WCHS Mrs. Herrick Honors Chemistry
1/125
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
126 Terms

What is this GHS symbol?
Oxidizers

What is this GHS symbol?
Flammable materials

What is this GHS symbol?
Explosive; self reactive

What is this GHS symbol?
Gases under pressure

What is this GHS symbol?
Acute toxicity

What is this GHS symbol?
Corrosion; severe skin burns and eye damage

What is this GHS symbol?
Health hazard

What is this GHS symbol?
Environmental hazard

What is this GHS symbol?
Irritant toxicity
What are the three most unique GHS safety symbols?
Exploding bomb, flame over circle, and health hazard
Which of the following are qualitative data?: Length, color, density, average atomic mass, & wavelength
Color
Which of the following are quantitative data?: Length, color, density, average atomic mass, & wavelength
Length, density, average atomic mass, and wavelength
What is the difference between the meanings of mass, volume, density, and their units?
Mass
Meaning: How much matter an object has
Units: grams (g), kilograms (kg)
Volume
Meaning: How much space an object takes up
Units: liters (L), milliliters (mL), cubic centimeters (c3)
Density
Meaning: How much mass is packed into a given volume
Units: g/mL, g/cm3
Which of the following is not made of matter?: Heat, air, sunlight, heterogenous mixture, helium, electrons, gamma rays
Heat, sunlight, and gamma rays
What is the difference between the test tube holder, beaker tongs, and crucible tongs?
A test tube holder is made to hold one test tube, beaker tongs are used to pick up beakers, and crucible tongs are used to hold hot beakers
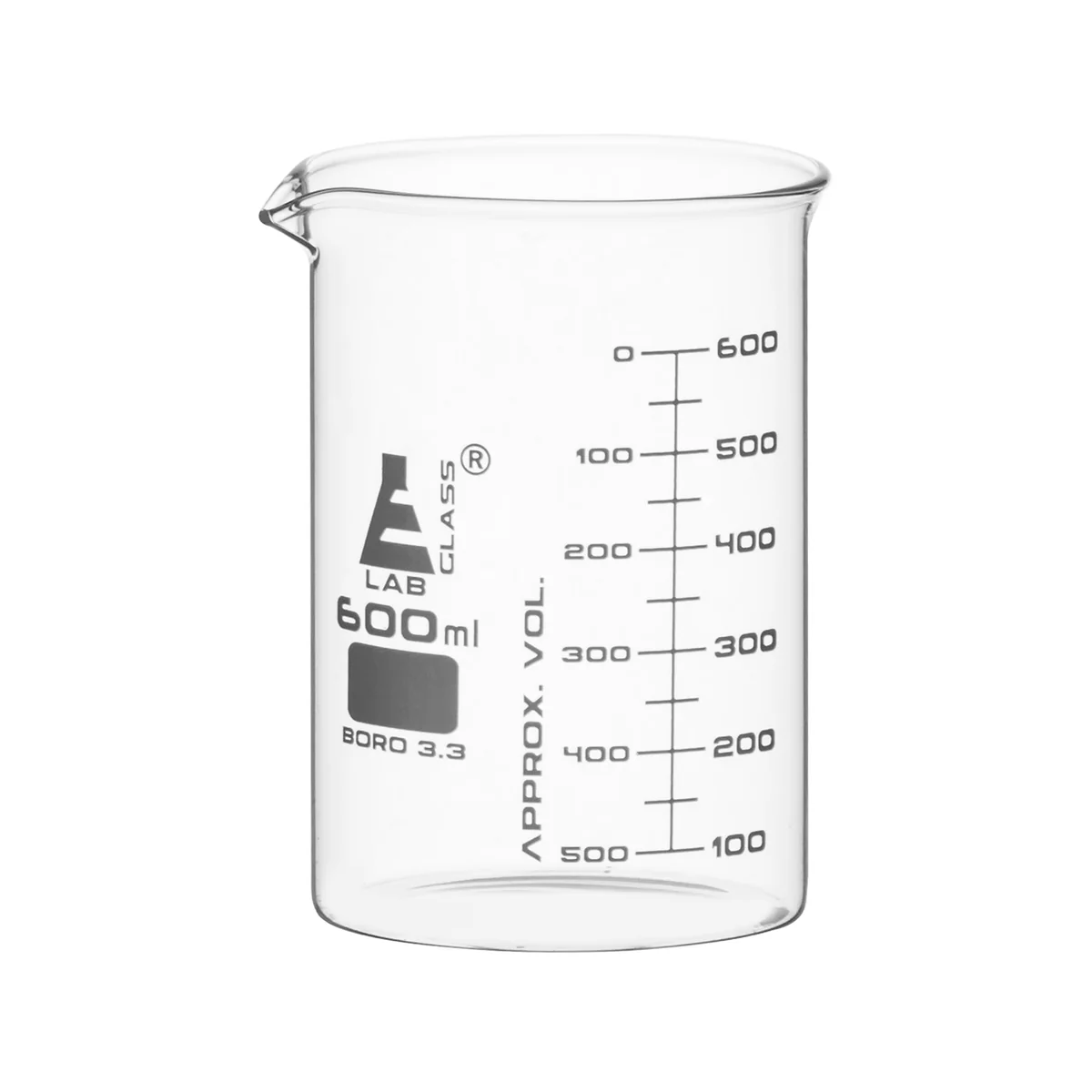

What is this piece of equipment called?
Beaker
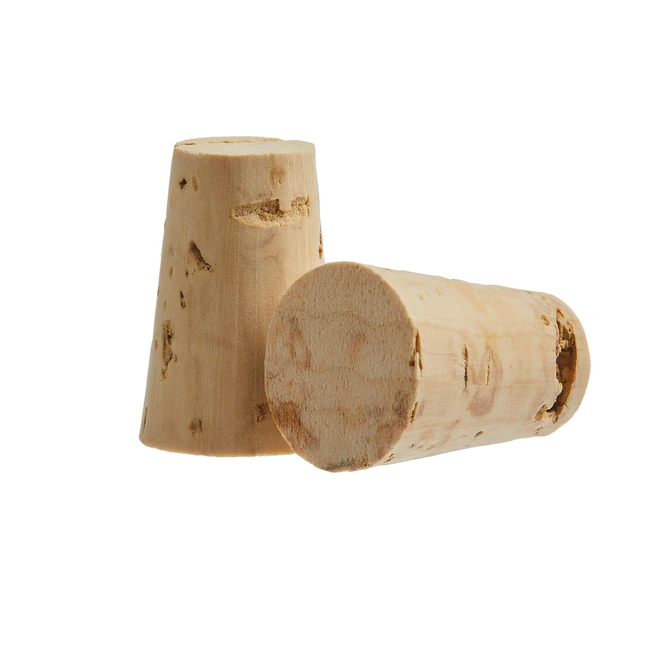

What is this piece of equipment called?
Corks

What is this piece of equipment called?
Erlenmeyer flask
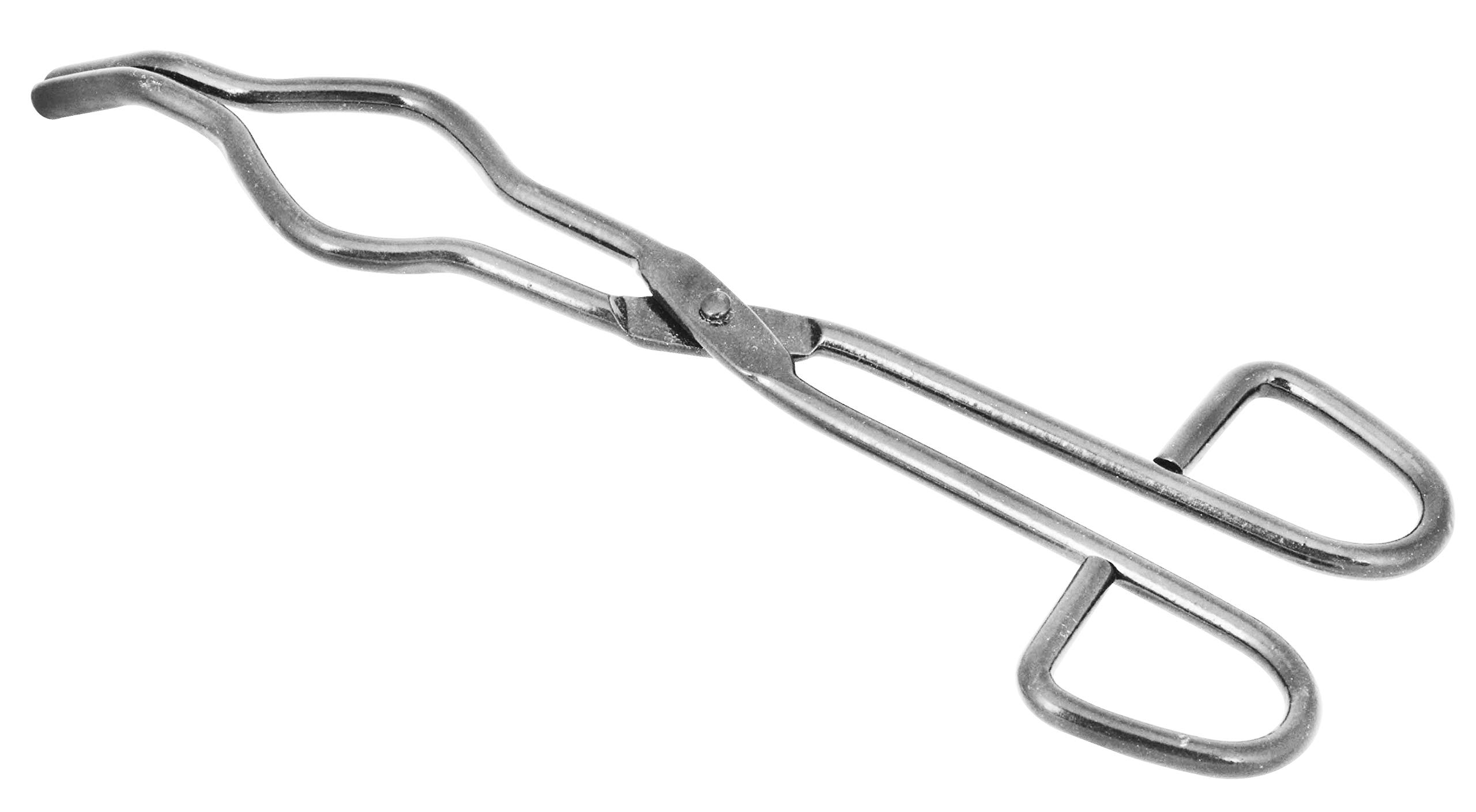

