Physics - Waves
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Wave
A periodic oscillation that transfers energy form one point to another
-Pulse: A wave or disturbance that is not repeated
-Periodic: A wave or disturbance that is repeated
Vibration/oscillation
A forward/backward motion in a straight line or along an arc (e.g. pendulum or spring)
Cycle
One complete vibration in a periodic motion
Period
Time taken for one complete cycle of a wave (T)
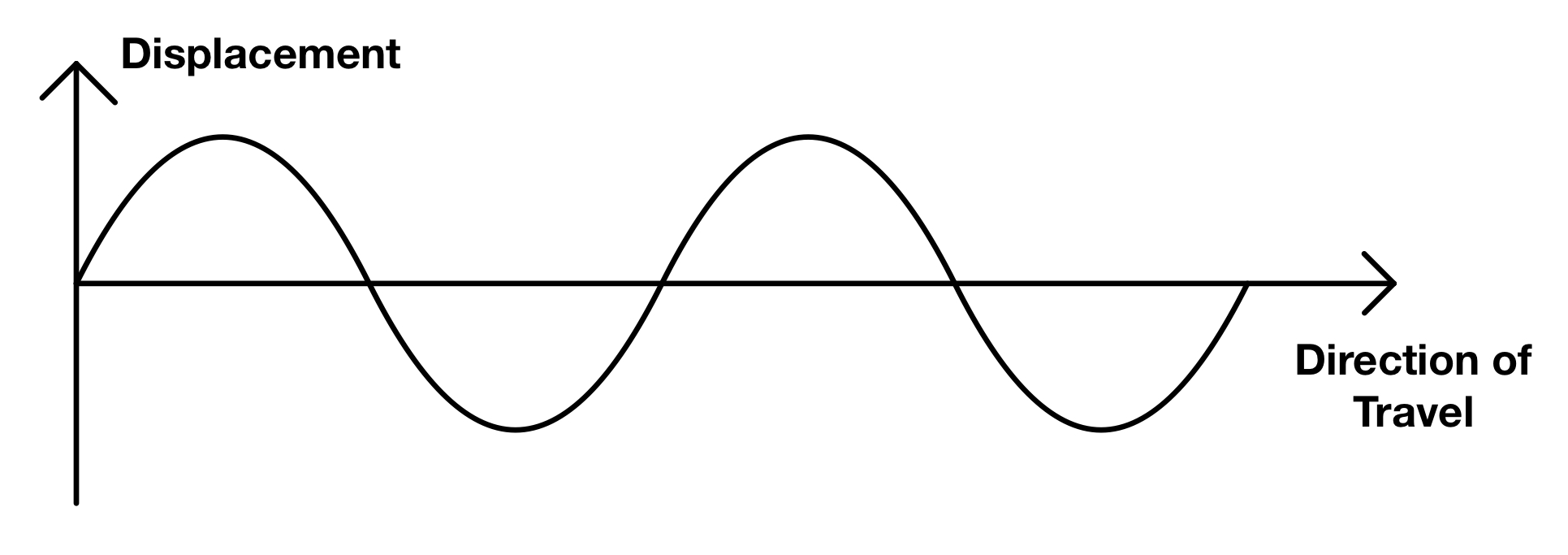
Wavelength
Distance between two successive points on a wave (i.e. between two crests or troughs) (λ)
Frequency
Number of complete cycles that pass a given point over a certain time period (hertz - hz)
Amplitude
Maximum displacement of a particle from it’s rest position (i.e. the crest or trough of a wave)
Mechanical wave
Requires a physical medium for energy to travel
-e.g. water, sound
Electromagnetic wave
Requires no physical medium for the energy to travel
-e.g. Light energy (photons) or radiation (also photons)
Medium
Substance a wave moves through
Transverse wave
