Renal Transplants & Dialysis
1/201
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
202 Terms
Atrophy, high resistance flow, RI usually >0.8
Describe medical renal disease
End-stage renal disease
What is hemodialysis usually used to treat
Filters waster from the blood through a semi-permeable membrane while being circulated outside the body
Describe how hemodialysis works
High flow in an easily accessed vessel
What is required for hemodialysis to work
Needs lots of flow to come out fast, filtered, and then get back in the patient fast
Why does hemodialysis require high flow
Tube goes into the peritoneum. The patient will has ascites and the tube will drain the fluid from the peritoneum. Then they will have filtered clear fluid go back into the patient
Describe peritoneum dialysis
Fluid will go out yellow and go back in clear
Describe the colour difference of the ascites fluid with peritoneum dialysis
Pt can do peritoneum dialysis at home but has to be responsible enough to do this whereas a pt doing hemodialysis will have to come into the hospital every few days
Describe the difference between peritoneum and hemodialysis
Hemodialysis
What does this image show
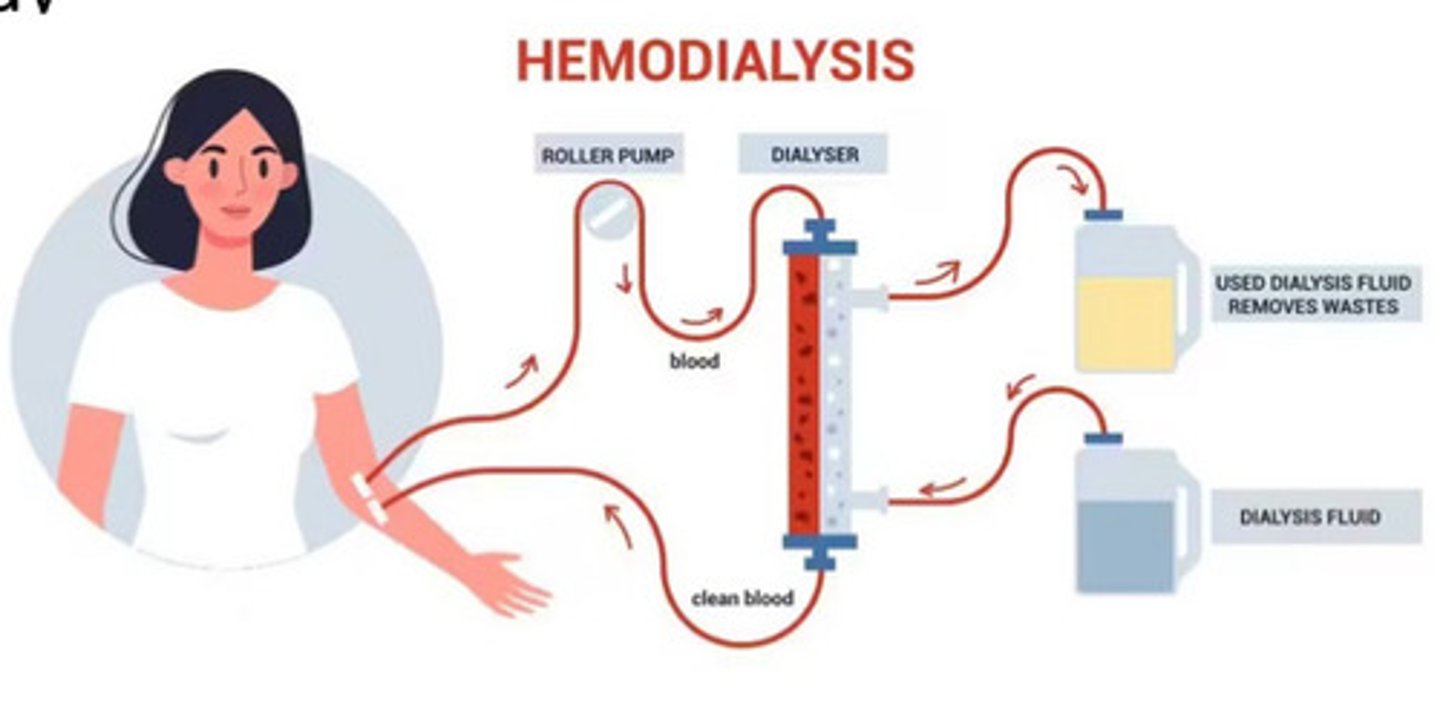
