electric fields and capacitance
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
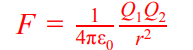
Coulomb’s Law
magnitude of force between two point charges in a vacuum is directly proportional to the product of their charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the charges
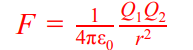
electric field strength
force per unit charge experienced by a charged object in an electric field
electric potential
work done per unit charge on a positive charge in bringing it from infinity to that point in the field
greatest at the surface of a charge
0 at infinity
electric potential difference
energy needed to move a unit charge between two points
capacitance
charge stored by a capacitor per unit potential difference
what is a capacitor
2 conducting parallel plates with a gap between them
they may be separated by a dielectric
when connected to a power supply, opposite charges build up on the plates so a uniform electric field is formed
permittivity
property of dielectrics
measure of the ability to store an electric field in the material
relative permittivity formula
ε =
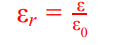
dielectric
formed of polar molecules, one end is positively charged and the other is negative
when there is no electric field, the molecules are arranged in random directions
when there is an electric field, they move and align themselves with the field
each molecule has its own electric field (the strength depends on the permittivity)
these oppose the field formed by the capacitor, so the electric field strength decreases
potential difference required to charge the capacitor decreases
capacitance increases as C = Q/V
how do you charge a capacitor
connect it in a circuit with a power supply and resistor
what happens in the charging of a capacitor
current flows and a negative charge builds up on the plate connected to the negative terminal
on the opposite plate electrons are repelled by the negative charge building up on the other plate
electrons move to the positive terminal
equal but opposite charges formed in each plate
potential difference is created
as the charge across the plates increases, the potential difference increases but electron flow decreases due to the increasing force of electrostatic repulsion
the current decreases and eventually reaches zero
how do you discharge a capacitor
connect it to a closed circuit with a resistor
what does the time constant (RC) represent in charging
time taken to charge a capacitor to 1 - 1/e of its initial value
what does the time constant (RC) represent in discharging
time taken to discharge a capacitor to 1/e of its initial value