What is this piece of equipment called?
Crucible tongs
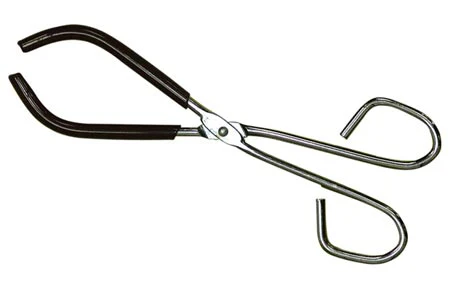
What is this piece of equipment called?
Beaker tongs

What is this piece of equipment called?
Rubber stoppers

What is this piece of equipment called?
Bunsen burner

What is this piece of equipment called?
Wire gauze
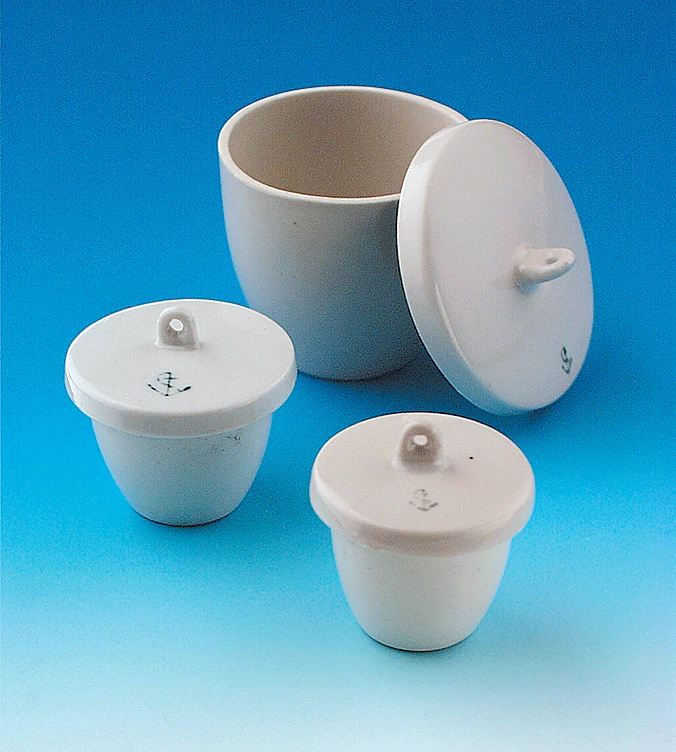

What is this piece of equipment called?
Crucible

What is this piece of equipment called?
Evaporating dish
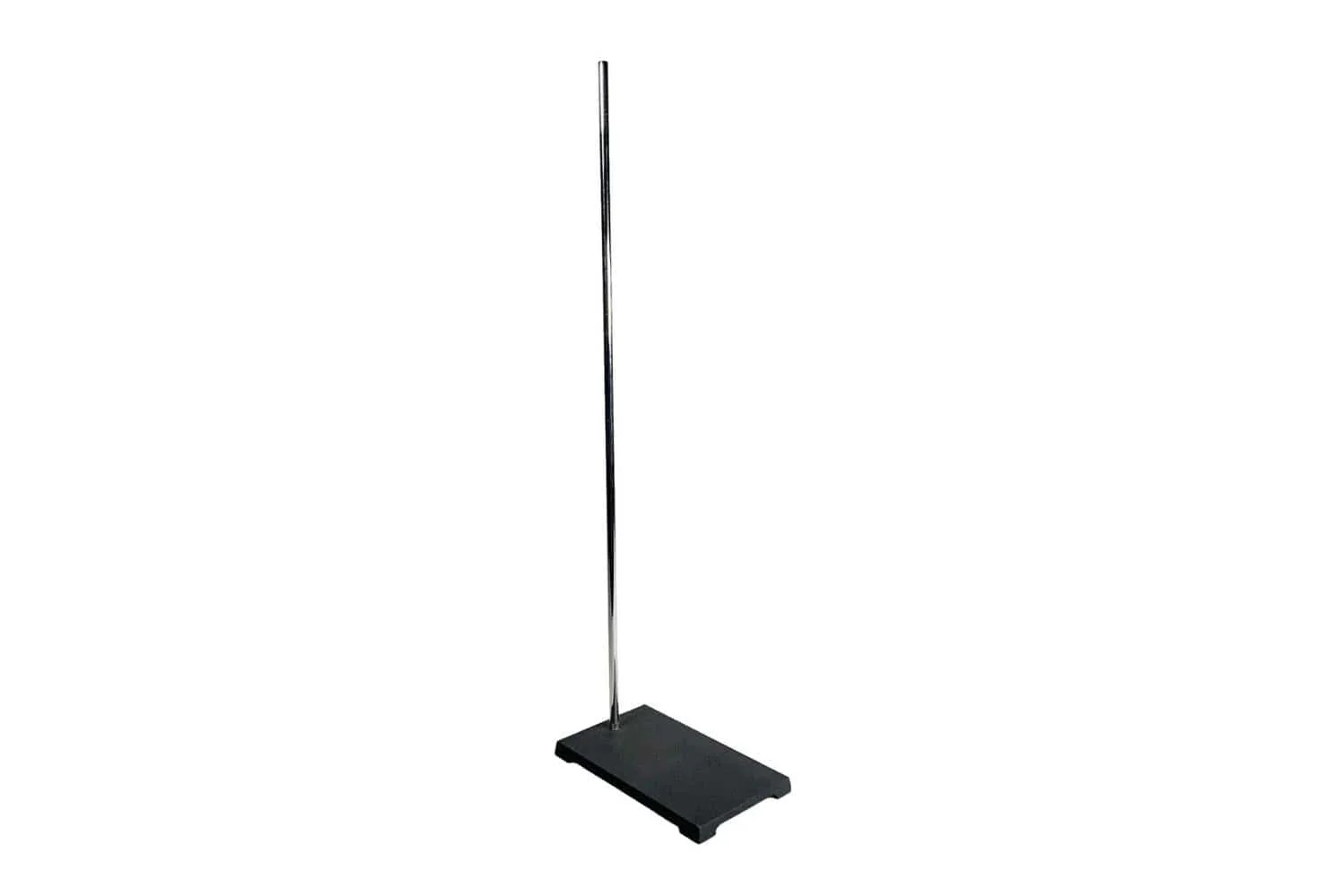

