Chemistry Organics 3.5
1/64
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
For an alcohol, name the group and name for a carbon chain length of 4
Group- OH
Butan-1-ol
For a haloalkane, name the group and name for a carbon chain length of 4
Group- X (halogen)
1-bromo butane
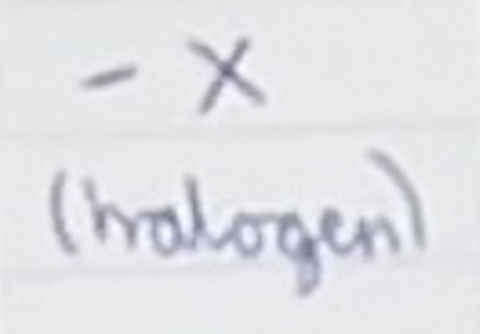
For an aldehyde, name the group and name for a carbon chain length of 4
Group- =O and H
Butanal
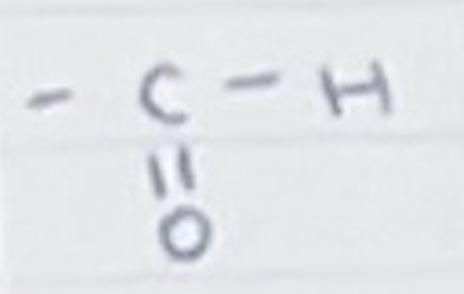
For a ketone, name the group and name for a carbon chain length of 4
Group- =O and H
Butan-1-one
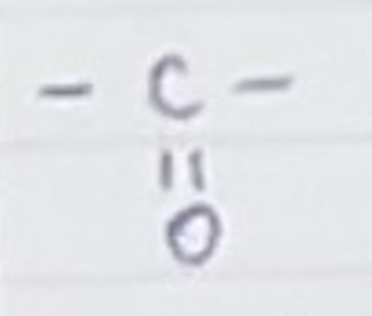
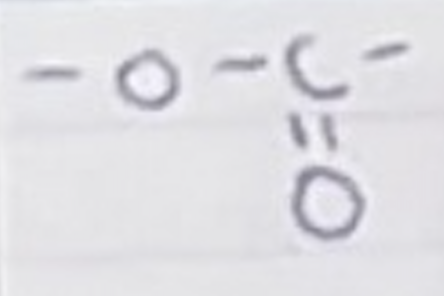
For a carboxylic acid, name the group and name for a carbon chain length of 4
Group- =O and OH
butanoic acid

For an amine, name the group and name for a carbon chain length of 4
group- -NH2
1-amino butane

What does volatile mean?
A substance's tendency to evaporate or vaporize
For an ester, name the group and name for a carbon chain length of 4
group -COO
Butylbutanoate
For an acyl chloride, name the group and name for a carbon chain length of 4
group -COCl
butanoyl chloride
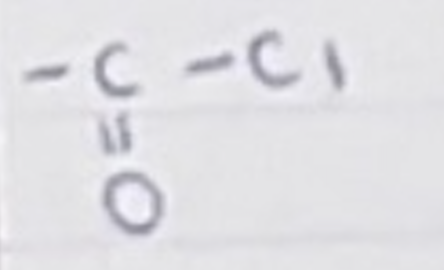
For an amide, name the group and name for a carbon chain length of 4
CONH2
butanamide
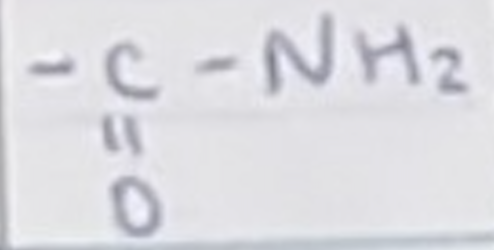
What is included in an ester link
coo
What is included in an amide/peptide link?
