Lesson 7 - Sexual Dysfunctions
1/26
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
What are sexual dysfunctions?
It refers to a lack of desire for or ability to achieve sexual satisfaction.
When can sexual dysfunctions occur?
It can occur at any stage of the sexual response cycle.
It is normal for couples to have sexual problems at some point in their relationship. But it is most common people between the ages of 40 and 65.
What is the sexual response cycle?
It is the sequence of physiological and emotional changes that occur when a person becomes sexually aroused and participates in sexually stimulating activities, including intercourse and masturbation.
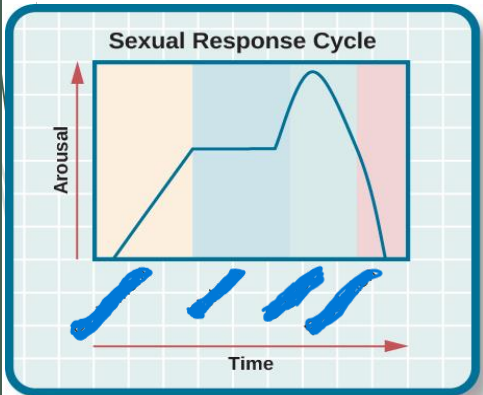
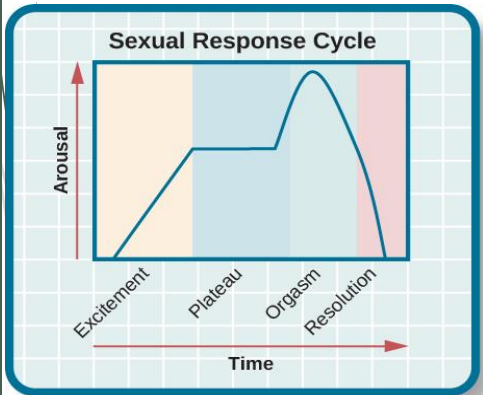
What are the features of desire?
Muscle tension increases.
Heart rate quickens and breathing quickens.
The skin may be red.
Nipples become hard or erect.
Increases blood flow to your genitals.
Erectile
They may feel that their vagina is "wet" or that their breasts are full.
A person may notice that their testicles swell or that their scrotum (the sac that holds the testicles) tightens, and they begin to secrete a lubricating fluid from the tip of their penis.
What are the features of arousal?
Changes in the desire phase are more intense.
The vagina continues to swell due to increased blood flow, and the walls of the vagina become darker in color.
Sexual organs are more sensitive.
Breathing, heart rate and blood pressure continue to increase.
Muscle tension continues to increase.
Muscle cramps may begin in the feet, face, and hands
Until when does an arousal last?
The arousal phase lasts until the pre-ecstasy.
What are the features of orgasm?
Involuntary muscle contraction or twitching.
Blood pressure, heart rate and respiration are their highest rates.
There is a forced release of sexual tension.
Vaginal muscle contraction.
Ejaculation
What is the peak of the sexual response cycle?
Orgasm
What is the resolution phrase?
During this phase, your body slowly returns to its normal function.
People may feel satiated and often tired.
Some women may return to orgasm with further sexual stimulation and experience additional orgasm.
Men usually need a period of recovery after orgasm, called a reflex period, during which they cannot reach orgasm again.
What are the types of sexual dysfunction?
Desire disorders: lack of sexual desire or interest in sex.
Arousal disorders: Inability to become physically aroused or aroused during sexual activity.
Orgasm Disorders: Delay or absence of orgasm (climax).
Pain Disorders: Pain during intercourse.
When are sexual dysfunctions most common?
It is more common in people over the age of 40, but it is often associated with ageing-related health decline.
What are Sexual Dysfunctions in Men?
Hypoactive Sexual Desire Disorder (Low Sexual Desire) - Lack of interest in sexual activity.
Erectile Dysfunction (ED) – Difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection.
Premature Ejaculation – Reaching orgasm too quickly, often causing distress.
Delayed Ejaculation – Difficulty or inability to reach orgasm despite stimulation.
What is the criteria for Male Hypoactive Sexual Desire Disorder?
