MGT 420 Human Resource Management Exam 1
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
What is HRM?
The application of organizational behavior principles to organizations with the goal of improving attitudes and behaviors of employees
Does HRM matter lead to a competitive advantage?
an organizations has a sustainable competitive advantage if it is better than competitors at something and can hold that advantage over a prolonged period of time
Resource-based view
Resource is valuable when rare and difficult to imitate
Resources include
financial
physical
interpersonal
Are good people rare?
Yes depending on the economy (rarer when economy is good)
Are good people inimitable?
Yes because
the create specialized knowledge about the job
they create culture
they make numerous small decisions
none of these can be copied
Case studies
we could examine companies that do well finanically and see whether they do a good job of managing HR
we could examine companies that struggle financially and see if they do a poor job or managing HR
Quantitative Analysis
we could also look at companies who have been recognized for their HRM quality, to see if their practives have seemed to create a sustainable competitive advantage
Quantitative Analysis example
are the 100 best more profitable than similar companies in those industries?
study found a “matched firm” for each of the 100 best of 1998
matched firms were similar in size and industry but never made the list
the 100 best firms outperformed their matches over a five year period
Who does HRM?
If you are in charge of employees then you will perform many HR tasks yourself
-Performance management
-Training
-Recruitment and selection
Your efforts may supplement or even replace this of the HR department
The changing role of HRM
Historically viewed as one of the less important organizational functions
But, HRM has become more important in recent years
Most importantly, the HR department has become more involved in strategic planning
Old role
Cost center
keep track of forms
policy and procedure enforcement
payroll and insurance
cost reduction oriented
example: putting new employees through orientation through orientation with videotape and a package of forms
New role
Strategic partner
employee development
integration with the core operations of the organization
change management
results oriented
example: developing a program to select employees for a dynamic work environment
Recapping HRM
HR can provide competitive advantage
HR is no longer seen as the party planning committee
most companies HR has a seat at the table
there is a chief human resources officer
decisions are based on data- similar to marketing and finance
companies that get it integrate HR into the core aspects of the business
Job analysis definition
the process of getting detailed information about jobs in organizations
Importance of job analysis
before you can know
what kind of people to recruit and select
what to train them on
what basis to evaluate and compensate them
you must understand the job they will perform
Job description
identify the essential tasks, duties, and responsibilities (TDRs) that a job entails
Job Specification
come up with knowledge, skills, abilities, and other factors needed to perform the most important tasks. In contrast to TDR’s, KSAO’s are characteristics of people and are not directly observable.
KSAO’s
Knowledge: a persons theoretical understanding, academic background, and specific expertise in a field. :Know what Trainable
Skills: practical, learned abilities that enable someone to perform tasks: Know how Trainable
Abilities: innate or developed personal attributes that allow for effectiveness in a role. :Can do Less trainable (born with)
Other: personal attributes including interests, personality traits, and or values: Less trainable (born with)
Job analysis- job description
Step 1: Divide a job into 4-5 major dimensions
Step 2: List 2 key tasks within each of those dimensions
Step 3: rate the tasks on frequency and importance
Step 4: Use the most frequent and important tasks to define the job
Example of KSAO’s
I can know what is wrong with my computer but not have the skills to fix it
K vs. S
I can be taugh to read a map but still not have a good sense of direction
S vs. A
O*NET
The occupational information network: an online resource that describes the tasks involved in many jobs, along with their KSAO
Government database by the US department of labor. it replaces an earlier resocue called the dictionary of occupational titles
How do we use this info?
Recruitment: the important tasks get grouped into a job description that defines the job. the accompanying KSAO’s are included in the job posting
Selection: the KSAO’s become the things we look for in resumes, references, interviews, ability tests, personality tests
Legal issues in selection: important tasks become essentail job functions under the americans with disabilities act. companies can refuse to hire disabled applications if they cannot perform these functions (vs. “marginal job functions”) with some exceptions
Training: we design training to improve the K’s and S’s inherent in important tasks. they also form the basis for our evaluation of training success
Performance management: performance of the important tasks and KSAOs is what gets measured with our evaluation instruments
Compensation: the KSAO’s become compensable factors used in job evaluation to assign a base salary to a given job. the rarer the KSAO, the more money the organization must pay for it.