No, it is just kinda of a bandaid fix to buy the patient more time until they can get a kidney transplant
Is hemodialysis a permanent fix
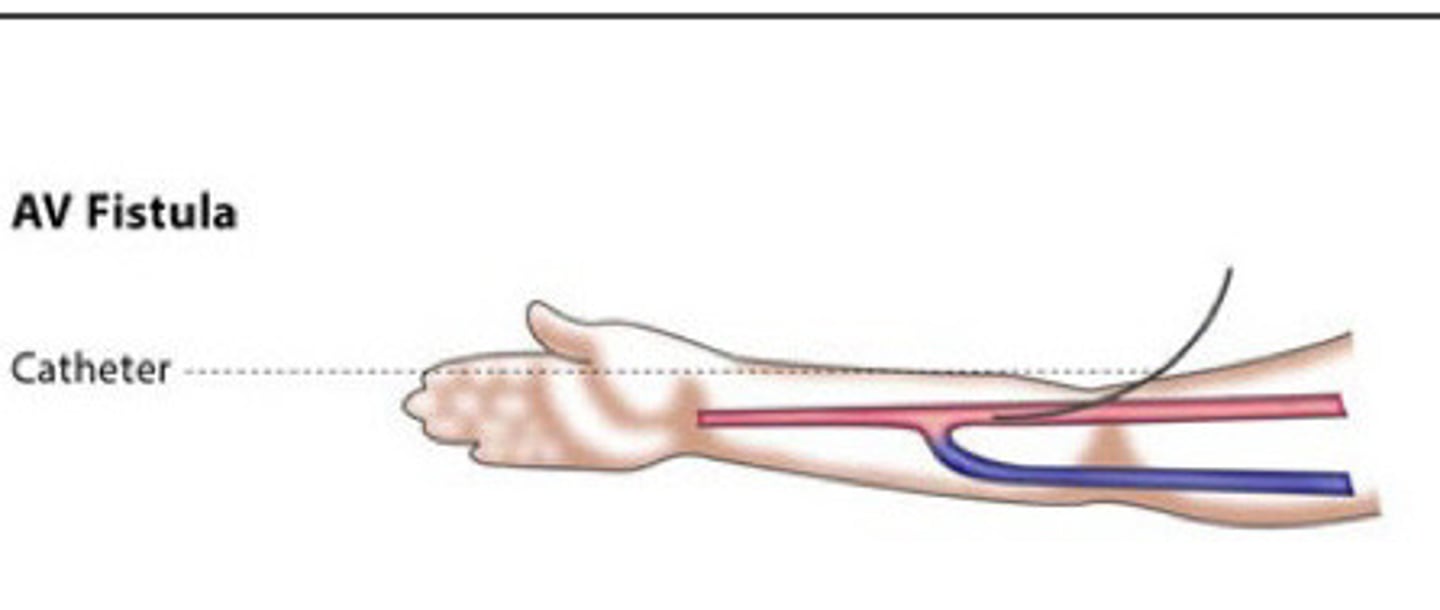
Fistula or graft
What are the 2 different ways that doctors may alter the pts vasculature to allow them to have hemodialysis
Create an AV connection to facilitate high volume flow with superficial access
What does a fistula and a graft both accomplish
Direct anastomosis created between a artery and vein (have to go in surgically and create the fistula)
Describe a fistula
Lower complication rates
What is the advantage of fistulas
Lower rate of maturation and higher risk of thrombus
What is the disadvantages of fistulas
10 weeks
About how long does it take for a fistula to be ready to be used for hemodialysis
The artery will gradually make the vein bigger from the higher pressure flow going into it but needs to be nice big and juicy in order to do dialysis (bc it requires high flow)
Describe what causes the vein to enlarge after a fistula surgery and why it takes a while to mature
Fistula
What does this image show
Indirect connection created between artery and vein using graft material (introducing foreign body into body)
