(6) Thyroid Hormones + Regulation
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
full name of thyroid hormone T4
thyroxine
full name of thyroid hormone T3
triiodothyronine
Which of the thyroid hormones is mostly secreted by the thyroid gland: T3 or T4?
T4 (thyroxine)
The thyroid hormones have the same function, but which is 4x more potent: T3 or T4?
T3
Which thyroid hormone is present in the blood in much GREATER quantities: T3 or T4?
T4
Which thyroid hormone is present in the blood for a LONGER period time: T3 or T4?
T4
1 mg of what substance needs to be ingested each week in order to maintain the normal quantities of T4?
iodide
(1/5 of the iodides ingested are absorbed by the thyroid gland for T4 production)
Almost all of which thyroid hormone is converted to the other in tissues: T3 to T4 or T4 to T3?
T4 to T3
structure formed by simple cuboidal epithelium surrounding a substance called colloid in the thyroid gland
follicle
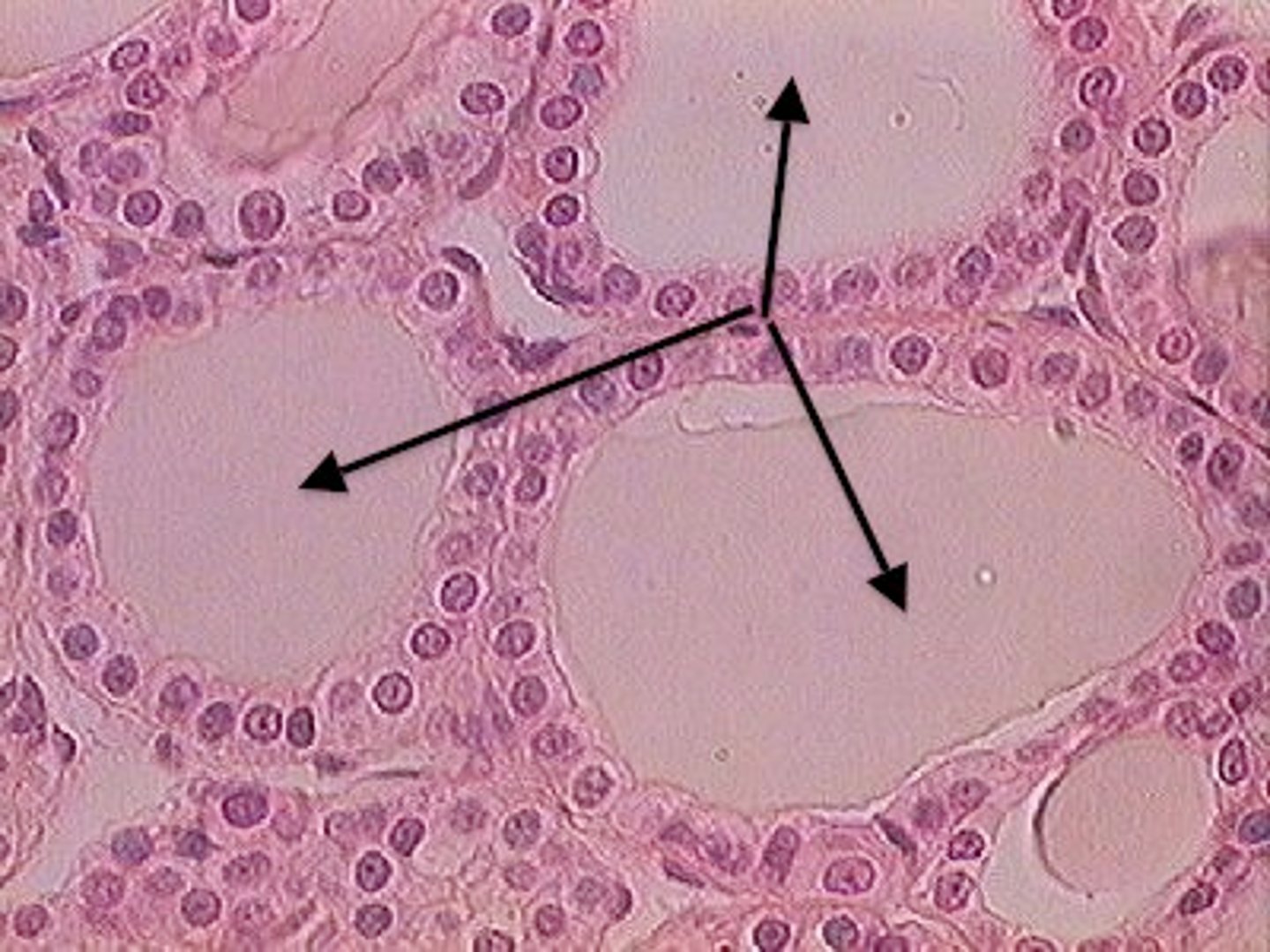
substance that fills thyroid follicles, which is secreted by the surrounding simple cuboidal epithelial cells and primarily consists of thyroglobulin
colloid
large glycoprotein found in colloid that contains the thyroid hormones
thyroglobulin
True or false: The thyroid gland is highly vascular.