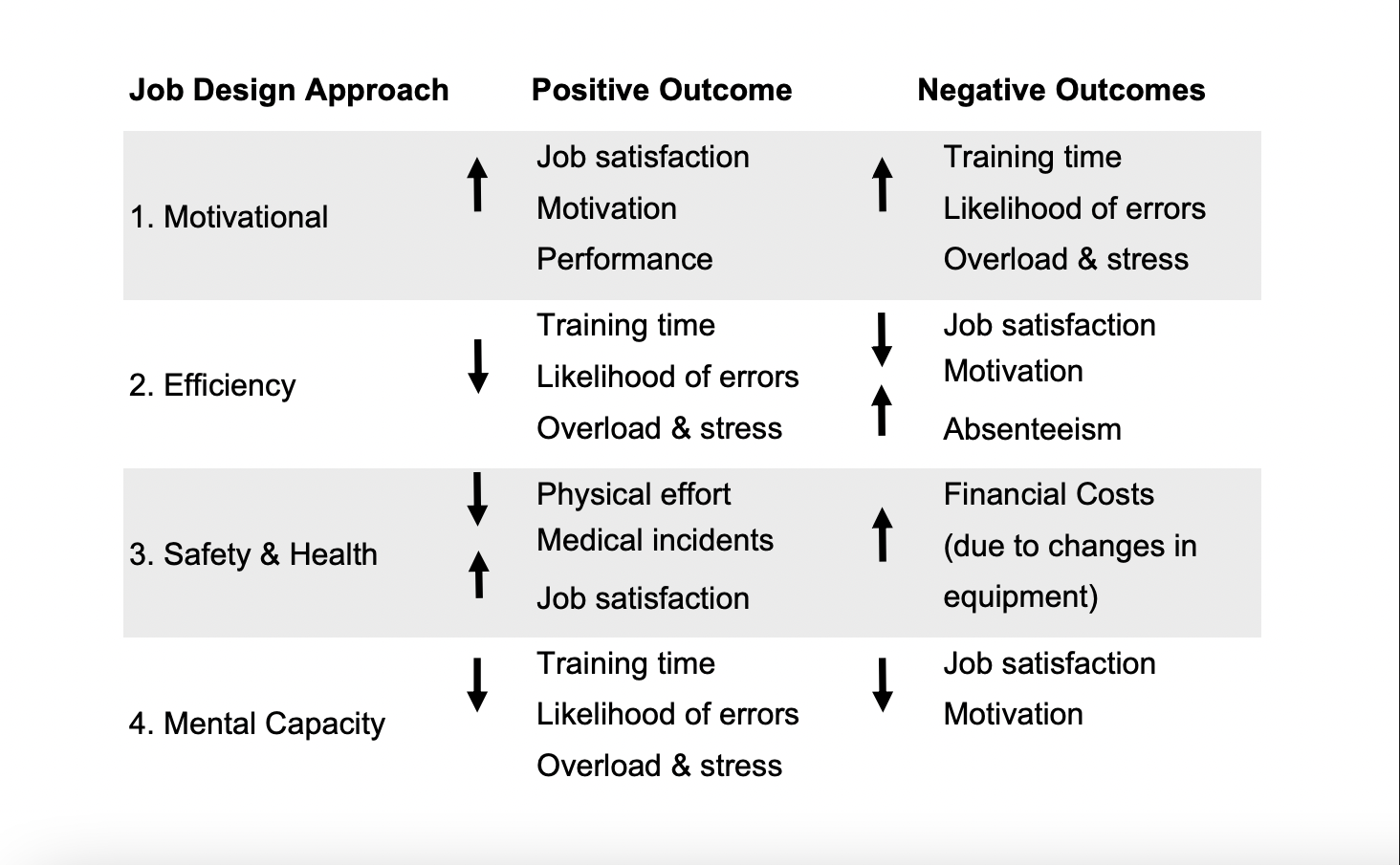
Job design
the process of defining the way work will be performed and the tasks that will be required in a given job
Motivational approach to job design
Human resources are easier to manage if jobs are designed to be intrinsically enjoyable
Jobs are more intrinsically enjoyable when work tasks are more challenging fulfilling
Five “core job characteristics” combine to make some jobs more rewarding than
Motivational approach (job characteristics model)
Job redsign: changing job characteristics
Job enlargement: broadening the types of tasks performed
to make jobs less repetitive and more interesting
Job enrichment: empowering employees by adding more decision-making authority to their jobs
Flexible work schedules:
flextime: control over hours worked
telework: working in other locations
compressed work week
Efficiency
Roots in classical industrial engineering: study of jobs to find simplest way to structure work to maximize efficiency
Emphasis on reduction of complexity of work
Less training; allows almost anyone to be trained quickly and easily perform the job
Used for highly specialized and repetitive jobs
Safety and Health
Based in ergonomics
Structure job tasks and the work environment to reduce physical fatigue and health problems
Mental Capacity
Similar to safety and health, but focuses on mental (cognitive) capacities and limitations rather than physical
Examples
decrease amount of information and memorization
increase lighting and make visual displays clear
provide easy to follow instructions
Trade offs in job design
*see page 57 of ppt
Key question: Are some of the job design approaches at odds with one another?
Skill Variety
Different tasks/skills/talents in one’s job
High: owner operator of garage who does electrical repair, rebuilds engines, does body work, and interacts with customers
Low: A bodyshop worker who sprays paint 8 hours a day
Task Identity
Completion of whole piece of work
High: A cabinetmaker who designs a piece of furniture, selects the wood, builds the object, and finishes it to perfection
Low: A worker in a furniture factory who operates a machines to make table legs
Task Significance
The impact of the job on others
High: Nursing sick patients in a hospital intensive care unit
Low: Sweeping hospital floors
