Proteoglycans and Glycoproteins
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Differentiate between Proteoglycans and glycoproteins.
Proteoglycans
Protein core
Glycoaminoglycan chains (w/ repeating disaccharides)
Glycoproteins
Protein core
Ogliosaccharide (no repeat disacc.)
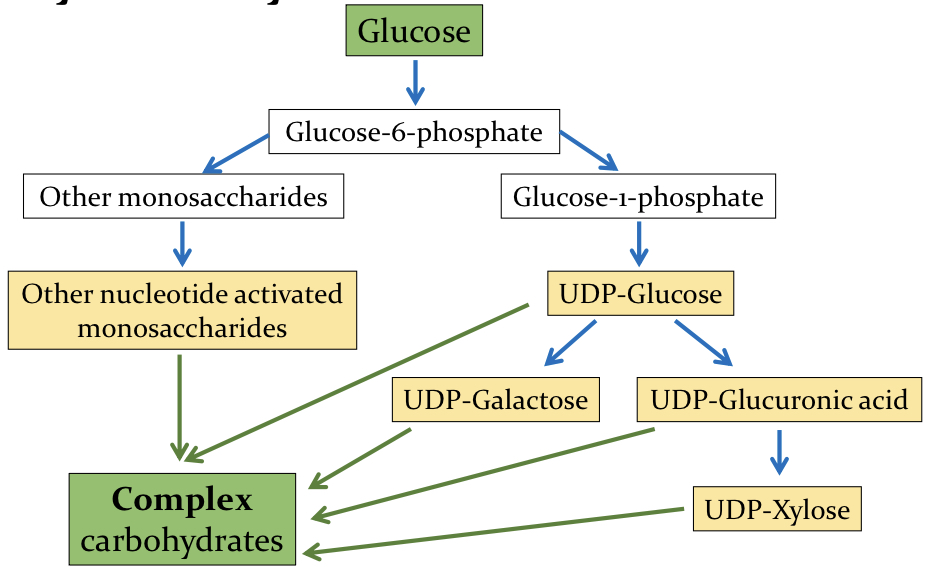
How are complex carbs built?
Monosaccs are added one at a time to growing carb.
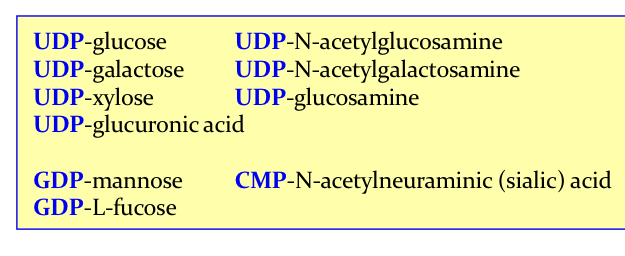
Needs to be nucleotide activated form ie most freq w/ UDP (also can be GDP or CMP, see in pic)
Nuc activated form is specific for a given monosacc
How is glucose used for complex carb synthesis and what pathways does it go through?
Describe glycotransferases?.
Catalyzes addition of monosaccs to other molecules
Specific for given monosacc
Hydrolysis of nuc linkage provides energy for formation fo the glycosidic bond
What are glycoaminoglycans(GAGs)?
Repeating disacc units of a acidic sugar (glucuronic or iduroninc acid) and N acetylated amino sugars
All but hyaluroninc acid attached to protein core and syn in the golgi
All negative charged but hyaluronic acid is sulfated
Neg charges attract water (sponges) —> confer resilience to tissues under compression.
Describe where hyaluronic acid is found and what it is used for in the OR?
Widespread structural glycoamioglycan in the human body
Found in cartilage, synovial fluid, vitreous humor of the eye
Major lube of the joints
Ess for embryogenesis, morphogenetic, and wound healing.
Used in eye surgery (healon) and for OA pain(intraartiuclar Synvisc injection)
What are chondroitin sulfates?
Sulfated @ 6th or 4th position of N acetyl galactoamine
Main GAG is aggregated in Proteoglycans —>aggregate w/ hyaluronic acid
Most abundant GAG in humans
Largest concentration in cartilage.
What is Dermatan Sulfate?
Differes form chondrotin-sulfate in carboxyl orientation
Mainly found in skin, blood vessels, and heart valves.
Increased conc in mitral valves is associated with thickening and abnormal displacement of the valve in the L atrium of the heart (mitral valve prolapse)
What is keratan sulfate and what is it associated with?
Only GAG w/o acidic sugar
2 types of KS
KS I: linked to amide of Asn (cornea)
KS II: linked to hydroxyl of Ser (cartilage)
Clinical: Carbohydrate sulfotransferase 6 (CHST6) deficiency —>undersulfated keratan sulfate in cornea —> muscular corneal dystrophy(cloudy cornea, vision impairment)
What is heparin and herparan sulfate associated with?
