Physics 1A Forces & Motion
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Milli (m)
10-3
Micro (µ)
10-6
Nano (n)
10-9
Pico (p)
10-12
Kilo (K)
10³
Mega (M)
106
Giga (G)
109
Tera (T)
1012
Define speed
How much distance an object is travelling in a certain amount of time / How many metres it is doing in one second.
What is the relationship between speed, distance, and time?
speed = distance/time
s=d/t
What is the main unit for speed?
metres per second
m/s
Define velocity
The rate of speed of an object in a certain amount of time with a direction
What is a scalar?
An object or quantity without only size (magnitude) and not direction.
What is a vector?
An object or quantity with size (magnitude) AND direction
What is an example of a scalar?
Time, Speed, Temperature, Mass, Distance
What is an example of a vector?
Displacement, Velocity, Acceleration, Force, Momentum
Define acceleration
The rate of change of velocity
What is the equation for acceleration?
acceleration = (final velocity - initial velocity)/time
a=(v-u)/t
What is the unit for acceleration?
m/s²
What happens to the equation if deceleration is what’s needed to be found?
Nothing, if the answer for an acceleration is negative, that means that the answer is deceleration.
What is Newton’s equation of motion?
v² = u² + 2as
What is the relation between velocity, displacement, and time?
v = s/t
What’s the velocity of an object at rest?
0 m/s
What is the IGCSE value for acceleration due to gravity?
10 m/s²
Why are graphs useful?
To figure out if two things are related, for quickly looking at data
What is the area under the graph if the gradient is acceleration in a Velocity-time graph?
Distance travelled
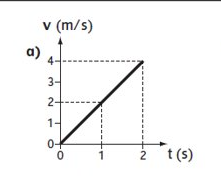
What does the graph show?
A constant acceleration of 2 m/s²
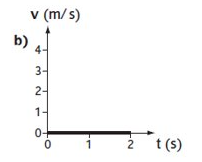
What does the graph show?
Stationary
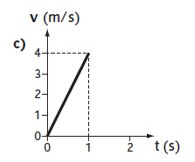
What does the graph show?
A constant acceleration of 4 m/s²
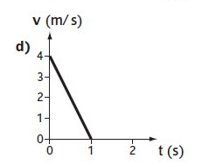
What does the graph show?
A constant deceleration of 4 m/s²
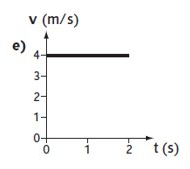
What does the graph show?
A constant velocity of 4 m/s
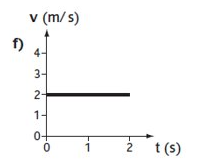
What does the graph show?
A constant velocity of 2 m/s
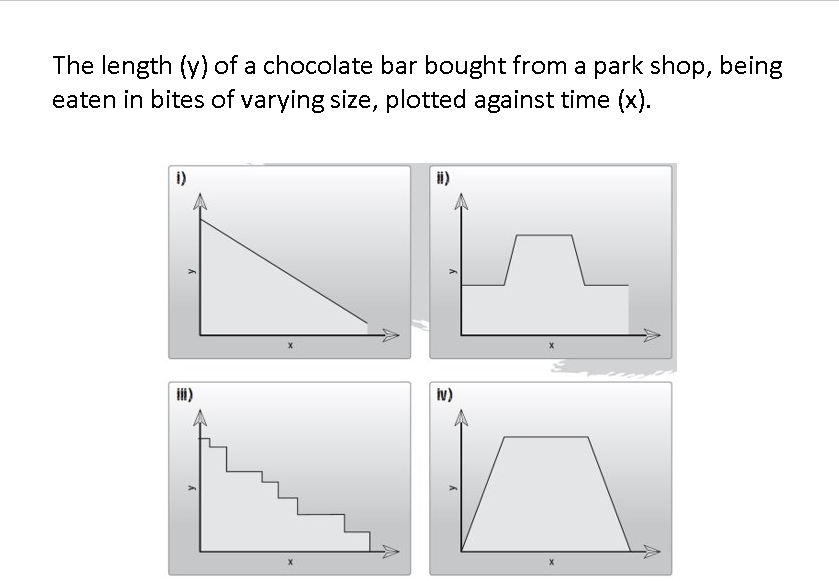
Which graph meets the statement?