Meaningfulness of work (psychological state)
the degree to which work tasks are viewed as something that “counts” in the employees system of philosophies and beliefs
—>Skill Variety, Task Identity, and Task Significance
Autonomy
Level of discretion in decision making
High: A telephone installer who schedules their own workday and decides the best techniques for a given installation
Low: A telephone operator who must handle calls as they come according to a routine, highly specified procedure
Responsibility for outcomes (psychological state)
the degree to which employees feel that they are “key drivers” of the quality of the work
—>Autonomy
Feedback
Amount of direct and clear information on performance
High: An electronics factory worker who assembles a radio and tests it to determine if it operates correctly
Low: An electronics facory worker who assembles a radio and then routes it to a quality control inspector who tests and adjusts it
Knowledge of results (psychological state)
the extent to which employees know how well or how poorly they are doing
—>Feedback
Planning
Planning encompasses the answers to the following questions
What kind of human resources will we need?
What kind of human resources will we have?
How do we bring those into alignment?
Demand forecasting
Supply forecasting
Demand forecasting
tells us how much labor we will need. Organizations often use a combination of all three: benchmarking, statistical methods, and educated guesses
Benchmarking
Tells us how much labor we will need
How much labor does a business like ours use? is there any reason why we may differ?
Statistical methods
Example: Sales this year correlate with labor demand next year
leading indicators: economic variables that suggest future conditions (price of corn in beef industry)
Pro: often much more accurate than subjective judgement
Con: Many important events in the labor market have no hsitorival precedent (covid 19)
Educated guesses
Take into account other factors (new product launches, changes with competitors)
Supply forecasting
How much labor will we have?
Requires us to anticipate how people will move up, through, and out of the company
Examine our business environment by asking these questions
Whats the unemployment rate?
How does that break down by age, gender, and background of the people we would target?
