(G12 EOT T1) AP physics C: Electromagnetism review 1/2
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Grade 12 EOT review by Shaikha :3 study well!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms

What is the unit of electric flux?
NM²/C
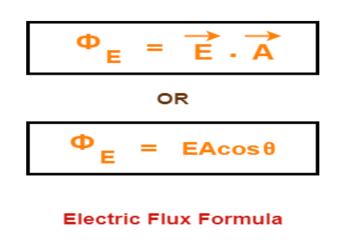
What is the formula of electric flux?
The electric flux through a surface is calculated by multiplying the electric field (E) by the area (A) of the surface, and considering the angle between the field lines and the normal to the surface.
What is the unit of electric field (E)?
N/C
What are the formulas of electric field?
F/q, Force over charge
V/d , The electric potential over the distance
Unit of voltage or potential?
V (volts)
Unit of area (A)?
m²
Unit of distance (d or sometimes r)?
m (meters)
Is there a unit for theta? (θ)
No
What is the SI unit of flux?
kgm³s-3A-1
What is the unit of Linear density? λ
q/λ
(I)(t)/λ
Unit = (A)(s) / m
What is the unit of surface charge density? σ
σ = q/a
σ = it/a
Final unit: As/m²
What’s the unit of volume charge density ρ?
ρ = q/v
it/v
AS/m³
Is Area a vector or a scalar?
Vector
Define Electric flux
The electric field that passes through a certain area
What are the factors of electric flux?
Electric field strength
Area of the surface
The angle between the electric field and the normal to the surface. (cos θ)
How does electric field strength affect electric flux?
The closer the field lines are, the stronger the field, the greater the flux.
What is the relationship between area and electric flux?
Directly proportional. The more area, the more flux.
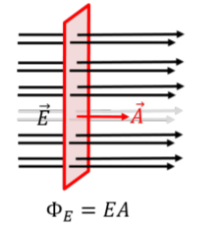
In the context of electric flux, what does it mean when the electric field is perpendicular?
It means that the angle between the area vector and the electric field is 0.
(cos(0) is = 1).
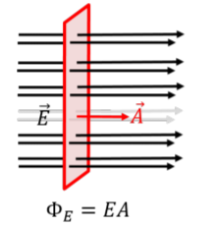
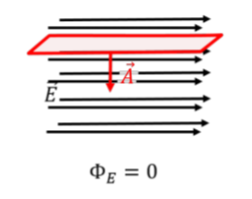
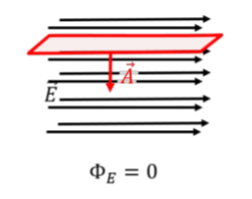
In the context of electric flux, what does it mean when the electric field is parallel?
It means that the angle between the area vector and the electric field is 90.
(cos(90) is = 0).
What is the formula of electric flux through a closed surface?
hint: one of Gauss’ law’s formulas
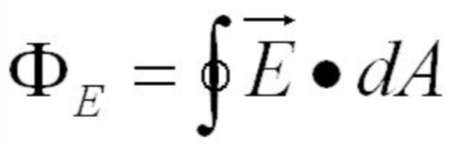
What are the two formulas of Gauss’ law?
q/ε0
See image
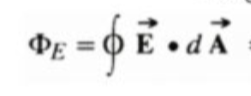
What is the value of ε0?
~8.85 × 10⁻¹²
(will be given in exam anyway)
What is the formula of work?
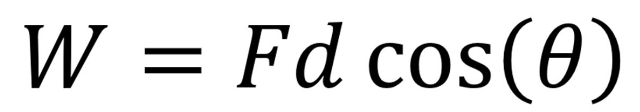
What is the formula of work when forces vary?
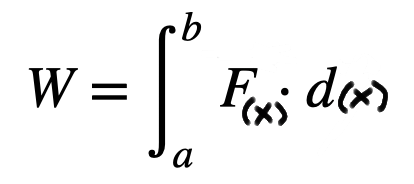
What is the formula of electric force?
kQq/r²
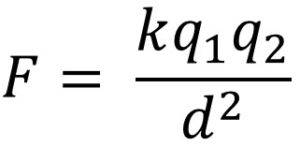
What is the formula of the work done from point i to point f?
