Edexcel A Level Politics
1/275
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
276 Terms
Additional Member System (AMS)
A hybrid electoral system that has two components or elements. The voter makes two choices. Firstly, the voter selects a representative on a simple plurality (FPTP) system then a second vote is apportioned to a party list for a second or 'additional' representative.

Affirmative Action
the policy of favoring historically disadvantaged members of a community.

altruism
Concern for the interest and welfare if others based on ration self interest or a belief that humans are social beings with a capacity for social solidarity.

Anarchical society and society of states
Theory that the states of the world can be members of a society despite the anarchical nature of the international system

Anti-permissiveness
A rejection of permissiveness, which is the belief that people should make their own moral choices, suggesting there is no objective right and wrong.

Assimilation
The process by which social minorities adopt the values, customs and beliefs of the majority.

Atomism
The idea that society is made up of self-interested and self-sufficient individuals (known as also known as egotistical individualism)
Authoritative works
Works written by experts describing how a political system is run, they are not legally binding but are taken as significant guides.

Authority
For Conservatives, this is the idea that people in higher positions in society are best able to make decisions in the interests of the whole society;authority thus comes from above. From the anarchic perspective authority is the the right of one person or institution to influence the behavior of, and is seen as commanding, controlling and corrupting.

Autocratic State
A state that is ruled by a single person with unlimited power.

autonomy
A form of self government or legislation, a combination of freedom and responsibility in which the individual is not subject to the will of the state or any other person.

Backbenchers
MPs or Lords who do not hold any government office.

Bipatisanship
Attempts within the structure of the US Congress to try and ensure that the tow main parties must work together in order to fulfill Congressional functions.
Bipolarity
International system revolving around two poles
Black Nationalism
A reaction to white oppression originating in the mid-20th century.

Cabinet
The Prime Minister and senior ministers, most of who lead a particular government department.

Campaign Finance
Refers to all funds raised to promote candidates, political parties or policy initiatives and their agendas during an election.

Capitalism
An economic system, organised by the market, where goods are produced for profit and wealth is privately owned

Change to conserve
The belief that society should adapt to changing circumstances rather than reject change outright and risk rebellion or revolution

Chauvinist Nationalism
A form of nationalism that believes one nation is superior to others, seeing them as a threat to their survival.

Checks and Balances
The division of power between the three branches of government where each branch has a direct ability to prevent action from another branch.
Civic Nationalism
A form of nationalism based on the active participant of its citizens and a shared equal vision of equal citizens

class consciousness
The self-understanding of social class that is a historical phenomenon, created out of a collective struggle
Class dealignment
The process where individuals no longer identify themselves as belonging to a certain class and for political purposes fail to make a class connection with their voting pattern.

Classical liberals
Classical liberalism is a philosophy developed by early liberals who believed that individual freedom would best be achieved with the state playing a minimal role.

coalition government
A government that is formed of more than one political party. It is normally accompanied by an agreement over policy options and office of state, as was the Conservative-Liberal-Democrat coalition from 2010-2015

Codification
A constitution that is written down in one document

collective responsibility
Principle by which ministers must support Cabinet decisions or leave the Executive.
Collectivisation
The abolition of private property and its replacement by collective ownership

Common Law
Laws made up by judges (rather than statute law) when the law in question doesn't cover a particular issue or is unclear
Common ownership
Ownership of the means of production so that all are able to benefit from the wealth of society and to participate in its running.

Communism
The communal organisation of social existence based on the common ownership of wealth.

Complex Interdependence
Theory that states and their fortunes are inextricably tied together.

Congressional caucuses
These are groups of US legislators who share special interests and meet to pursue common legislative objectives, e.g. black caucus, women's caucus and Hispanic caucus.

Confidence and supply
The rights to remove the government and to grant or withhold funding. Also used to describe a type of informal coalition agreement where the minority partner agrees to provide these things in exchange for policy concessions.

conservative justice
A justice with a strong belief in 'stare decisis' with s more narrow view of the US constitution, more likely to believe in a literal interpretation of the wording, and believing in a generally smaller government.

Constitution
A set of rules determining where sovereignty lies in a political system, and establishing the precise relationship between the government and the governed.

Constitutional rights
The rights specifically outlined for citizens within the US Constitution, Bill of Rights and subsequent Amendments.

Conventions
Traditions not contained in law but influential in the operation of a political system.

Co-operation
Working collectively to achieve mutual benefits.

