Understanding Tissues in Human Anatomy and Physiology
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
107 Terms
Tissues
Collections of specialized cells and cell products organized to perform a limited number of functions.
Histology
The study of tissues.
Epithelial Tissue
Tissue that includes most glands and the epithelia, is a-vascular, and is composed completely out of cells making tight contact.
Connective Tissue
Tissue that connects tissues physically or chemically.
Muscular Tissue
Tissue that causes motion and generates heat.
Nervous Tissue
Tissue that connects tissues electrically.
Gastrulation
A phase early in embryonic development where the single layered blastula folds inward and is reorganized into a 3-layered structure known as a gastrula.
Protostomes
Animals in which the first invagination opening becomes the mouth.
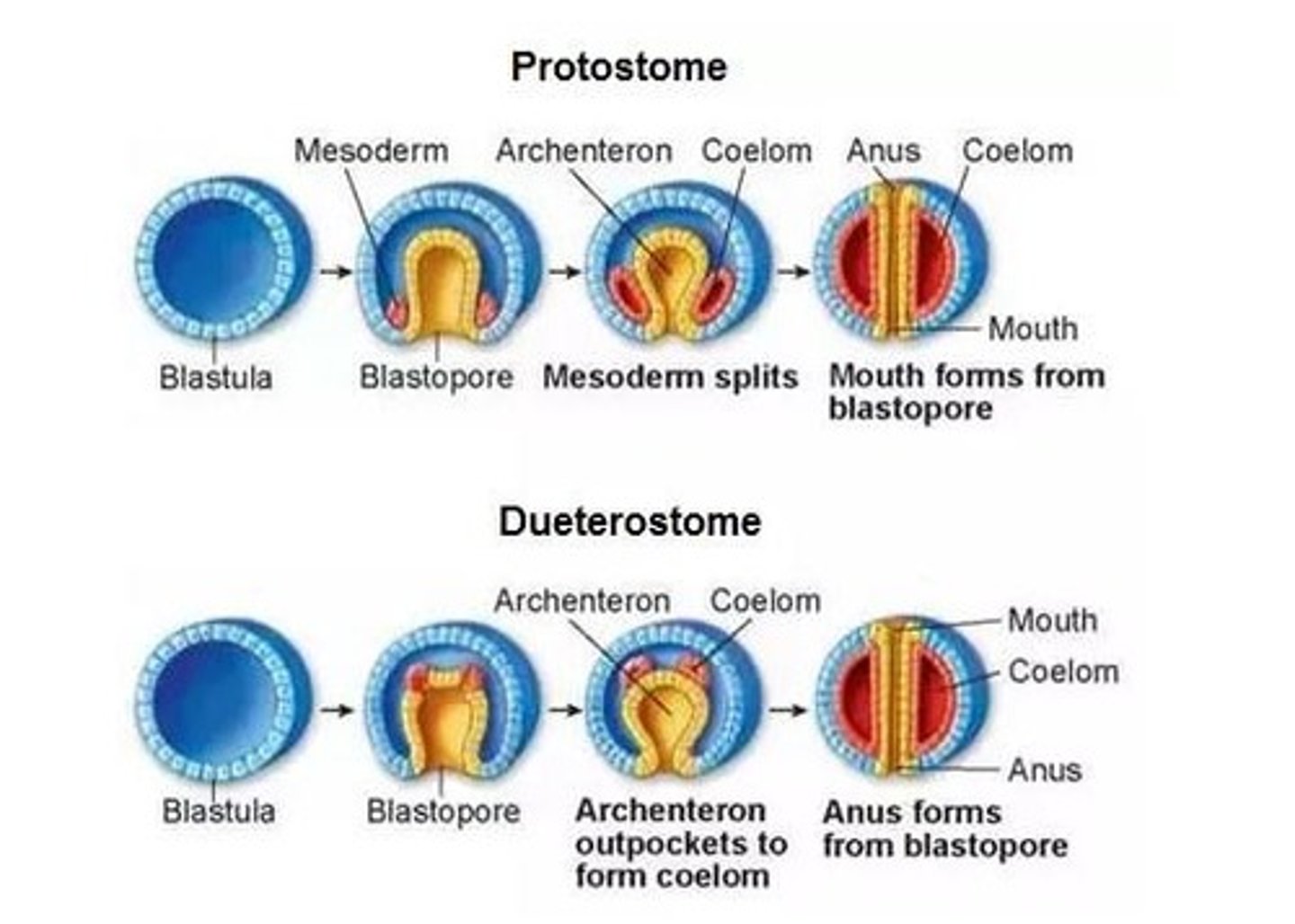
Deuterostomes
Animals in which the first opening becomes the anus; all chordates, including humans, are deuterostomes.
Primary Germ Layers
The three layers of cells in a gastrula that are the origin of most of the tissues of the future organism.
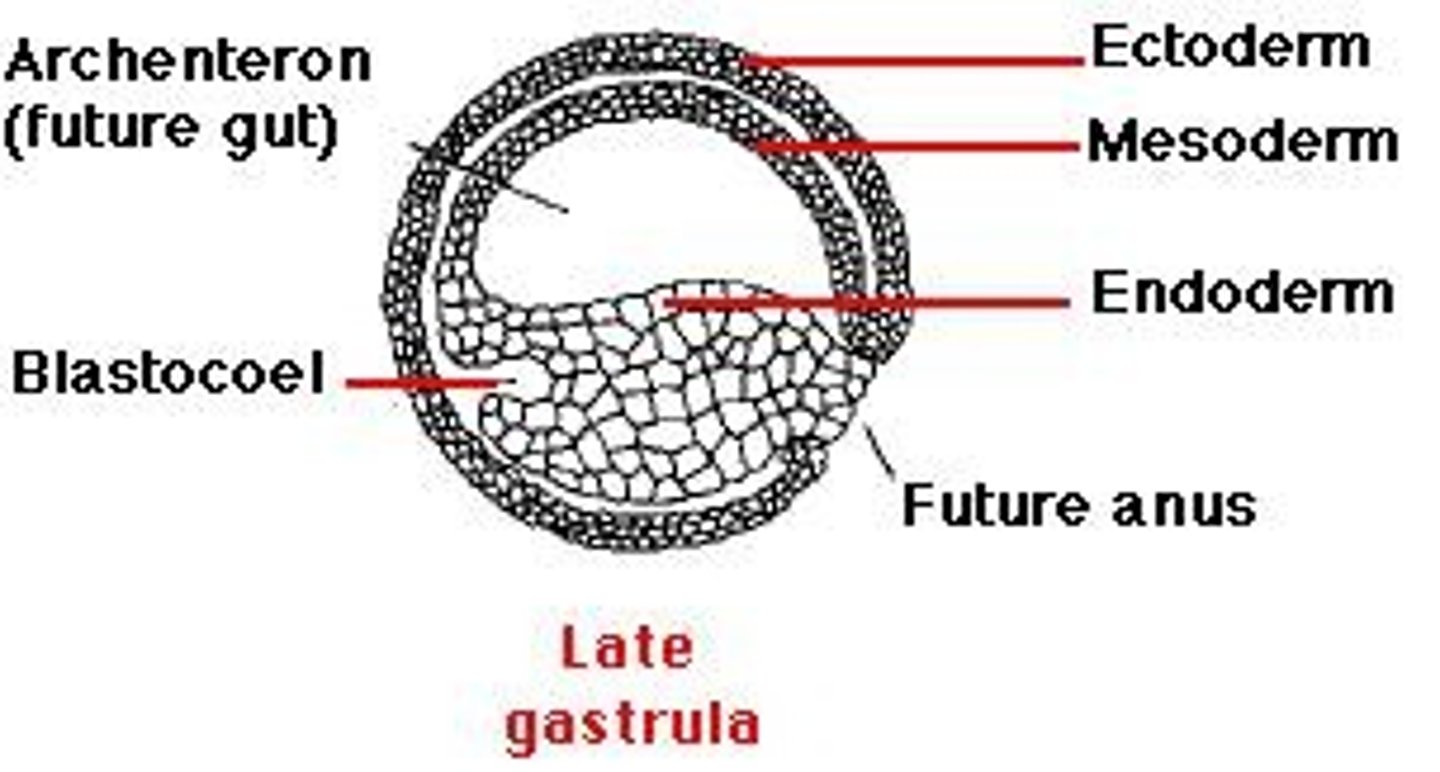
Endoderm
The most internal germ layer that forms the lining of the gut and other internal organs.