oscillations that are perpendicular to velocity of wave
-Most waves
-Light/electromagnetic radiation is transverse
Longitudinal wave
Oscillations that are parallel with the velocity of the wave
-Sound is most common example
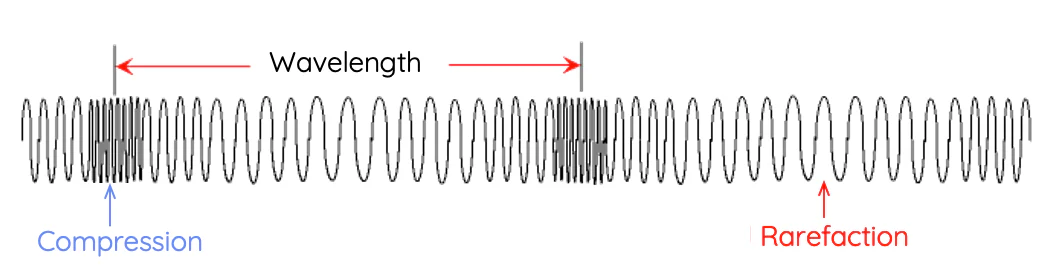
Sound waves
Sound waves are longitudinal and involve:
-Compression: Air gets squished together and there are more particles in a smaller space
-Rarefaction: Air gets less dense with particles and spread out more
They are mechanical and require medium to travel
-Travels fastest through solids as particle are more tightly packed allowing sound waves to transmit more efficiently and quickly
-330-350m/s
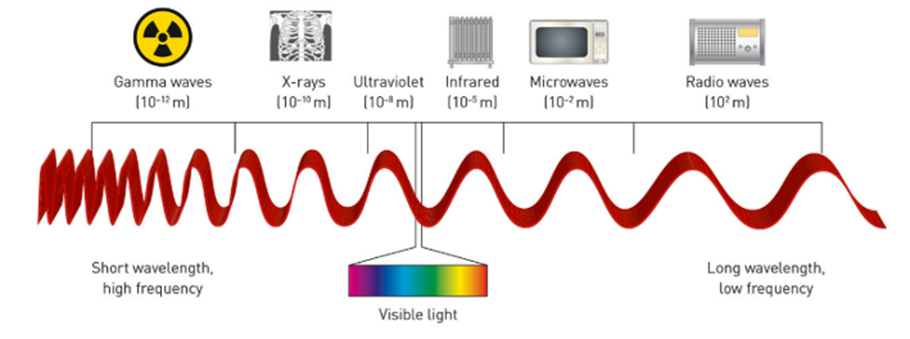
Light waves (EM spectrum)
-Transverse
-Type of EM wave is determined by the wavelength/frequency (longer wave, lower frequency
-300000000m/s
Displacement vs time
Can find:
-Amplitude
-Frequency
-Period
Displacement vs distance
Can find:
-Amplitude
-Wavelength
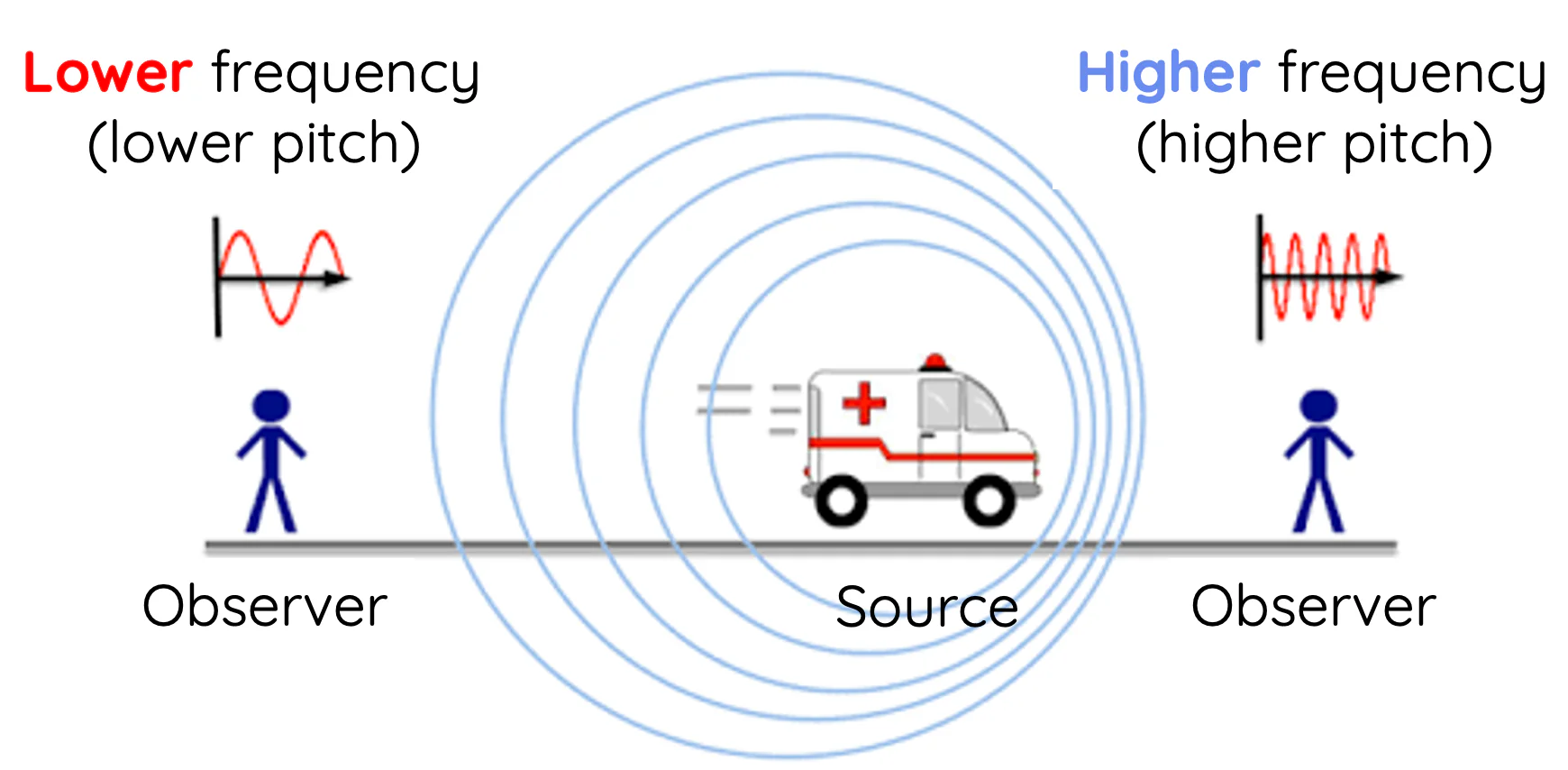
Doppler effect