Is there seasonality in those rates?
Transitional matrix
Lists jobs categories held in one period (eg sales manager) and shows the proportion of employees in each of those job categories in the future
Answers 2 question
Where did people who were in each job category go?
Where did people now in each job category come from?
Benefits of a transition matrix
Provides snapshot of movement of people within an organizaition
Can identify jobs that appear to be dead ends or have excessive exit rates/terminations
indicates opportunities to solve those problems through changing HR policies/practices
How to correct a surplus?
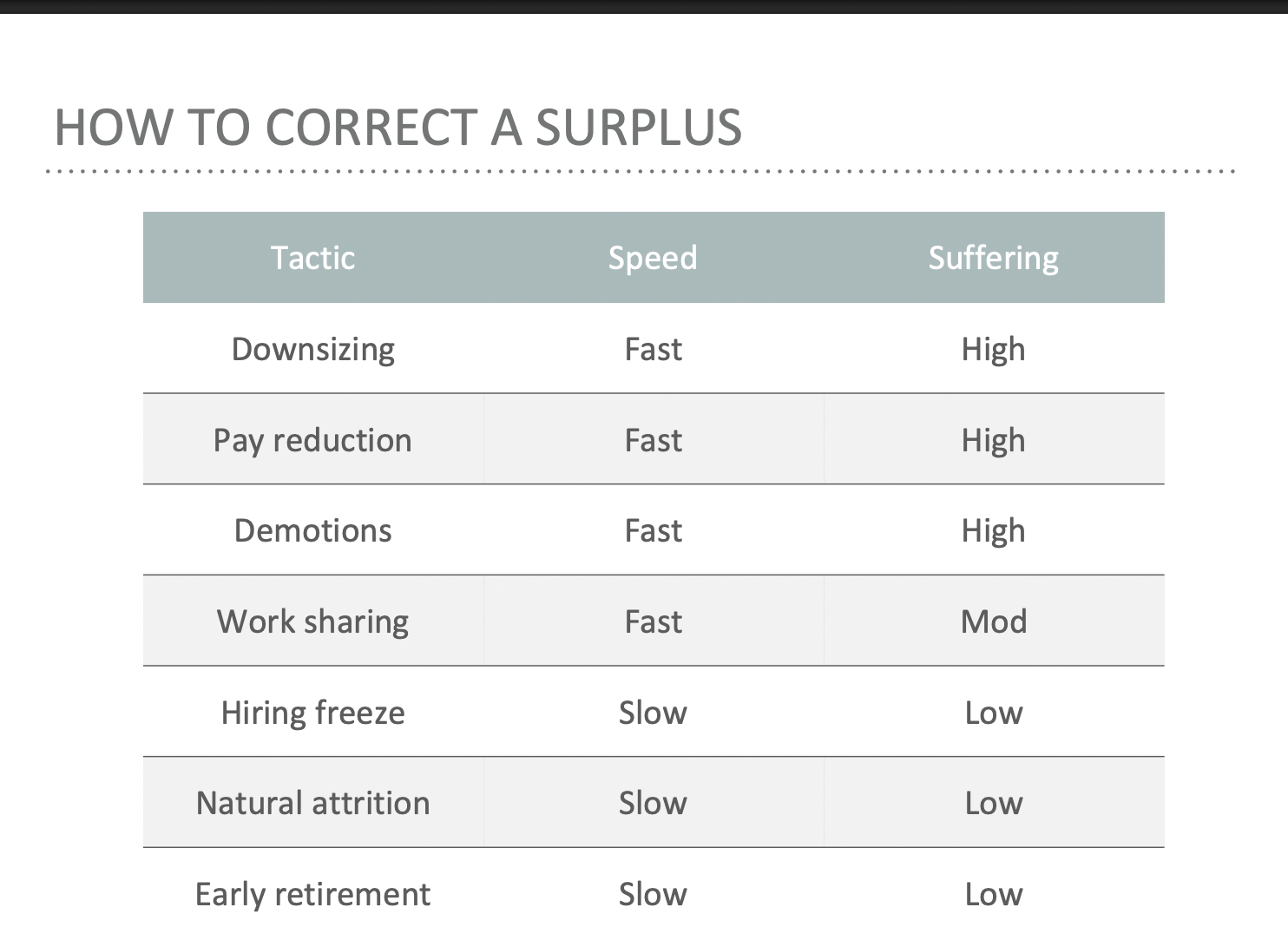
Downsizing
The planned elimination of large numbers of personnel with the goal of enhancing the organization’s competitiveness,
85% of Fortune 1000 firms downsized between 1987 and 2001, in order to reduce labor costs, take advantage of new technologies, and decrease bureaucracy due to use of work teams or because of corporate mergers, and pave way for use of foreign labor
80% of these firms were profitable at the time of the layoffs
Why doesn’t it work?