Mesoderm
The middle germ layer that forms muscle, the skeletal system, kidneys, and the circulatory system.
Ectoderm
The most exterior germ layer that forms skin, brain, the nervous system, and other tissues.
A-vascular
A characteristic of epithelial tissue meaning it has no blood vessels.
Polarity
A characteristic of epithelial cells where one end is attached and one end is open to a surface.
Apical Side
The part of the epithelia that touches the open space.
Basolateral Side
The part of the epithelia that touches the connective tissue.
Basal Lamina
The area to which the bottom of the epithelial cells attach, separating them from underlying connective tissues.
Cell Junctions
Structures that bind epithelial cells tightly together, preventing passage between them.
Regeneration Rate
Epithelial cells exhibit a high rate of regeneration due to lots of mitosis for damage and repair.
Blastula
A tiny, hollow ball of cells formed from mitotic cell divisions of a zygote.
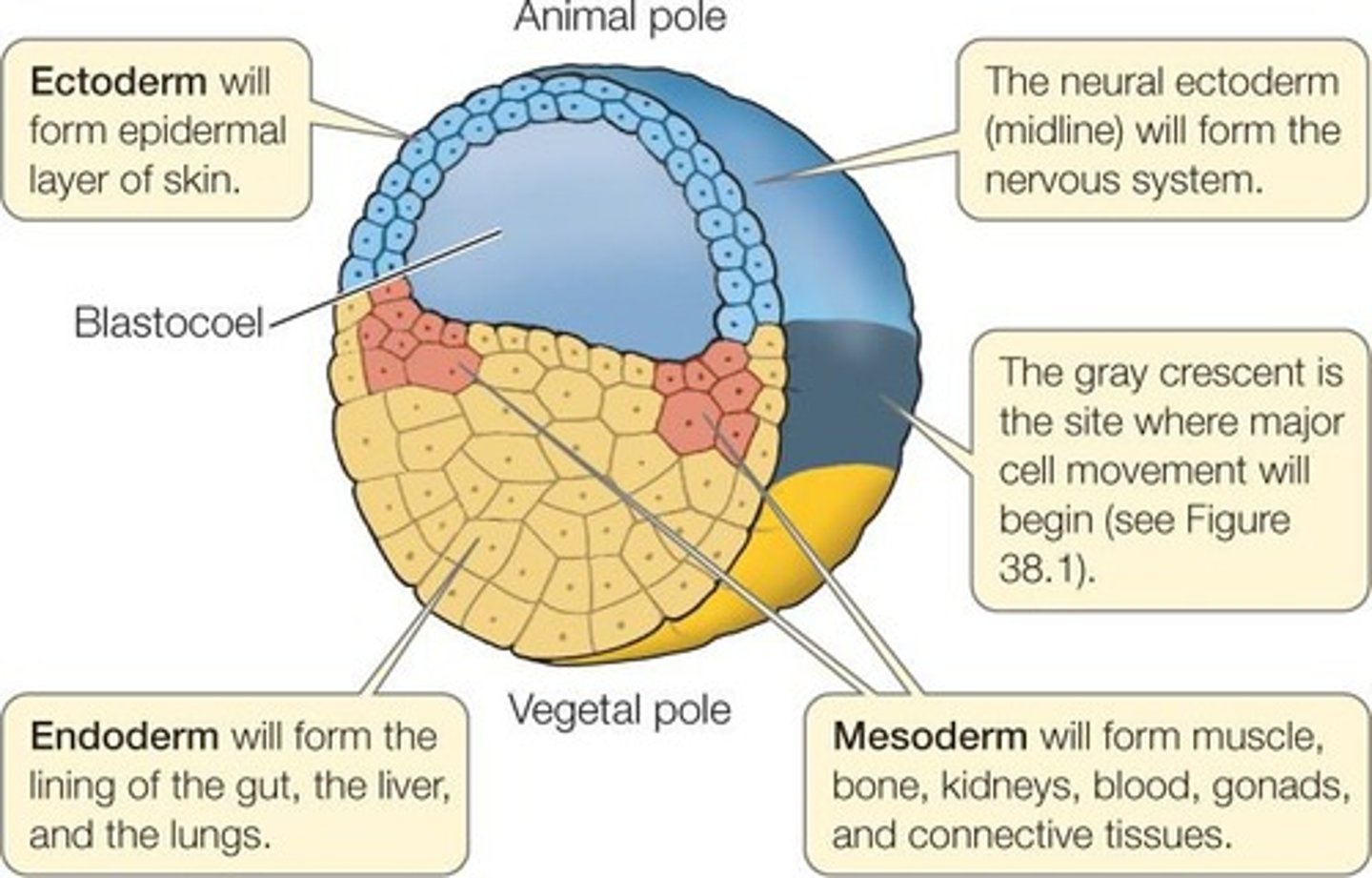
Zygote
A fertilized cell formed after fertilization.
Invagination
The process during gastrulation where the blastula folds inward.
First Layer of Protection
Epithelial tissue is your first layer of protection.
Physical Protection
Epithelial tissue provides physical protection such as skin or inside the mouth.
Protection Against Abrasions
Epithelial tissue protects against abrasions, dehydration, destruction.
Control Permeability
Epithelial tissue controls permeability such as in the intestine or kidneys.
Protective Barriers
Some epithelial tissues form protective barriers.
Sensation
Epithelial tissue provides sensation including touch, vision, taste, smell.
Neuro-epithelia
Neuro-epithelia contains special neurons.
Specialized Secretions
Epithelial tissue produces specialized secretions such as gastric lining, nasal lining, serous fluid, and goblet cells.
Secretory Functions
Epithelial tissue performs secretory functions in glands, including hormones, enzymes, saliva, and tears.
Transport Functions
Epithelial tissue performs transport functions in structures like alveoli of lungs and glomerulus of nephron.
Physical Integrity
Epithelial tissue maintains physical integrity, such as the epidermis of skin.