What is this piece of equipment called?
Ring stand
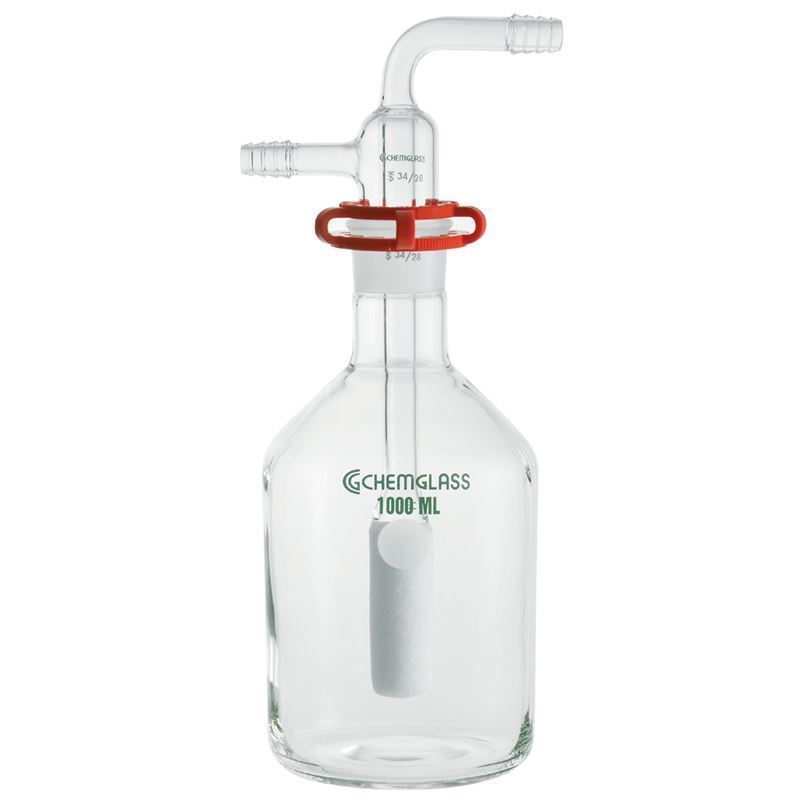

What is this piece of equipment called?
Gas bottle

What is this piece of equipment called?
Iron ring
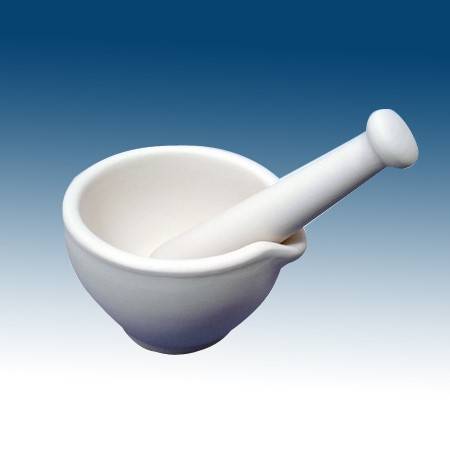

What is this piece of equipment called?
Mortar and pestle
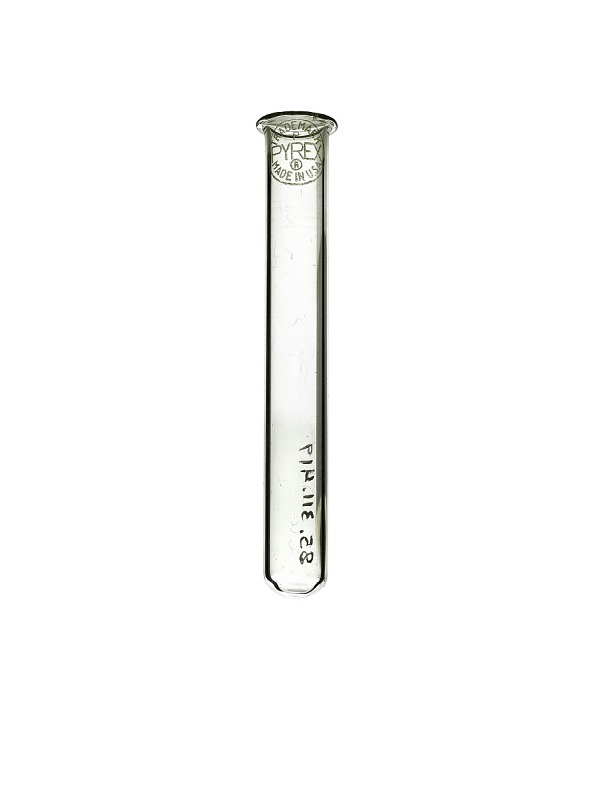

What is this piece of equipment called?
Test tube

What is this piece of equipment called?
Utility clamp
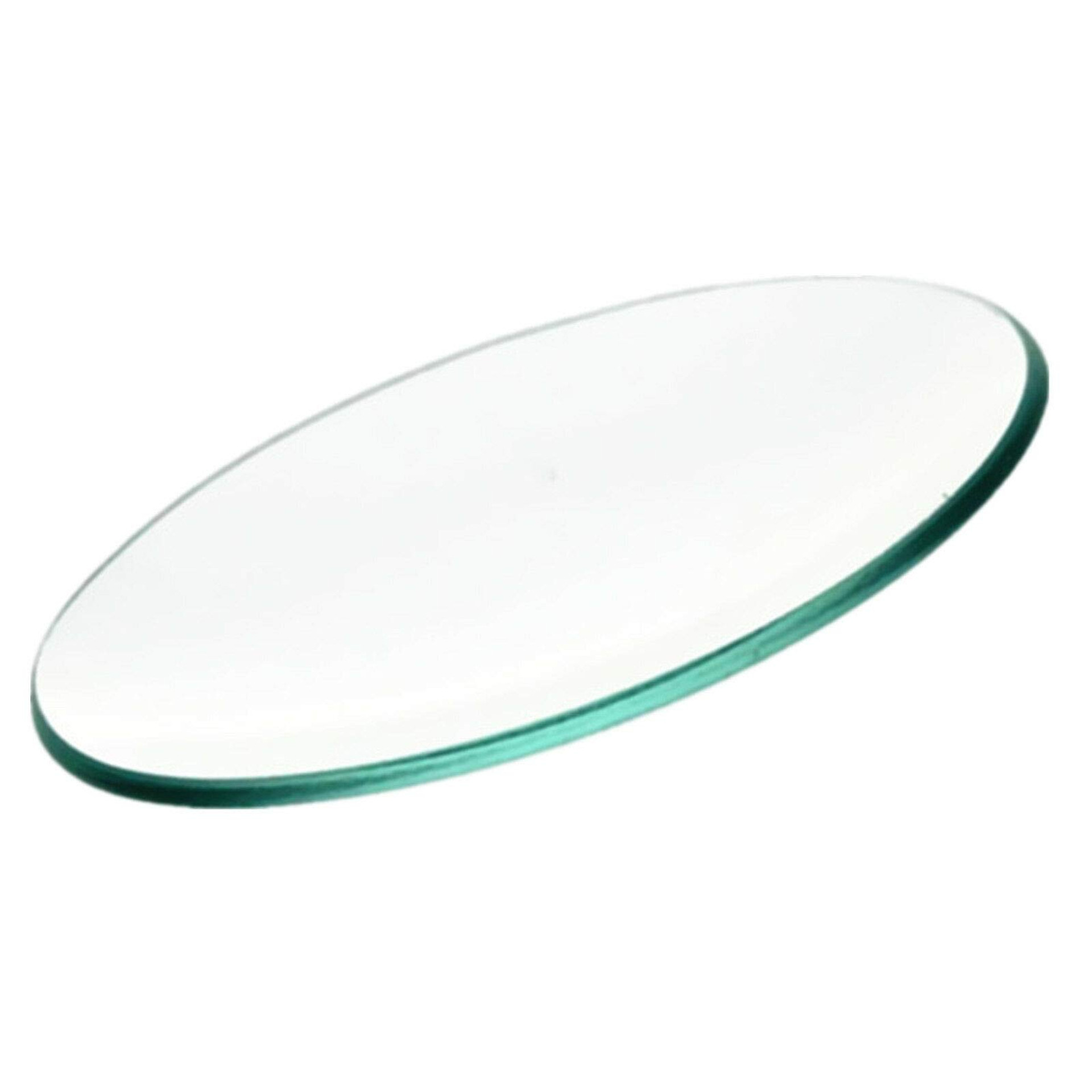

