Plant Physiology Exam 4
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
What causes light change in the environment?
Season, weather, and habitat
What is the function of phytochromes?
Photo-receptor proteins that regulate growth
What is the function of protochlorophyllide?
precursor molecule for chlorophyll
What is the function of cryptochromes?
UV-A and blue light photoreceptors
What does phytochrome Pr do?
Absorbs red light and converts it to Pfr
What kind of reaction is the conversion of Pr to Pfr and vice-versa?
A photoconversion reaction
Which is biologically active and triggers a plant response, Pfr or Pr?
Pfr
Phytochrome synthesis
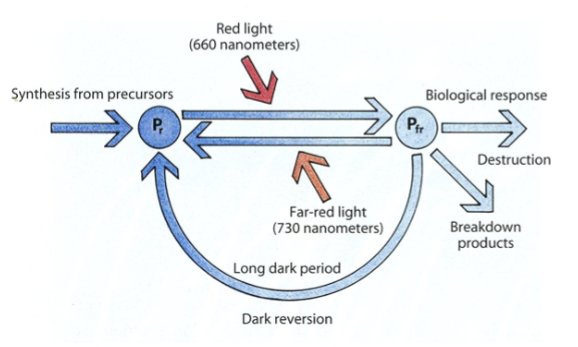
What are the proportions of Pr and Pfr during the day?
40% Pr and 60% Pfr
What is the purpose of photoconversion?
Helps plants know where they are in the environment
Where are phytochromes found?
Actively growing tissues (meristems)
What is Phytochrome A responsible for?
Responsible for etiolated form of developing shoot and hypocotyl elongation
Attributes of Phytochrome A
Functions under FR light
Phytochrome A is destroyed by light
Primary photoreceptor for sensing VLFR
What is Phytochrome B responsible for?
Responsible for stem elongation in shaded plants
Attribtues of Phytochrome B
Regulates LFR and HIR responses
Responsible for photoreversible reactions
Phytochrome C-E attributes
Less common than phyA & B
Roles still uncertain
Likely they function in a variety of processes such as shade-avoidance, elongation, expansion, and flowering
What occurs once the hypocotyl gets above ground?
FR:R drops and the plant develops
Define etiolation
Growth in the dark
What does Etiolation result in?
Lack of greening
Reduced leaf width
Leaves don’t unroll
Elongated stem
Apical hook retained
What part of the leaf does blue-light stimulate change in?
The stomata
How can the stomatal responses to blue-light be described?
Rapid, reversible, and impact the whole-plant growth dynamics
Is the response to blue-light developmentally specific?
No
What is the relationship between red and blue light in the stomata?
Blue light stimulates opening and photosynthesis, red light saturates it, and blue light again can cause a greater opening of the stomata
What plant growth responses do the genes cry1 and cry2 regulate?
Hypocotyl elongation
What plant growth responses do the genes phot1 and phot2 regulate?
Blue-light sensitivity
Are blue-light responses photoreversible?
No
What is a major similarity between cryptochromes and phytochromes?
They have apoprotein and chromophores that absorb light
What ties cryptochromes to animals and plants?
They are present in both (suggests similar evolutionary history)
Interactions among pigments
Redundancy and/or cross-talk in responses is common among photoreceptors
What is driving the gene class constans to vary
The plant’s circadian rhythm
What is regulating the gene class FT to vary
The amount of sun in a day or the “photoperiod”
Which gene class is regulating flowering?
FT expression
Why is simple little arabidopsis important?
It was the first plant to have its genome fully sequenced due to it being a “model organism”
Absisic acid plays a large role in stomatal regulation. Name another key role:
Dormancy and growth regulation
Seedling hypocotyl growth through darkness is called:
Etiolation
Downward bending foliage following ethylene exposure is called:
Epinasty
The role of phytochromes in seedling germination was discovered in which species?
Lettuce
Blue light plays an important role in guard cell opening/closing
True
What type of hormone has little transport from the site of endogenous production?