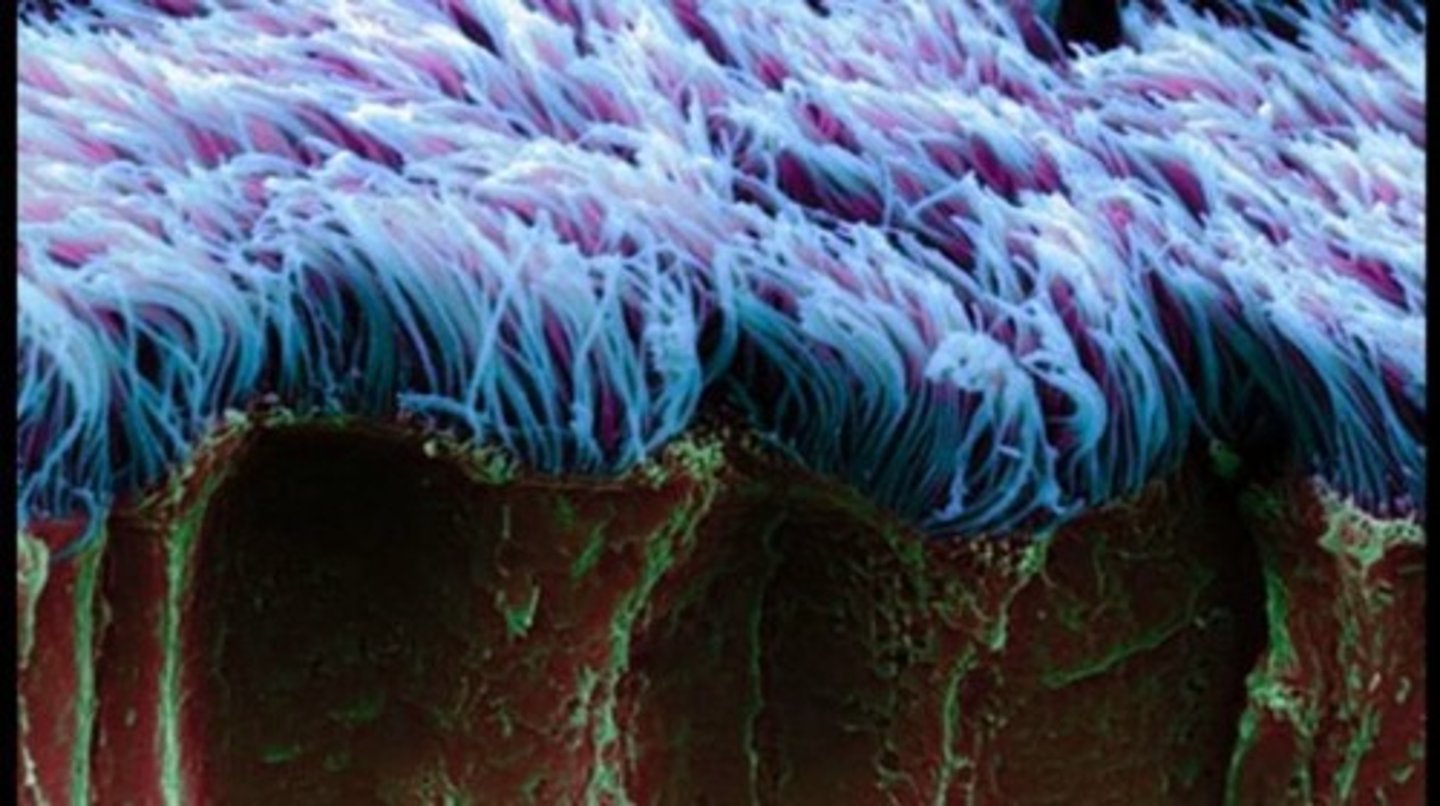
Ciliated Epithelia
Ciliated epithelia move materials across their surface, such as in the lining of the trachea and oviducts.
Polarity of Epithelial Tissue
Epithelial tissue exhibits polarity with apical surfaces and basolateral surfaces.
Apical Surfaces
Apical surfaces show specialization, mainly in simple epithelia.
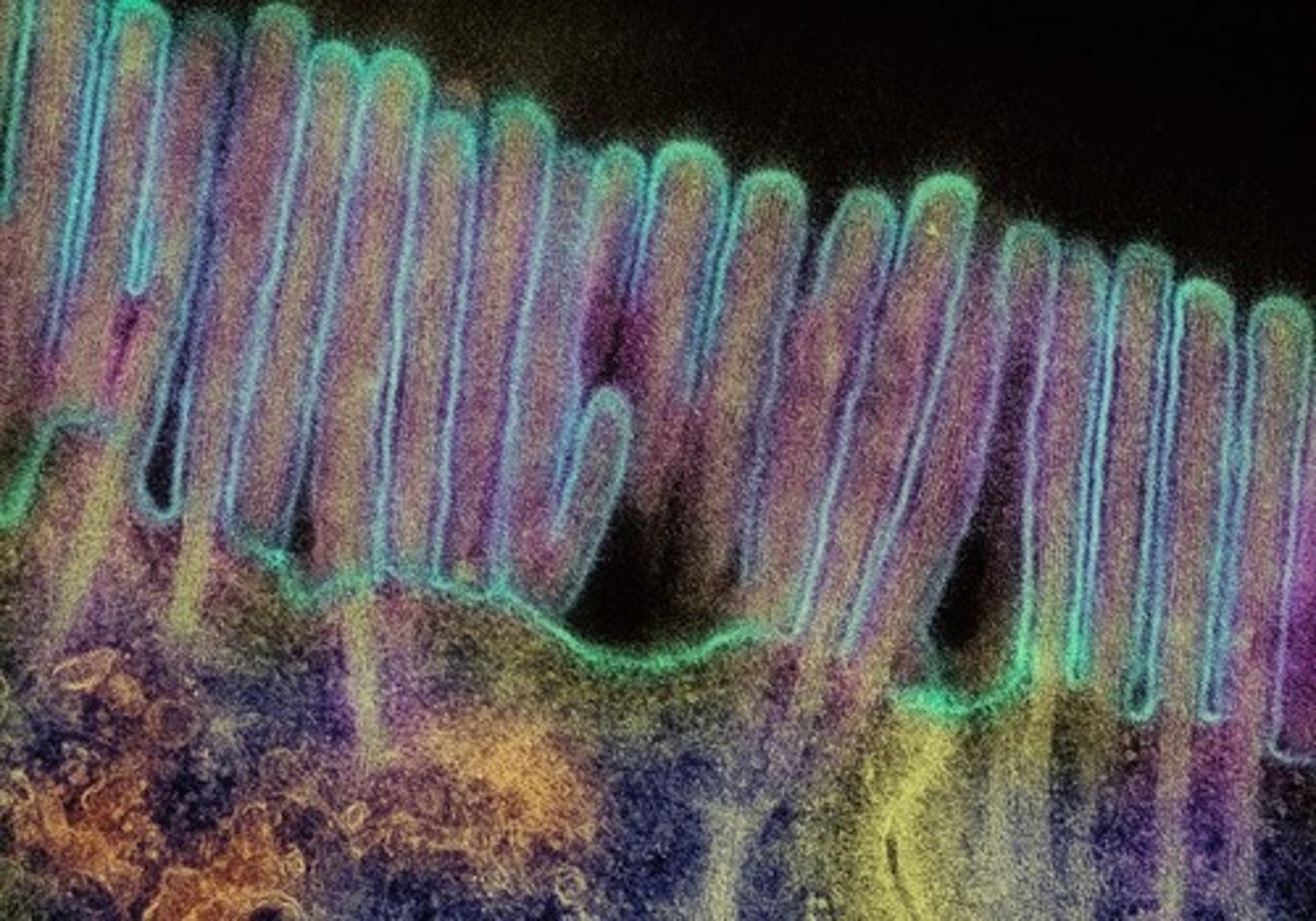
Microvilli
Microvilli increase cellular membrane surface area for increased absorption or secretion.
Cilia
Cilia create tiny 'whip' like actions on the surface of the tissues to facilitate movement.
Structure/Function Correlation
Epithelial tissues provide a structure/function correlation.
Lining Internal or External Surfaces
Epithelial tissues line internal or external surfaces.
Open Space in Histology
Epithelial tissue always has an area where there is 'open space' in histological slides.
Transverse Cut Example
The drawing illustrates a transverse cut through the body at the abdominal area with tubular structures.
Parietal and Visceral Peritoneum
'a' and 'b' are examples of the parietal and visceral peritoneum.
Epithelial cells
Cells that line the surfaces and cavities of organs and structures throughout the body.
Epithelial tissue identification
The presence of open space lined with distinct cells making tight contact indicates epithelial tissue.
Artifact in tissue slides
Openings without cells lining them are most likely artifacts from the slide preparation.
Real opening in epithelial tissue
A real opening is indicated by the presence of cell nuclei lining the opening.
Effectiveness of epithelia
The barrier effectiveness of epithelia depends on the integrity of the barrier and tight cell contact.
Hemi-desmosomes
Structures that attach a cell to extracellular structures, anchoring basal epithelial cells to the basement membrane.
Lamina lucida
The layer produced by epithelial cells in the basement membrane.
Lamina densa
The layer produced by connective tissue in the basement membrane.
