the brain
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
brainstem
connects brain and spinal cord, regulates vital functions
pons and medulla
pons
coordinates movement
influences sleep, dreaming, and arousal
medulla
located at the top of the spinal cord
controls life sustaining functions like heartbeat, breathing, and swallowing
damage = death
reticular formation
system of nerves controlling arousal and attention
notices changes in environment
cerebellum
balance and motor control
cerebral cortex
wrinkled outer covering of the brain
limbic system
involved in emotions, motivation, memory, and learning
thalamus, hypothalamus, pituitary gland, hippocampus, amygdala
thalamus
relay station for all sensory information except smell
hypothalamus
controls pituitary gland to maintain homeostasis: body temperature, thirst, hunger, sleeping, and waking
pituitary gland
master gland of the endocrine system
growth hormone
produces hormones to influence other glands
hippocampus
forms long term memories
you would remember if you saw a hippo on campus
amygdala
fear response (fight or flight)
corpus callosum
bridges the right and left hemispheres, allows them to communicate with each other
parietal lobe
bodily sensations
contains primary sensory cortex
frontal lobe
higher mental functions: planning, personality, complex decision making
contains primary motor cortex
temporal lobe
processes audio, hearing, learning, memory, and language
contains auditory cortex
occipital lobe
processes visual information from the eyes
contains visual cortex
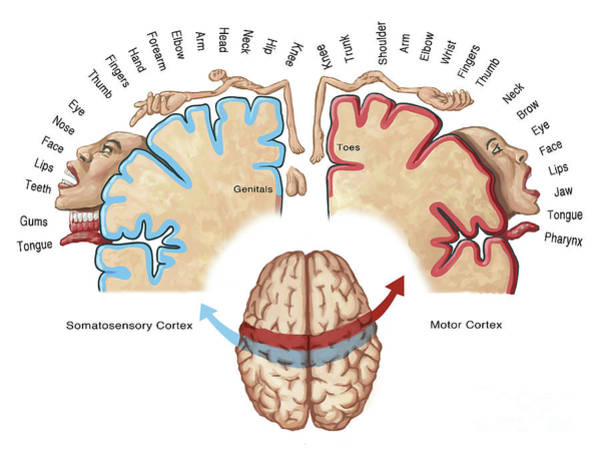
