7: Carbohydrates and the Glycoconjugates of Cell Surfaces
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
carbohydrates
- hydrates of carbon
- general formula of (CH2O)n with n >= 3
- major form of stored energy
- important structural roles
Monosaccharides
- simple sugars
- cannot be broken down into simple sugars under mild conditions
Oligosaccharides
- 2-10 simple sugar residues linked by glycosidic bonds
Polysaccharides
polymers of the simple sugars
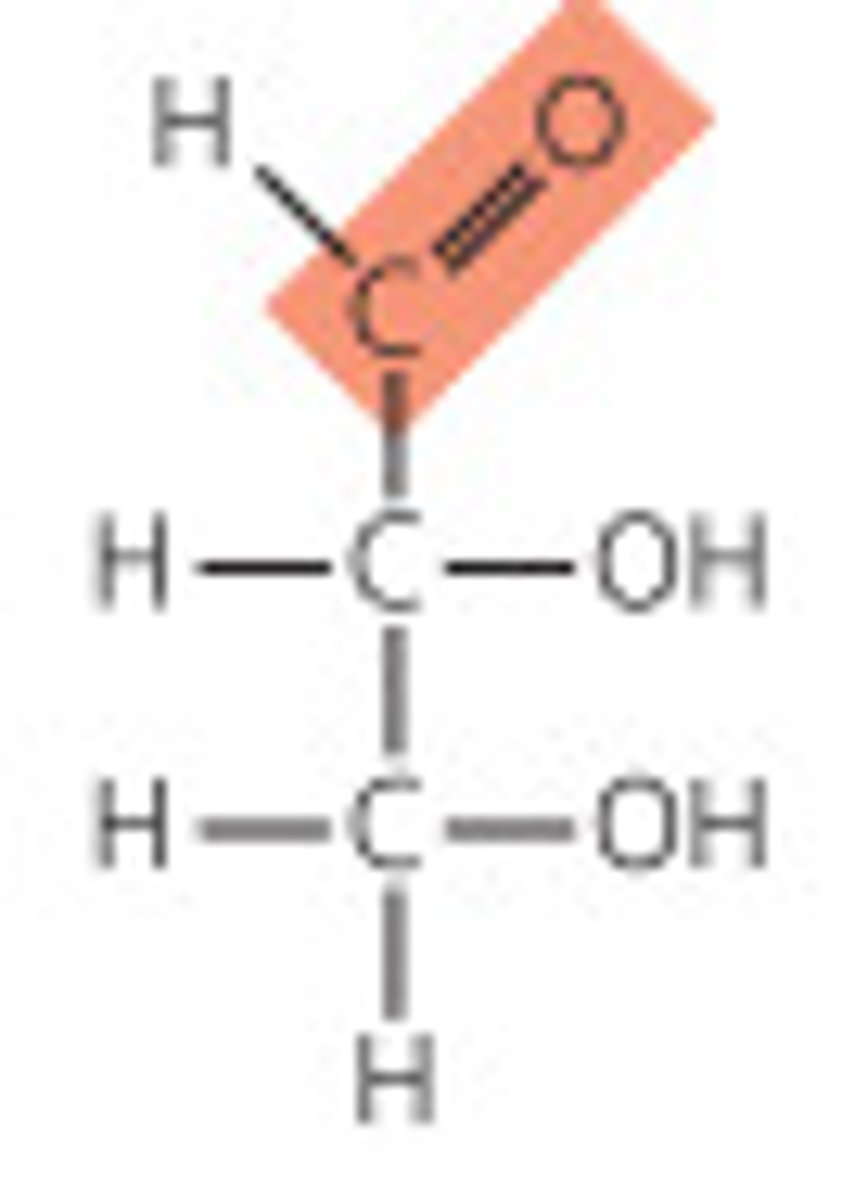
aldoses