What is this piece of equipment called?
Watch glass
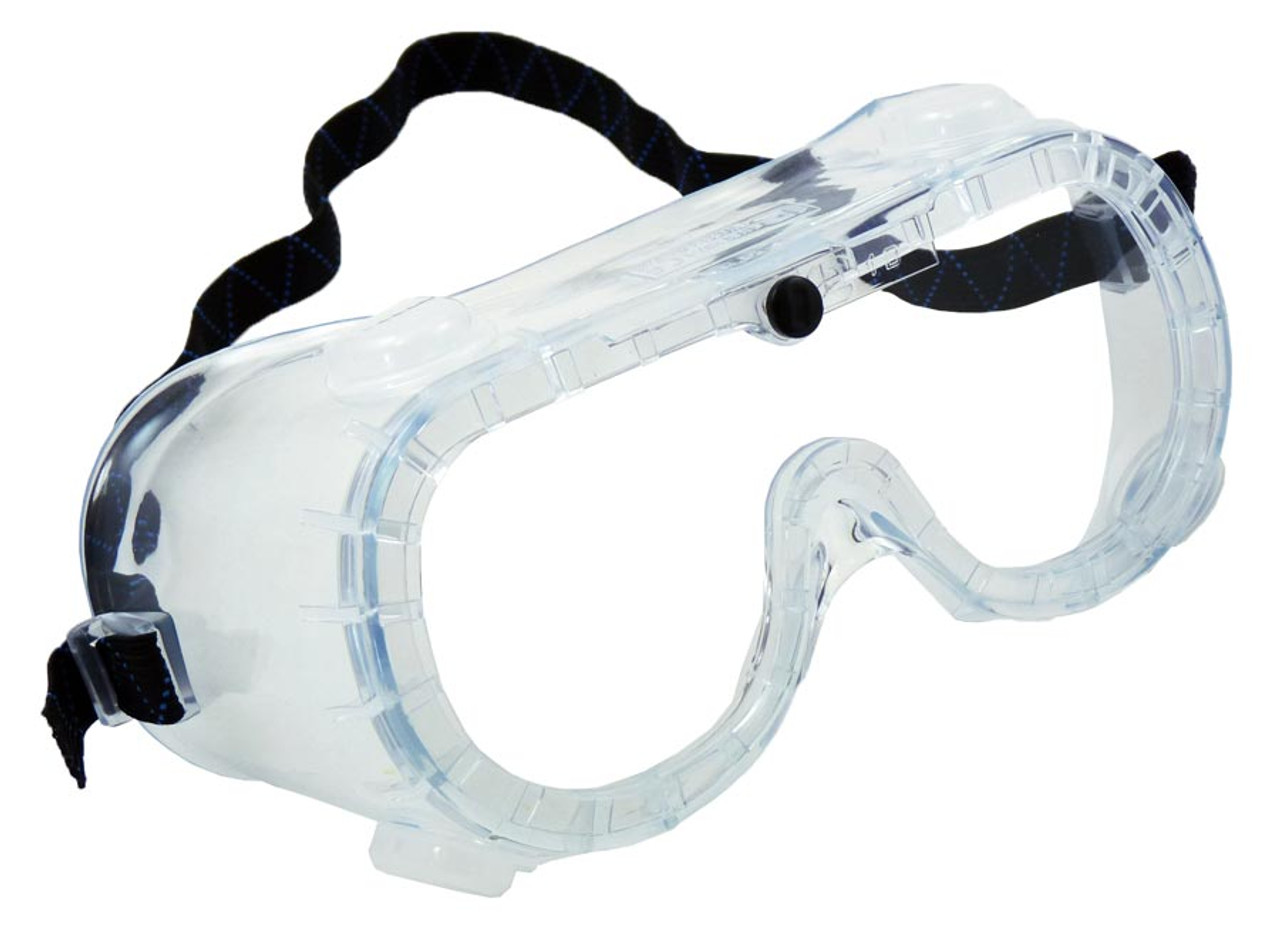
What is this piece of equipment called?
Safety goggles
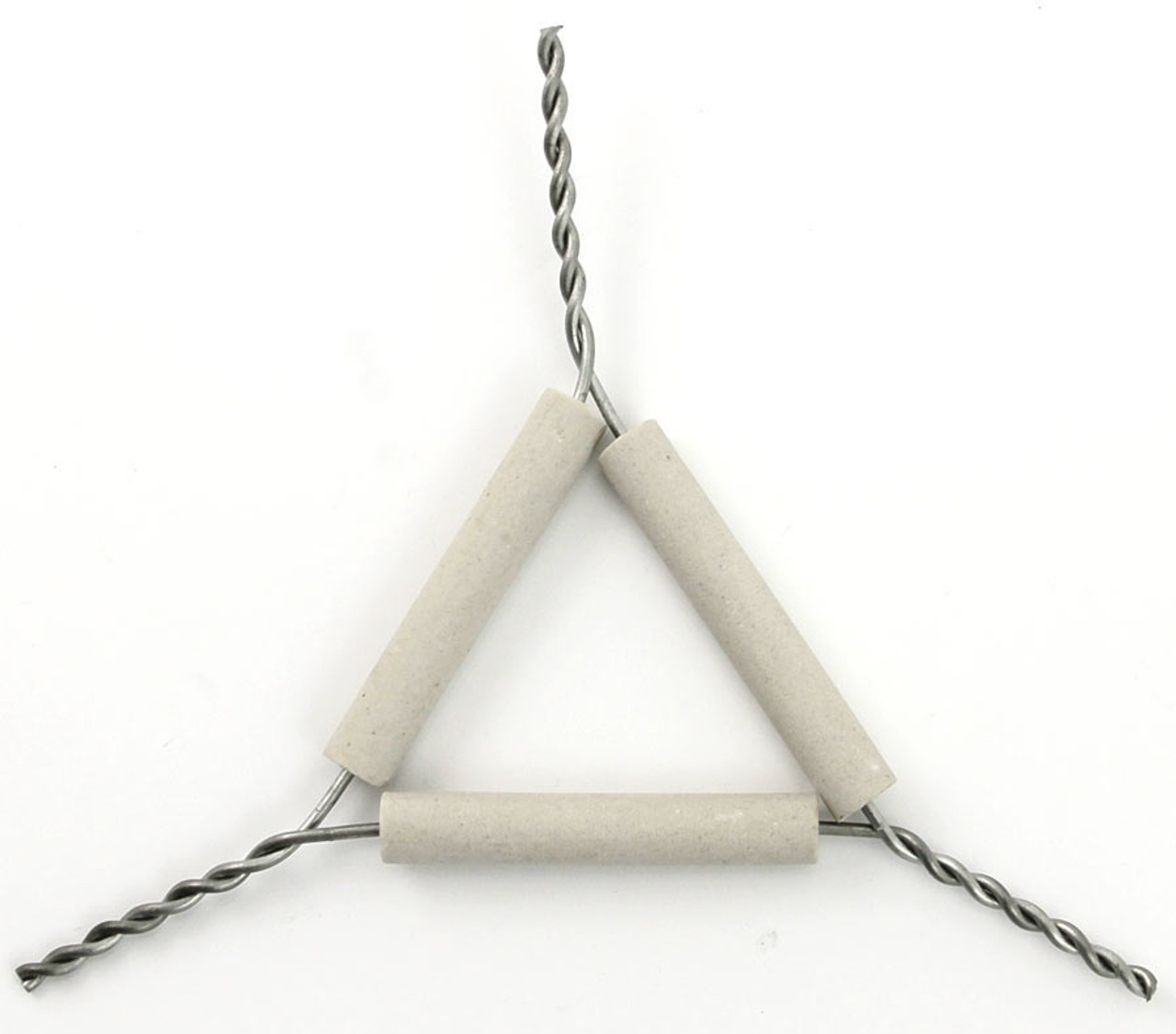

