proteins
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
how do they differ from lipids and CH
in addition to C, H and O always contain N and many also contain S and some contain P
what are proteins
polymers made of amino acid monomers
polypeptide
chains of amino acids
amino acids
all have the same basic structure
Be able to draw the general formula for amino acids
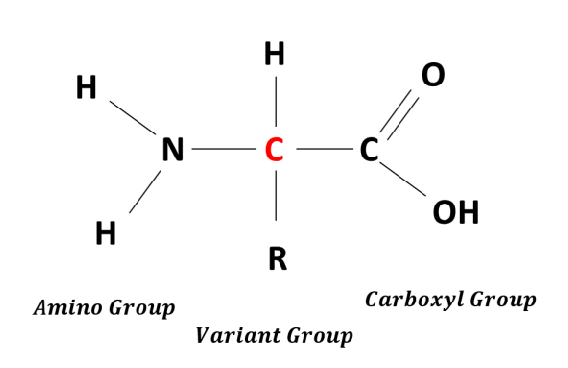

basic structure of amino acids
attached to a central carbon atom :
an amino group- NH2 at the N terminal of the molecule
a carboyl group COOH at the C terminal of the molecule
a hydrogen atom
the R group
the R group
is different in each amino acid
at ph7 which is the ph of the cell
the amino group gains an H and becomes positively charged
the carboxyl gorup looses an H and becomes acidic
therefore at ph 7
an amino acid has both a postive and a negative charge —> zwitterion ions
forming bonds
the amino group of one amino acid reacts with the carboxyl group of another amino acid with the elimination of water
forming
a peptide bond and the resulting compound is a dipeptide
type of reaction
peptide bond
the chemical bond formed by the condensation reaction between the amino group of one amino acid and the carboxyl group of another
there are
20 different amino acids used to make up proteins so there are thousands of different proteins and their shape is determined by the specific sequence of amino acids in the chain
primary structure
order of amino acids in a poylpeptide chain determined by the base sequence on one strand of the DNA molecule
this is because
there are 20 DAC that can be joined in any order and combination so there is huge number of possible polypeptides
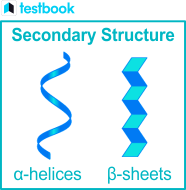
secondary sturcture
the shape that the PP forms as a result of hydrogen bonding between the O on the carboxyl groups and the H on amino gorups in the peptide along the chain
this is because
this bonding causes the long PP to be twisted into a 3D shape
type 1
spiral shape- alpha helix : protein keratin has a high proportion of alpha helix
the second type
beta pleated sheet which is a less common arrangement: the protin fibroin in silk has a high proportion of beta pleated sheet

teritary sturcture
when the alpha helix of the secondary protein structure can be folded and twisted to give a more complex compact 3D s structure
what is the shape maintained by
hydrogen bonds
ionic bonds
disulphide bonds
hydrophobic interactions (what cause the.. watch the vid mate)
these bonds
are i
quaternary sturcture
some PP chains combine with another PP chain becaue some are not functional unless they are in combination
another possibility
they may be associated with non protein groups and form large complex molecules such as haemoglobin
for example
the insulin molecule which has two chains
shapes
the role of proteins depend on their molecular shape
type 1
fibrous proteins which have long thin molecules and their shape makes them insoluble in water so they have structural functions as in bone
example 1 of fibrous proteins
keratin the protein in hair, the pp are in parallel chains or sheets with many cross linkages forming long fibres
example 2
collagen, fibrous proteins are strong and tough providing strength and toughnenss needed in tendons
describe the structure of collagen
a single fibre (tropocollagen) consists of three identical PP chains twisted around each other like a rope and the chains are linked by hydrogen bonds making the molecule very stable
type 2 of proteins
globular proteins which are compact and folded into spherical molecules making them soluble- metabolic functions
example
haemoglobin consisting of 4 folded PP chains at the centre of each of which is the iron containing group haem
Identify amino acids given a structural formula and r group
how to test a sample of a solution for protein
add of few drops of buiret reagent (NaOH and CuSO4)
what happens
the NaOH and CuSO4 react to make blue CuOH which interacts with the peptide bonds present in the protein to make biuret which is purple
concentrations
at low protein concentrations- the colour change is difficult to detect by eye , the more concentrated the darker the purple colour
type of test
qualitative but could be used as a semi quantitative comparing the intensity of purple in two identically treated solutions
greater accuracy
measuring the absorbance of the purple biuret in a colorimeter using a yellow filter gives an estimate of relative concentration of proteins present in a sample but to detect the concentration of a specific protein a biosensor is used
STEPS OF PROTEIN TRAFFICKING
Transcription of DNA to mRNA
mRNA formed leaves nucleus to one of the ribosomes on the RER
In ribosome translation of mRNA to form a polypeptide
Protein made on ribosomes enter RER and travels through the membrane bound sacs of the ER
STEPS OF PROTEIN TRAFFICKING
As the protein passes through the ER it is processed and assumes 3-dimensional shape
When the protein reaches the end of the ER sac a vesicle containing her protein is pinched off the ER sac
Steps for protein trafficking
The transport vesicles from RER move material from the ER to Golgi apparatus , they fuse to form flattened sacs of the Golgi apparatus
When the vesicles reach the Golgi apparatus the vesicles fuse with the Golgi apparatus on the receiving face proteins are then modified within the Golgi apparatus
Steps
Vesicles containing modified proteins are pinch off the Golgi apparatus
They then fuse with the cell surface membrane and release their contents releasing proteins by exocytosis
Examples of globular proteins
Enzymes, antibodies, plasma proteins and hormones