- monosaccharides that contain an aldehyde function
- simplest one is glyceraldehyde
- numbering of carbons is starts one at the aldehyde carbon
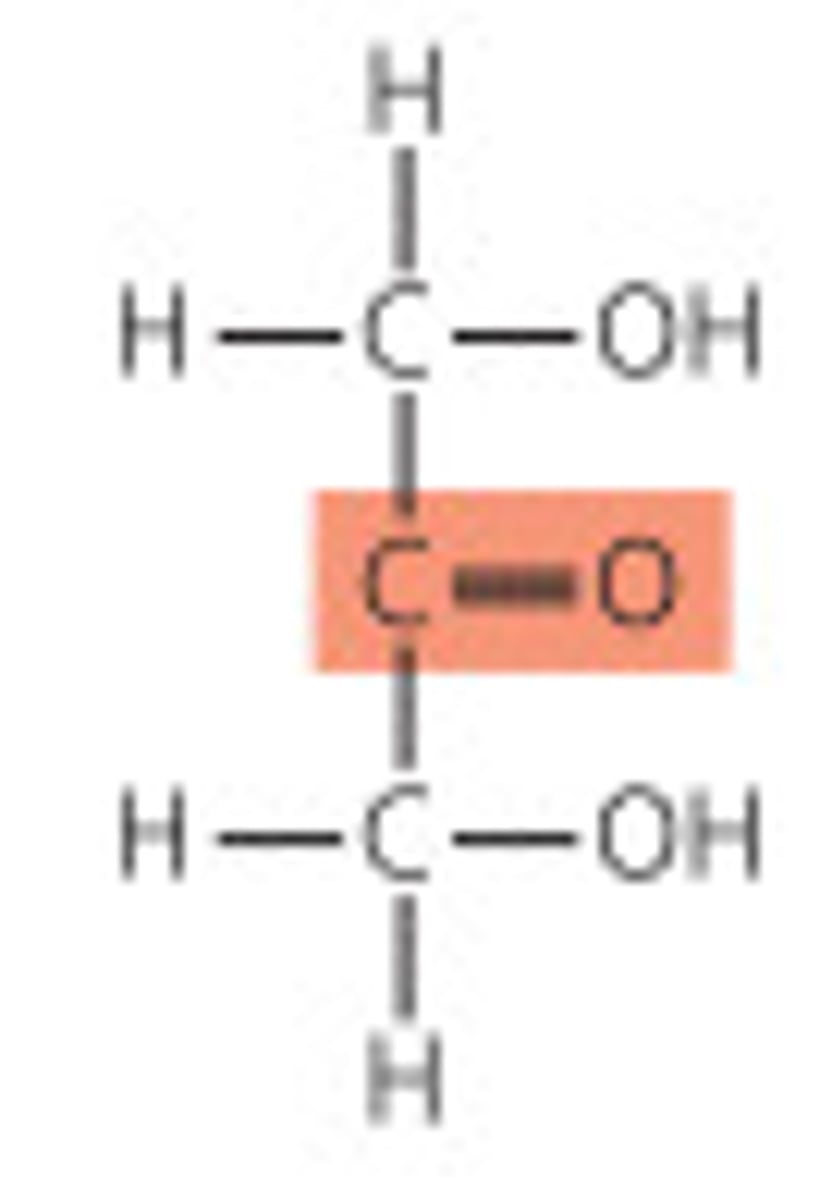
ketoses
- monosaccharides that contain a ketone group
- simplest one is dihydroxy-acetone
- numbering of carbons start at the end closest to the carbonyl carbon
most naturally occurring stereochem of carbs is _______ isomers
D
- D/L is based on the highest numbered asymmetric carbon
- isomer is D if hydroxyl group on the highest numbered carbon is drawn on the right in a flat projection