motor cortex
controls voluntary movement
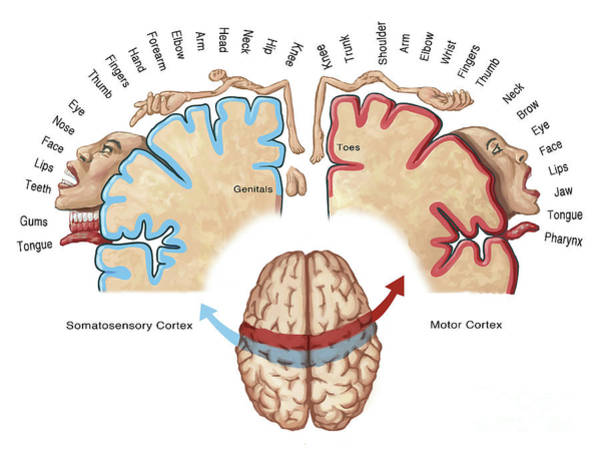
somatosensory cortex
processes sensory information from skin and internal body receptors
split brain research
studying patients who have had their corpus callosum removed
send messages to each side
Broca’s Area
speech production
Wernicke’s Area
language understanding
Broca’s Aphasia
speech is impaired, understands everything
Wernicke’s Aphasia
understanding is impaired, can speak fine, but it doesn’t make sense
brain plasticity