Classification of epithelia
Epithelia are classified based on the number of cell layers and the shape of apical surface cells.
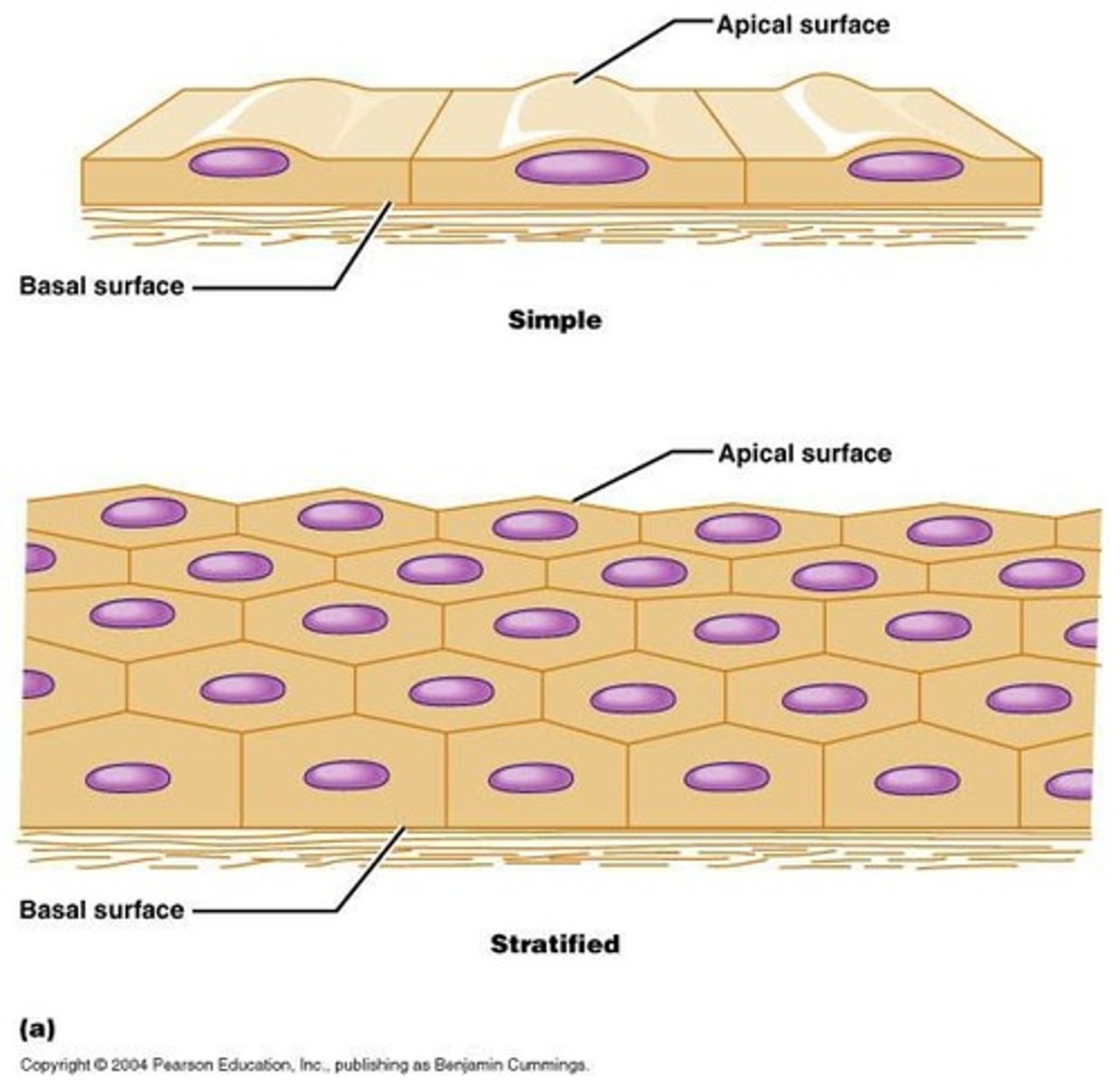
Simple epithelium
A single layer of cells.
Pseudostratified epithelium
A single layer of cells that appears to have multiple layers due to dense nuclei.
Stratified epithelium
Two or more layers of cells.
Squamous cells
Flat-shaped cells.
Cuboidal cells
3D square-shaped cells.
Columnar cells
3D rectangle-shaped cells.
Naming epithelia