Cosmopolitan integration
The maximum freedom for minority, as well as majority individuals, to mix with, borrow and learn from other cultures.
Cultural Feminism
A form of difference that seeks to challenge the dominance of male culture in society, instead seeking to promote 'women's values'.

Cultural globalisation
Growing transmission of ideas, ideas, meanings and values around the world.

Culture
Involves values, customs and beliefs that are passed on through the generations via learning.

Developmental individualism
The idea that individual freedom is linked to human flourishing.
Democratic Deficit
A flaw in the democratic process where decisions are taken by people who lack legitimacy, not having been appointed with sufficient democratic input or subject to accountability.

Dependancy Theory
Emphasises structural imbalances within capitalism that impose dependency on poorer states.

Devolution
The dispersal of power, but not sovereignty within a political system.

Dialectic
A process of development that occurs through the conflict between two opposing forces. In Marxism, class conflict creates international contradictions within the society, which drives historical change.
Discrimination
Less-favorable treatment of some groups of people compared to other groups.

Disillusion and apathy
A process of disengagement with politics and political activity. Having no confident in politics and politicians as being able to solve issues and make a difference. Manifested in low turnout at elections and poor awareness of contemporary events.
Direct Action
A whole range of political actions from non-violent to violent actions taken outside of the legal and constitutional framework.

Direct Democracy
All individuals express their opinions themselves and not through representatives acting on their behalf. This type of democracy was emerged in Athens in classical times and direct democracy can be seen today in referendums:from an anarchist perspective, citizens making law and policy decisions in person rather than through elected representatives in a form of popular self-government.

diversity
Different races and cultures within a state are possible, positive and should be celebrated, although the extent to which diversity should extend is continuous

divided government
When the US House of Representatives, Senate and Presidency are not all controlled by one party.

Domestic politics
Issues within the US that directly concern citizens, e.g. health care, gun control and racial issues

Economic globalisation
Growing economic integration and interdependence of economies through intensified cross-border movement of goods, services, technologies and capital.

Egotistical individualism
The idea that individual freedom is associated with self-interest and self-reliance

Elective dictatorship
A government that dominates Parliament, usually due to a large majority, and therefore has few limits on its power.

Electoral mandate
the permission granted to a political leader or winning party by the constituency to govern and act on their behalf e.g. to President Obama in 2008 and 2012. the mandate is more or less in effect for as long as the government is in power.

Emerging power
A state that is considered to be rising, primarily in economic power and influence
Empiricism
The idea that knowledge comes from actual experience and not from abstract theories.

Enabling state
A larger state that helps individuals to achieve their potential and be free.

