AP Chem - Unit 9
0.0(0)Studied by 10 people
0%Unit 9: Applications of Thermodynamics Mastery
0%Exam Mastery
Build your Mastery score
Supplemental Materials
Card Sorting
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
electrochemistry last one :0
Last updated 1:08 AM on 3/27/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
1
New cards
entropy (S)
**the measure of disorder** in the dispersal of matter or energy in a sample of matter
2
New cards
changes in entropy (𝚫S) measure
how dispersed the matter or energy is in a particular system
3
New cards
entropy increases when
matter becomes more dispersed
in cases where:
* phase changes from solid to liquid and from liquid to gas
* individual particles become more free to move and occupy a large volume
* volume of a gas increases
* gas molecules are able to move within a larger space at the same speed
* number of moles of product > reactants
* temperature increases
* distribution of KE among gas particles broadens as temperature increases
in cases where:
* phase changes from solid to liquid and from liquid to gas
* individual particles become more free to move and occupy a large volume
* volume of a gas increases
* gas molecules are able to move within a larger space at the same speed
* number of moles of product > reactants
* temperature increases
* distribution of KE among gas particles broadens as temperature increases
4
New cards
entropy change
𝚫S reaction = ΣS products - ΣS reactants
5
New cards
entropy is measured in
joules
6
New cards
at absolute entropy
every substance has a nonzero value
7
New cards
when calculating entropy the
number of moles of each substance (in the balanced equation) must be considered
8
New cards
signs of entropy change can be predicted
by the state and number of moles of reactants and products
9
New cards
\+𝚫S
* solid → liquid → gas
* number of moles increase from reactant to products
* number of moles increase from reactant to products
10
New cards
\-𝚫S
* gas → liquid → solid
* number of moles decreases from reactant to products
* number of moles decreases from reactant to products
11
New cards
gibbs free energy (G)
describes whether a reaction is thermodynamically favorable or unfavorable
12
New cards
changes that are thermodynamically favorable
* proceed to equilibrium without external intervention
* does not happen quickly just because it is favorable
* does not happen quickly just because it is favorable
13
New cards
gibbs free energy change (𝚫G)
𝚫G reaction = ΣG products - ΣG reactants
14
New cards
𝚫G < 0
thermodynamically favorable
15
New cards
𝚫G > 0
thermodynamically unfavorable
16
New cards
with 𝚫G = ΔH - TΔS
thermodynamically favored can be predicted from the signs of ΔH and ΔS
17
New cards
MEMORIZE FOR UNIT 9
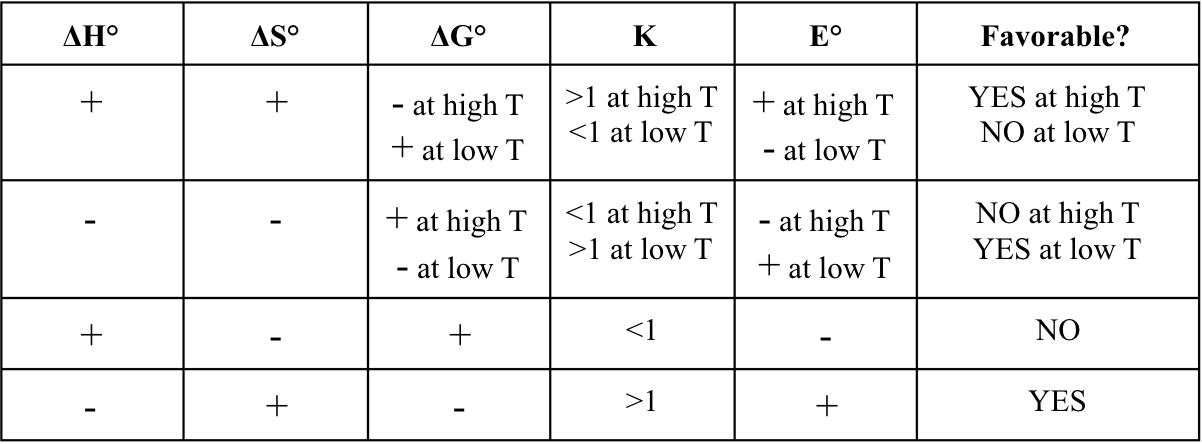
18
New cards
19
New cards
20
New cards
21
New cards
processes under kinetic control
* thermodynamically favorable
* large activation energy and thus very slow
* catalysts have no effect on thermodynamic favorability
* large activation energy and thus very slow
* catalysts have no effect on thermodynamic favorability
22
New cards
products are favored at equilibrium
* thermodynamically favored
* ΔG° < 0 and K > 1
* ΔG° < 0 and K > 1
23
New cards
reactants are favored at equilibrium
