Q4_Lesson 1 - Electric Potential Energy in a Uniform Electric Field
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Energy
whether it is mechanical, chemical, or electrical, comes in two forms
kinetic and potential
two forms of energy
Potential energy
stored energy of an object at rest
kinetic energy
Potential energy is converted into____when an object moves
True
(T/F) ALL electrical circuits require the storage of energy before transformed into light, heat, and motion
electric potential energy
stored energy in a circuit
accelerates
Once the ball begins to fall off from the table, it _______ and the potential energy is transformed into kinetic energy
Electric charges, mass of objects
_____ in an electric field are comparable to the ____ in a gravitational field
electric potential energy
determines how much stored energy a charge has
Electric potential energy
defined as the energy needed to move a charge against an electric field
conservative forces
Potential energy can only be defined for ___
conservative forces
where the force required to move an object from one position to another is independent of the path taken
Electrostatic force
force required in the interaction of charges
Electrostatic force
example of a conservative force
Electric potential
amount of work required to bring the unit positive charge from infinity to a certain point
electric potential energy
amount of energy required to move a charge against the electric field
Electric force (F)
required to move an electric charge that contains potential energy either towards an opposite charge or against a like charge
UA > UB
What can you say about the relative magnitudes of UA and UB when the work is positive?
UA < UB
What can you say about the relative magnitudes of UA and UB when the work is negative?
change in kinetic energies (ΔK)
the total work done is equal to the ____
KA – KB
change in kinetic energies (ΔK) formula

The work done expressed in terms of internal energy U,
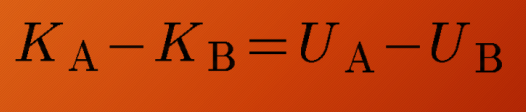
We can equate the change in K and change in U
Law of conservation of mechanical energy
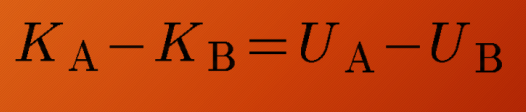
WA→B, J
UE, J or Nm
q0E, C
F, N
r, m
k, 9.0 ✕ 109 Nm2 /C2
m, kg
a, m/s2
P, J/s or W
Symbol and Unit of:
Work done by force
Electric potential energy
Enclosed electric charge
Force
Radius
Coulomb’s constant
Mass
Acceleration
Power
equally distributed parallel, does not change.
In a uniform electric field, the electric field lines are ______ to each other and the
strength of the field ____
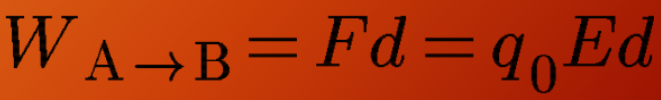
work done by the electric field
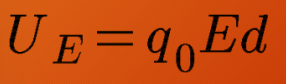
potential energy for the electric force
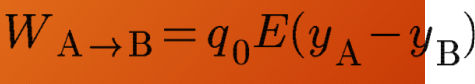
work done by the electric force
increases
The potential energy U ____ if the charge q0 moves in the direction opposite of the electric force
decreases
The potential energy U ___ if the charge q0 moves in the direction similar to the electric force
shared property
In some cases, the potential energy U becomes a “___” of two charges
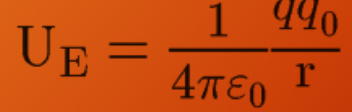
Electric Potential Energy of Two Charges
law of conservation of mechanical energy
when applied to electric charges, refers to the total kinetic and potential energies present in a system
downward
In a uniform electric field, where the strength of the field is not altered, the work done by the electric field is determined by the product of the force magnitude and the displacement component in the ____ direction of the force