CON(H)
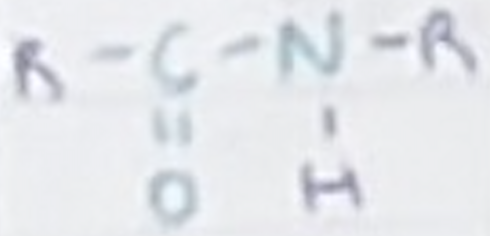
What is included in an amino acid
H2N- -COOH
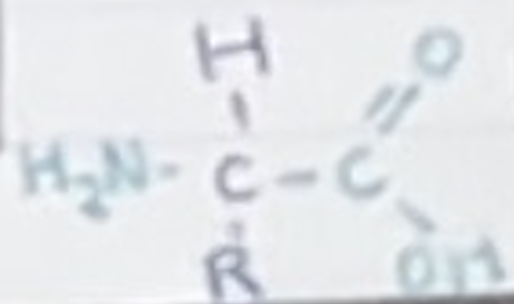
For adding H2O test explain:
What the test is for…
Results…
Any extra notes…
Test for polar substances such as acids and alcohols, or for acid chlorides
Single layer- means substance is soluble (polar)
Double layer- means substance is in soluble (non-polar)
Acid chlorides spit and fume
For blue litmus test explain:
What the test is for…
Results…
Any extra notes…
Tests for acids and acid chlorides
Litmus turns red from liquid- acid
Litmus turns red from vapour- acid chloride
For red litmus test explain:
What the test is for…
Results…
Any extra notes…
Tests for amines
Litmus turns blue- amine
Note: amines react with water to make OH
For bromine water test explain:
What the test is for…
Results…
Any extra notes…
Tests for double and triple carbon-carbon bonds
Orange colour or Br2 disappears- double or triple bond present (unsaturated)
For neutral KMnO4 test explain:
What the test is for…
Results…
Any extra notes…
Tests for double and triple carbon bonds
Purple colour of KMnO4 changes to brown precipitate- double or triple bond present (unsaturated)
What does ppt stand for?
precipitate
For Cr2O72- test explain:
What the test is for…
Results…
Any extra notes…
Tests for alcohols and aldehydes
Orange solution turns green- alcohol or aldehyde present
Note: Tertiary alcohols don’t react
For MnO4- test explain:
What the test is for…
Results…
Any extra notes…
Tests for alcohols and aldehydes
Purple solution turns colourless- alcohol or aldehyde present
Note: Tertiary alcohols don’t react
For the Lucas test explain:
What the added solution includes…
What the test is for…
Results…
Any extra notes…
Concentrated HCl with ZnCl2 catalyst
Tests for primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols
Does not go cloudy- primary alcohol
Goes cloudy in about 15 minutes- secondary
Goes cloudy in less than a minute- tertiary
Note; cloudiness is due to formation of chloroalkane which is not soluble in the water present
For the Tollen’s reagent test explain:
What the added solution includes…
What the test is for…
Results…
Any extra notes…
alkaline [Ag(NH3)2]+
Tests for aldehydes, including glucose
Silver mirror forms on inside of tube- aldehyde present
Notes: ketones and alcohols don’t react
Aldehyde reduces Ag+ to Ag
For the Fehling’s reagent or Benedict’s solution test explain:
What the added solution includes…
What the test is for…
Results…
Any extra notes…
alkaline Cu2+ complex
Tests for aldehydes, including ketones
Red precipitate of Cu2O (or orange or yellow solution)- aldehyde present
Notes: ketones and alcohols don’t react
Aldehyde reduce Cu2+ to Cu+
For Na2CO3(aq) / NaHCO3(aq) test explain:
What the test is for…
Results…
Any extra notes…
Tests for carboxylic acids
Fizzing (CO2)- carboxylic acid present
Note: acid-carbonate
What are the 3 types of isomers?