Describe a graft for dialysis
Higher rate of complication rates
What is the disadvantage of graft
Higher rate of maturation (pretty much ready to go right away) and lower risk of thrombus
What are the advantages of a graft
Bc will have higher flow right away (whereas the fistula may have some areas of low flow which can cause thrombus)
Why are grafts at a lower risk for thrombus formation
Graft
What does this image show

From high pressure artery to low pressure vein
Describe how the blood flows in grafts and fistulas
As distal as possible in the non dominant hand (like to start at the wrist)
Where do they usually to the grafts or fistulas
Groin but it affects day to day life so is last resource
What is another possible location for a graft or fistula
Starting at the wrist allows them to keep moving up if it fails. The kidney transplant list is long so they often have to keep going through fistulas and grafts
Explain why they usually start distally in the arm with grafts and fistulas
Cephalic V to radial A, basically V to radial A, upper arm connections (above the antecubital fossa)
What are the 3 major fistula types
Cephalic vein to radial artery
What fistula is more commonly preferred/most common
Brescia-cimino fistula
What is the name given to the cephalic vein to radial artery fistula
At the wrist
Where is a Brescia-Camino fistula located
Basilic vein to radial artery
What would be the next choice for a fistula
Above the ante cubital fistula
Where would an upper arm fistula be located
Brescia-Camino fistula
What does this image show

Forearm fistula
What does this image show

Av grafts
What does AVG stand for
AV fistula
What does AVF stand for
50%
What % of people is it not possible to make an AVF (fistula)
Graft
What would be used if a fistula is not possible in the patient
Teflon
What are the grafts usually made out of
PTFE or gortex
What are 2 examples of grafts commonly used
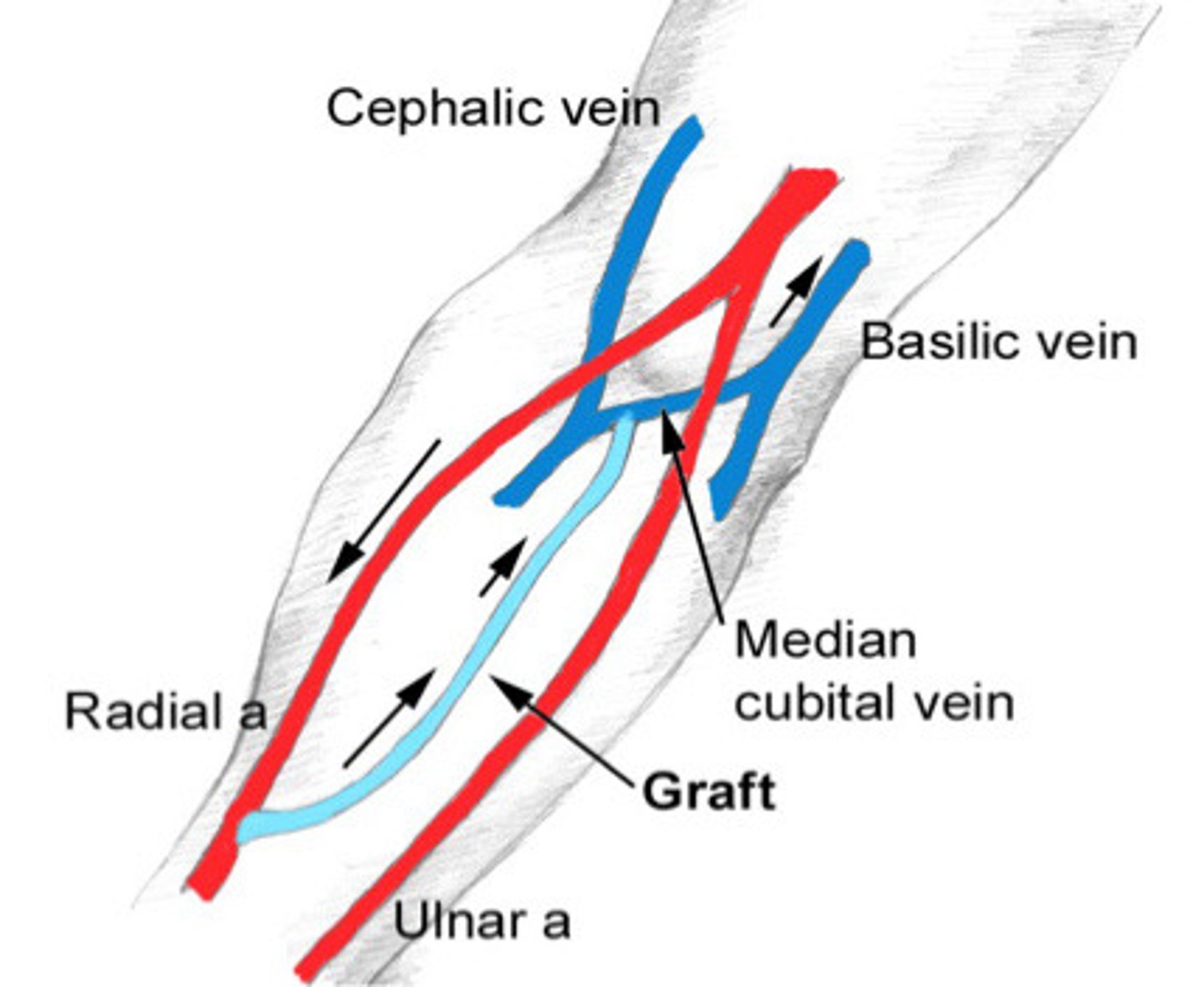
Straight graft
What does this image show
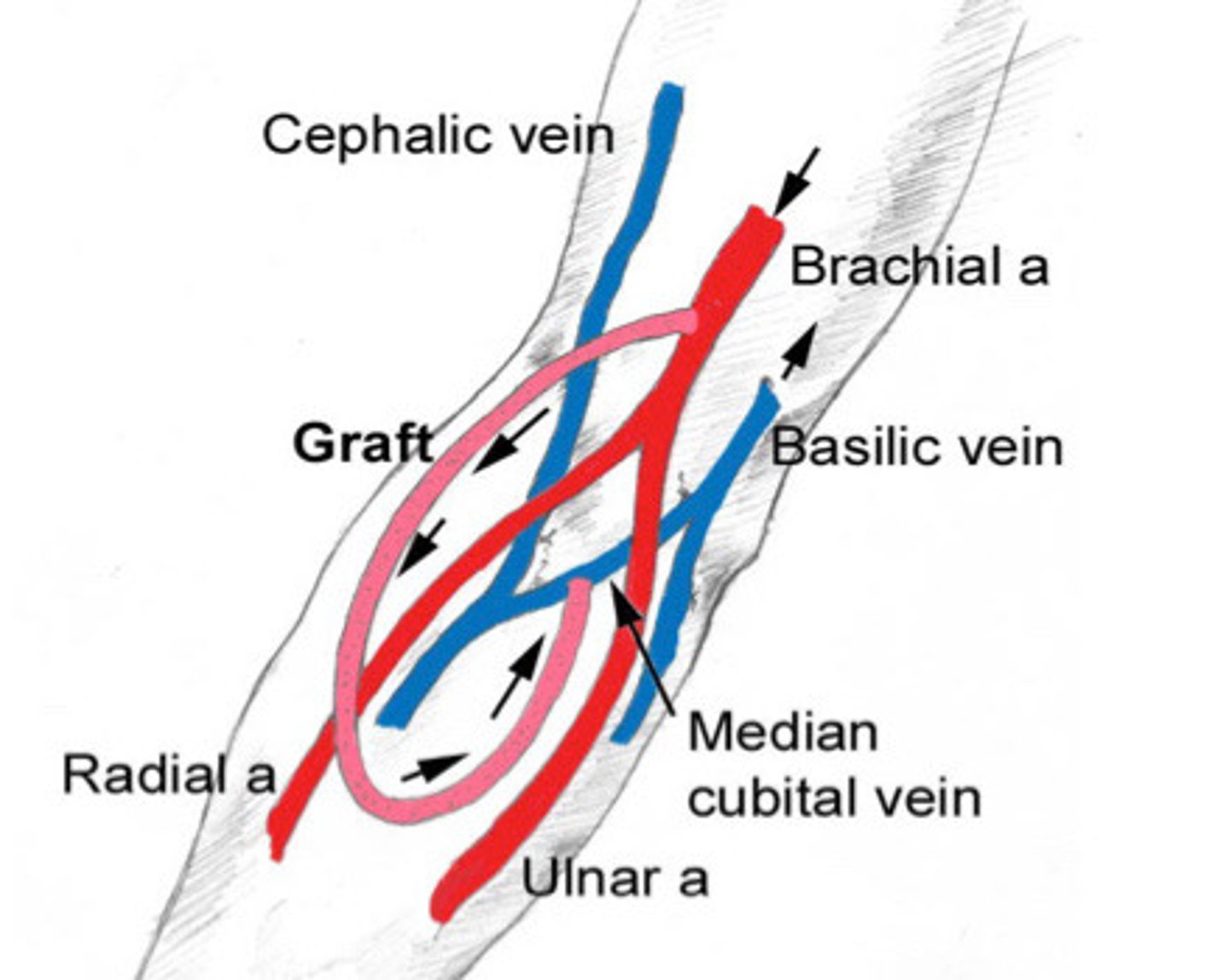
Loop graft
What does this image show
Assess artery and veins for fistula suitability
What is the purpose of us in the pre op assessment
Assess of stenosis, occlusion, or non-stenotic indications
What is the purpose of us in the post op assessment
Full UE arterial and venous study plus the vessels down into the forearm
What vasculature do we assess pre op