The wrong people may be let go, taking with them vital parts of the organizational memory
Many downsizing cut too deep, causing the organization to replace workers and incur those expenses
The effects on so-called “survivors” can be severe
It can significantly alter the culture and climate of the organization
Temporary employees
About 5-10% of the workforce are temp employees
Advantages:
saves benefits costs
reduces need for selection
reduces need for training
these employees are unhindered by existing culture and may have valuable experiences from other firms
Disadvantages
may cause friction with regular employees
A 2 tier system may be created
extra role behaviors will be limited
Outsourcing
Using an outside firm to perform some service rather than doing it “in house”
Advantages:
take advantage of economies of scales
foreign labor may have different wage standards
Disadvantages
no control over performance mgt and compensation
may have long term effects on economy
can be bad for employee morale
Outsourcing has gradually shifted from being a strategy for correcting a shortage to a permanent means of structuring work
Such outsourcing often takes the form of offshoring as job functions are completed over seas
How to correct a shortage
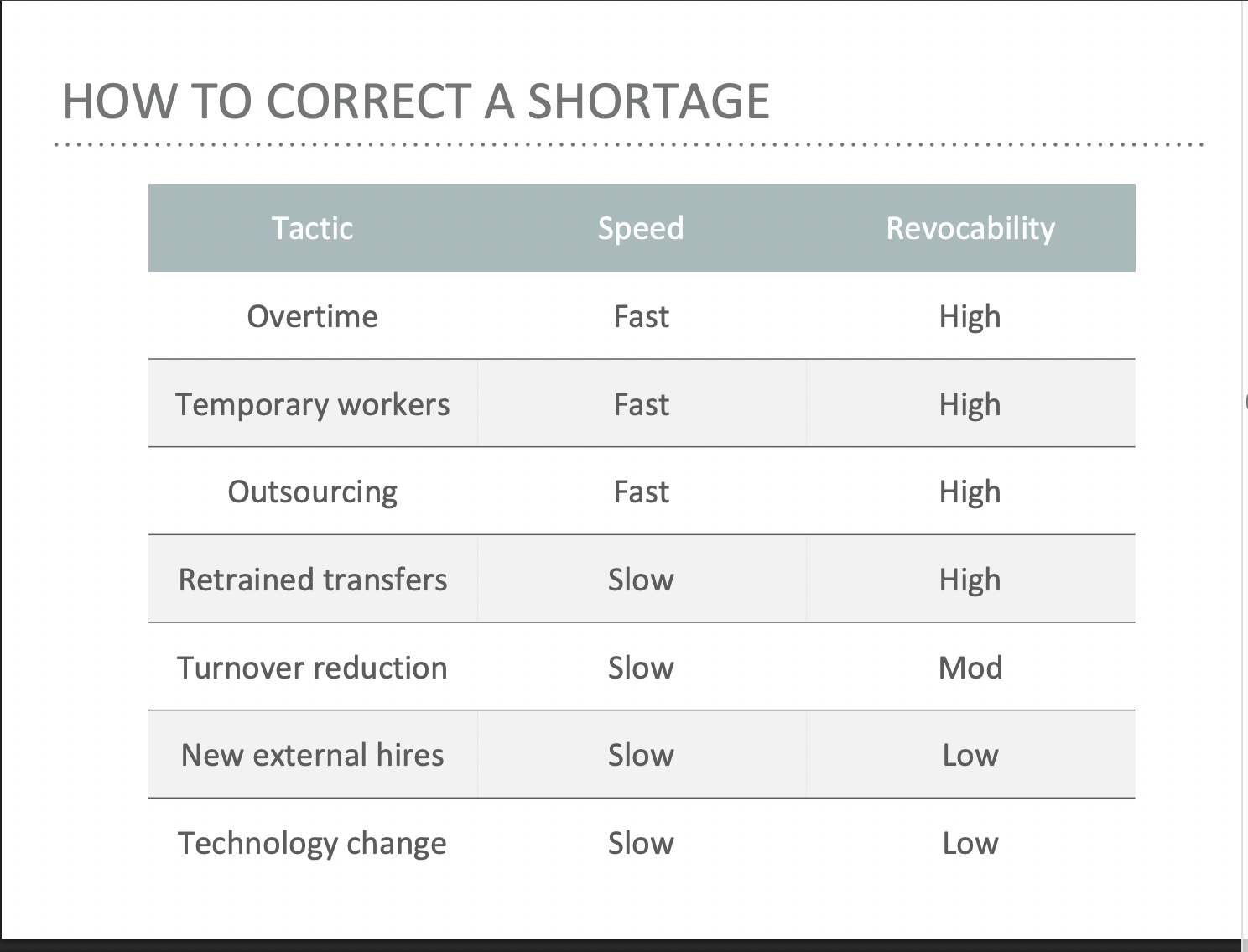
Recruitment
The practices and activities firms use to identify and attract potential employees
Recruitment is used to initially staff an organization, to replace workers, and to cope with a labor shortage
Recruitment achievement indicators
Three goals:
Attract a lot of applicants
Attract applicants who “fit” the position
Increase likelihood of offer acceptances
4 recruitment influences
Vacancy characteristics
Personnel policies
Recruitment sources
Recruiter characteristics
Vacancy characteristics
What the job will provide
job security
advancement opportunites
core job characteristics
pay and benefits
location and travel requirements