Graph (iii)
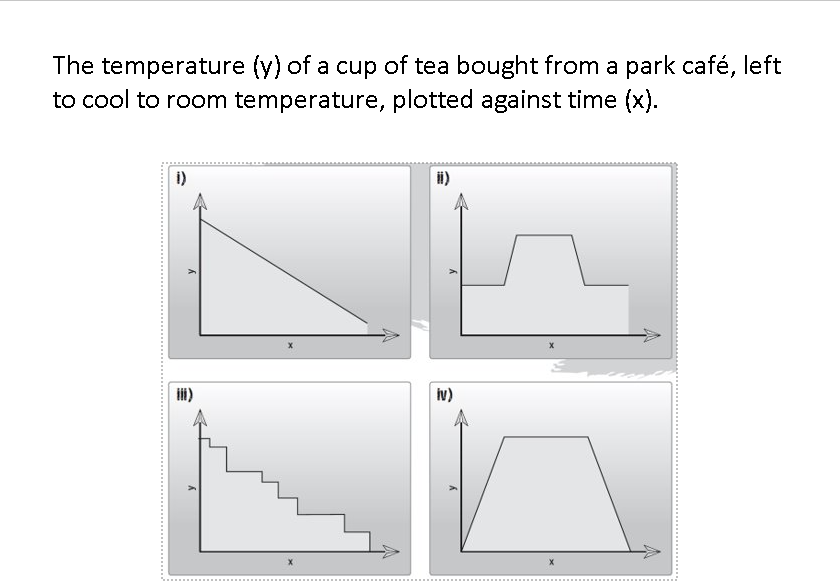
Which graph meets the statement?
Graph (i)
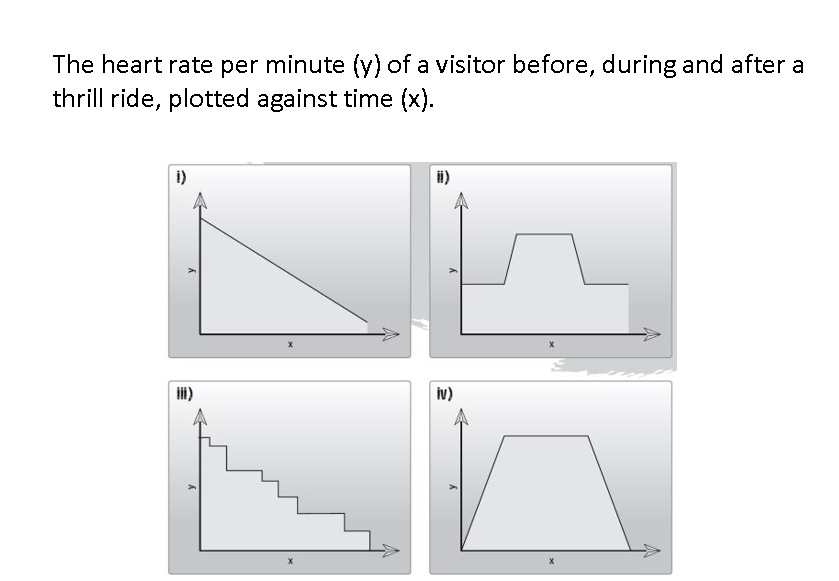
Which graph meets the statement?
Graph (ii)
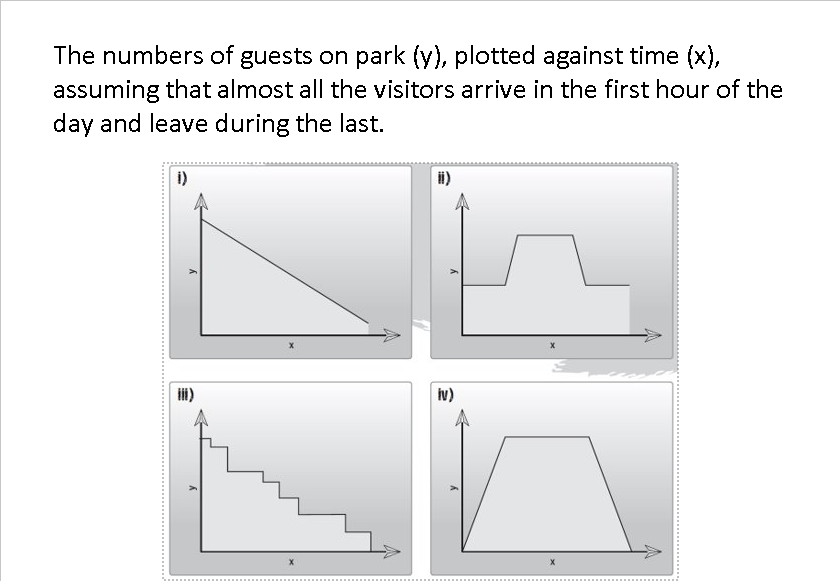
Which graph meets the statement?
Graph (iv)