What is this piece of equipment called?
Pipestem triangle
True or false: The first thing when using a fire extinguisher is to aim at the base of the fire
False; the first step is to pull the pin
True or false: You should always use lots of cream first on a thermal burn
False; cool the burn under water
How many significant figures are in 0.005506?
4
What has more volume when comparing two objects with the same mass?: An object with a higher density or an object with a lower density
An object with a lower density, the mass is spread out over a larger space
What is the official unit for time?
Seconds
What is the official unit for temperature?
Celsius
What is the official unit for mass?
Kilogram
What is the official unit for length?
Meter
What is the official unit for amount of substance?
Mole
Give an example of a base unit
Meter
Give an example of a derived unit
Speed (m/s)
Classify the following as elements, compounds, or mixtures?:
1. Living tissue
Lemonade with pulp
Ice
Smokey air
Aluminum foil
Soil
Baking Soda
Hydrochloric acid solution
Mixture
Mixture
Compound
Mixture
Element
Mixture
Compound
Mixture
What are the 7 diatomic elements?
Bromine
Iodine
Nitrogen
Chlorine
Hydrogen
Oxygen
Fluorine
Are the diatomic elements classified in another group of matter?
No
Can mixtures be separated?
Yes, by physical means
Can elements be separated?
No
Discoveries of Democritus
Matter is made of atoms
Atoms are tiny & indivisible
Atoms move in empty space
Different atoms= different matter
Discoveries of JJ Thompson
Discovered the electron (-)
Proposed the plum pudding model
Showed atoms are not indivisible— they have smaller parts
Discoveries of Rutherford
Gold foil experiment →discovered the nucleus