Radial and brachial
What arteries do we assess
Cephalic, basilic, medial cubital
What veins do we assess
Plaque, irregularities, atypical connections, vessel caliber, anatomical variants
What do we assess for pre op
At least 2mm
What is the mmt requirement for an artery if wanting to use it for fistula or graft
At least 2.5mm
What is the mmt requirement for a vein if want to use it as a AVF
At least 4mm
What is the mmt requirement for a vein if want to use it for a graft
True
T/F: the mmt for a vein is different depending if they are using a graft or fistula but the artery mmt is the same regardless which one they are planning on us using
Stenosis
What is the most common complication of an fistula or graft
At or within 2cm of the anastomosis of the graft/fistula
Where is the most common site for stenosis
Yes, but not that common bc tends to have a wide body
Can you also get a stenosis directly in the graft
Thrombosis of the graft
What is the most common cause of failure within the first month of a graft or fistula
Hyperplasia forming around the graft or vein which will obstruction the venous outflow
What is another cause of failure
Thrombosis downstream within the subclavian vein
What else may be see with a thrombus of the graft/fistula
All along the veins of the arm, not JUST where the graft/fistula is
Where in the body is at an increase risk for thrombosis after a fistula or graft
AVF maturity, pseudoaneurysm, hematoma, peri-graft abscess, aneurysmal fistula dilation
What are some non stenotic indications of post op assessment
500ml/min flow, >/=4mm, within 5mm of the skin surface
What are the 3 parameters of a AVF maturity
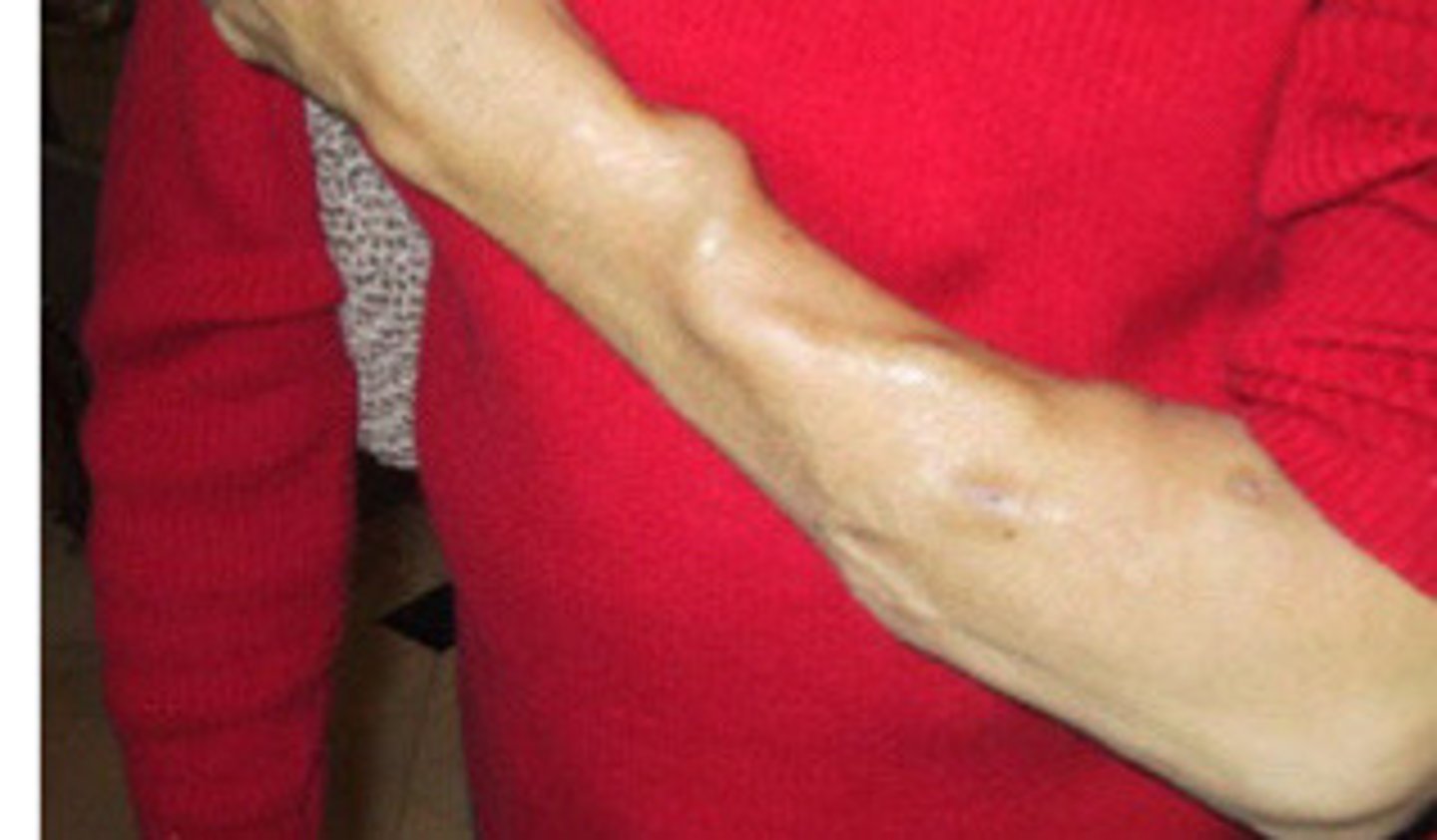
The fistula may get big enough that it can lead to dilation of the fistula due to the weak vein walls
Why is there an increase of anuerysmal fistula dilation over time
Aneurysmal dilation
What does this image show
Regular surveillance, pulsatile mass, decrease thrill, poor dialysis, arm edema, infection, arterial steel syndrome
What are some indications for a Doppler ultrasound
Highest frequency possible (9-12MHz)
What probe should you use
High flow settings, increase the scale and decrease the gain
How should you adjust your Doppler settings
Supine or sitting
What should the patient position be
Survey entire arm, assess pre/graft/fistula/post, document draining veins (bc increased risk of thrombus here)