Epithelia are named according to the shape of the apical cells.
Simple Squamous Epithelium
A type of epithelium consisting of a single layer of flat cells.
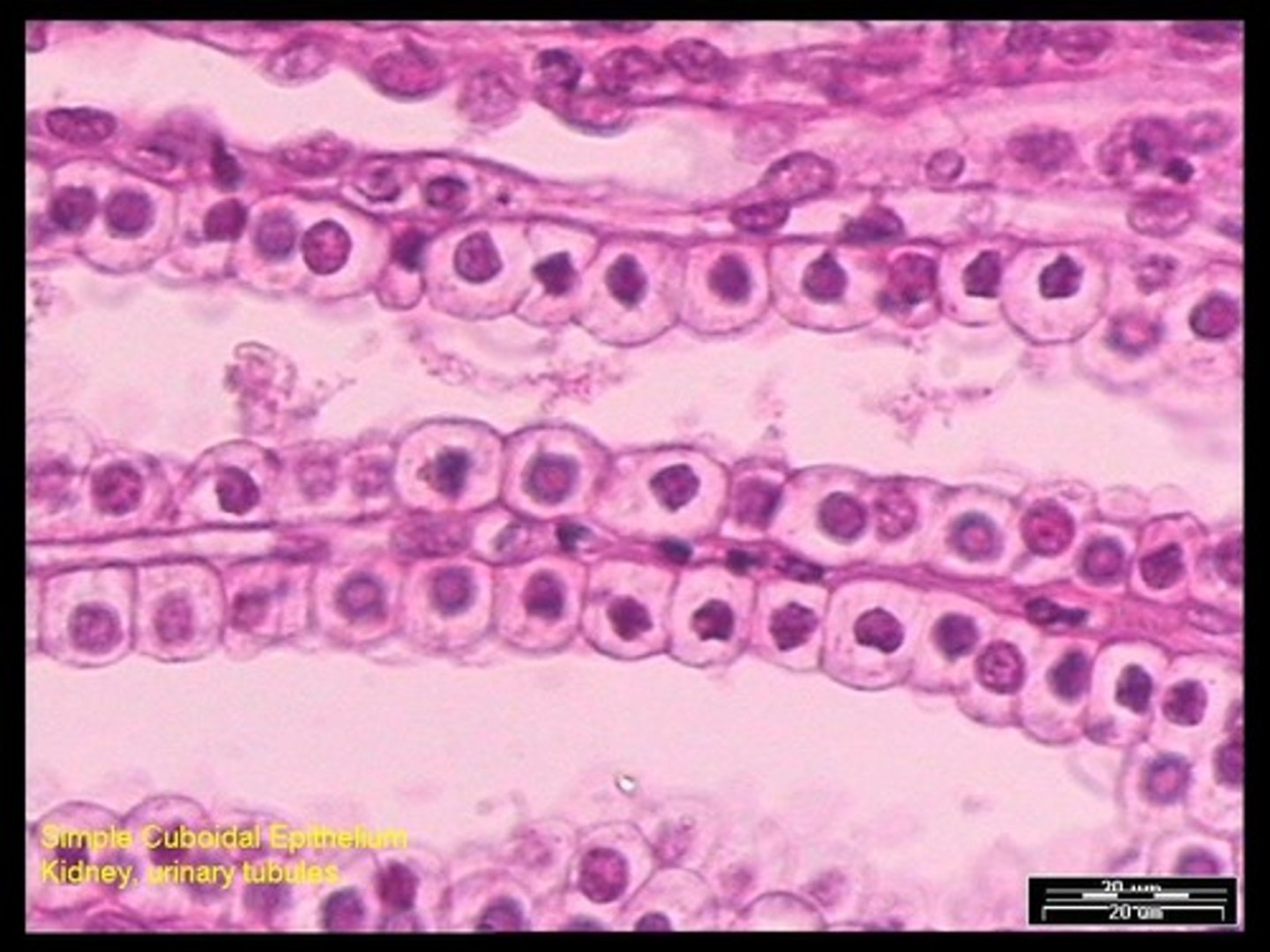
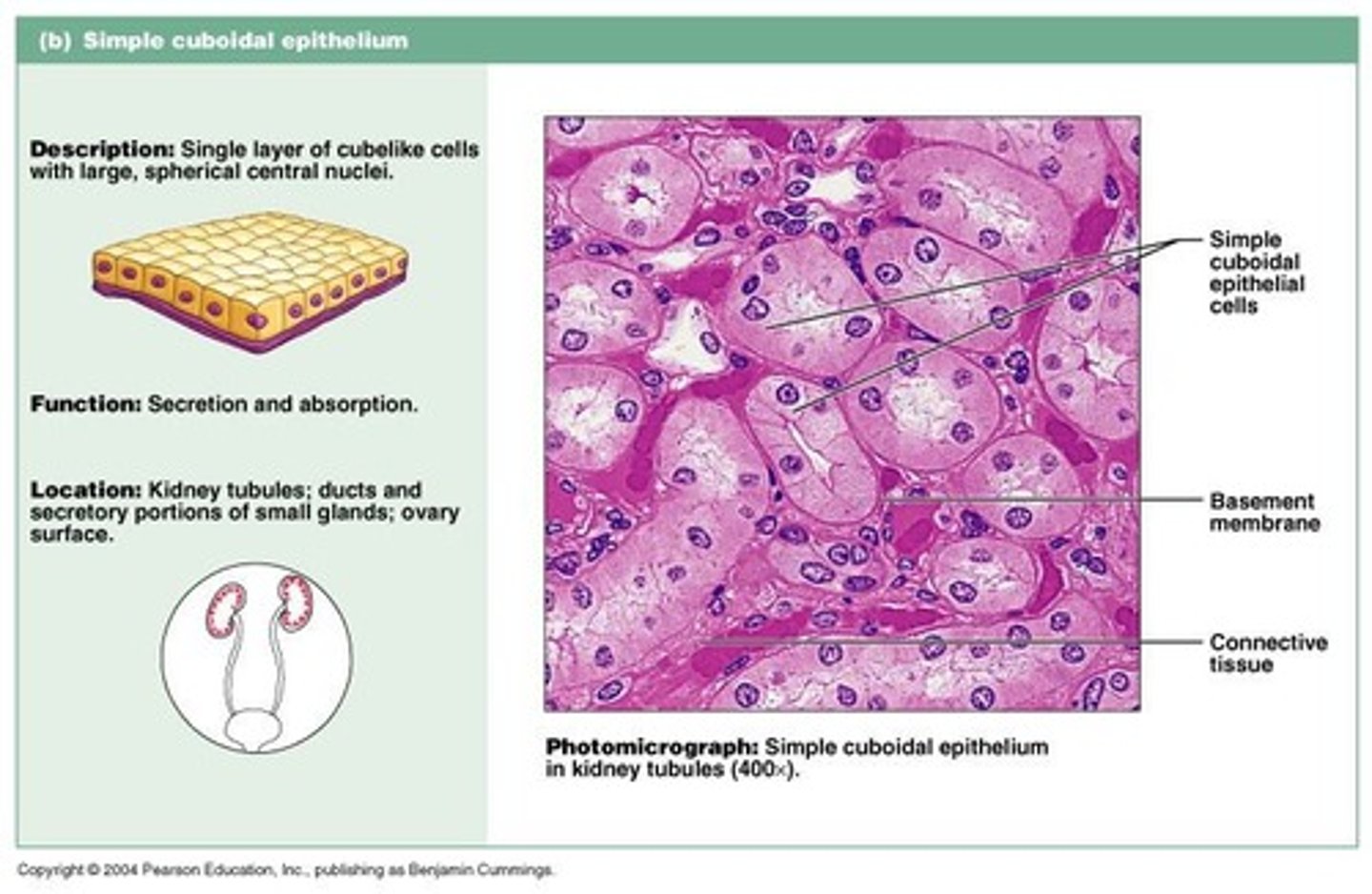
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
A type of epithelium consisting of a single layer of cube-shaped cells.
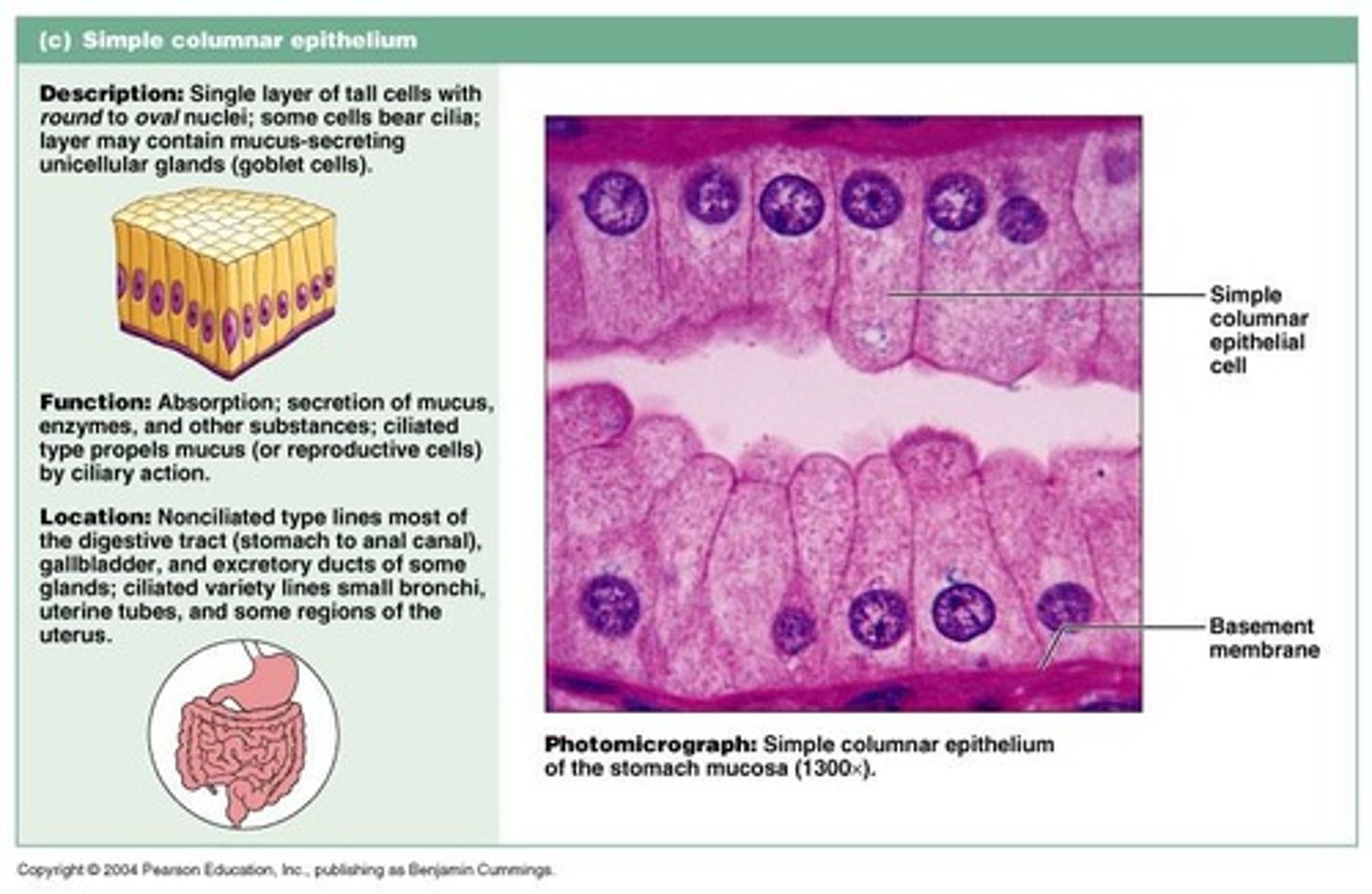
Simple Columnar Epithelium
A type of epithelium consisting of a single layer of column-shaped cells.
