water
62
New cards
example of cultural development
increases years in education
63
New cards
example of environmental development
sustainability
64
New cards
`two types of variable
single and composite
65
New cards
economic measures of development
GDP, GNI, GDP per capita, PPP (purchasing power index)
66
New cards
social measures of development
HDI (life expectancy, GNI and literacy rate), gender inequality index.
67
New cards
environmental measures of development
green GDP, ADI (air quality index), % of waste recycled.
68
New cards
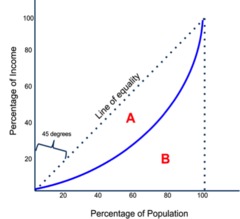
inequality measures of development
lorenz curve, gini coefficient
69
New cards
reasons globalisation has increased he mixing of cultures
- migration due to open borders and better transport
- rural to urban migration
- rural to urban migration
70
New cards
main reasons for migration to the uk
job opportunities, healthcare and education, equality and war (in home countries)
71
New cards
what are the issues caused by mass migration?
- strain on services
- xenophobia
- xenophobia
72
New cards
Immigration-
Movement of individuals INTO a country
73
New cards
Emmigration-
movement of individuals OUT of a country
74
New cards
net migration
immigration - emigration
75
New cards
Ethnoscapes
an area that clearly indicates that a culture is dominant
76
New cards
example of an ethnoscape
China town
77
New cards
Diaspora
A dispersion of people from their homeland
78
New cards
the British values
democracy, the rule of law, individual liberty, mutual respect and tolerance of those with different faiths and beliefs
79
New cards
ways a country can control globalisation
- censorship
- limit migration into the country
-trade protectionism
-cultural protection
-resource nationalism
- limit migration into the country
-trade protectionism
-cultural protection
-resource nationalism
80
New cards
censorship
restricting access to ideas and information (eg the great firewall of china and state controlled media in north Korea)
81
New cards
Limiting Migration examples
Trumps wall & Brexit due to fear of cultural erosion
82
New cards
trade protectionism
the government increasing tariffs in order to limit the import of goods and services. to protect domestic businesses
83
New cards
Cultural Protectionism
The process of attempting to protect, maintain and promote the unique aspects of a culture.
84
New cards
examples of cultural protectionism
- in France, 40% of songs on the radio must be French
- Canadas first nations (over 600 groups of native people who are being given back the right to their land as well as compensation)
- Canadas first nations (over 600 groups of native people who are being given back the right to their land as well as compensation)
85
New cards
Resource Nationalism
the tendency of people and governments to assert control over natural resources located on their territory.
86
New cards
privatisation
when government run businesses are taken over by the private sector
87
New cards
an example of privatisation
the trains in the UK
88
New cards
Nationalism
when the government take control of a private sector business
89
New cards
an example of nationalism
the TNC Bechtel (USA) owned all of Bolivias water supply due to the IMFs structural adjustment policy
90
New cards
increased localism
he increase of goods produced and bought within a local area for the benefit of people
91
New cards
ecological footprint
the impact of a person or community on the environment, expressed as the amount of land required to sustain their use of natural resources.
92
New cards
Sustainability
the ability to grow and maintain at a certain level or rate without causing harm to the environment
93
New cards
local action examples
'the Winchester action on climate change'
94
New cards
Transition Towns
A settlement where individuals and businesses have adopted 'bottom-up' initiatives with the aim of making their community more sustainable and less reliant on global trade.
95
New cards
local sourcing +ives and -ives
+more spending on local businesses
+reduces TNCs and therefore worker exploitation
+increases self sufficiency
-can be viewed as exclusive
-fewer TNCs= less employment
-some products have to be produced under synthetic conditions which may harm the environment and is expensive.
+reduces TNCs and therefore worker exploitation
+increases self sufficiency
-can be viewed as exclusive
-fewer TNCs= less employment
-some products have to be produced under synthetic conditions which may harm the environment and is expensive.
96
New cards
Ethical consumption
a deliberate choice of product for ethical reasons considering the social and environmental cost of the good purchased.
97
New cards
ethical consumption case study-
M&Ss 'Plan A'
- 100 commitments to source responsibly, to reduce waste and to help the community (2007)
- new goals (2020)- continue to be carbon 0, and to have 100% recyclable packaging by 2022
- 100 commitments to source responsibly, to reduce waste and to help the community (2007)
- new goals (2020)- continue to be carbon 0, and to have 100% recyclable packaging by 2022
98
New cards
ethical consumption case study 2-
Fairtrade
+prioritises paying workers a fair wage
- not everyone can afford to buy the products resulting in less pay for the workers
+prioritises paying workers a fair wage
- not everyone can afford to buy the products resulting in less pay for the workers