Similar but differs in sulfation pattern (heparin more sulf)
Heparin sulfate:
Part of Perlecan (major proteoglycans in basement membrane)
Component of cell surface mole/receptors.
Heparin:
Stored in mast cells
Used as a anticoagulant (management of MI and DVT)
What is a protein which at least one GAG chain is attached?
Proteoglycans
Either cell surface receptors or ECM molecules
Attached to protein core via spec linkage To either hydroxy of Ser or amide of Asn
***cartilage Proteoglycans (Aggrecan)
Highest conc of GAG, main proteoglycans (aggrecan) ~ 100
GAG mainly chondrotin sulfates w/ some keratan sulfatates
“Brush bottle” appearance
What is the role of GAGs in the organization of the cartilage ECM?
Aggrecan is retained in cart ECM via non covalent interaction w/ hyaluronic acid and link protein(small glycoprotein)
Large GAG content provides tissue w/ resilience under compression
Clinical rel: OA, RA, and SLE are accompanied by excessive degration of cartilage proteoglycans —>defective cartridge func
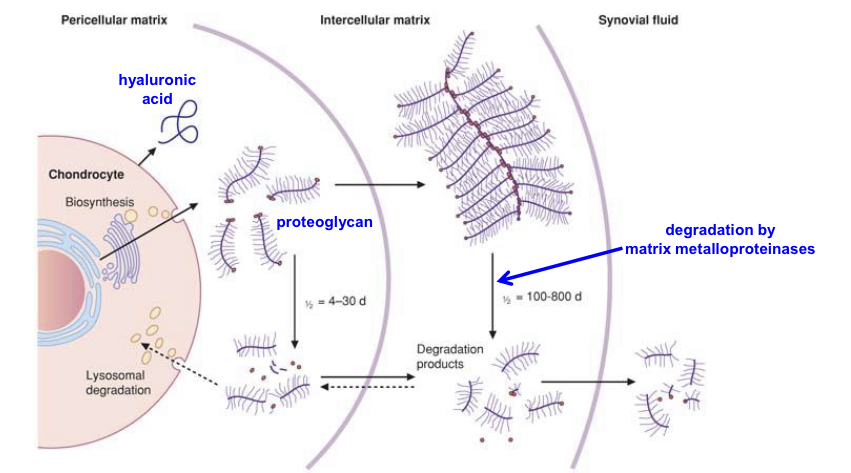
Describe the synthesis of proteoglycans.
Syn of amino sugar
AA derived from glucose. Glutamine provides amino group.
Syn of glucuronic acid (cytosol)
From UDP glucose via oxidation
Syn of core protein (ER)
HA doesn’t require protein core for syn
Syn of GAG chain ( Golgi, but for HA plasma membrane)
On trisacc links at serine and sometime asparagine of the core protein
Glycosyltransferases —> prod growing GAG via adding UDP sugars
Sulfation (Golgi)
Sulfotransferases add sulfate groups to GAG —> donor is PAPS (3 phosphoadenosyl 5 phosphosulfate)
How are these GAGs degraded?
Taken up by the cell via endocytosis
Transported to lysosome —.degraded by specific enzymes
Clinical tie: Deficient lysosomal degradation of GAGs —> more severe diseases (mucopolysaccharidoses - lysosomal storage dis)
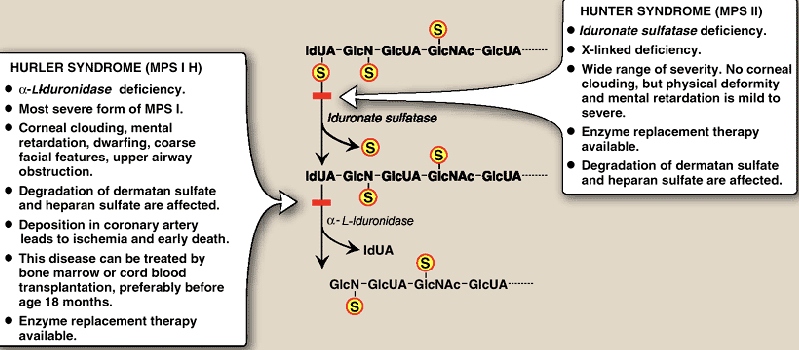
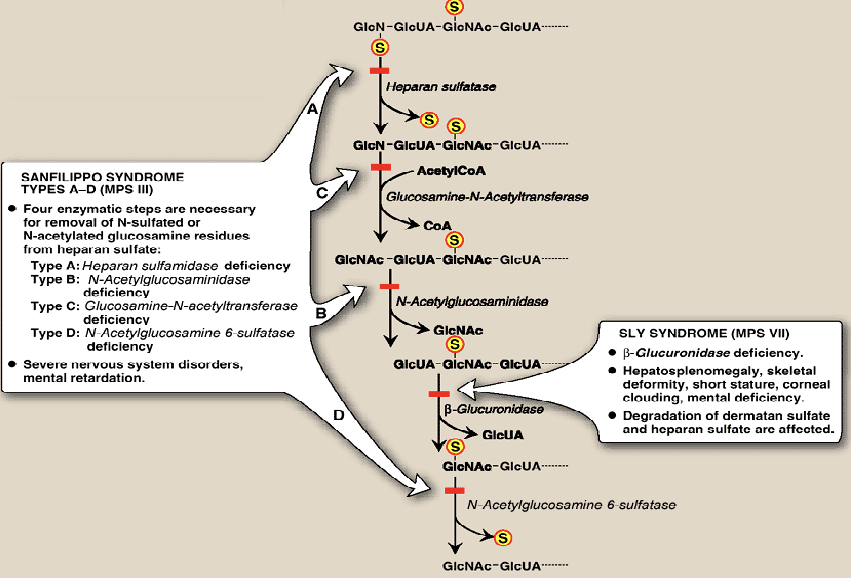
What is Hunter and Hurler syndrome? What are their symptoms, causes, and treatments?