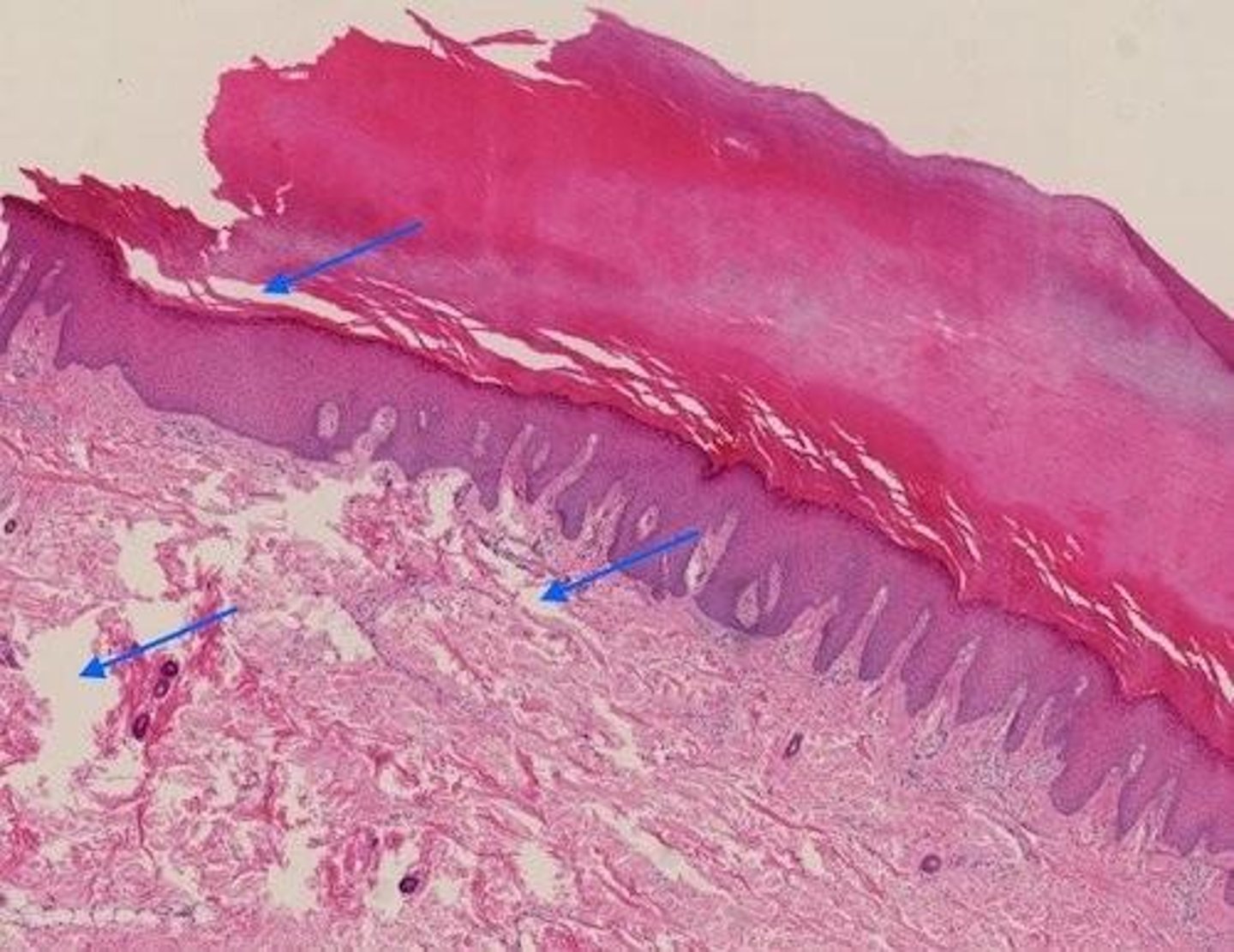
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
A type of epithelium with multiple layers of flat cells, keratinized in skin.
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
A type of epithelium with two or more layers of cube-shaped cells.
Stratified Columnar Epithelium
A type of epithelium with two or more layers of column-shaped cells.
Transitional Epithelial Tissue
A type of epithelium that can change shape, typically found in the bladder.
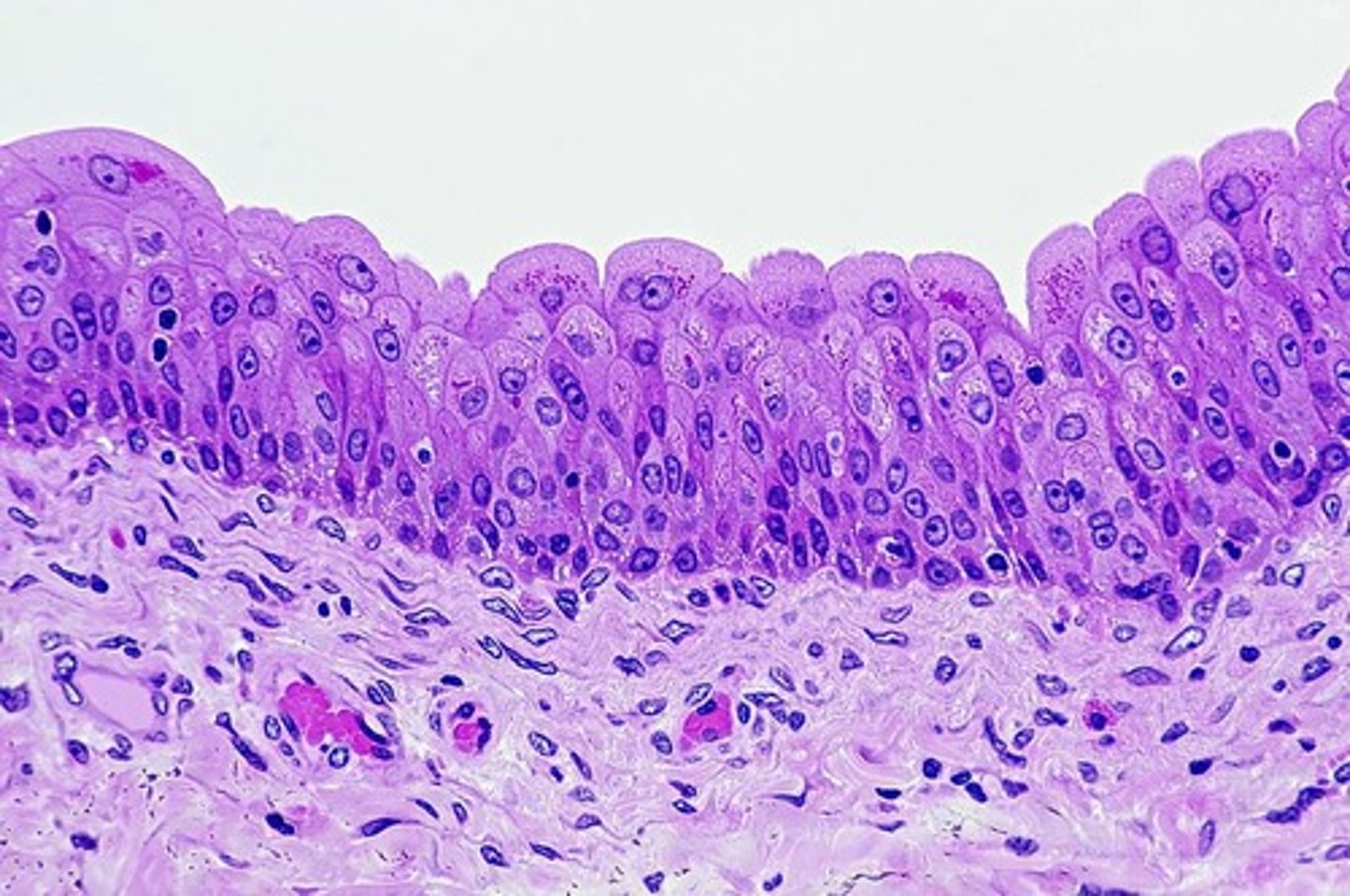
PseudoStratified Epithelial Tissues
A type of epithelium that appears stratified but is actually a single layer.