Nucleus is tiny, dense, and positively charged
Most of the atom is empty space
Electrons orbit around the nucleus
Discoveries of Bohr
Electrons orbit the nucleus in fixed energy levels
Electrons can jump between levels by absorbing or releasing energy
Discoveries of Dalton
Proposed Atomic Theory
All matter is made of indivisible atoms
Atoms of the same element are identical
Atoms of different elements combine in fixed ratios to form compounds
Chemical reactions involve rearranging atoms, not creating or destroying them
Discoveries of Schrodinger
Developed the Schrodinger wave equation
Describes where electrons are most likely to be
Introduced the concept of orbitals
Helped form the quantum mechanical model of the atom
Discoveries of Heisenberg
Formulated the Uncertainty Principle
It’s impossible to know both an electron’s exact position and momentum at the same time
Helped develop quantum mechanics
Discoveries of Aristotle
Believed all matter is made of four elements: water, air, earth, fire
Thought mater is continuous (no atoms)
Ideas were widely accepted for 2,000+ years
No experimental evidence for his ideas
Discoveries of Chadwick
Discovered the neutron (neutral)
Explained missing mass in atoms
Completed the modern picture of the nucleus (protons + neutrons)
_____ radiation is the most dangerous and penetrating to tissue
Gamma
_____ waves have the longer waves, low frequency and energy
Radio
Of visible light, ____ has the shortest waves, highest frequency and energy
Violet light
True or false: The atomic number can be a number with decimal places
False
True or false: The mass of an isotope, that gives off a beta particle, does decrease
False
What is the difference between the excited state and ground state of an electron, and which has to occur to see the color of light to be given off?