describes the change in frequency or wavelength of a wave as perceived by an observer when the source and observer are moving relative to each other
Reflection
occurs when a wave changes direction at the boundary between two mediums, returning to the medium it starts in
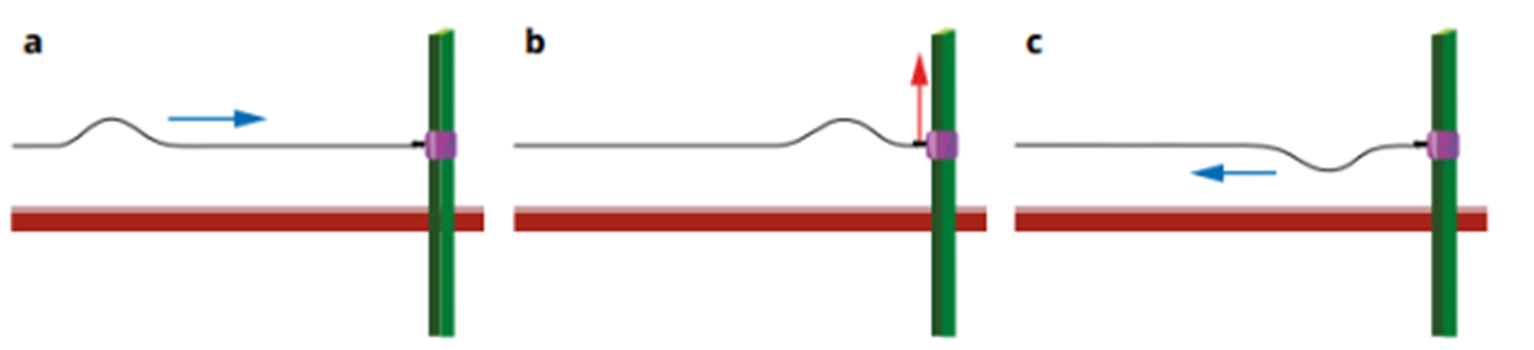
Fixed boundaries
the wave will be reflected and inverted when returning back. This is also called a phase reversal (the phase switches – i.e. peaks become troughs)
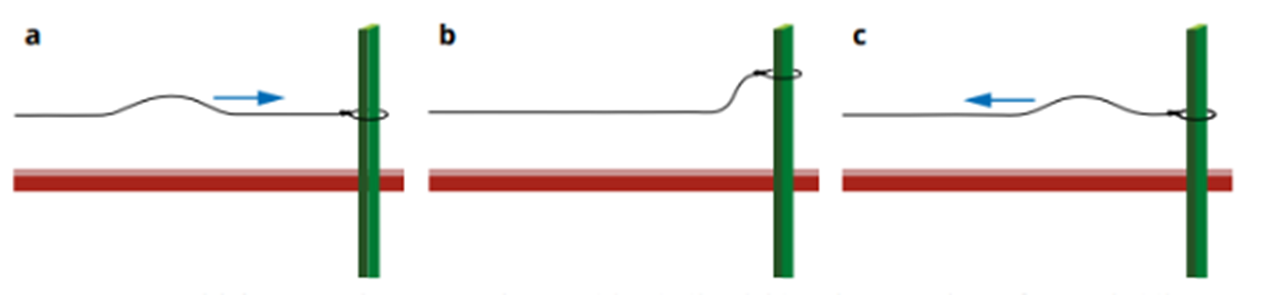
Free boundaries
the wave will be reflected back in the same way as the incident wave
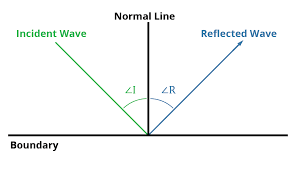
Reflected waves law
The angle of incidence of wave (from the normal) will be equal to the angle of reflection of the reflected wave.
Refraction
Refraction is when waves ‘bend’ as they move from one medium to another
-Speed and wavelength can change (slower wave, shorter wavelength
Angles of refraction
1.If wave slows down - bends towards normal
2.If wave speeds up - bends away form the normal
BEING SLOW IS NORMAL
Speed of sound is dependent on…
1.Elasticity (or stiffness)
