Optical telescopes (ch1?)
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
AQA A-level physics options - astrophysics. Telescopes; ch1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
What does it mean when a telescope is in normal adjustment?
the focal points of the eyepiece and the objective lenses meet
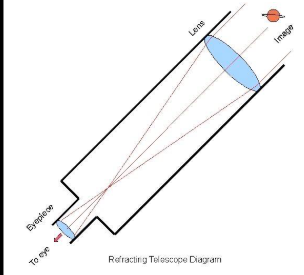
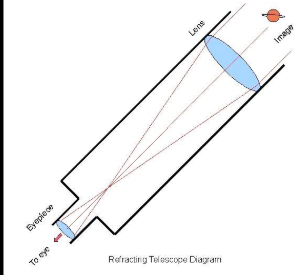
label the telescope diagram
Lens = objective lens
eyepiece = eyepiece lens
Where rays meet is called the focal point
Equation for magnification in normal adjustment (with focal lengths)
M = fo / fe
Where fo is focal length of objective lens and fe is the focal length of the eyepiece lens.
What are the disadvantages of refracting telescopes?
large diameter lenses are difficult to manufacture
large diameter lenses are heavy and tend to distort under their own weight
suffer from chromatic aberration
suffer from spherical aberration
not easy to maneuver quickly
difficult to mount heavy observing equipment and electronics
large magnifications require large objective lenses and long focal lengths therefore require big observatories and domes.
What is chromatic aberration?
When light of different colours enter the tube, they all refract at different angles, therefore have different focal points. As the angle of refraction is dependent on wavelength. This causes a distortion in images.
(similar to material dispersion)
What is spherical aberration?
Lenses: When the shape of the objective lens is not perfectly spherical, resulting in multiple focal points and image distortion.
Mirrors: When the mirror plane is not perfectly spherical/parabolic, parallel light rays reflecting off a spherical mirror do not converge to a single focal point
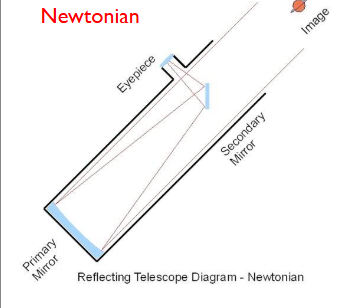
Draw a diagram of a Newtonian reflecting telescope
The primary mirror is ideally parabolic, eliminating spherical aberration
the spherical mirror is flat
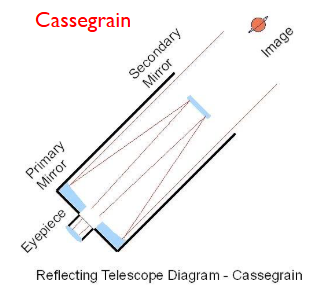
Draw a diagram of a Cassegrain reflecting telescope
primary mirror is ideally parabolic, eliminating spherical aberration
the secondary mirror is convex (bends rays towards eyepiece)
Advantages of reflecting telescopes
large mirrors can be made easily, they are lighter and easier to support than lenses
Mirror surfaces can be made nm thick, giving excellent image properties
Mirrors only use front surface for reflection
No chromatic aberration
No spherical aberration if mirrors are parabolic
Make lightweight telescopes, allowing for easy maneuverability for fast response to astronomical events
smaller segmented mirrors can be used to form a large composite objective mirror
What are the limitations of ground-based telescopes?
atmosphere absorbs and scatters light (ozone, O2, CO2, dust)
Atmospheric turbulence reduces image quality
Light pollution
How does atmospheric turbulence reduce the image quality of a telescope?
Caused by changes in the refractive index of the atmosphere e.g. due to wind. Light is scattered randomly and results in stars appearing to twinkle. If refractive index of the atmosphere is constant, they do not twinkle.
What is an airy disk?
The bright central region in an optical diffraction pattern caused by light entering a circular aperture.
Each point in an image has its own airy disk. So when the airy disks are large, sometimes two separate objects overlap and become indistinguishable.
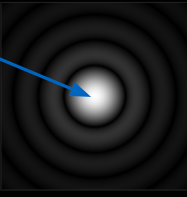
How do airy disks form?
Light enters a circular aperture
This causes light rays to diffract, resulting in a circular diffraction pattern
sinθ = nλ/d where d is the diameter of the telescope, n is the order, λ is the wavelength of light, and theta is the angle between central maximum and order n.θ ≈ λ D
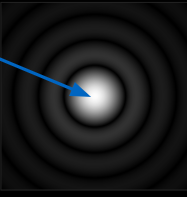
What is the Rayleigh criterion?
θ ≈ λ/D, sinθ can be approximated to θ using the small angle approximation for sine.
Identifies the minimum subtended angle between two objects whose images can be resolved.
The minimum angle occurs when the central maximum of the diffraction pattern of light from one object coincides with the first minimum of the diffraction pattern of the second object.
What does it mean for two objects to be barely resolvable?
When the central peak of one of the airy disks overlaps with the first minimum of the other airy disk. This is part of the Rayleigh criterion.
Equation and definition for angular resolution.
θ = x/L where x is the distance between objects, and L is the distance from the telescope.
Angular resolution = resolving power. When θ is small, the resolution is high.
What is LGP?
Light gathering power, collecting power for optical telescopes.
This is directly proportional to the diameter of the objective element of the telescope squared. The larger the LGP, the brighter the image.
(area, larger area = more light collected)
what is meant by the minimum angular resolution?
The minimum angle an instrument can distinguish between two small objects for a specific wavelength of EM radiation, as determined by the Rayleigh criterion.