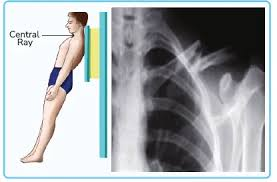
Anatomical Terms Radiographic Procedures
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Caudad
Towards the Feet
Cephalad
Towards the head
Central
Midpoint of the organ
Peripheral
Out towards the edge
Medial
Towards the midline
Lateral
Away from Midline
Distal
Furthest from point of attachment
Proximal
Closer to point of attachment
Parietal
Wall/lining of body cavity
Ipsilateral
Situated at the same side of the body
Contralateral
Opposite side of the body
Palmar
Palm of hand
Plantar
Sole of foot
Dorsum
Top of foot
Projection
Path of Central Ray
Position
Posture of the patient
View
How the body part is seen by the image receptor
Method
Specific radiographic projection that is named after some1
Axial
angle of the central ray that is 10 degrees or more
Tangential View
CR traces along the surface of a bone or object, rather than passing directly through it
Lateral View
CR passes through the side of the body
Oblique View
CR enters at a side angle
Decubitus
Central Ray is Horizontal to floor
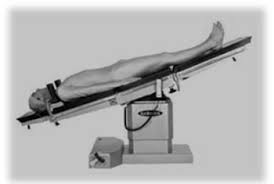
Trendellenburg Method
Head is LOWER than the feet
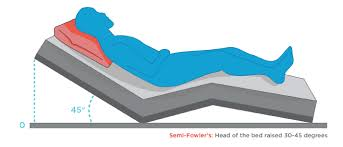
Fowler Method
Head is HIGHER than the feet
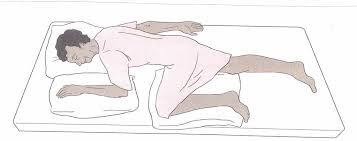
Sim’s Position
patient lies on their left side with the right knee drawn up towards the chest and the left arm extended behind them
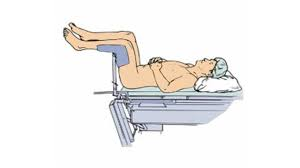
Lithotomy Postition
lying supine with the legs flexed at the hips and knees, and supported in stirrups or boot-like leg holders.
Evert
Foot turning away from the body
Invert
Foot turning towards (into) the body
Lateral position
Laying on the side
Oblique Positions
Right Posterior Oblique (RPO)
Left Posterior Oblique (LPO)
Right Anterior Oblique (RAO)
Left Anterior Oblique (LAO)
Circumduction
Circular Movement of a Limb
Tilt
Tipping or Slanting of a body part
Deviation
Moving away from the normal postion
Lordotic Position
Upright position where pt is leaning backwards