Ground= low energy
Excited= high energy
Light/color= electron falling back to ground state
Which has lower frequency?: Yellow, red, blue, or green light
Red→yellow→green→blue→violet
Which has longer wavelength?: X-rays, infrared, gamma rays, or microwaves
Microwaves→infrared→x-rays→gamma rays
True or false: As the wavelength of a wave decreases, then its frequency increases
True
True or false: Energy is being absorbed by an atom when its electrons are going back to ground state
False, energy is being emitted
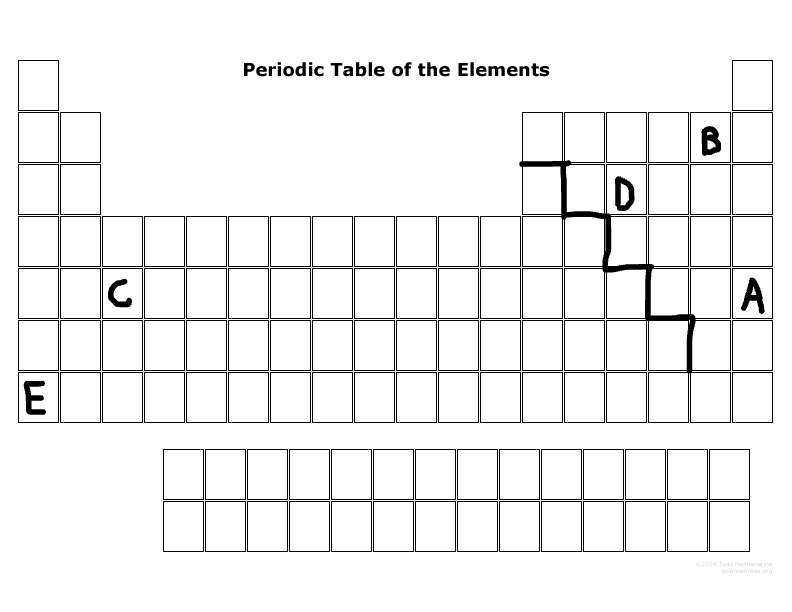
What is the family name that B is part of?
Halogens
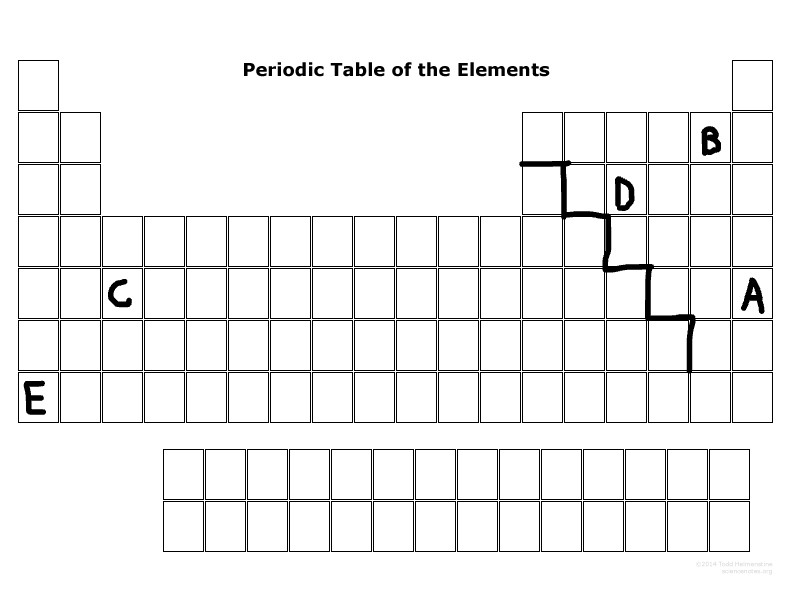
What is the family name that E is part of?
Alkaline metal
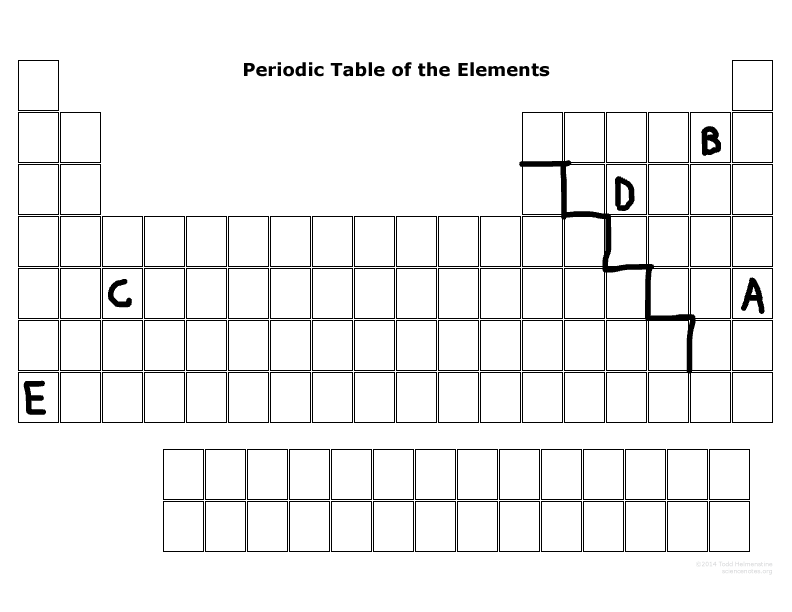
What period number is C located in?
5
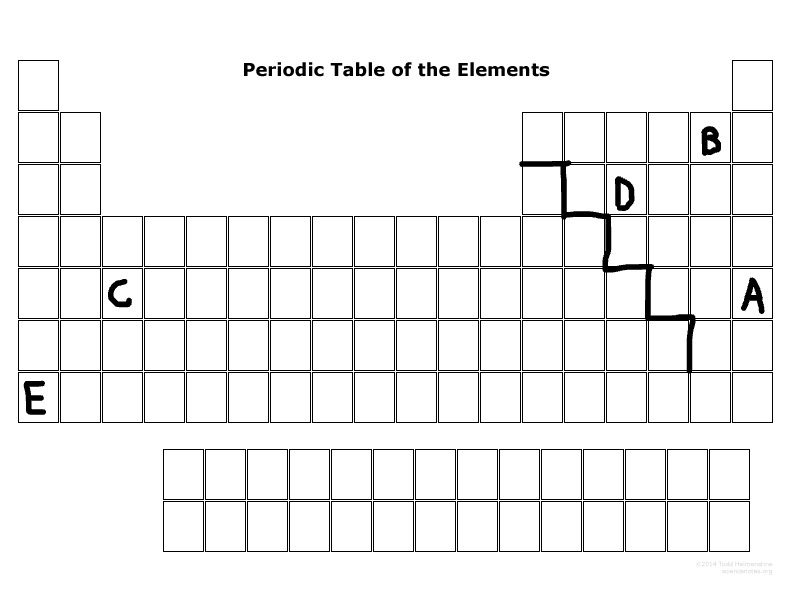
What major group is E? (metal, nonmetal, or metalloid)
Metal
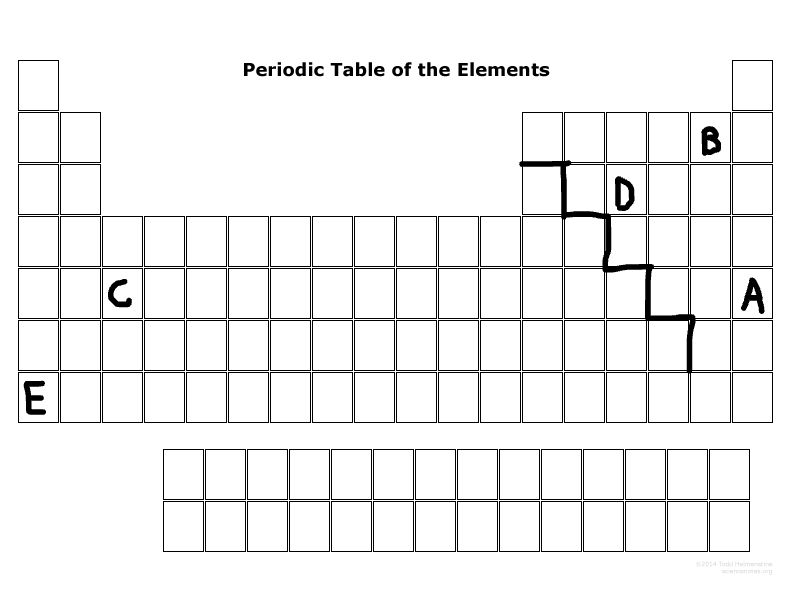
What major group is D? (metal, nonmetal, or metalloid)
Nonmetal
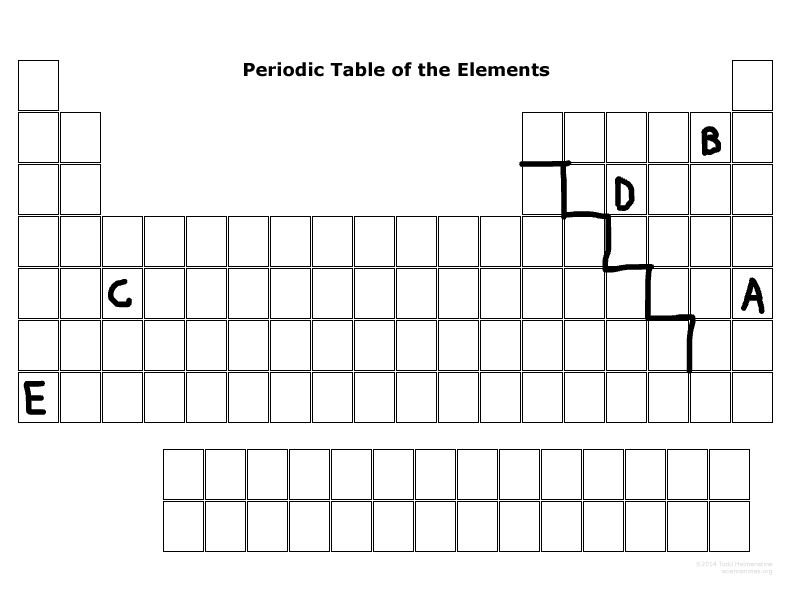
Which elements are representative elements?
E, D, B, A
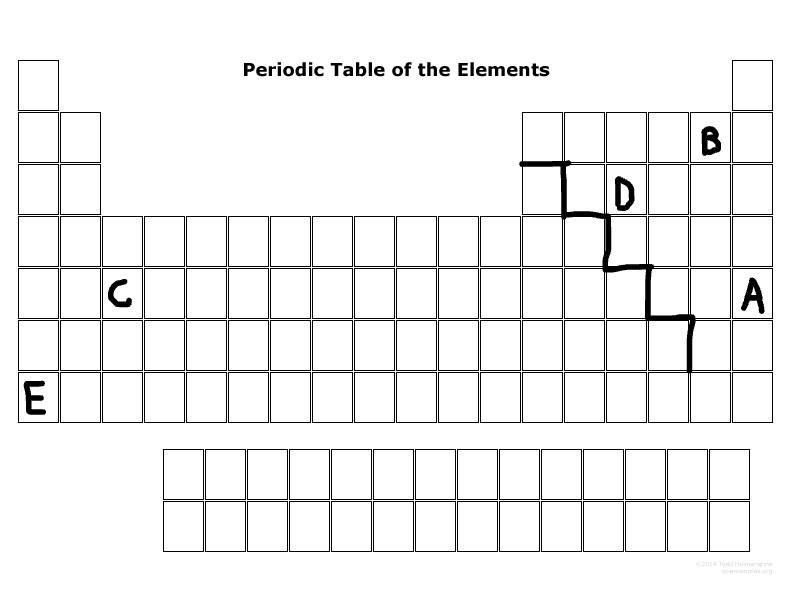
Which element(s) are transition metal(s)?
C
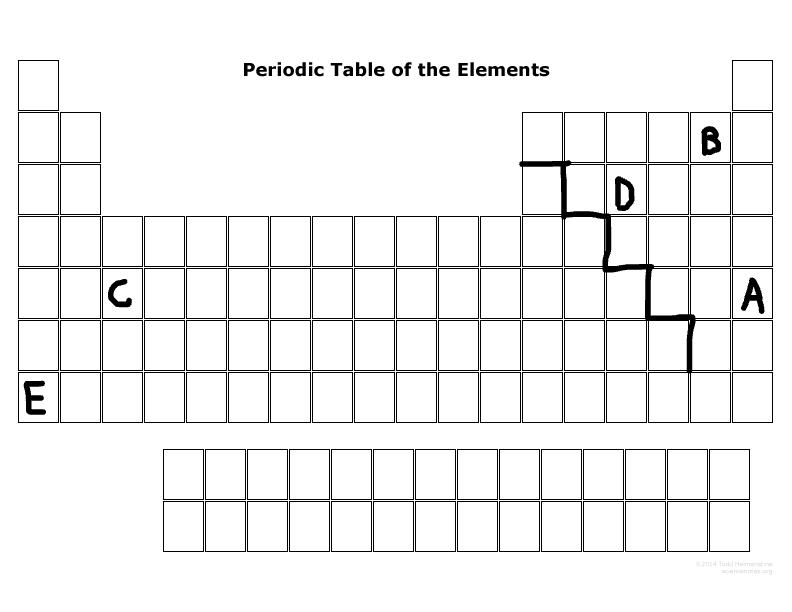
Which element(s) are in the S block?
E
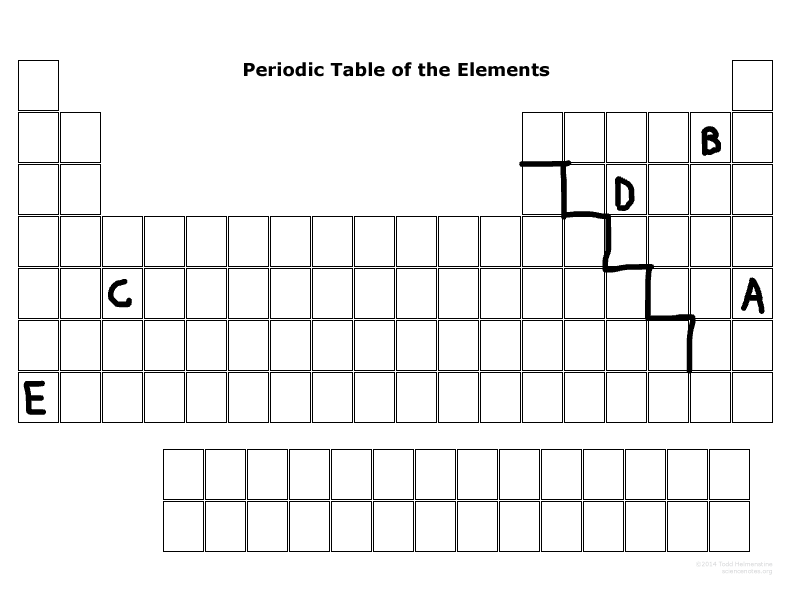
Which elements are in the P-block?
D,B,A
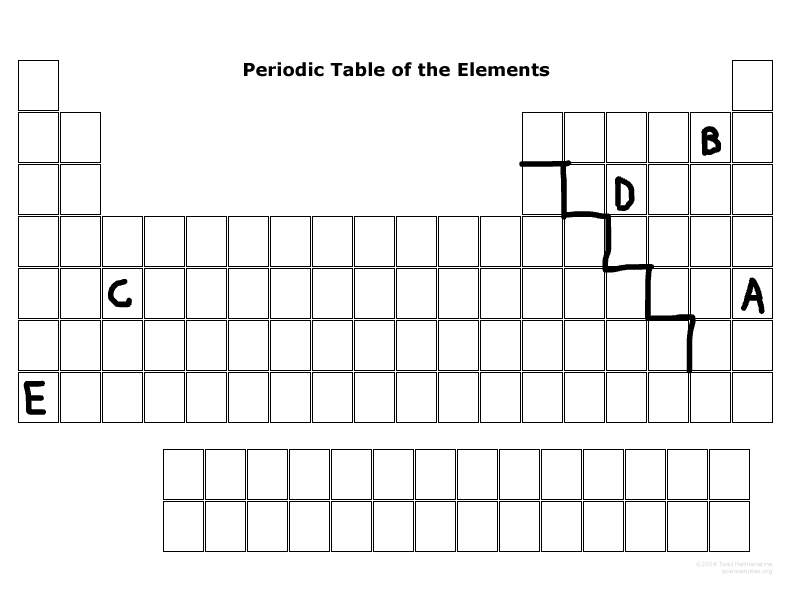
Which elements can become a cation more easily than an anion?
E & C
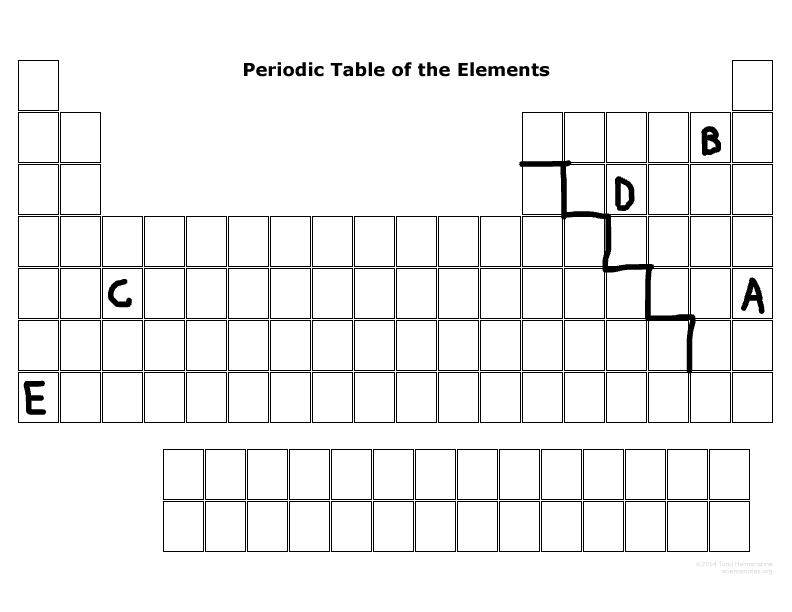
Which elements can become an anion more easily than a cation?
D, B, A
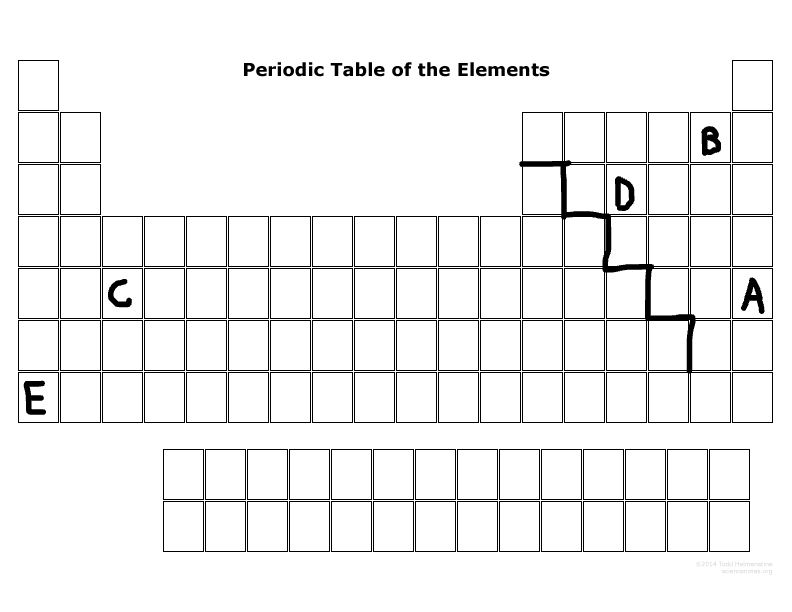
Which elements are the most reactive in their major families?
E & B