* thermodynamically unfavored
* ΔG° > 0 and K < 1
* ΔG° > 0 and K < 1
24
New cards
free energy and equilibrium constant relationship

25
New cards
coupled reaction
* an unfavorable reaction can be coupled with a favorable one to make the process occur
* can be coupled if the two reactions share a common intermediate
* hess’s law is applied to determine the ΔG
* the sum must be negative making the reaction favorable
* can be coupled if the two reactions share a common intermediate
* hess’s law is applied to determine the ΔG
* the sum must be negative making the reaction favorable
26
New cards
electrochemical cell
a device that can convert energy released by a favorable reaction to electrical energy or can drive a unfavorable reaction
* contains and anode and cathode
* contains and anode and cathode
27
New cards
cathode
* where oxidation occurs
* cations
* cations
28
New cards
anode
* where reduction occurs
* anions
* anions
29
New cards
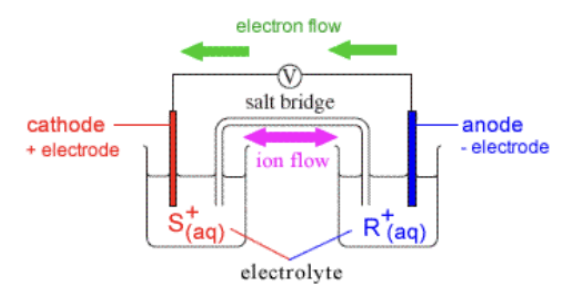
galvanic (voltaic) cells
* thermodynamically favorable reaction
* anode and cathode in separate half cells
* salt bridge needed - allows for movement between half cells
* necessary for current to flow in the circuit
* produces electrical energy
* + voltage value
* electrons flow from anode to cathode
* anode and cathode in separate half cells
* salt bridge needed - allows for movement between half cells
* necessary for current to flow in the circuit
* produces electrical energy
* + voltage value
* electrons flow from anode to cathode
30
New cards
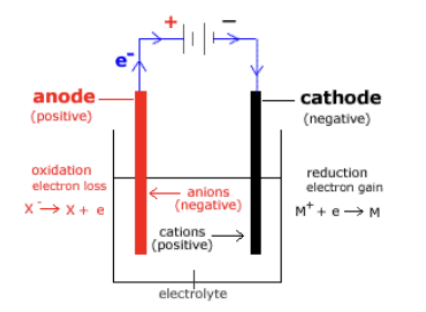
electrolytic cells
* thermodynamically unfavorable reaction
* anode and cathode in the same chamber
* power source needed (no salt bridge)
* uses electrical energy
* - voltage values
* electrons flow
* anode → power source → cathode
* occurs in ionic solution or liquid
* cations → cathode and anions → anode
* anode and cathode in the same chamber
* power source needed (no salt bridge)
* uses electrical energy
* - voltage values
* electrons flow
* anode → power source → cathode
* occurs in ionic solution or liquid
* cations → cathode and anions → anode
31
New cards
electric potential difference (voltage) involves
* a reaction occurring in an electrochemical cell
32
New cards
E°red
* standard reduction potentials
* 1 M solutions, 1 atm of pressure for gases, 25℃
* 1 M solutions, 1 atm of pressure for gases, 25℃
33
New cards
to get oxidation potentials
* the reduction half-reaction and sign of voltage must be reversed
* do not multiply stoichiometric coefficients in the equation
* do not multiply stoichiometric coefficients in the equation
34
New cards
more positive the E°V
more favorable the reduction
35
New cards
cell’s standard potential (E°cell)
* calculated with E°cell = E°cathode - E°anode
36
New cards
voltaic cells (favorable reactions)
positive overall cell potential
37
New cards
electrolytic cells (unfavorable reactions)
negative overall cell potential
38
New cards
ΔG° is proportional to
* - cell potential for the reaction when its constructed
* moles of e- transferred
* moles of e- transferred
39
New cards
ΔG° = -nFE°cell
* +E°cell = -ΔG°
* -E°cell = +ΔG°
\
F = faraday’s constant = 96485 C/m e-
* -E°cell = +ΔG°
\
F = faraday’s constant = 96485 C/m e-