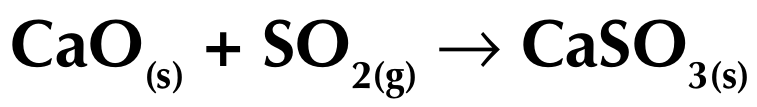3.3.2 Alkanes
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
Alkanes
Saturated hydrocarbons, hence they only contain carbon and hydrogen atoms
Fractional distillation
First, the crude oil is vaporised at about 350 °C
The vaporised crude oil goes into the bottom of the fractionating column and rises up through the trays
The largest hydrocarbons don’t vaporise at all, because their boiling points are too high
As the crude oil vapour goes up the fractionating column, it gets cooler, creating a temperature gradient
Because boiling points of alkanes increase as the molecules get bigger, each fraction condenses at a different temperature
The fractions are drawn off at different levels in the column
The hydrocarbons with the lowest boiling points don’t condense
They’re drawn off as gases at the top of the column
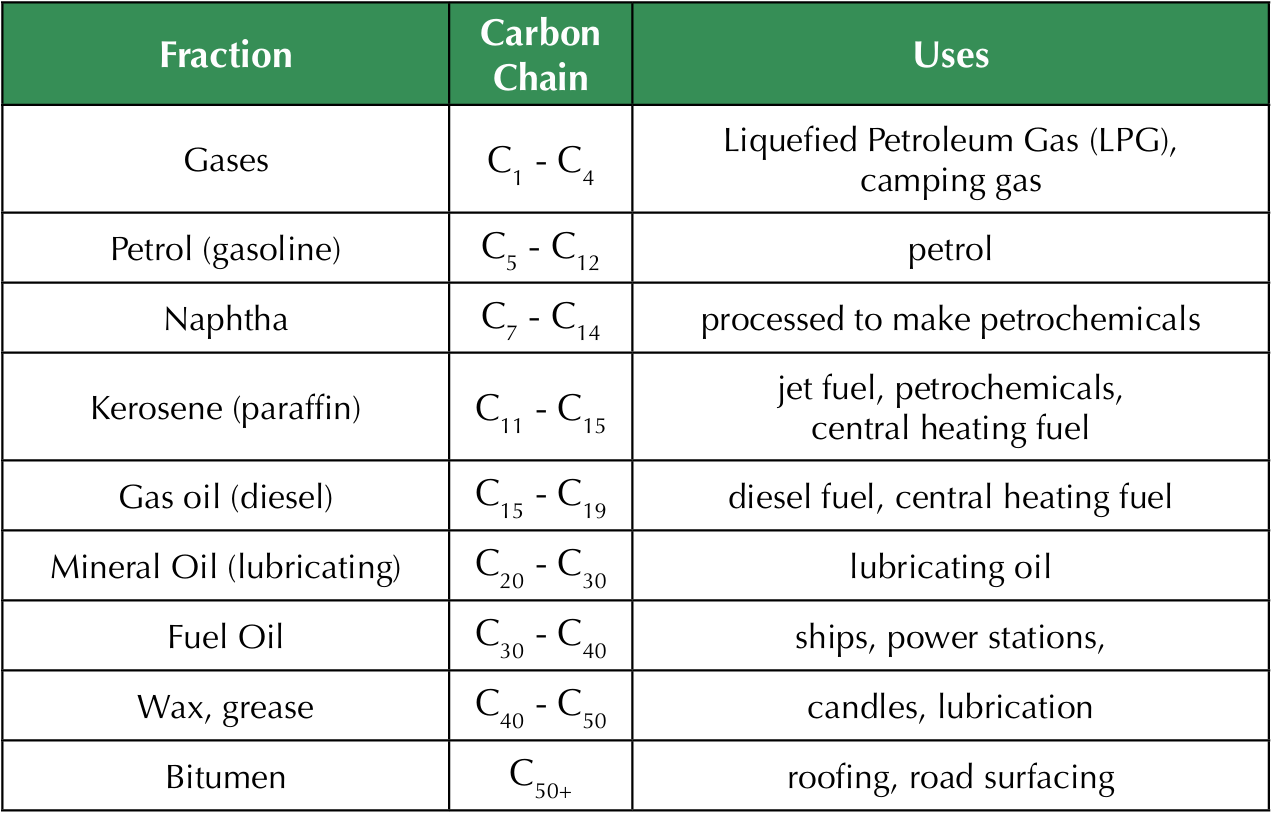
Uses of crude oil fractions
Cracking hydrocarbons
Involves breaking carbon-carbon bonds in alkanes to form an alkene and a smaller alkane
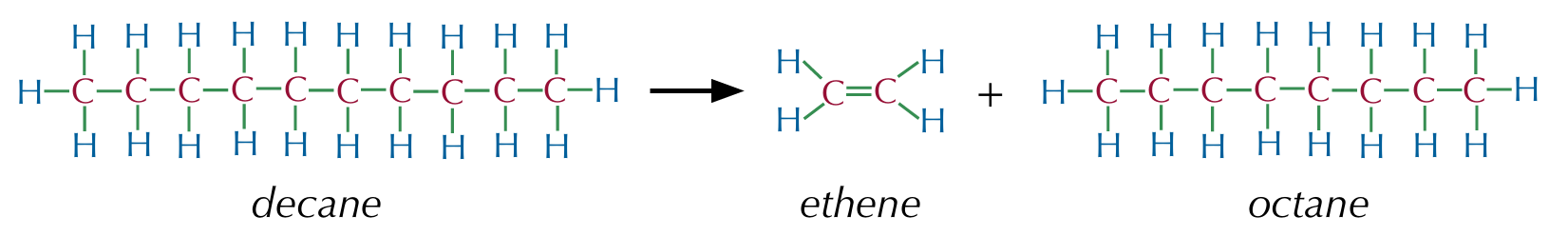
Thermal cracking
Takes place at high temperatures (1000°C) and high pressures (70atm), producing a lot of alkanes
Catalytic cracking
Takes place at high temperatures and slight pressure with the presence of a zeolite catalyst, producing aromatic hydrocarbons and alkanes needed to produce motor fuels