Functions of Simple Squamous Epithelium
This is the thinnest epithelial layer possible, providing a slick, friction-reducing lining in lymphatic and cardiovascular systems.
Filtration in Capillaries
Filtration process occurs in capillaries where simple squamous epithelium is present.
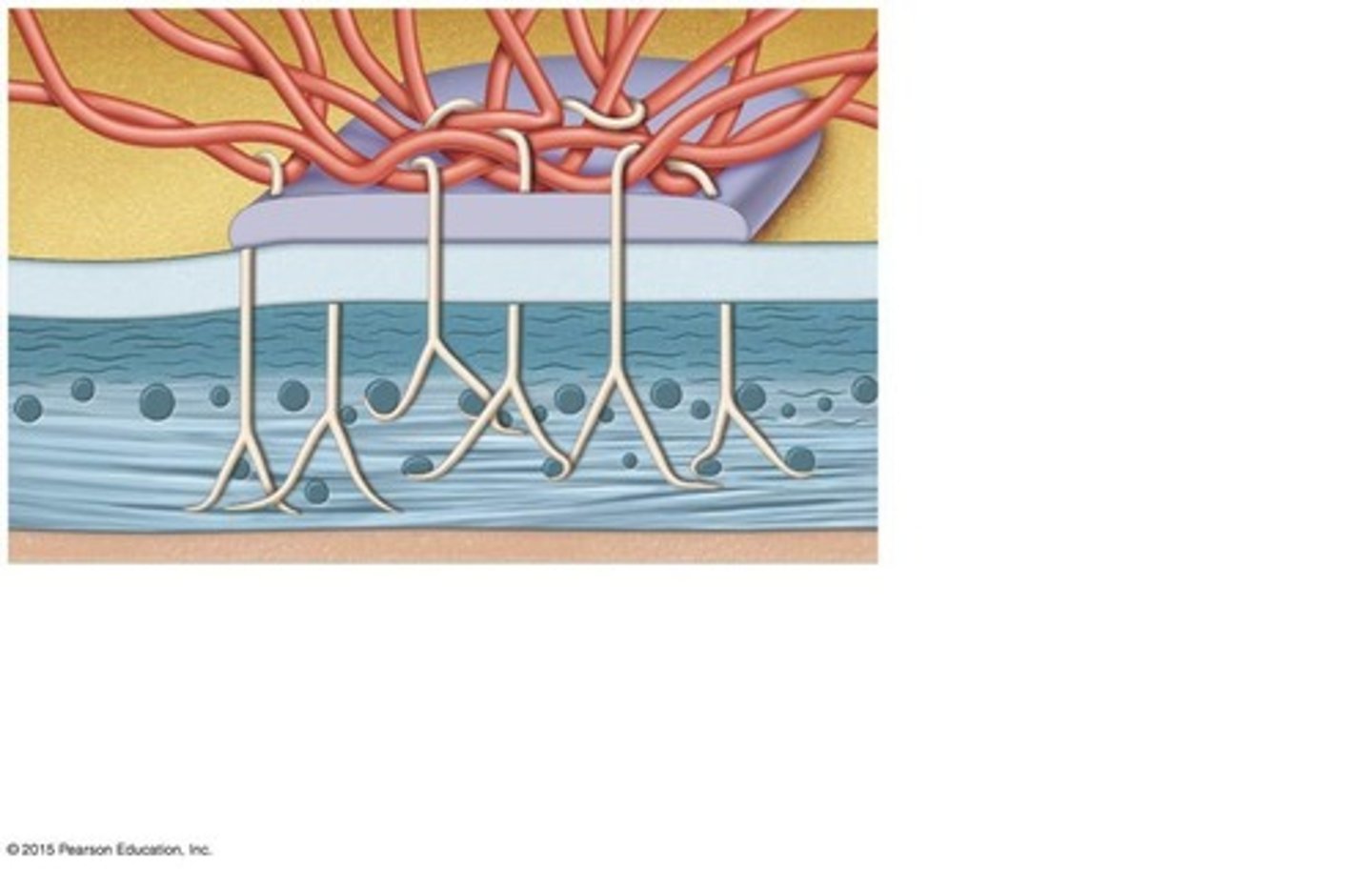
Diffusion in Lung Alveoli
Diffusion occurs in lung alveoli, which are lined with simple squamous epithelium.
Serosa Membranes
All serosa membranes (pleura, peritonea, pericardium) have thin, simple squamous epithelia.
Endothelial Layer
The lining of all blood vessels is called the endothelial layer, made from simple squamous cells.
Bowman's Capsule
Part of a nephron, where initial filtration occurs and is lined with simple squamous cells.
Glomerulus
A 'tuft' of capillaries involved in the filtration process within Bowman's capsule.
Locations of Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Present in kidney tubules, ducts and secretory portions of small glands, and ovary surface.
Nephron Tubules
Simple cuboidal epithelium is found in nephron tubules in kidneys.
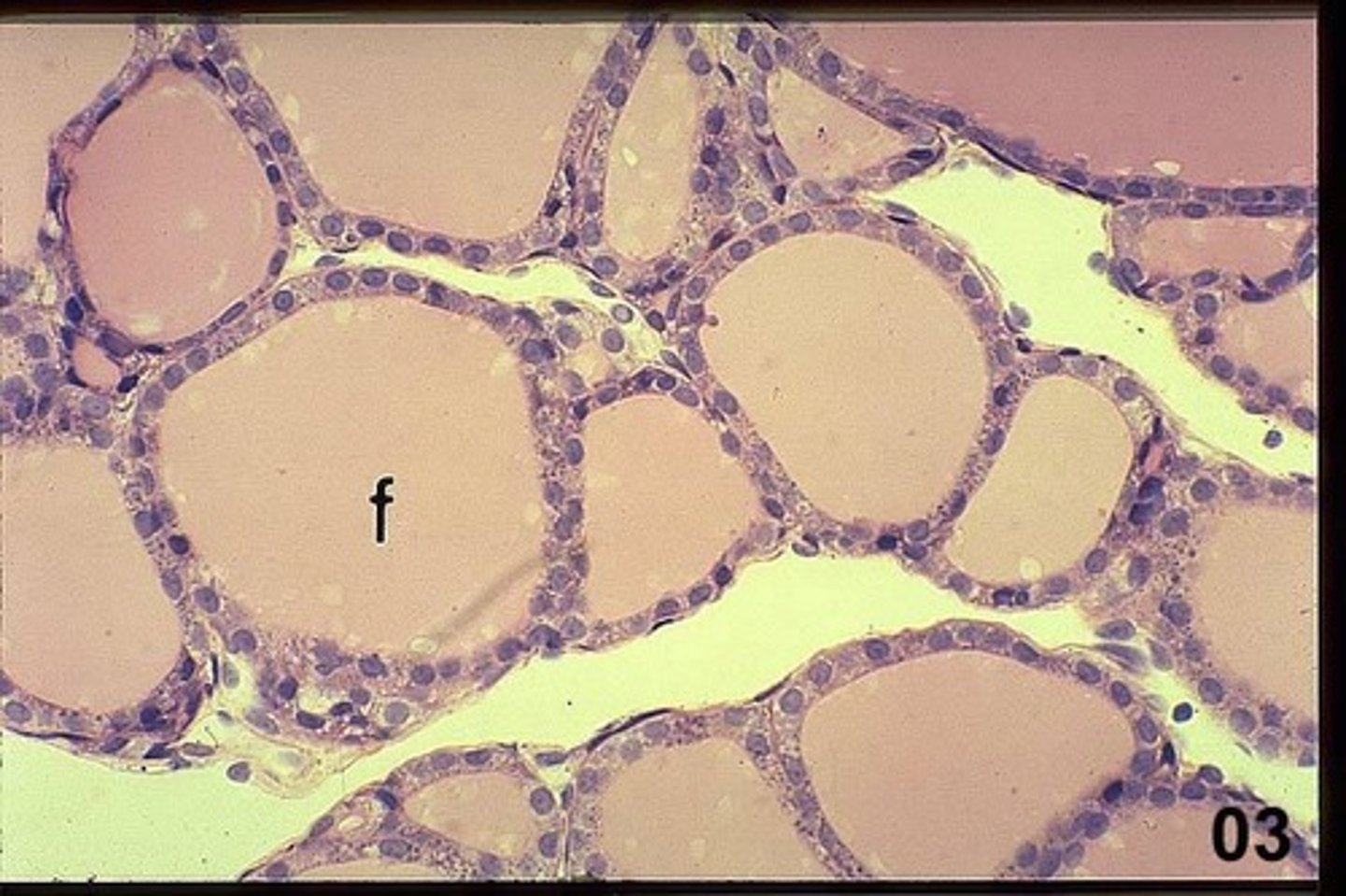
Follicles in Thyroid Gland
Simple cuboidal epithelium is also present in the follicles of the thyroid gland.