true
When synthesizing thyroid hormones, where in the body is iodine reduced to iodide so that the iodide can be taken up by the thyroid? (iodine trapping)
GI tract
Thyroid hormone synthesis 1a: Iodides are transported from the blood into thyroid cells via iodine trapping, which involves what kind of transporter? What kind of transport does it use?
Na/I symporter, secondary active transport
Thyroid hormone synthesis 1b: Iodides are transported from the blood into thyroid cells via what process involving a Na/I symporter? This process concentrates the iodide in the cell up to 250x its concentration in the blood.
iodine trapping
What stimulates the increased activity of the Na/I symporter to get more iodides into thyroid cells for increased production of T3 and T4? (iodine trapping)
TSH
Thyroid hormone synthesis 2a: After iodides are transported into thyroid cells by the Na/I symporter, what enzyme is at the apical side of the cell and responsible for converting iodide ions into active iodine?
thyroperoxidase
Thyroid hormone synthesis 2b: Thyroperoxidase converts iodide ions into active iodine via what chemical process?
oxidation
Thyroid hormone synthesis 3a: Oxidized iodine binds to residues of what amino acid on the thyroglobulin molecule in the follicle?
tyrosine
Thyroid hormone synthesis 3b: Oxidized iodine binds to tyrosine residues on what molecule in the thyroid follicle, sped up by thyroperoxidase?
thyroglobulin
Thyroid hormone synthesis 3c: Oxidized iodine binds to tyrosine residues on the thyroglobulin molecule in the follicle, sped up by what enzyme?
thyroperoxidase
Thyroid hormone synthesis 4: When 1 iodine binds to tyrosine on thyroglobulin, what molecule results?
MIT (monoiodotyrosine)
Thyroid hormone synthesis 5: When 2 iodines bind to tyrosine on thyroglobulin, what molecule results?
DIT (diiodotyrosine)
Thyroid hormone synthesis 6: What hormone results when MIT and DIT are coupled together?
T3 (triiodothyronine)
Thyroid hormone synthesis 7: What hormone results when two DITs are coupled together?
T4 (tetraiodothyronine)
Thyroid hormone synthesis 8: Once T3 and T4 are synthesized by the coupling together of DIT and/or MIT, where are the thyroid hormones stored? (for up to 2-3 months)
follicle
Thyroid hormone synthesis 9a: ____ extensions from the apical membrane of the thyroid glandular cells surround small amounts of colloid until it is internalized into the cytosol via pinocytosis.
pseudopod
Thyroid hormone synthesis 9b: What hormone triggers the pinocytosis of thyroglobulin into the thyroid cells?
TSH
Thyroid hormone synthesis 10: The pinocytotic vesicles that took thyroglobulin into the thyroid cell fuse with lysosomes containing proteinases, that do what to thyroglobulin?
cleave it to release T3 and T4
Thyroid hormone synthesis 11: Molecules of T3 and T4 newly released from thyroglobulin ___ ___ through the plasma membrane of the thyroid glandular cell into the circulation.
freely diffuse
(since they are lipid soluble)
25% of iodinated tyrosine residues become T3 or T4. The rest are cleaved by what enzymes and recycled back to iodine & tyrosine for future thyroid hormone production?
iodinase, deiodinase
Once T3 and T4 have reached circulation, they are mainly bound to what plasma protein?
thyroxine binding globulin
(also albumin)
Which thyroid hormone has a HIGHER affinity for plasma proteins and therefore is released to tissues at a SLOWER rate: T3 or T4?
T4
(so T4's latent period, or amount of time before it starts showing effects, is longer than T3's latent period)
What happens to T3 and T4 upon entering tissue cells?
bind to cytoplasmic proteins, stored until needed (for days to weeks)
Once secreted (or injected) into the blood, what is the latent period of T4 before any effect on metabolic rate is seen? When is the maximum effect seen?
2-3 days, 12 days
(activity persists for up to 2 months)
Once secreted (or injected) into the blood, what is the latent period of T3 before any effect on metabolic rate is seen? When is the maximum effect seen?
6-12 hours, 2-3 days
Which thyroid hormone has a greater affinity for its receptor: T3 or T4?