-Measure of how easily something will return to its og shape (solid>liquid>gases)
2.Density
-How closely packed particles are together (solids>liquid>gases)
Refraction of waves: light
Light will travel slower as density increases, hence:
-Solid will be slowest, gas the highest
-Light will refract towards normal if it goes into a denser material as it slows down
Refraction of waves: sound
Sound will travel faster as density increases
-Sound will be fastest, gas the lowest
-Sound will refract away from the normal as it goes into a denser material as it will speed up
Behaviour after refraction (if wave speeds up)
-the angle of refraction is greater than incidence (bends away from normal)
-Wavelength will increase
Behaviour after refraction (if wave speeds up)
-Angle of refraction is smaller than incidence (bends towards normal)
-Wavelength will decrease
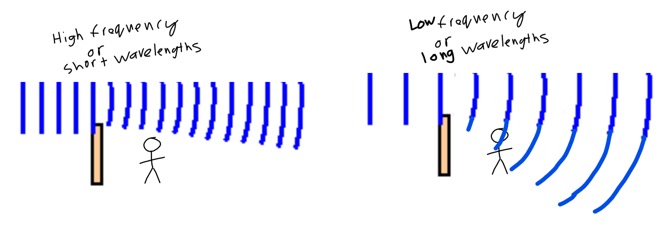
Diffraction
-The spreading of waves when it encounters a barrier or a slit/gap
-Bigger the gap - the less diffraction and vice versa
-Lower frequency and longer wavelength the better a wave tends to diffract