Mechanical Waves
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
a disturbance that transfers energy from one place to another
wave
4 kinds of waves
sound, light, water, radio
waves that transfer energy through matter
mechanical waves
waves that require a substance (called a medium) to travel through
mechanical waves
water, sound, seismic
3 examples of mechanical waves
waves that transfer energy through a field
electromagnetic waves
waves that do not require a substance (medium) to travel through
electromagnetic waves
light, radio, ultraviolet, x-rays
4 examples of electromagnetic waves
mechanical waves need ___ to travel
matter
any material that a wave can travel through is called a ___
medium
a medium can be any type of ___, ___, or ___
solid, liquid, gas
there are 2 types of mechanical waves: ___ and ___
transverse, longitudinal
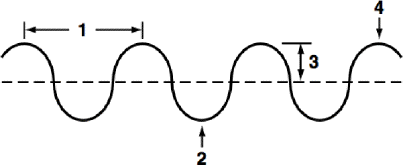
define section 1 of the diagram
wavelength
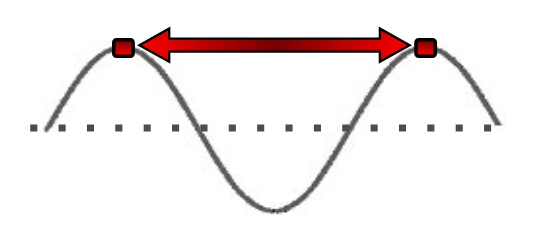
the distance between 2 consecutive crests or 2 consecutive troughs
wavelength
this shows the ___ of a ___ wave
wavelength; transverse
the distance between 2 consecutive compressions or 2 consecutive rarefactions
wavelength
this shows the ___ of a ___ wave
wavelength; longitudinal
the number of wavelengths passing by a point in a certain timeframe
frenquency
___ is measured as the number of crests or troughs that pass by in 1 second—measured in Herz
frequency
what is frequency measured in? what is the abbreviation? (answer: ____, (__) )
Herz, (Hz)
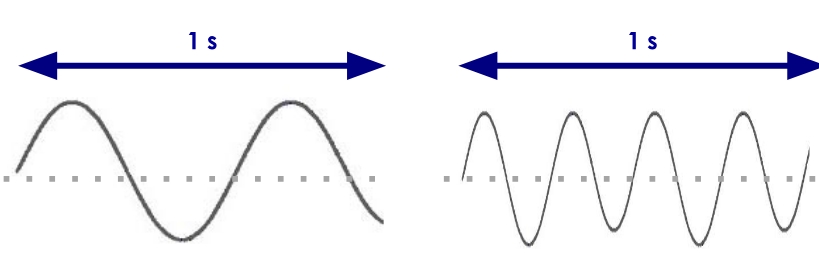
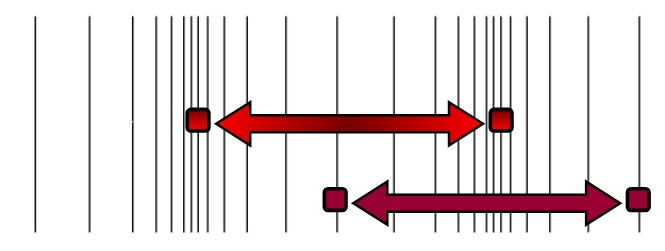
the diagram on the left has a ___ wavelength and ___ frequency
longer; smaller
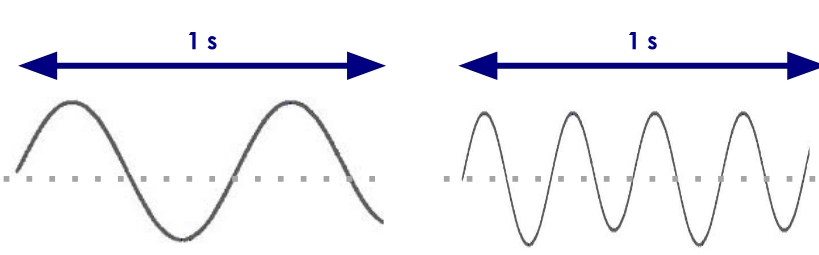
the diagram on the right has a ___ wavelength and ___ frequency
shorter; larger
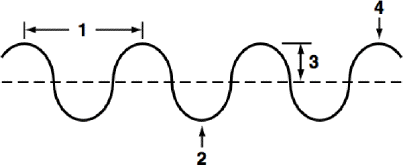
define section 2 of the diagram
trough
the lowest part of the wave
trough
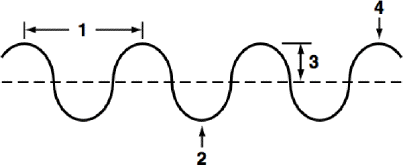
define section 3 of the diagram
amplitude
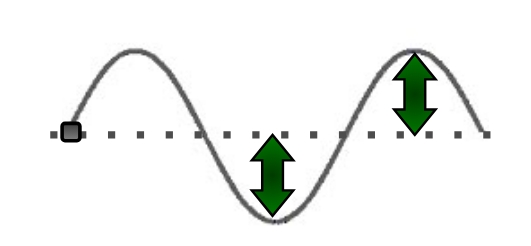
the distance from the rest position to the top of a crest or the bottom of a trough
amplitude
tells you how much energy a wave has
amplitude
lower amplitude = ____ energy
less
higher amplitude = ____ energy
more
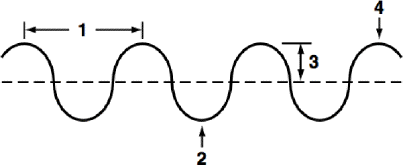
define section 4 of the diagram
crest
the highest point of the wave
crest
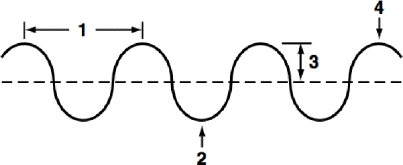
define the dotted line in the center of the wave
rest position
the undisturbed position of particles or fields when they are not vibrating; also known as the equilibrium
rest position
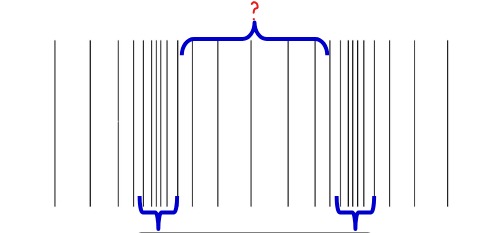
rarefaction
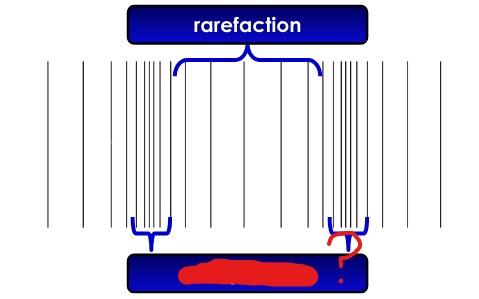
compression
when a wave bounces and goes in a new direction
reflection
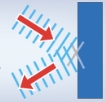
reflection
the wave bends around an object or through holes in the object
diffraction