Describe the graft and fistula ultrasound technique
Fistula diameter an depth from the surface
What should you measure in 2D
Tributaries
What else should you try to document in 2D
Colour bruit
Describe the normal colour
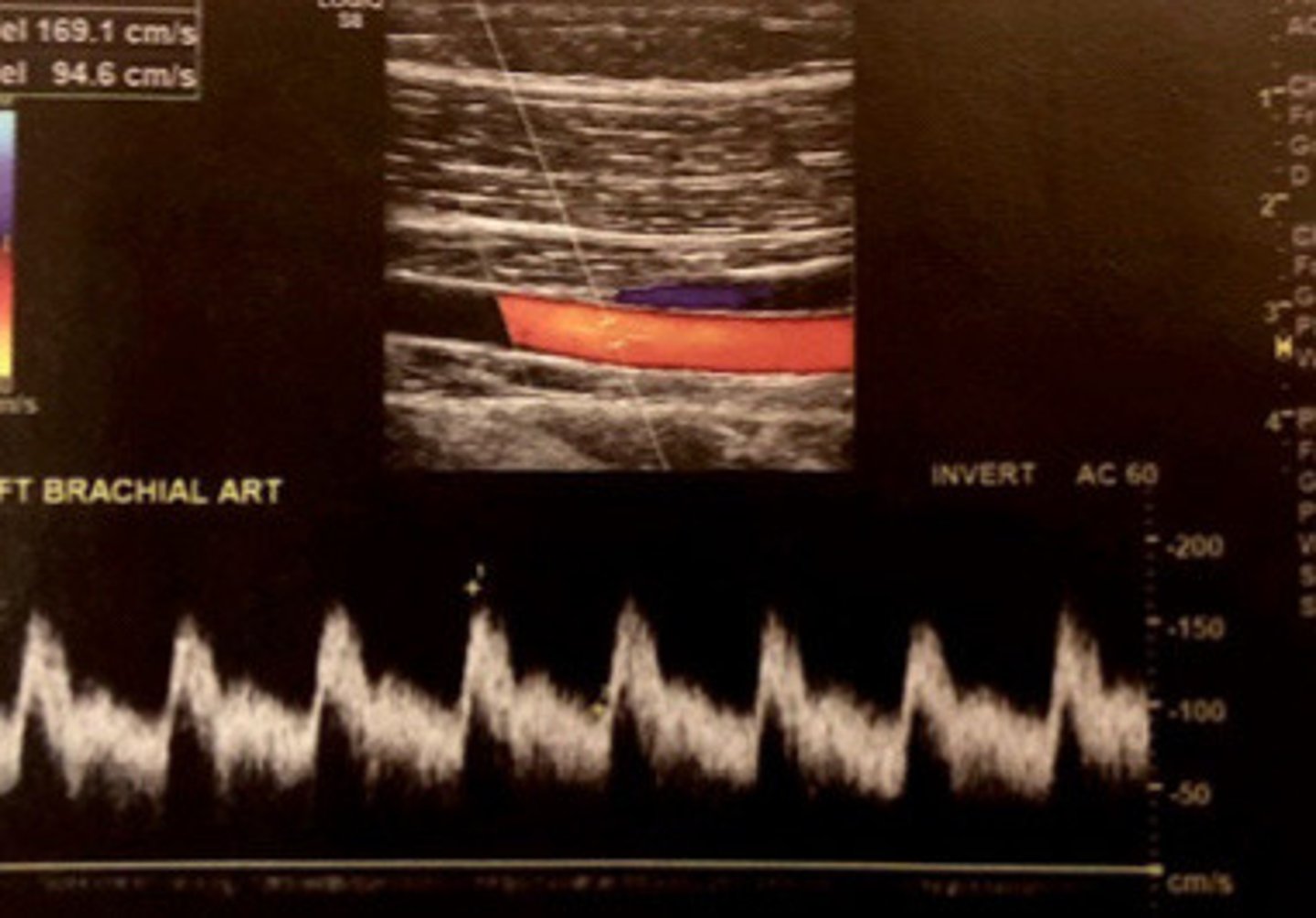
Low resistance before and within the graft with constant antegrade flow
Describe the waveform of the fistula and graft
Normal flow in fistula or graft
What does this image show
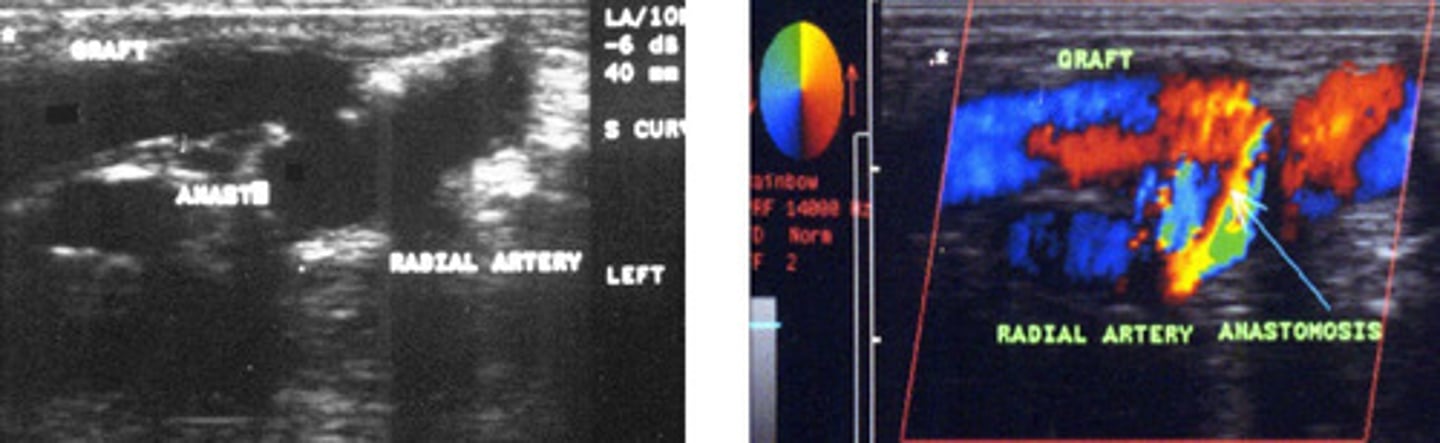
Double line
What appearance allows us to tell when there is a graft present
Radial artery to cephalic vein straight graft-> showing colour bruit so normal
What does this image show
Proximal to anastomosis, throughout the fistula/graft, and venous outflow
Where should you record the PSV
Outflow volume
What do you need to calcite
Timed average velocity
What does TAV stand for
3 cycles
How many cycles is considered in the TAV
Dimeter of vessel and TAV
What 2 things do you need to calculate outflow volume
Q = TAV x area x 60
What is the equation for outflow volume
Ml/min
What units is outflow volume expressed in
>800ml/in
What is a normal flow volume
500-800 ml/min
What flow volume indicates mild stenosis
<500ml/min
What flow volume indicates severe stenosis
500mL/min
If a graft or fistula is demonstrating a outflow volume of anything less than ________________ it indicates severe stenosis which is very worrisome
Determine degree of stenosis
What does flow ratios are used for
At stenosis and >2cm prox to the stenosis
Where do you take mmts for the flow ratios
<3
What is the normal flow ratio of the fistula at the anastomosis
<2
What is the normal flow ratio for the fistula at the draining vein
<2
What is the normal flow ratio for the gray
Bc it is just naturally higher at this location due to the size difference
Why is the flow ratio at the fistula at the anastomosis
<400cm/s
What is the normal PSV for grafts and fistulas
Around 30-100cm/s
What is the normla graft outflow vein PSV
Bc is receiving flow from the artery
Why is the graft outflow vein normal PSV pretty high
Normal PSV in a graft/fistula
What does this image show

Increased velocity, lack of Respirophasicity, occluded grafts showing high resistance
What are some abnormla flow characteristics
>400cm/s
What is considered increased velocity in graft and fistula
Subclavian and IJ veins
Where would the lack of Respirophasicity be in