Structural/constitutional, geometric, optical/stereo
Explain structural/constitutional isomers
Same empirical formula but different arrangement of atoms
Explain geometric isomers and requirements
Same empirical formula but different arrangement
Must have a double bond present and have different atoms (or groups of atoms) attached to the cs in the double bond
Explain optical/stereo isomers/ enantiomers and requirements
Same empirical formula but different arrangement
Must have 4 different groups attached to the central (chiral) carbon
Explain properties of alcohols
melting/boiling point (and compare to corresponding alkane)
polarity
solubility
melting and boiling points increase with increasing carbon chain length, higher than alkanes due to hydrogen bonding
polar, but polarity decreases with increasing carbon chain length
smaller alcohols (1-3c) are infinitely soluble in water, but larger alcohols are insoluble due to non-polar carbon chains
Explain hydrogen bonding:
The OH end of the alcohol is attracted to the H atom on a neighbouring molecule, resulting in a strong intermolecular attraction between the molecules that require more heat energy to break.
Fill in the gaps:
Water _______ alcohols such asc______ form ______ _________ bonds with water, which can ___________ the _____molecular attractions of the __________ molecules. Due to the length of the _______ chain, the _______ chain molecules have more ___________ ______ to ______ attractive forces.
Water soluble alcohols such as ethanol form strong hydrogen bonds with water, which can overcome the intermolecular attractions of the alcohol molecules. Due to the length of the carbon chain, the longer chain molecules have more temporary dipole to dipole attractive forces.
Finish the sentence:
For a substance to dissolve in water…
There must be an attraction between the molecule and the water molecule.
What is a long carbon chain on a molecule sometimes called in terms of solubility?
long hydrophobic ‘tail’
Explain properties of aldehydes
melting/boiling point (and compare to corresponding alkane)
polarity
solubility
Boiling point increases with increasing carbon chain length, higher than alkanes due to permanent dipole-dipole forces
polar, but polarity decreases with increasing carbon chain length
smaller aldehydes (1–4c) are soluble in water, but larger aldehydes are insoluble due to long hydrophobic (non-polar) carbon chain.
Explain properties of ketones:
melting/boiling point (and compare to corresponding alkane)
polarity
solubility
Boiling point increases with increasing carbon chain length, higher than alkanes due to permanent dipole-dipole forces
polar, but polarity decreases with increasing carbon chain length
smaller ketones (1-5c) are soluble in water due to hydrogen bonding, but larger alcohols are insoluble due to long hydrophobic (non-polar) carbon chain.
Explain a nucleophilic substitution reaction:
The bonds between the C and Cl and O atoms are polar because O and Cl are both very electronegative and therefore draw electrons away from from the carbon, creating a dipole on the carbon centre. This means the carbon centre is susceptible to ‘attacks’ from nucleophiles (substances such as water that have lone pairs of electrons).
What is hydrolysis in easy terms
Break a molecule using water
Explain properties of amines:
melting/boiling point (and compare to corresponding alkane)
polarity
solubility
Boiling point increases with increasing carbon chain length, higher than those of less polar compounds with similar molar masses.
polar, but polarity decreases with increasing carbon chain length
smaller amines (1-5c) are soluble in water due to hydrogen bonding, but larger alcohols are insoluble due to long hydrophobic (non-polar) carbon chain.
What is a polypeptide?
A polypeptide is formed from many amino acids with amides (peptide bonds) between the amino acids. H2N- CONH -COOH
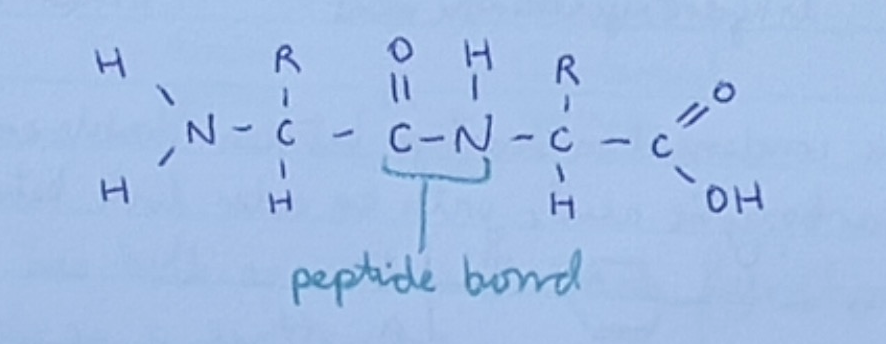
What type of molecule is a protein?