W = -(Uf - Ui)
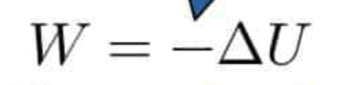
How do we find U from electric force?
kQq/r
When a charge moves against or along the direction of the electric field, how does that affect it’s potential energy?
(+) Charge | (-) Charge | |
Along E | Lose PE | Gain PE |
Opposite E | Gain PE | Lose PE |
What is the formula of electric potential or voltage (V)?
V=U/q
U=Electric PE
q= test charge
What are the two units of electric potential?
J/C
V (volts)
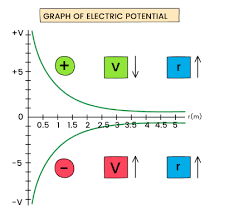
What happens to V as you get closer or farther to a negative and/or positive charge?
An electric potential is always positive and decreases away from a positive charge, and is always negative and increases away from a negative charge.
If you are infinitely far away from either a (-) or (+) charge, the potential will always be 0
What is the formula of potential difference?
ΔV = Vf - Vi
V = U/q or Kq/r
What is the formula of potential in a uniform electric field?
PE=-qEd
V=-Ed
q = charge will always be negative
E = field strength
d = displacement
What is an equipotential surface?
An equipotential surface is a three-dimensional surface on which every point has the same electric potential. This means that if a charged particle moves along this surface, no work is done by or against the electric field
What are the properties of an equipotential surface?
The potential surface ΔV between 2 points is 0
Net work is always 0 from point A to point B
Electric field lines are perpendicular to the surface
What happens to potential, the closer we get to the charge in an equipotential surface?
It gets higher the closer we get to a charge
In an equipotential surface, what happens to potential as we move along the electric field?
Decreases
In terms of a conducting/metal sphere, What happens to the electric potential and the field as we move from inside to out?
(remind me to take a pic of my notebook)
Electric potential inside a conducting sphere will be constant but as we leave the surface, it begins to decrease.
Electric field inside the sphere will always be 0 but as we leave the surface it decreases.
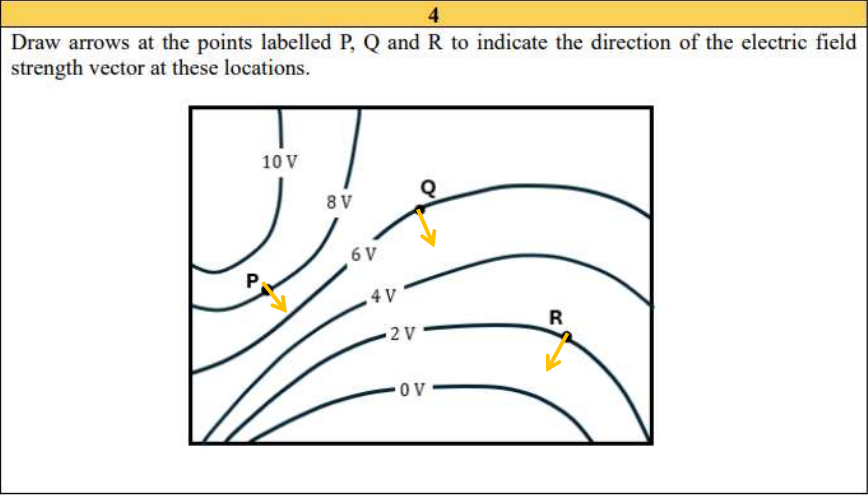
Where will electric field lines point to in an equipotential surface?
Always points in the direction of decreasing potential (from higher voltage to lower voltage).
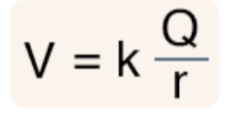
Between a bigger and a smaller sphere, which will have more potential?
(hint: pay attention to r)
The smaller sphere will have more potential as the r is less.
(Remember, r is inversely proportional to potential!)
Where will current flow from?
A) high to low potential
B) low to high potential
A
Current flows from high to low potential conventionally