enantiomers
- stereoisomers that are non-superimposable mirror images of each toehr
diastereomers
- pairs of isomers that have opposite configuration at one or more chiral centers but NOT mirror images
epimers
- two sugars that differ in configuration at only ONE chiral center
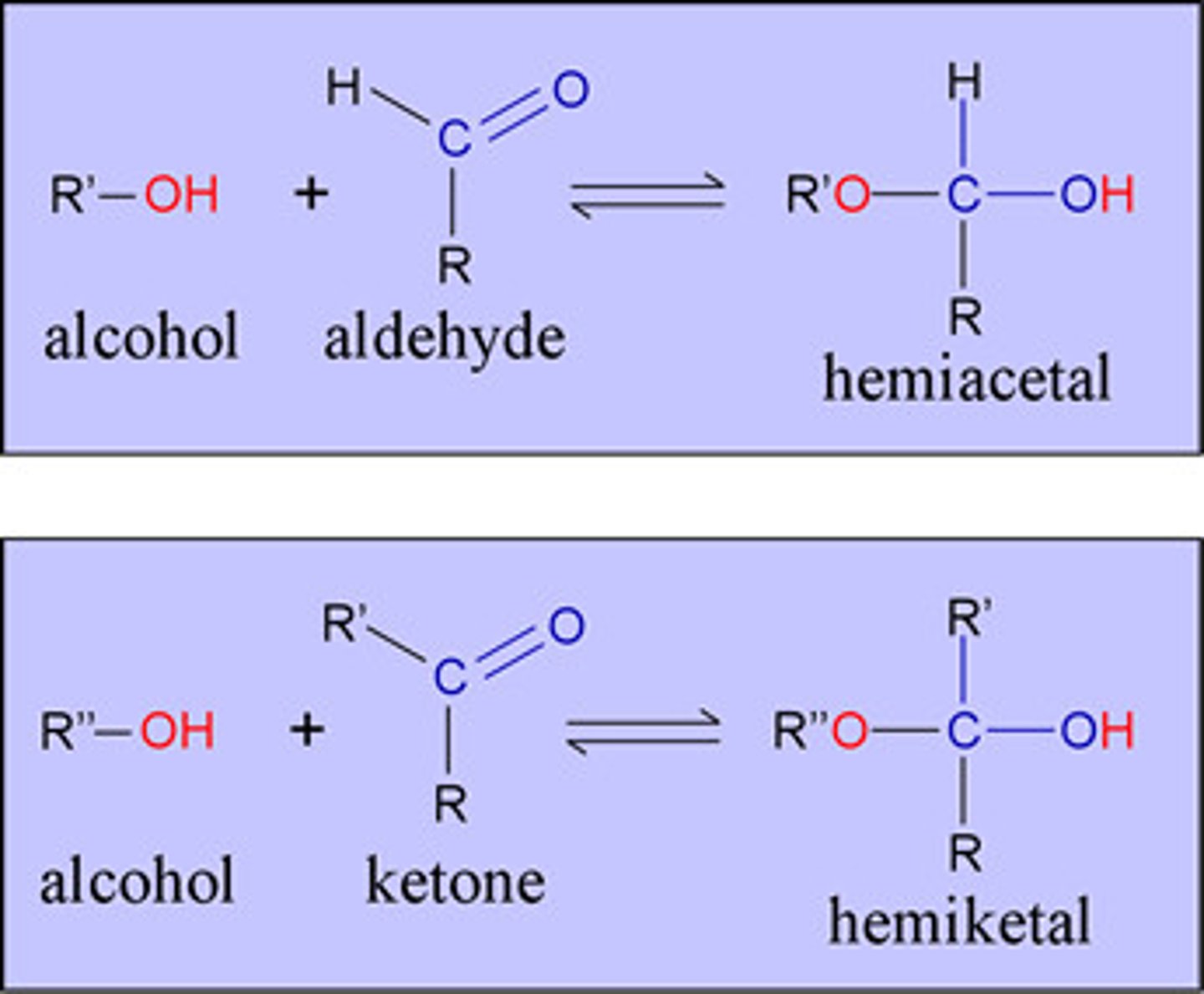
hemiacetal and hemiketal
- rxn of an alcohol group of a carbohydrate with the internal carbonyl aldehyde or chetone form
- rxn introduce an additional asymmetric center
cyclization of linear sugars