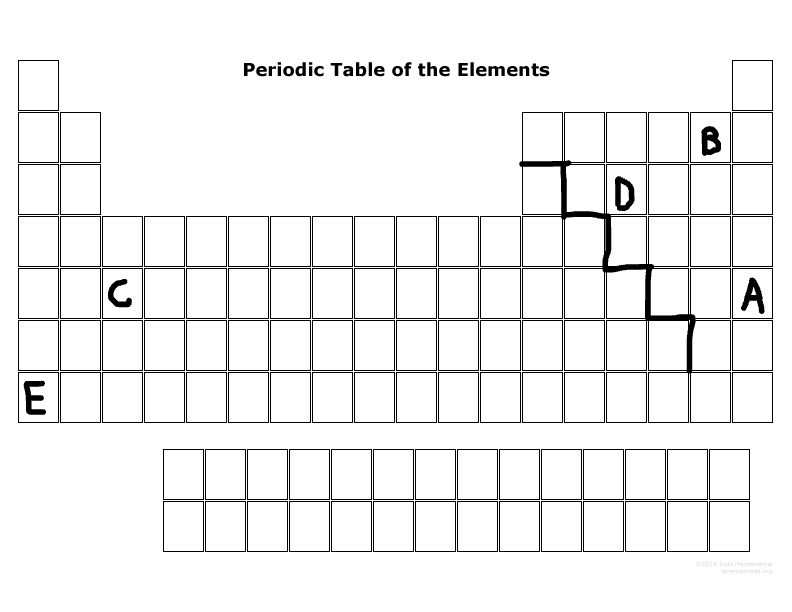
Which element is not reactive at all?
A
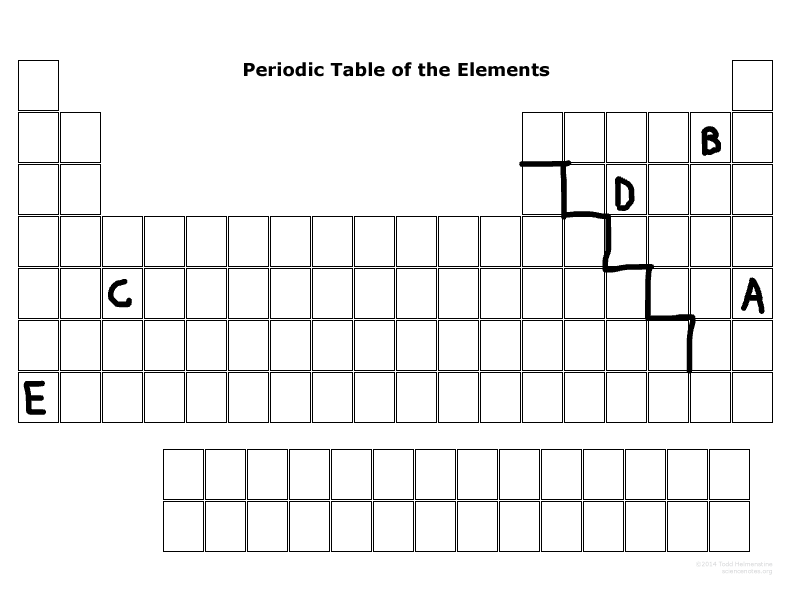
Which element has the most electronegativity?
B
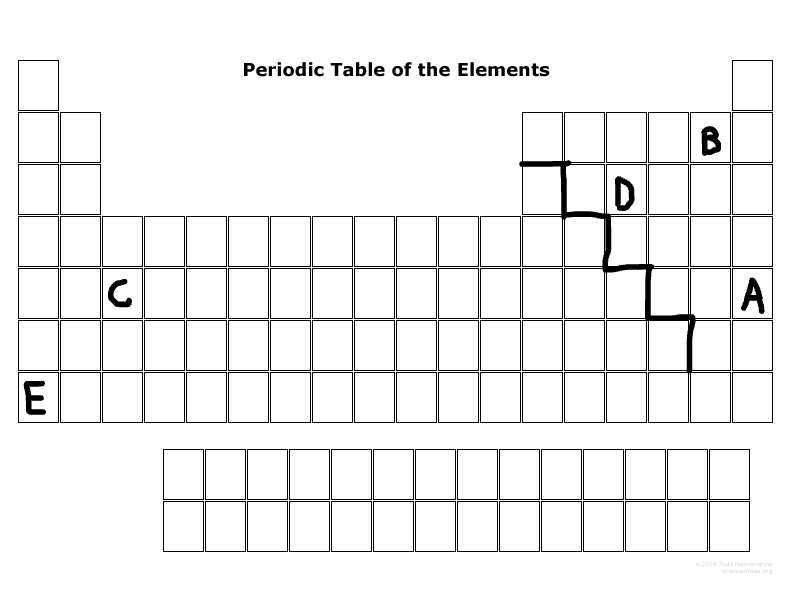
Which element is the largest size in its period?
E
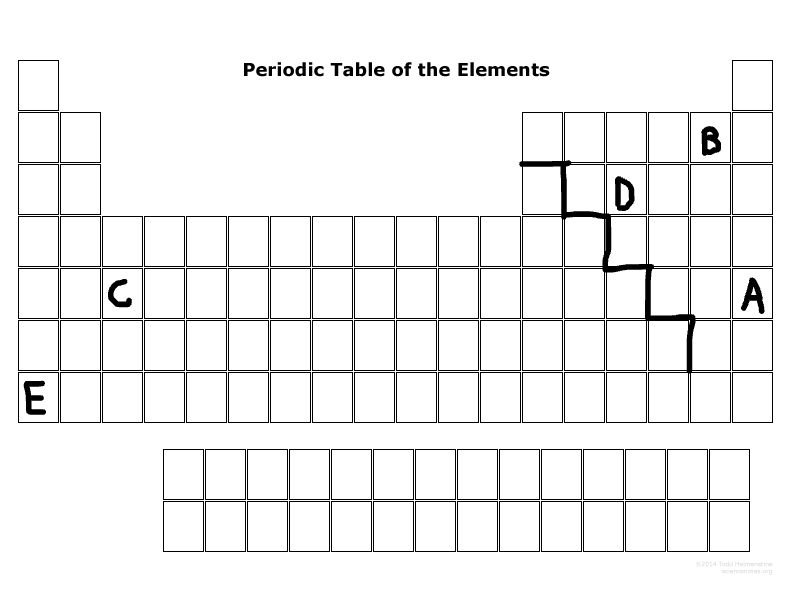
Which element has the least ionization energy?
E
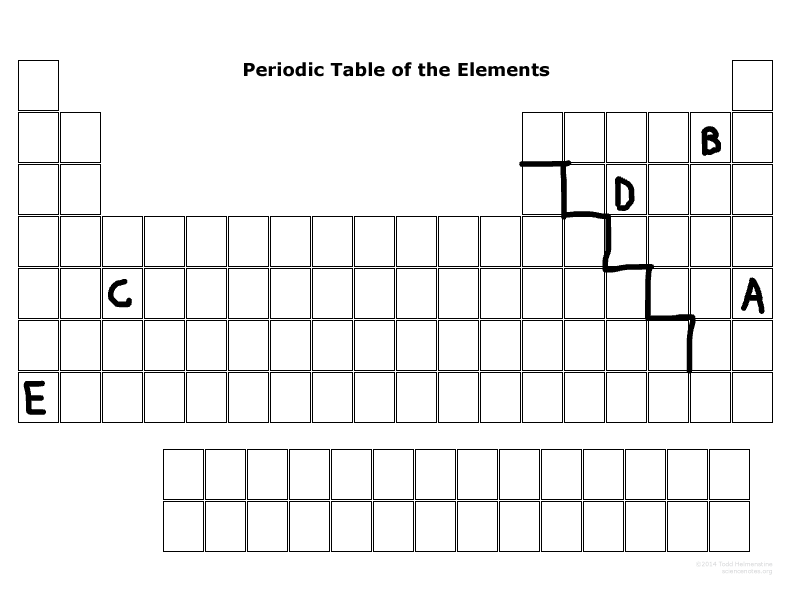
Which element is the smallest size in its period?
B
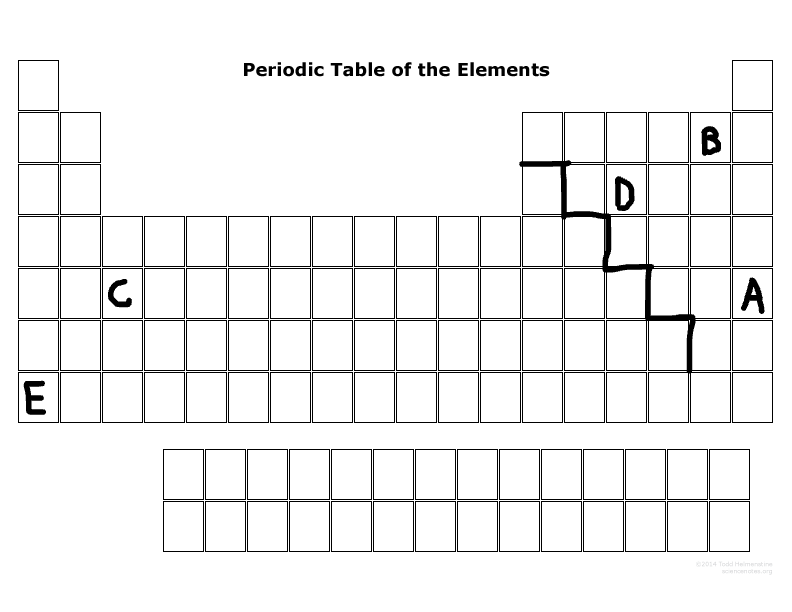
Which two elements tend to want to lose electrons due to their number of outermost electrons?
E & C
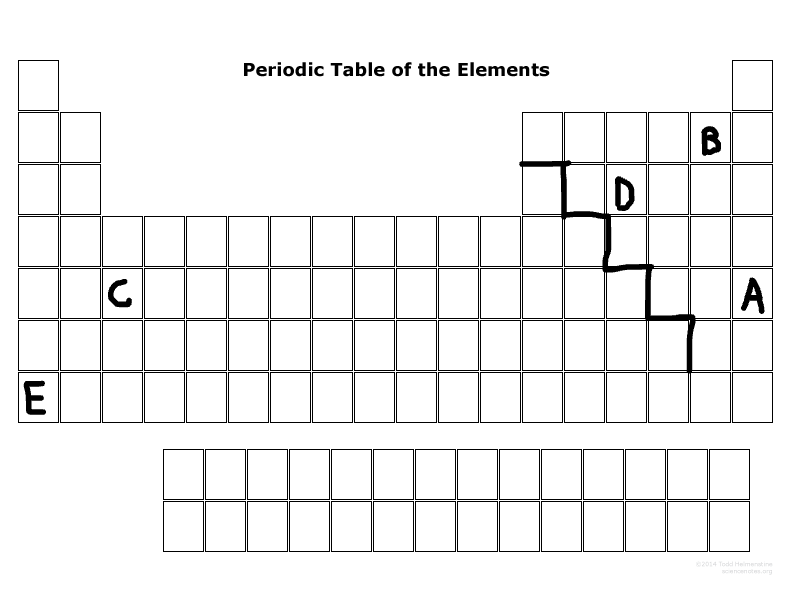
Which two elements tend to want to gain electrons due to their number of outermost electrons?
D & B
Are neutral or cations usually smaller?
Cations
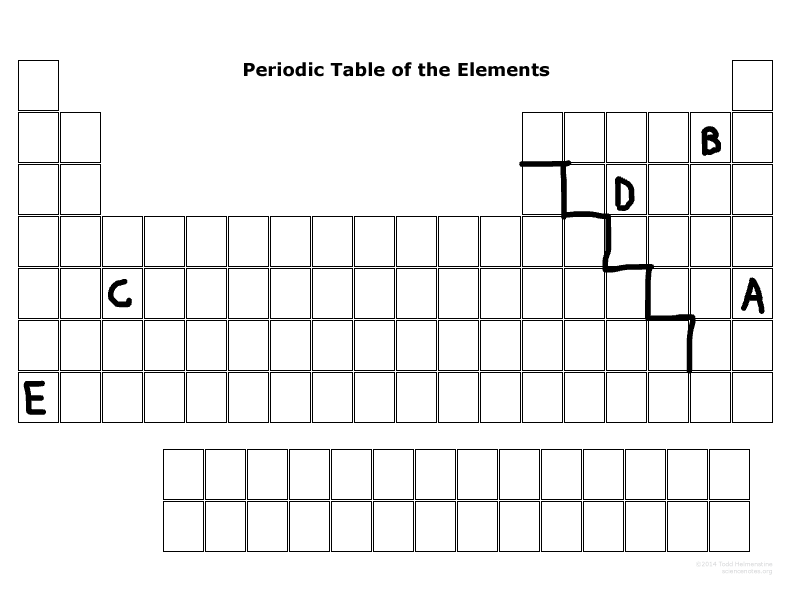
List the valance electrons of element E, B, and D, and will they lose or gain electrons?
E:
1, lose electrons
B:
7, gain electrons
D:
5, gain electrons
Another name of homogenous mixtures are: colloids, emulsions, solutions, suspensions
Solutions
Atom
Smallest unit of an element that is still the element
Element
Category of matter made up of only one type of atom
Diatomic atom
Atoms of 7 elements that bond together in pairs when in a pure substance
Compound
Matter composed of 2 or more atoms of different elements chemically bonded in a fixed proportion
Matter
Anything that has mass and takes up space
Pure substance
Type of matter that has a definite formula to represent it
Heterogeneous mixture
Type of mixture that does not have uniform composition (unevenly mixed)
Homogeneous Mixture
Type of mixture that has uniform composition (evenly mixed)
Are neutral atoms or anions normally bigger in size?
Anions