the brain’s ability to change in response to experience
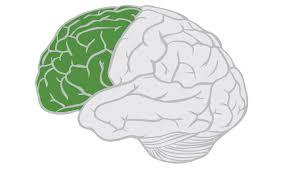
frontal lobe
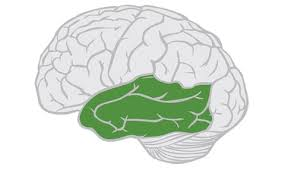
temporal lobe
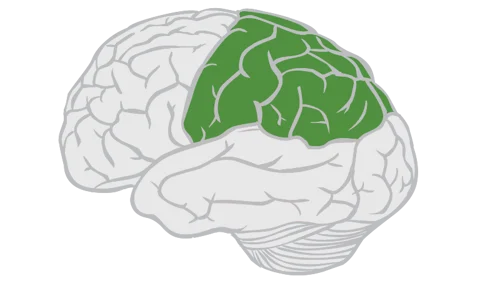
parietal lobe
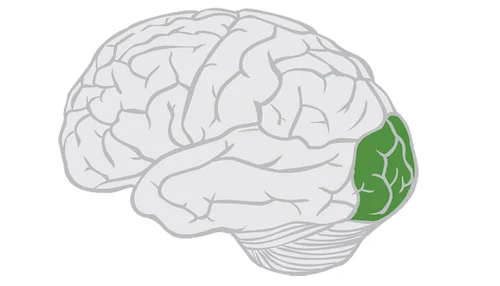
occipital lobe
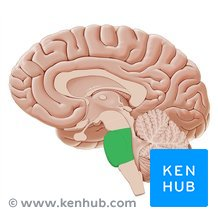
pons
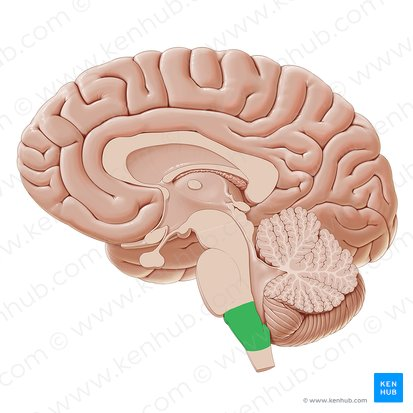
medulla
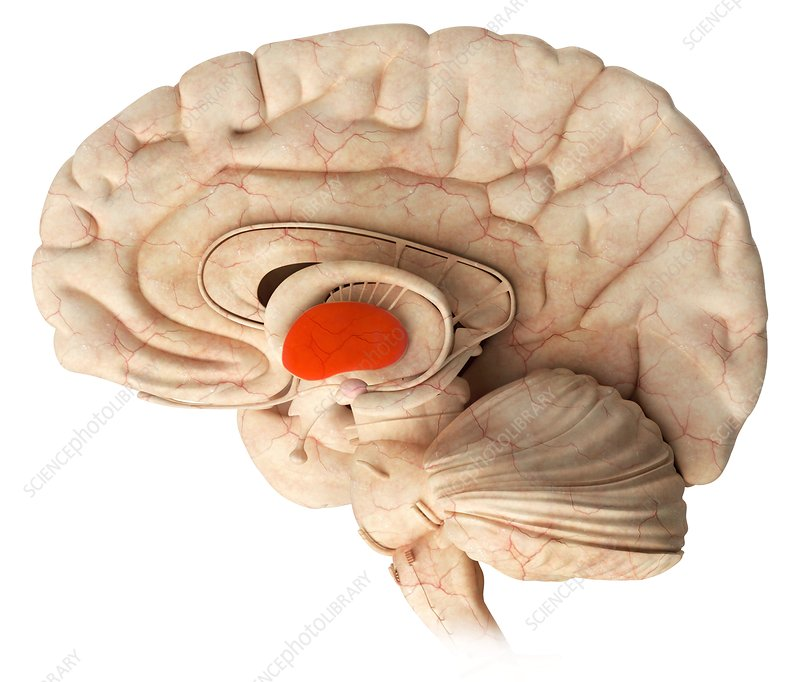
thalamus
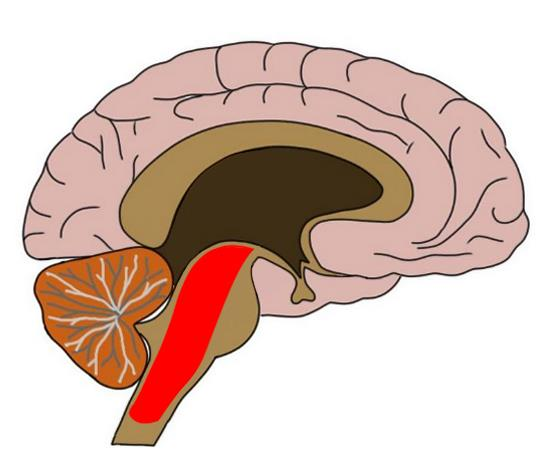
reticular formation
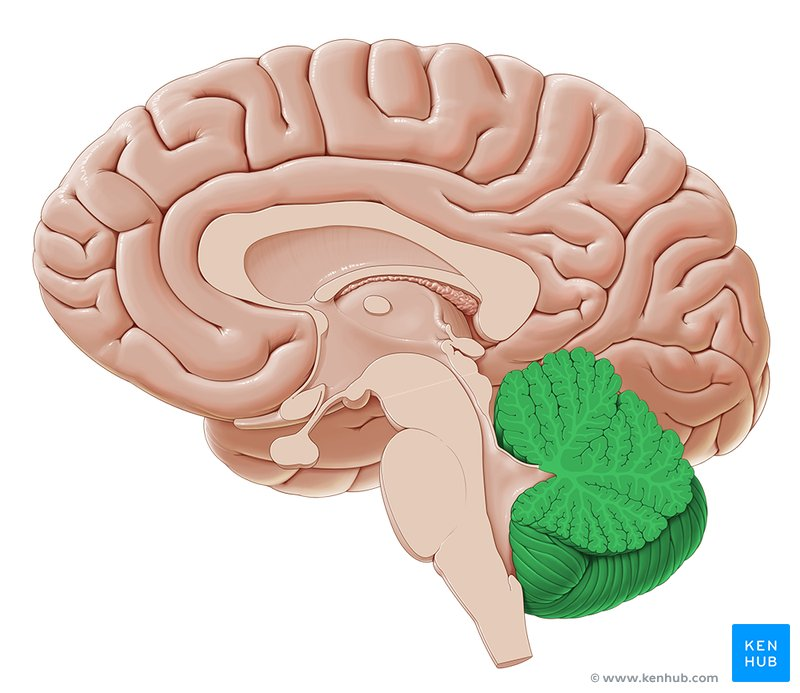