entrechment
A system by which the US Constitution is protected from change by law;in this case by the amendment process of article V.
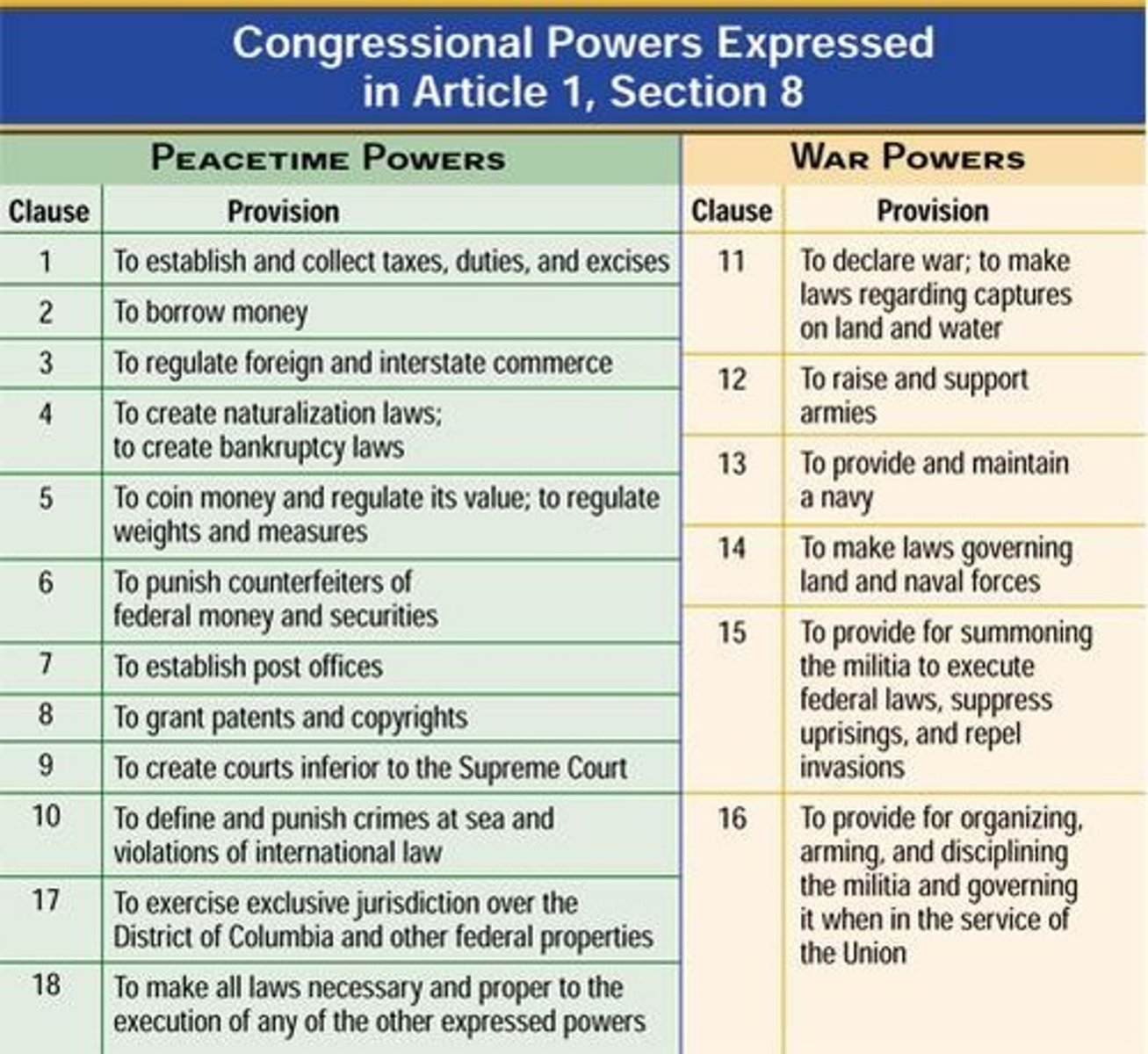
enumerated powers
Such powers are stated explicitly in the US Constitution- for example article I, Section 8 provides a list of congressional powers.
Equality and difference feminism
Feminists who argue that men and women are fundamentally different from one another.
Equality of opportunity
The idea that all humans irrespective of sex, should have an equal opportunity to succeed on society.

Essentialism
The belief that biological factors are significant in the different character and behavior of men and women.
Ethnicity
A form of nationalism based on the belief that a nation has a shared cultural heritage and ancestry.

European Intergration
Process of industrial, political, legal and economic and social cultural integration of states on Europe.
European Union (EU)
Political-economic of 28 members (2015) located in Europe; a political and economic union of a group of European countries.

Evolutionary Socialism
A parliamentary route, which would deliver a long-term, radical transformation in a gradual, piecemeal way through legal and peaceful means, via the state.
executive
the collective group of prime minister, cabinet and junior ministers sometimes known as 'the government'.
Executive Branch
the executive branch, headed by the US president, is one of the three branches of the US government;the other two are the legislative branch (headed by congress) and the judiciary (headed by the supreme court).

executive orders
A direction to the federal bureaucracy on how the president would like a piece of legislation to be implemented.

Exclusive nationalism
A form of nationalism that believes that it takes time to be a part of the nation, as membership is based on shared history and language.
Factions
The groups (factions) that make up a political parties-ideological wings, particular age and occupation groups, citizens concerned about particular issues-are now a feature of modern politics.

failed state
A state that is unable to operate as a widely viable political unit.