Goblet Cells
Cells with glandular function found in simple columnar epithelium that secrete mucus.
Functions of Simple Columnar Epithelium
Important in absorption and secretion.
Non-ciliated Simple Columnar Epithelium
Lines the digestive tract and gallbladder.
Ciliated Simple Columnar Epithelium
Lines small bronchi, uterine tubes, and some regions of the uterus.
Goblet Cell in Simple Columnar Epithelium
Pointer indicates goblet cell (uni-cellular gland) within the simple columnar epithelium.
Colon Region Goblet Cells
The colon region has many goblet cells within its simple columnar epithelium.
Simple columnar epithelia
Typical for the lining of the digestive system, involved in absorption and secretion; surface area increased by villi and microvilli.
Villi
Finger-like projections that increase surface area in the digestive system.
Function of PseudoStratified Epithelium
Secretion and propulsion of mucus.
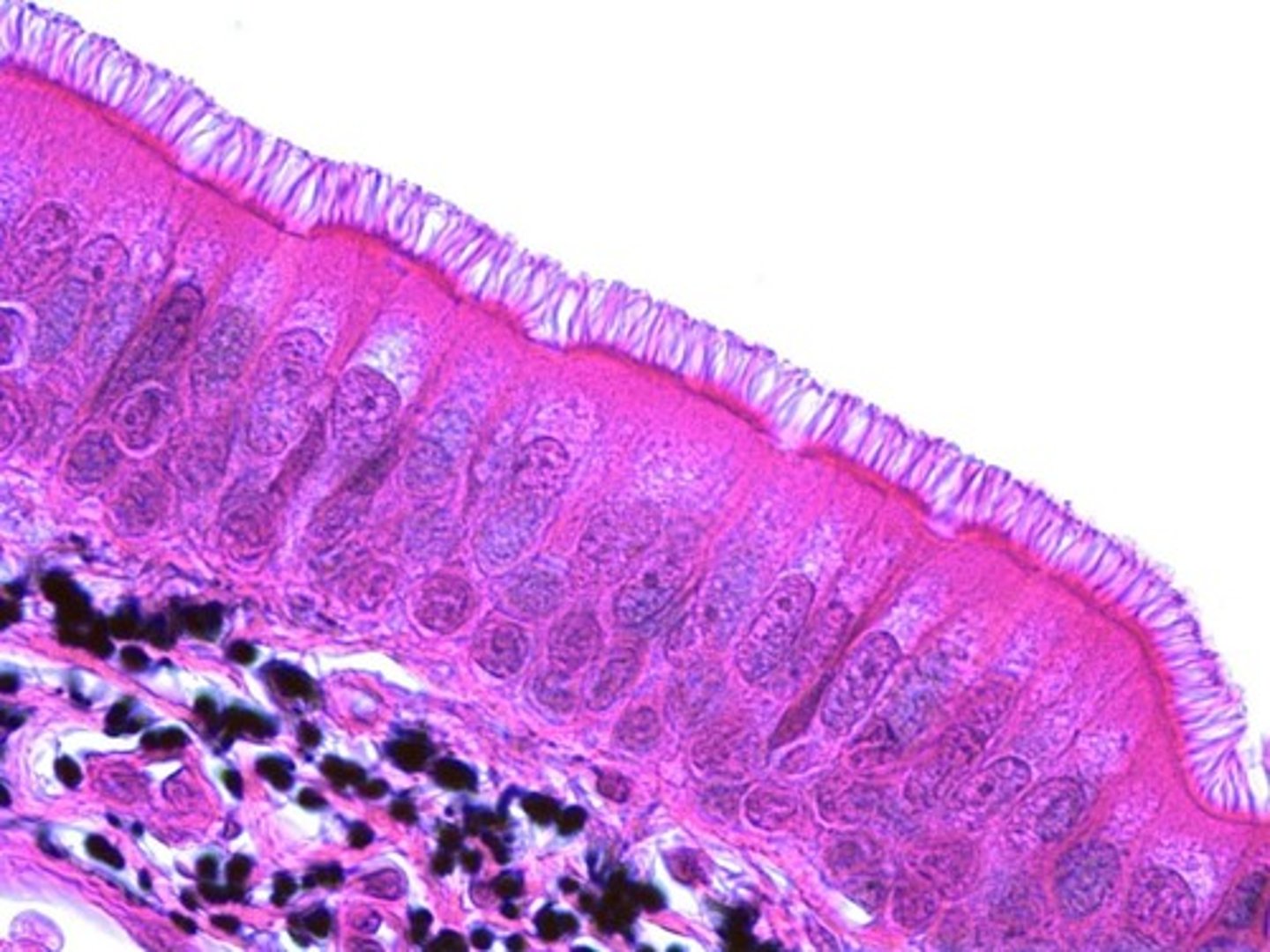
Location of PseudoStratified Epithelium
Present in the trachea (ciliated) and the male sperm-carrying ducts (non-ciliated).
Typical locations for Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Skin epidermis and every entrance and exit point into the body, such as mouth, nose entrance, anus, and exit of urinary and reproductive tracts.
Keratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Found in the epidermis of the skin, characterized by keratinized cells.
Non-Keratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Found inside the body, lacking the wavy top layer and still providing protection against abrasion.
Glands
Structures derived from and attached to epithelial tissues, classified into endocrine and exocrine glands.
Endocrine glands
Glands that release hormones into surrounding fluid and the bloodstream; they are ductless.
Exocrine glands
Glands that secrete substances through ducts onto the surface of the gland, often derived from epithelial tissues.
Function of Exocrine glands
Secrete substances like saliva or sebum through ducts.
Ciliated PseudoStratified Epithelium
Type of pseudostratified epithelium with cilia, commonly found in the trachea.
Non-Ciliated PseudoStratified Epithelium
Type of pseudostratified epithelium without cilia, found in male sperm-carrying ducts.
Protection function of Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Provides protection to underlying areas subjected to abrasion.
Top layer of Keratinized SSE
Wavy top layer of dead keratinized cells that protects against dehydration and injury.
Non-Keratinized SSE
Does not have a wavy top layer and protects inside regions of the body against abrasion and damage.