cerebellum
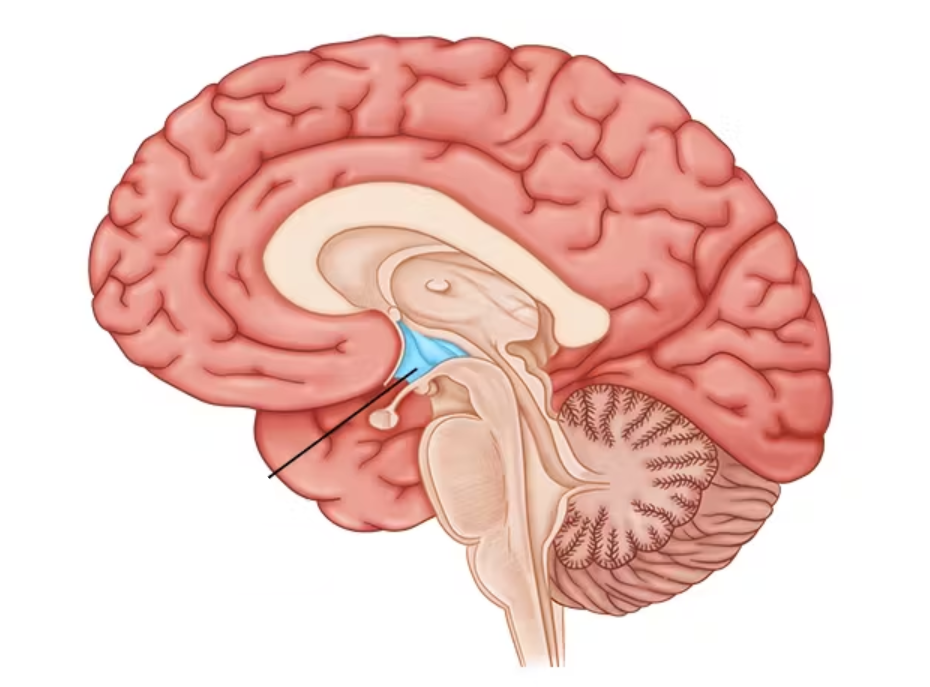
hypothalamus
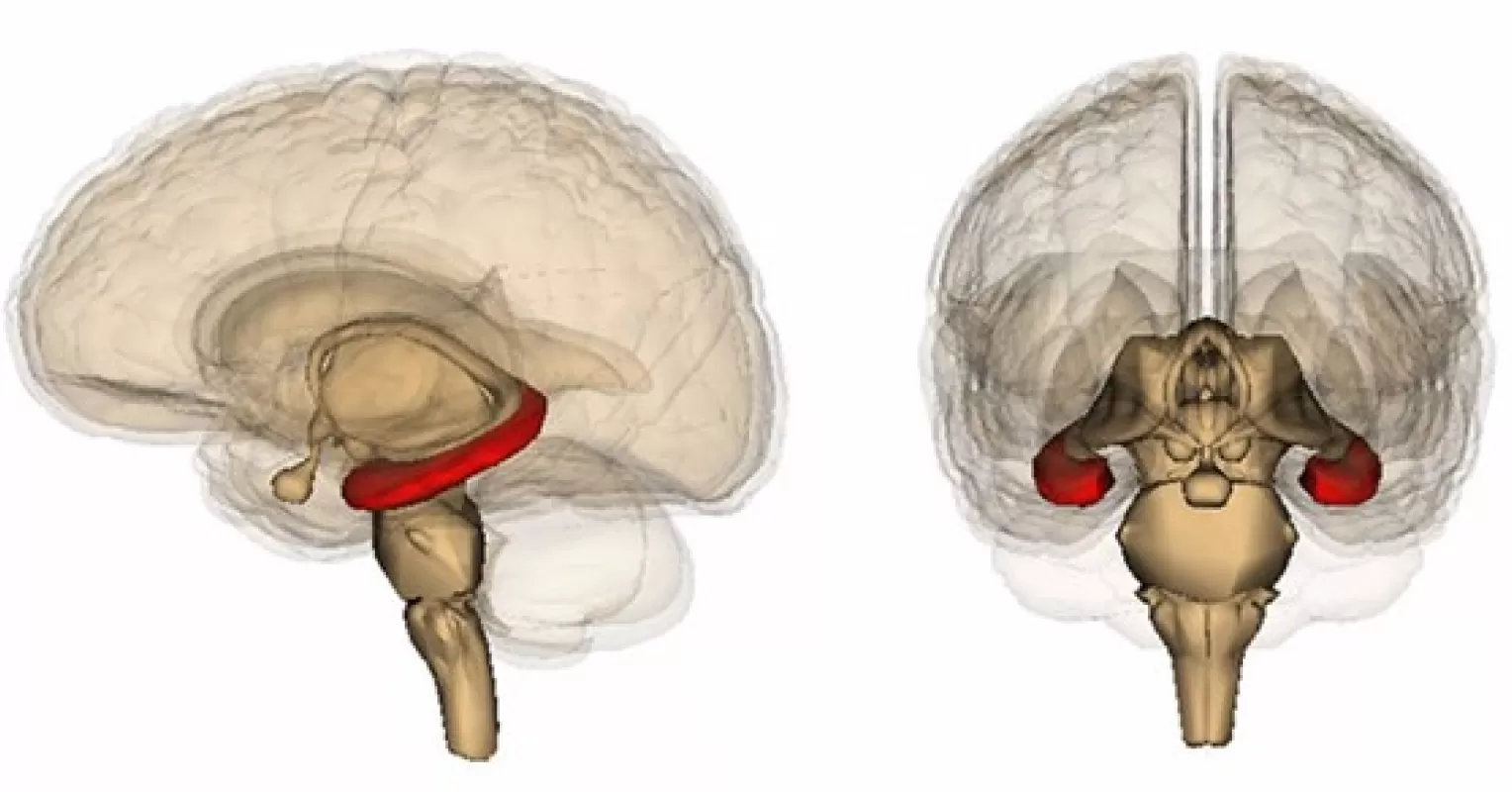
hippocampus
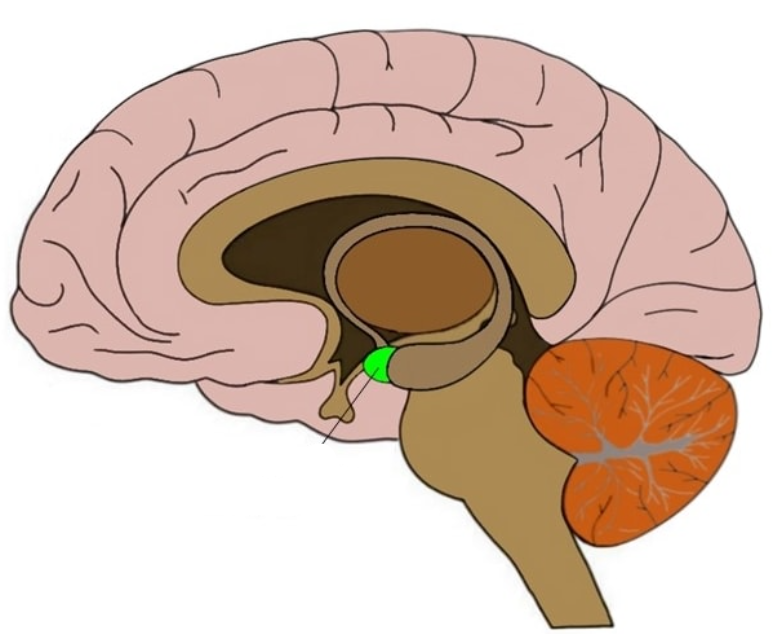
amygdala
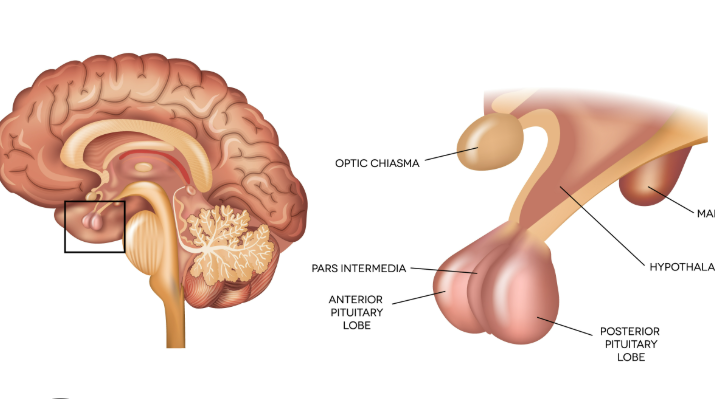
pituitary gland
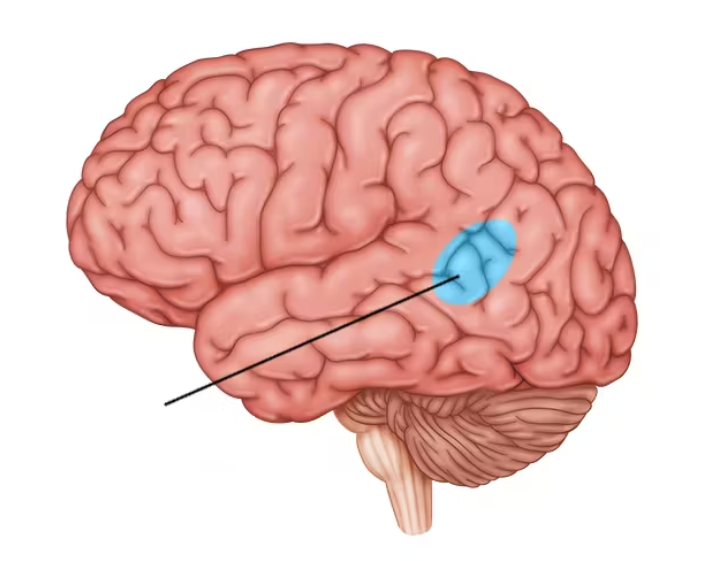
wernicke’s area
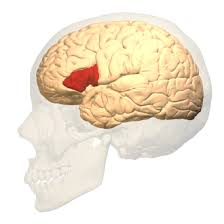
broca’s area
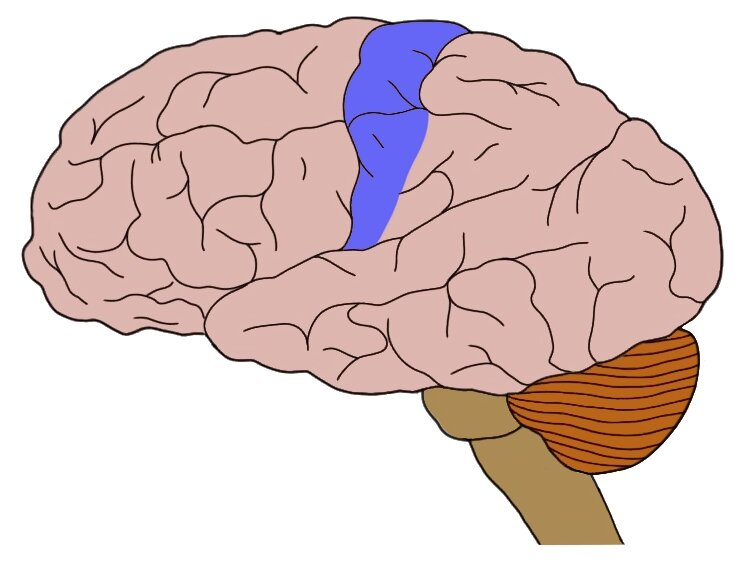
primary sensory cortex
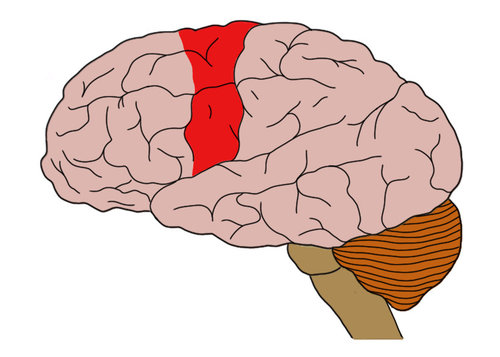
motor cortex
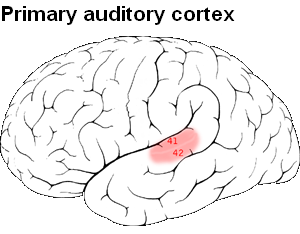
auditory cortex
visual cortex