Chp 3 - Phonetics: Describing Sounds
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
Phonetics
study of speech sounds
(IPA) International Phonetic Alphabet
used to transcribe any language phonetically
Phoneme
Unit of sound that makes a difference in the meaning of a word
Consonant
sound characterized by closure or obstructions of the vocal tract
Vowel
sound characterized by an open vocal tract
Minimal Pair
two words that differ by only a single phoneme in the same position (e.g. pit and bit)
Phonemic Transcription
written recording of sounds using the distinctive phonemes of a language, resulting in a one-to-one correspondence between a sound and a symbol
How we describe consonants
Voicing
Place of Articulation
Manner of Articulation
Voicing
controlling the vibration of the vocal cords as the air passes through to make speech sounds
Voiced Consonants
Voicless Consonants
Place of Articulation
the places in the oral cavity where airflow is modified to make speech sounds
Manner of Articulation
the way we move and position our lips, tongue, and teeth to make speech sounds
Natural Class
set of sounds that have certain phonetic features in common
Voiced Consonants
speech sounds produced when the vocal cords vibrate in the larynx (voice box), creating a buzzing or humming sound in addition to articulation made by the mouth (ex - b, d, g, v, z, m, n, l, r, w)
Voiceless Consonants
air passes through the mouth with no vibration in the larynx (voice box) (ex - p, t, k, f, s)
All Vowels are…
Voiced
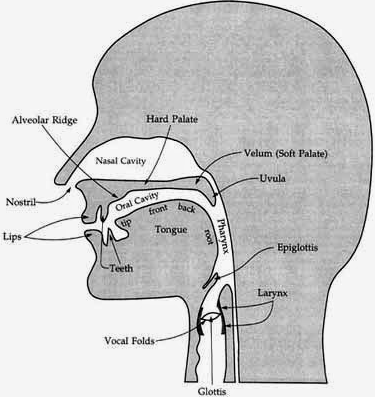
Articulators
parts of the body involved in speech production: tongue, teeth, lips, glottis, velum, vocal folds
Places of Articulation
Bilabial
Labiodental
Interdental
Alveolar (Av-ee-lir)
Palatal
Velar (vee-lir)
Glottal
Bilabial
sounds made by bring both lips almost together or entirely together (ex - p, b, m, w, wh)
Labiodental
sound made with the lower lip against the upper front teeth (ex - f, v)
Interdental
sounds made with tip of the tongue between front teeth (THick- voiceless, THough - voiced)
Alveolar (Av-ee-lir)
sounds are made with the tip of the tongue at or near the ______ ridge - bump/ridge at the top of mouth adjacent to teeth (t, d, s, z, n, l, r)
Palatal
sounds are made with the tongue near your _____ - the hard part of the roof of your mouth. Right behind Alveolar ridge. (ex - sh, Genre, ch, j, y)
Velar (Vee-lir)
sounds are made with tongue near the ______ - soft part of the roof of your mouth behind the palate (ex - k,g, ng)
Glottal
sound is made at _______ - space between vocal folds/cords (ex - h)
M and W are also sometimes classified as…
velar or labiovelar instead of bilabial because the back of the tongue is raised toward the velum during production of the sound
Manner of Articulation
how the sound is made with respect to airflow.
Stops
Fricatives
Affricates
Nasals
Glides
Liquids
Stops
sounds is made by obstructing the airstream in the oral cavity (ex - p, b, t, d, k, g)
Fricatives
sounds formed by a nearly complete stoppage of the airstream (ex - f, v, THick, THough, s, z, sh, meaSure)
Affricates
sounds are made by briefly stopping the airstream completely and then releasing the articulators slight so that friction is produced; these sounds start AND stop as fricatives
(ex - ch, j)
Nasals
sounds are made by lowering the velum and letting the airstream pass primarily through the nasal cavity (ex - m, n, ng)
Glides
sounds are made with only a slight closure of the articulators - if vocal tract were any more open, the result would be a vowel ( ex - y, w, wh, h)
Liquids
sounds are made when an obstruction is formed by the articulators but is not narrow enough to stop the airflow or to cause friction (L, r)
L is often described as a _____ when discussing it in manner of articulation
lateral liquid - the tongue touches the roof of the mouth near the alveolar ridge, and air flows around the sides of the tongue
R is often describe as a ______ when discussing it in manner of articulation
bunched liquid - the tongue is bunched up under the palate when producing the sound
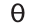
IPA symbol for
thin, thank, author, bath, breath
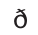
IPA symbol for
then, though, wither, bathe, breathe
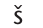
IPA symbol for
ship, charade, dishes, nation, fish, rash
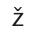
IPA symbol for
genre, measure, casual, rouge, garage
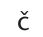
IPA symbol for
chip, cello, riches, kitchen, ditch, which

IPA symbol for
gem, jump, bludgeon, bridge, ridge, judge
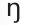
IPA symbol for
ringer, singing, wing, tongue

IPA symbol for
what, which, awhile
Larger Groupings of Sounds
Labials
Sonorants
Obstruents
Labials
bilabials and labiodentals
Sonorants
consonants produced with a relatively open passage for the airflow (i.e. nasals, liquids, and glides)
Obstruents
sounds produced with a greater stoppage of airflow (i.e. stops, affricates, and fricatives
Nasality Exchange
nasal feature moves from one segment of a word to another (i.e. banana → madana)
Vowels that are said in the high and front portion of mouth
bEAt, bIt
Vowels that are said in the mid and front portion of mouth
bAIt, bEt
Vowels said in the low and front portion of mouth
bAt
Vowels said in the mid and central part of the mouth
tunA, bUt
Vowels said in high and back portion of the mouth
bOOt, pUt
Vowels said in the mid and back portion of the mouth
bOAt, bAWdy
Vowels said in the low and back portion of the mouth
bOdy
Rounded vowels
only for vowels said in the high and mid back portion of mouth
Tense vowels
made with more muscular construction
i in bEEt, e in bAIt, u in bOOt, o in bOAt
Lax vowels
any vowel sounds that are not tense
Natural Class distinction between vowels
Stressed vs Unstressed
Lax vs Tense
Lip Rounding/ Rounding vs No Rounding
Stressed Vowels
Unstressed Vowels