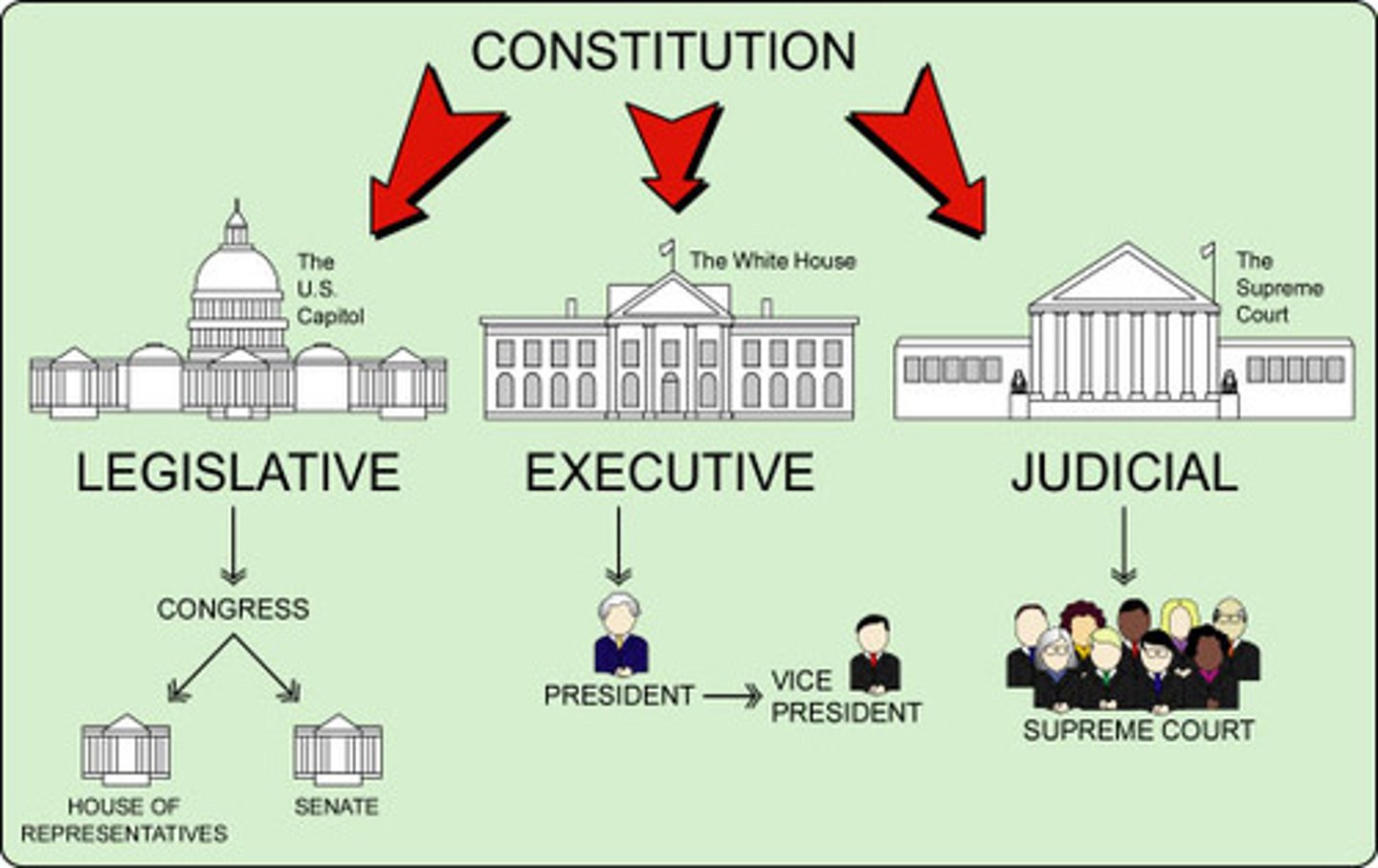
Federalism
Legal and political structures where power is distributed between two distinct levels of government on the basis that neither is subordinate to the other; the US system in which sovereignty is shared between a central government (federal government) and the individual states, with each having their own specific rights
Filibuster
When a US Senator gives a prolonged speech on the floor of the Senate in order to obstruct legislative progress of a bill or confirmation of appointments to the executive or judiciary.

first-past-the-post (FPTP)
An electoral system where the person with the most number of votes is elected. Victory is achieved by having one more vote than other contenders - it is also called a plurality system.

Formal Equality
The idea that all individuals have the same legal and political rights in society.
Foundational equality
Rights that all humans have by virtue of being born which cannot be taken away (also known as natural rights and inalienable rights).

Four freedoms (EU)
The principle of free movement of goods, services, capital and people within the EU's single market.
Franchise/suffrage
Franchise and suffrage both refer to the ability/right to vote in public elections. Suffragettes were women campaigning for the right to vote on the same terms as men.

Fraternity
The bonds of comradeship between human beings.

G7 (8)
Group of seven/eight states.

G20
Group of 20 states

gender equality
The idea that society should treat everyone the same, irrespective of their gender.

Gender Steoreotypes
The different way society expects men and women to behave according to traditional gender roles.
Global actor
Entity that participates or acts in international relations.
Global commons
Areas and resources that are un-owned and consequently beyond national juriadiction.

Global governance
movement towards political integration of transnational actors aimed at negotiating responses to problems that affect more than one state or region;complex process of decision making on a global scale.

Globalisation
Emergence of a complex web of interconnectedness in many forms.