Brassinosteroids
Which scientist was one of the first to work on plant tropisms?
Charles Darwin
Which hormone type can be used to increase crop yields?
Brassinosteroids
Plant secondary metabolites have important benefits to humans, via drug discovery and pharmacological innovation
True
Which hormone class produces the triple response?
Ethylene
What is a hormone and why are they important
An organic molecule synthesized in one region of a plant and transported to other regions to create an effect. They are important as they are necessary for plant life and create drastic responses at low concentrations
When Auxin is high and cytokinin low, what tissue forms?
Root tissue
When auxin is low and cytokinin is high, what tissue forms?
Shoot tissues
I am a flower grower in Guatemala that wants to supply flowers to US supermarkets. Which hormone(s) can I use to ensure that cut flowers still have a shelf life in a location 2,000+ miles away?
Cytokinins as they delay senescence, mobilize nutrients, and are utilized in floral development
From the previous question, how can I minimize early senescence during the shipping process (what steps do I take to keeping the flowers fresh during transport)
Utilize cytokinins and minimize the production of auxin, using any other ethylene blockers available as well
Primary site of synthesis for auxin:
meristematic tissues
Primary site of synthesis for Brassinosteroids
Terpenoid pathway
Primary site of synthesis for Abscisic Acid
Nearly all plant cells (mature leaves, roots, and seeds)
Primary site of synthesis for Gibberellins
Growing shoots and seeds
Primary site of synthesis for Cytokinins
Root tissue
Primary site of synthesis for ethylene
All tissue, common in fruit
Define homeostasis
The tendency towards equilibrium between interdependent elements
True/False: Positive feedback loops maintain homeostasis
False
True/False: Negative feedbacks are important in hormone synthesis, metabolism, and catabolism
True
What are the two types of phytochromes?
Pr and Pfr
Which form of phytochrome is the" “biologically active form"?
Pfr
How are chlorophyll, phytochrome, and cryptochromes similar?
They all rely on light in some way
Are phytochromes or cryptochromes photoreversible? How do you know?
Phytochromes are photoreversible (…)
Please list 4 physiological processes mediated by phytochromes
Seed germination, etiolation, shade avoidance, …
How does a secondary metabolite vary from a primary metabolite?
Secondary metabolites are much more specialized than their counterpart and cannot occur without the primary metabolite.
Terpenes
Type example: Essential oils
Primary function: Plant defense
Phenols
Type example: Lignins
Primary function: Variety of functions; defense, support, pollinator attraction, fruit dispersion, UV light dissipation, and plant competition
N-containing organic compounds
Type example: Alkaloids
Primary function: Plant defense thru offense
Is Jasmonic acid an induced or a constitutive defense response? Please provide specific examples to defend your choice
Jasmonic acid is an induced defense response as it only activates when it is triggered. Jasmonic acid is only produced AFTER a plant lands on a venus flytrap, as an example.
What are glucosinolates matched to?
N-organic acid
What are tannins matched to?
Phenols
What are essential oils matched to?
Terpenes
What is salicylic acid matched to?
Phenols
What are alkaloids matched to?
N-organic aicds
What are phytoecdysones matched to?
Terpenes
What are cyanogenic glycosides matched to?
N-organic acids
What are flavinoids matched to?
Phenols
What are cardenolides matched to?
Terpenes
What are lignins matched to?
Phenols
What are pyrethroids matched to?
Terpenes
Permanent growth response to light
Phototropism
Rapid and reversible growth response to light
Heliotropism
Effective in pollination, defense, and carnivory
Thigmotropism
Roots exhibit negative response to light stimuli
Phototropism
Amyloplasts and statoliths used as sensors
Gravitropism
Uses a pulvinus for movement
Heliotropism
Commonly associated with vines
Thigmotropism
Auxin accumulates to inhibit growth
Phototropism
What are trichomes
Single or multiple-celled outgrowths of the epidermis, they function in absorption of water and nutrients and defend against insects by covering the leaves
What are thorns?
Modified stems