A protein is a polypeptide
Explain a condensation polymer:
A condensation polymer forms from the loss of a small molecule (eg HCl or H2O) and the monomers join together to form a long chain. A condensation polymer has an amide or ester bond.
What types of groups do molecules have to have for polyesters to form?
carboxylic acid or acid chloride and hydroxyl groups
What types of groups do molecules have to have for polyamides to form?
carboxylic acid and amine groups
What is formed when a carboxylic acid is added to alcohol
an ester link and H2O
What is formed when an acid chloride is added to alcohol
an ester link and HCl
What is formed when a carboxylic acid is added to an amine
peptide/amide link and H2O
Explain steps to making triglyceride (fat or oil)
Glycerol (propan,1,2,3-triol) + fatty acid (carboxylic acids) —> triglyceride + water

Explain steps of saponification (sodium salt)
Triglyceride + 3NaOH —> glycerol + soap (sodium salt)
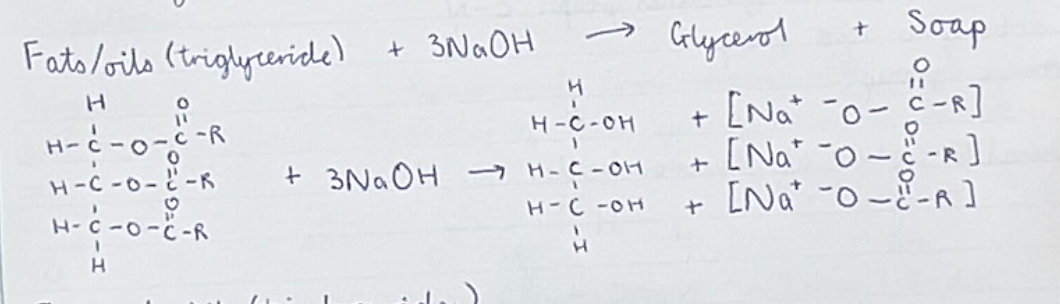
Give formula for hydrolysis reaction of an ester in acidic conditions:
Ester + H3O+ —> carboxylic acid + alcohol
Give formula for hydrolysis reaction of an ester in basic conditions:
Ester + OH- —> carboxylate ion + alcohol
Give formula for hydrolysis reaction of an amide in acidic conditions:
Amide + H3O+ —> carboxylic acid + ammonium ion (NH4+)
Give formula for hydrolysis reaction of an amide in basic conditions:
Amide + OH- —> carboxylate ion + NH3
What carboxylic acid derivative is the least reactive?
amides
Fill in the gaps:
Acid _________ exist as pungent, ______ liquids. They are ______ reactive substances. They have relatively ___ melting and boiling points because they do not have ________ bonding. Acid chlorides are not ______ but they react rapidly with water (spitting ______ ___ ______s).
Acid chlorides exist as pungent, fuming liquids. They are highly reactive substances. They have relatively low melting and boiling points because they do not have hydrogen bonding. Acid chlorides are not acidic but they react rapidly with water (spitting alcohol and amines).
Give formula for reaction of acid chloride and water and state what type of reaction this is:
RCOCl + H2O —> RCOOH + HCl
this is a nucleophilic substitution reaction
Acid + metal —>
salt + hydrogen
Acid + base —>
salt + water
Acid + metal carbonate —>
salt + water + carbon dioxide
What is a strong acid?
An acid which dissociates completely in solution
What is a weak acid?
An acid which only partially dissociates in solution
Are carboxylic acids weak or strong acids and what does this mean?
Carboxylic acids are weak acids so they only dissociate partially in solution
What is the formula for a haloalkane to amine reaction and name the type of reaction:
Haloalkane + NH3(alc) —> amine + hydrogen halide
Explain amine’s role as a base and how this affects it’s solubility:
Amines are weak bases and are similar to to ammonia in that they can behave as proton (H+) acceptors. The nitrogen atom has a lone pair of electrons that can bind to H+ to form an ammonium ion (NH4+). Smaller amines are soluble in polar solvents (eg water) due to attraction between the water molecules and these lone electron pairs.