Chapter 1 - The Properties of Gases (copy)
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/41
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
1
New cards
Partial pressure
\
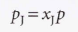
2
New cards
Virial equation of state
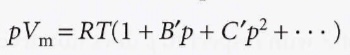
3
New cards
van der Waals equation
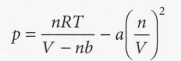
4
New cards
Compression factor (Z)
The ratio of its measured molar volume to the molar volume of a perfect gas at the same pressure and temperature.
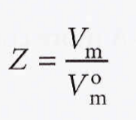
5
New cards
STP
Standard temperature and pressure, which is 0°C and 1 atm.
6
New cards
metal container
Has diathermic walls.
7
New cards
molar volume of a perfect gas at STAP
24\.789 dm^3 mol^- 1.
8
New cards
Intermolecular forces
They are important at low temperatures since molecules travel slowly meaning they can be captured by one another.
9
New cards
Van der Waals coefficients
The constants a and b.
10
New cards
Mechanical equilibrium
A condition of equality of pressure on either side of a movable wall.
11
New cards
STAP
Standard ambient temperature and pressure, which is 298.15 K and 1 bar.
12
New cards
Temperature
The property that indicates the direction of the flow of energy through a thermally conducting, rigid wall.
13
New cards
Daltons Law
When all the gases are perfect, the partial pressure is the pressure each gas would occupy if it occupied the same container alone at the same temperature.
14
New cards
vacuum flask
An adiabatic container.
15
New cards
critical constants
Related to the van der Waals coefficients.
16
New cards
Principle of corresponding states
The observation that real gases at the same reduced volume and reduced temperature exert the same reduced pressure.
17
New cards
Diathermic boundary
If there’s a change when two objects with different temperatures come together.
18
New cards
Kelvin
Unit of temperature used in thermodynamics.
19
New cards
Thermal equilibrium
When there’s no change of state if two objects are in contact through a diathermic boundary.
20
New cards
Boyles and Charles Laws
Limiting laws, meaning they are only true to a certain limit.
21
New cards
Diathermic
Thermally conducting.
22
New cards
Elastic collision
Collision in which the total translational kinetic energy of the molecules is conserved.
23
New cards
Vapor pressure
Pressure corresponding to CDE, when both liquid and vapor are present in equilibrium.
24
New cards
molar volume of a perfect gas at STP
22\.414 dm^3 mol^- 1.
25
New cards
Gas
A collection of molecules/atoms in continuous random motion with an average speed that increases with temperature raise
26
New cards
Pressure
Force divided by the area where the force was applied
27
New cards
Most common units for pressure
Pascal, atmosphere, and bar
28
New cards
Barometer
Used to measure the pressure done by the atmosphere
29
New cards
Pressure gauge
Used to measure the pressure of a gas inside a container
30
New cards
Temperature
The property that indicates the direction of the flow of energy through a thermally conducting, rigid wall
31
New cards
Measures of temperature
Celcius, Fahrenheit, or Kelvin,
32
New cards
R
Constant of proportionality, gas constant
33
New cards
Perfect or ideal gas
A gas that obeys this equation exactly under all conditions
34
New cards
Molar volume formula
Vm = RT/p
35
New cards
Repulsive forces
Contribute to expansion
36
New cards
Attractive forces
Contribute to compression
37
New cards
Intermolecular forces
They are important at low temperatures since molecules travel slowly meaning they can be captured by one another
38
New cards
Boyle temperature
The temperature where Z → 1 with zero slope at low pressure or high molar volume
39
New cards
Critical temperature (Tc)
The temperature at the critical point
40
New cards
Critical pressure (Pc)
The pressure at the critical point
41
New cards
Critical molar volume (Vc)
The volume at the critical point
42
New cards
Perfect gas isotherms
Obtained at high temperatures and large molar volumes