The most important predictor of whether a candidate selects the job
Personnel policies
Second biggest factor
What policies affect vacancy desirability?
Lead-the-market pay
Paying more than current market wages
Promoting from within
Opportunities for advancement
Image advertising
Promoting the organization as a good place to work
Recruitment sources
Internal
Promote from within
External
Advertisements
Employment agencies
Government, headhunters
Colleges and universities
Biggest source for entry-level positions
Complemented by internship programs
Electronic recruiting
Referrals
usually results in a good fit
Recruitment sources pt 2
Advantages
Internally: Cheaper and faster
Externally: Brings in fresh ideas
Disadvantages
Internally: Not practical in smaller firms
Externally: Riskier
Yield ratios
Expresses the percentage of applicants who successfully move from one stage of the recruitment and selection process to the next
Cost per hire
The total amount of money spent to fill a job
The cost of using a particular recruiting source/number of people hired to fill that type of vacancy
Recruiter Characteristics
Small impact on job acceptance
Larger impact on decision to accept a second interview
Rarely trained (and can sometimes have a strong negative effect as a result)
More effective if recruiting function separated from selection function
Recruiter characteristics
How to enhance recruiter impact
provide timely feedback
Avoid offensive behavior
Recruit with teams rather than individual recruiters
Applicants do use the recruiter to judge “person-organization fit”
What do recruiters want?
someone close to their age
someone nice
someone honest and informative
Many recruiters find themselves unsure about whether to “sell” a job or be realistic about its negative aspects
initial turnover (within first 6 months) is particularly damaging to an employer
Realistic job preview
Can improve the following
perceptions of employer fairness
initial turnover