T3
(since most T4 is converted to T3, 90% of receptors bind T3)
Where is the thyroid hormone receptor located?
nucleus
How do thyroid hormones cause an increase in metabolic activity throughout the body?
bind to receptor, activate gene transcription and protein translation
What does it mean that thyroid hormones can have permissive actions on many cells?
other hormones won't have their full effect unless thyroid hormone is present
What is the main effect of thyroid hormones on metabolism?
increases it (to 60-100% above normal)
What does thyroid hormone do to the need for energy?
increases
(increases number, size, and activity of mitochondria)
What does thyroid hormone do to the rate of protein synthesis and catabolism?
increases (to increase metabolism)
What does thyroid hormone do to the rate of carbohydrate metabolism?
increases
(since it increases metabolism in general)
What does thyroid hormone do to the rate of fat metabolism?
increases
(since it increases metabolism in general)
Does thyroid hormone cause vasoconstriction or vasodilation?
vasodilation
(more metabolism, more oxygen consumption, more blood flow for oxygen delivery)
What does thyroid hormone do to heart rate, contractility, and cardiac output?
increases
refers to the effects of the thyroid hormones mimicking the sympathetic nervous system, since they increase cardiac myocyte and pacemaker cell response to catecholamines
sympathomimetic effect
What does thyroid hormone do to respiration rate?
increases
(due to increased O2 demand for metabolism)
What does thyroid hormone do to secretion of digestive juices and GI motility?
increases
(for more metabolism)
What does thyroid hormone do to rate of hormone secretion of most other endocrine glands?
increases
(increased metabolism increases need for additional hormone stimulation by tissues)
What does thyroid hormone do to target cell responsiveness to catecholamines? (epi and norepinephrine)
increases
(sympathomimetic effect, which is a permissive action of the hormone)
What two hormones stimulate secretion of thyroid hormones?
TRH, TSH
(but then those thyroid hormones have a negative feedback effect and prevent further release of TRH and TSH)
How do levels of T3 and T4 affect TRH and TSH release?
prevent it
(negative feedback)
hormone secreted by the hypothalamus that regulates secretion of TSH by the anterior pituitary
thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH)
What secretes TRH?
hypothalamus
After being released by the hypothalamus, TRH binds its receptor on what cells in the anterior pituitary gland, releasing phospholipase C?
thyrotropes
enzyme activated when TRH binds its receptor on thyrotropes in the anterior pituitary
results in production of the second messengers DAG and calcium, which result in TSH release
phospholipase C
How do cold temperatures influence TRH secretion?
stimulate it
How do excitement and anxiety influence TRH secretion?
inhibit it
If there is increased thyroid hormone in bodily fluids, does this increase or decrease TSH and TRH secretion?
decrease
What secretes TSH?
anterior pituitary
After being secreted by the anterior pituitary gland, TSH binds to receptors on what cells to stimulate the adenylyl cyclase signaling cascade?
thyroid follicular cells
enzyme activated when TSH binds to receptors on the basal surface of the thyroid glandular (follicular) cells
adenylyl cyclase
What does TSH do to...?
- secretion of T3 and T4 by thyroid gland
- proteolysis of thyroglobulin
- activity of Na/I symporter
- iodination of tyrosine
- # & size of thyroid glandular cells (due to excess T3 and T4 leading to hypertrophy and hyperplasia)
increases
Which of the following would inhibit the release of thyroid hormone?
A. thyroid stimulating hormone
B. thyroid binding globulin
C. triiodothyronine
D. thyroid releasing hormone
C
____ is the hypothalamic hormone that causes the anterior pituitary to release ____, thus resulting in thyroid hormone release.
A. thyroid releasing hormone, thyroid stimulating hormone
B. thyroid stimulating hormone, thyrotropin releasing hormone
C. thyrotropin releasing hormone, thyroid stimulating hormone
D. thyroid hormone, thyrotropin releasing hormone
E. thyrotropin releasing hormone, thyroid hormone
C
Which biochemical event does not take place during thyroid hormone synthesis?
A. One monoiodotyrosine molecule combines with one di-iodotyrosine molecule to form one tri-iodothyronine molecule.
B. Four iodine molecules combine with one tyrosine molecule to form one tetraiodothyronine molecule.
C. Two iodine molecules combine with one tyrosine molecule to form one di-iodotyrosine molecule.
D. Two di-iodotyrosine molecules combine to form one molecule of thyroxine.
E. None of the above take place.
B
During thyroid hormone secretion...
A. The follicular cells phagocytize a piece of colloid
B. T4 and T3 are removed from thyroglobulin by lysosomal enzymes in the follicular cell; then they diffuse out of the cell and into the blood
C. T4 and T3 are secreted by exocytosis of the colloid that has been internalized by the follicular cells
D. Both a and b occur
E. Both a and c occur
D