diffraction
the wave bends as it passes into and through an object
refraction

refraction
the wave is absorbed and disappears
absorption

absorption
___ are a traveling form of energy because they can ___ motion
waves; change
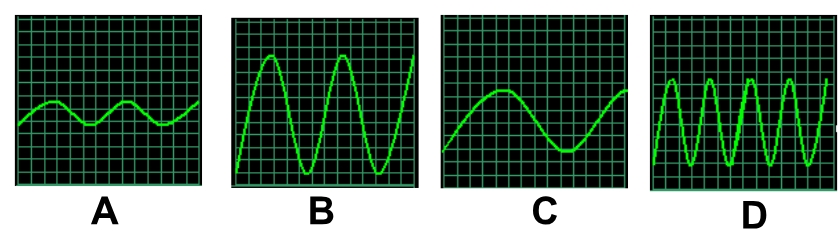
which sound wave has the highest amplitude?
B
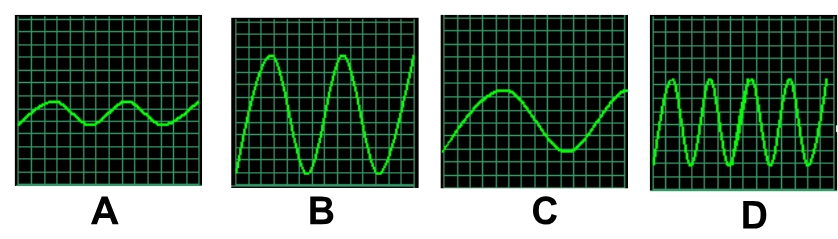
which sound wave has the longest wavelength?
C
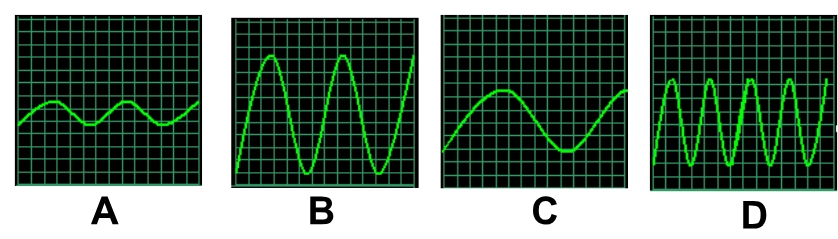
which sound wave has the highest frequency?
D
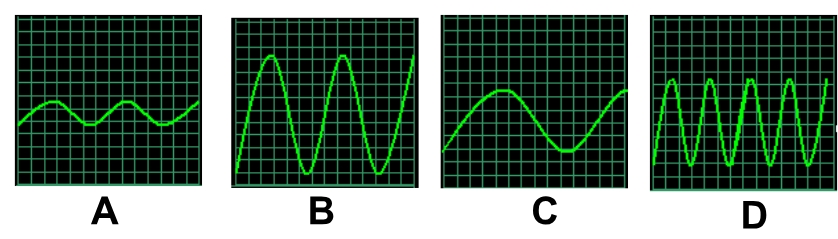
which sound wave has the most energy?
B