What is Sanfippo syndrome types A-D (MPSIII)? WHat is Sly syndrome (MPSVII)? WHat are their causes, treatments, and symptoms?
What are glycoproteins, what are they found in and why are they important?
Protien within ogliosaccs attached covalentyl
No repeating disacc units
Much small than GAGs
Functions are wide spread:
Cell surface recognition molecules/receptors (binding sites for pathogens)
Blood group antigens
ECM molecules (laminins, collagens, fibronectin)
Plams proteins (ogliosacc chains increased solubility of proteins)
What is the difference between O and N linked oligosaccarides?
O linked
Attached to hydroxyl group of Ser or Thr, most linear
N linked
Attached to amide of asparagine, branched, either minor fish or complex
General rule:
1st protein is syn in the ER, then monosacc is nucleotide acitivated, then added via glycotransferases
O linked
Bulit in Golgi
N linked
Builds lipid (dolichol{side product of cholesterol syn}) in the membrane of the ER
Oglio precursor transferred to protein in the ER—→completed in the Golgi
What is the role of N linked ogliosaccs in lysosomal targeting of proteins?
Delivering the lysosomal enzymes into the lysosome req phosphorylation of mannose on N linked ogliosacc of the lysosomal enzyme.
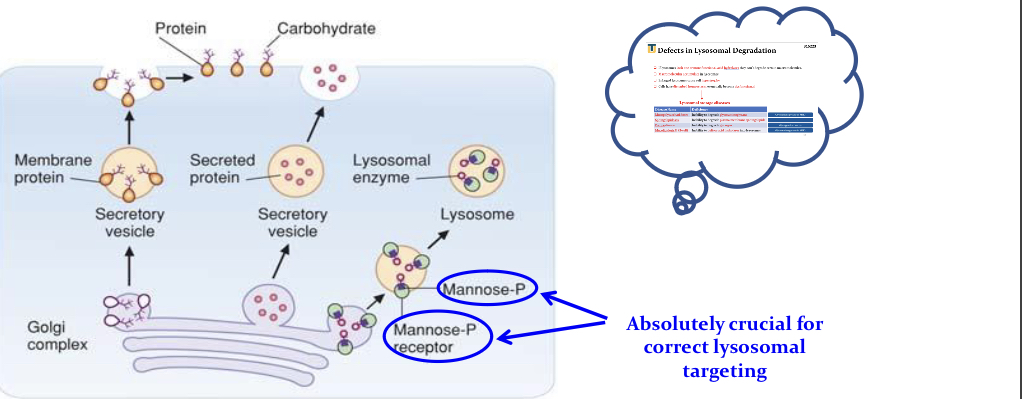
What is mucolipidosis II (I cell disease)?
Type of lysosomal storage diseases
Deficient mannose phosphorylation on lysosomal enzymes:
Not delivered tot he lysosome(instead are secreted)
Macromol are not degraded (enlarged lysosome, Inclusion bodies)
What are examples of glycoproteins in the MSK?
Osteonectin
Bone glycoproteins
Interacts with bone mineral and collagen fibers
Facilitates collagen fiber mineralization
Link proteins
Cartilage glycoprotein
Stab interaction btwn hyaluronan and aggrecan
Dystroglycan
Skeletal muscle cell membrane GP
Binds to laminins —>med cell attachment to adj cell membrane
Clinical rel: Defective glycoaminoglycans of dystroglycan lerads to muscular dystrophy.