Governing competency
The perceived ability of the governing party in office to manage the affairs of the state well and effectively. It can also be a potential view of opposition parties and their perceived governing competency if they were to secure office.

Government
From an anarchist perspective, government is a particular system of rule, from monarchy monarchism to dictatorship to liberal democracy based on deceit and violence.

government department
A part of the executive, usually with specific responsibility over an area such as education, health or defence.

Great power
State that is recognized as having the ability and expertise to exert its influence on a global scale.
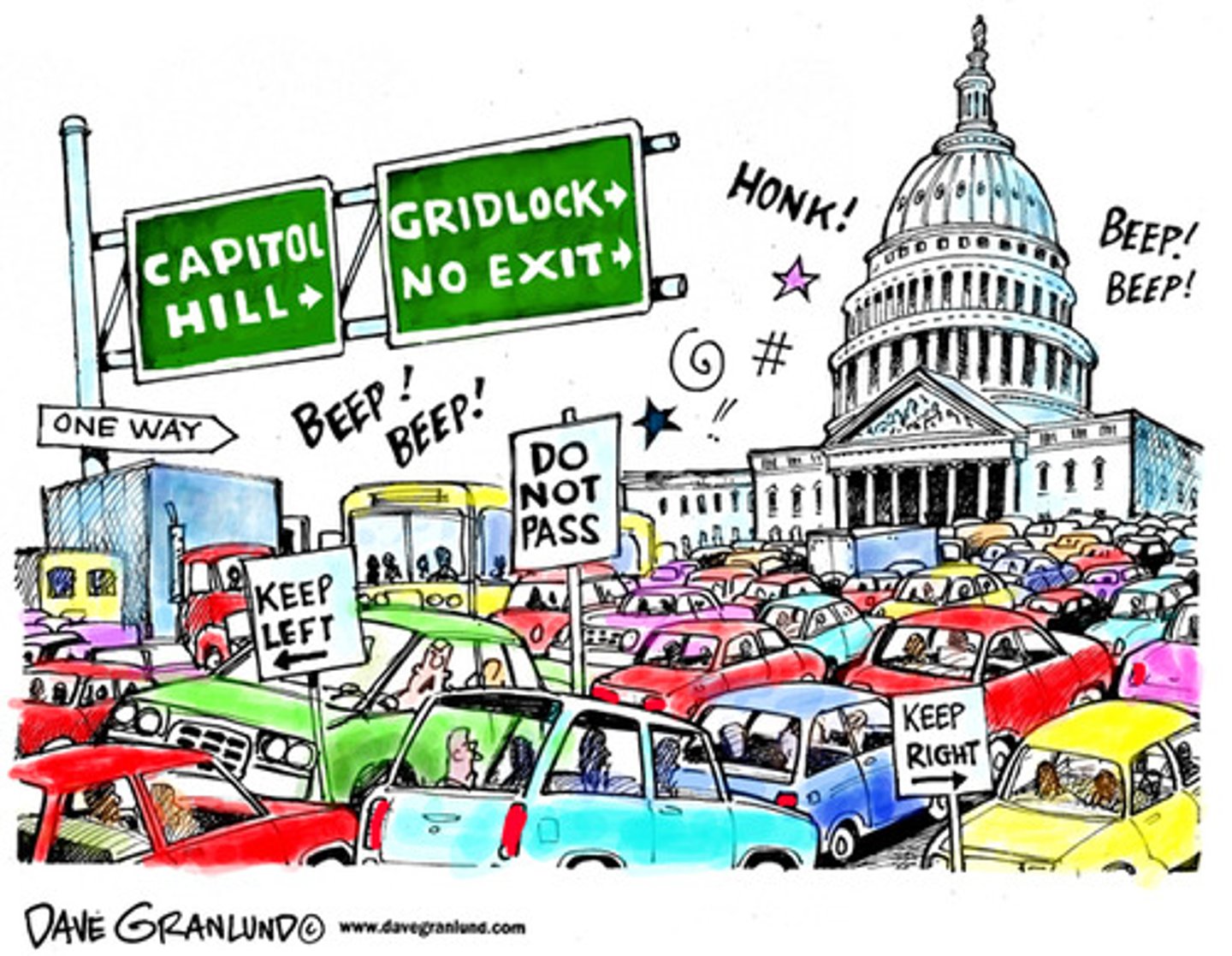
Gridlock
A situation in US politics where the president and congress are equally powerful, constantly preventing each other from acting, resulting in difficulty in passing legislation.
Group differentiated rights
Rights that belong to a group, in contrast to a right held by individuals, includes self government rights, polyethnic rights and representation rights.