Persistently or recurrently deficient (or absent) sexual/ erotic thoughts or fantasies and desire for sexual activity. The judgment of deficiency is made by the clinician, taking into account factors that affect sexual functioning, such as age and general and sociocultural contexts of the individual’s life.
The symptoms in Criterion A have persisted for a minimum duration and cause clinically significant distress in the individual of approximately 6 months
What is the criteria for Erectile Disorder?
At least one of the three following symptoms must be experienced on almost all or all (approximately 75%–100%) occasions of sexual activity
Marked difficulty in obtaining an erection during sexual activity.
Marked difficulty in maintaining an erection until the completion of sexual activity.
Marked decrease in erectile rigidity.
What is the criteria for Premature (Early) Ejaculation?
Persistent or recurrent pattern of ejaculation occurring during partnered sexual activity within approximately 1 minute following vaginal penetration and before the individual wishes it.
Note: Although the diagnosis of premature (early) ejaculation may be applied to individuals engaged in nonvaginal sexual activities, specific duration criteria have not been established for these activities.
What is the criteria for Delayed Ejaculation?
Either of the following symptoms must be experienced on almost all or all occasions (approximately 75%–100%) of partnered sexual activity
Marked delay in ejaculation.
Marked infrequency or absence of ejaculation Criteria for Delayed Ejaculation
What are the Sexual Dysfunctions in Women?
Female Sexual Interest/Arousal Disorder – Low sexual desire or difficulty becoming aroused.
Genito-Pelvic Pain/Penetration Disorder (GPPPD) – Pain during intercourse, vaginal tightness, or fear of penetration.
Female Orgasmic Disorder – Difficulty or inability to reach orgasm despite sufficient stimulation.
What is the criteria for Female Sexual Interest/Arousal Disorder?
Lack of, or significantly reduced, sexual interest/arousal, as manifested by at least three of the following:
Absent/reduced interest in sexual activity.
Absent/reduced sexual/erotic thoughts or fantasies.
No/reduced initiation of sexual activity, and typically unreceptive to a partner’s attempts to initiate.
Absent/reduced sexual excitement/pleasure during sexual activity in almost all or all (approximately 75%–100%) sexual encounters (in identified situational contexts or, if generalized, in all contexts).
Absent/reduced sexual interest/arousal in response to any internal or external sexual/erotic cues (e.g., written, verbal, visual).
Absent/reduced genital or nongenital sensations during sexual activity in almost all or all (approximately 75%– 100%) sexual encounters
What is the criteria for Genito-Pelvic Pain/Penetration Disorder?
Persistent or recurrent difficulties with one (or more) of the following:
Vaginal penetration during intercourse.
Marked vulvovaginal or pelvic pain during vaginal intercourse or penetration attempts.
Marked fear or anxiety about vulvovaginal or pelvic pain in anticipation of, during, or as a result of vaginal penetration.
Marked tensing or tightening of the pelvic floor muscles during attempted vaginal penetration.
What is criteria for Female Orgasmic Disorder?
Presence of either of the following symptoms and experienced on almost all or all (approximately 75%–100%) occasions of sexual activity
Marked delay in, marked infrequency of, or absence of orgasm.
Markedly reduced intensity of orgasmic sensations.
What are the Sexual Dysfunctions which take place in both Men/Women?
Substance/Medication Induced Sexual Dysfunction
What is Criteria for Substance/Medication Induced Sexual Dysfunction?
A clinically significant disturbance in sexual function is predominant in the clinical picture.
What are the causes of sexual dysfunction?
Physical causes
Psychological causes
What are the physical causes?
Many physical or medical conditions can cause problems with sexual function.
These conditions include diabetes, heart and blood vessel (blood vessel) disease, neurological disorders, hormone imbalances, chronic diseases such as kidney or liver failure, and alcohol use disorders and substance use disorders.
What are the psychological causes?
Decreased concern about sexual performance
Marital or relationship problems
Depression
Feelings of guilt
Body image concerns
Includes the effects of past sexual trauma
What drugs can cause sexual dysfunction?
Some antihistamines and decongestants can cause problems with erection or ejaculation.
Antidepressant
Antipsychotic drugs
Antihypertensive drugs
Hormonal drugs