Using a catalyst cuts costs, because the reaction can be done at low pressure and a lower temperature, the catalyst also speeds up the rate of reaction, saving time, and hence money
Complete combustion of an alkane
When an alkane is burnt (oxidised) in excess oxygen, producing carbon dioxide and water
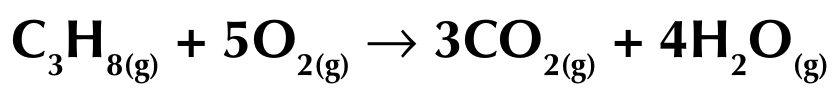
Incomplete combustion of an alkane
When an alkane is burnt (oxidised) in limited oxygen, producing carbon (soot), carbon monoxide and water

Oxides of nitrogen
Nitrogen oxides are a series of toxic and poisonous molecules which have the general formula NOₓ
Nitrogen monoxide is produced when the high pressure and temperature in a car engine cause the nitrogen and oxygen atoms from the air to react together
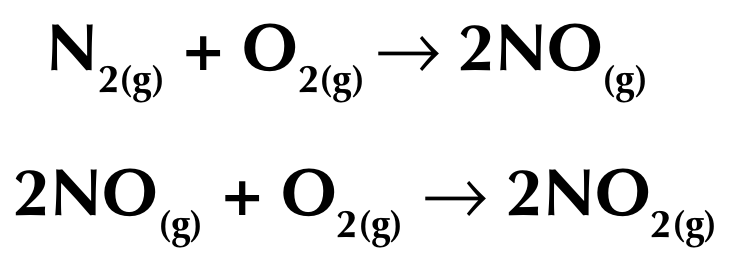
Removal of poisonous gases
Catalytic converters remove toxic gases from the exhaust pipes of cars, including oxides of nitrogen, carbon monoxide, carbon and unburned hydrocarbons
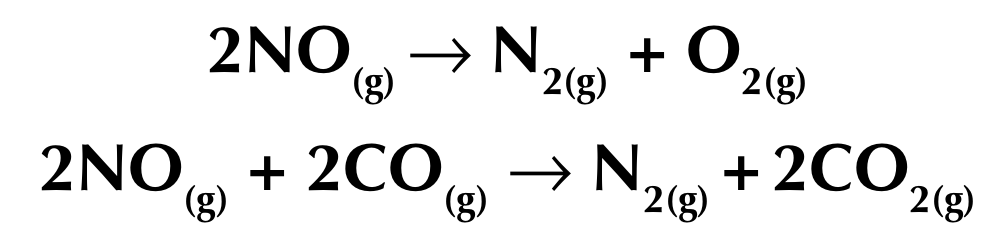
Sulfur dioxide
Some fossil fuels contain sulfur, and when burnt (in a car engine or power station), the sulfur reacts with oxygen to form sulfur dioxide
Sulfur dioxide dissolves in moisture and is converted into sulfuric acid, the cause of acid rain
Removal of sulfur dioxide
Powdered calcium carbonate (limestone) or calcium oxide is mixed with water to make an alkaline slurry
When the flue gases (which contain sulfur) mix with the alkaline slurry, the sulfur dioxide gas reacts with the calcium compounds to form a harmless salt (calcium sulfite)