- in solution, sugars will become cyclic and form pyranose or furanose
pyranose
- six membered ring sugar
- usually from hemiacetal
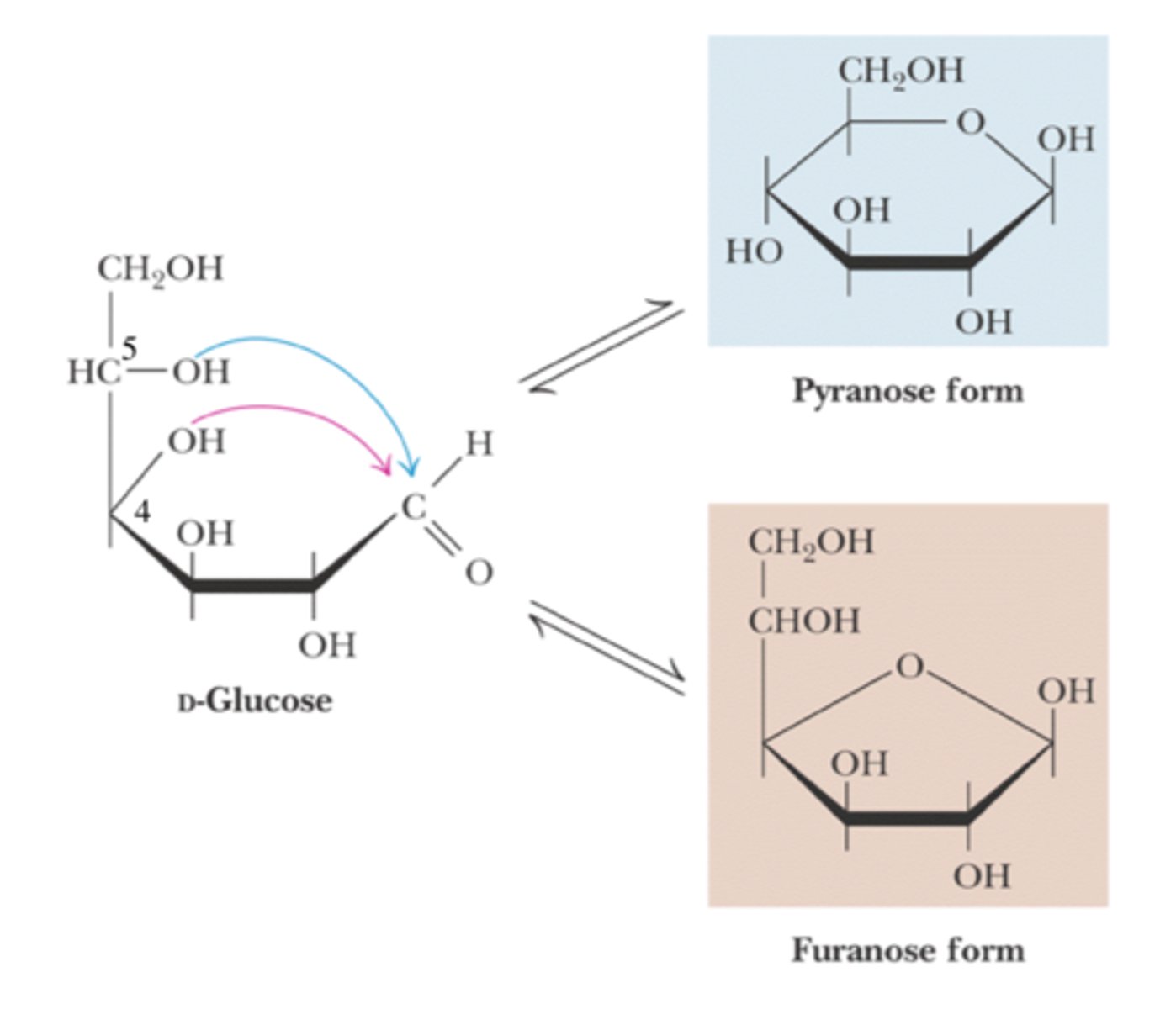
furanose
- 5 membered ring sugar
- usually from hemiketal
anomers
- cyclization of D-glucose generates of mixture of α and β -> called anomers
- mutarotation in solution
how do we tell if a sugar is alpha or beta ?
- D sugar -> OH up -> alpha ; Oh down -> beta
- L sugar -> reverse of D
phospho sugars
- aka sugar esters
- phosphorylated through an ester linkable
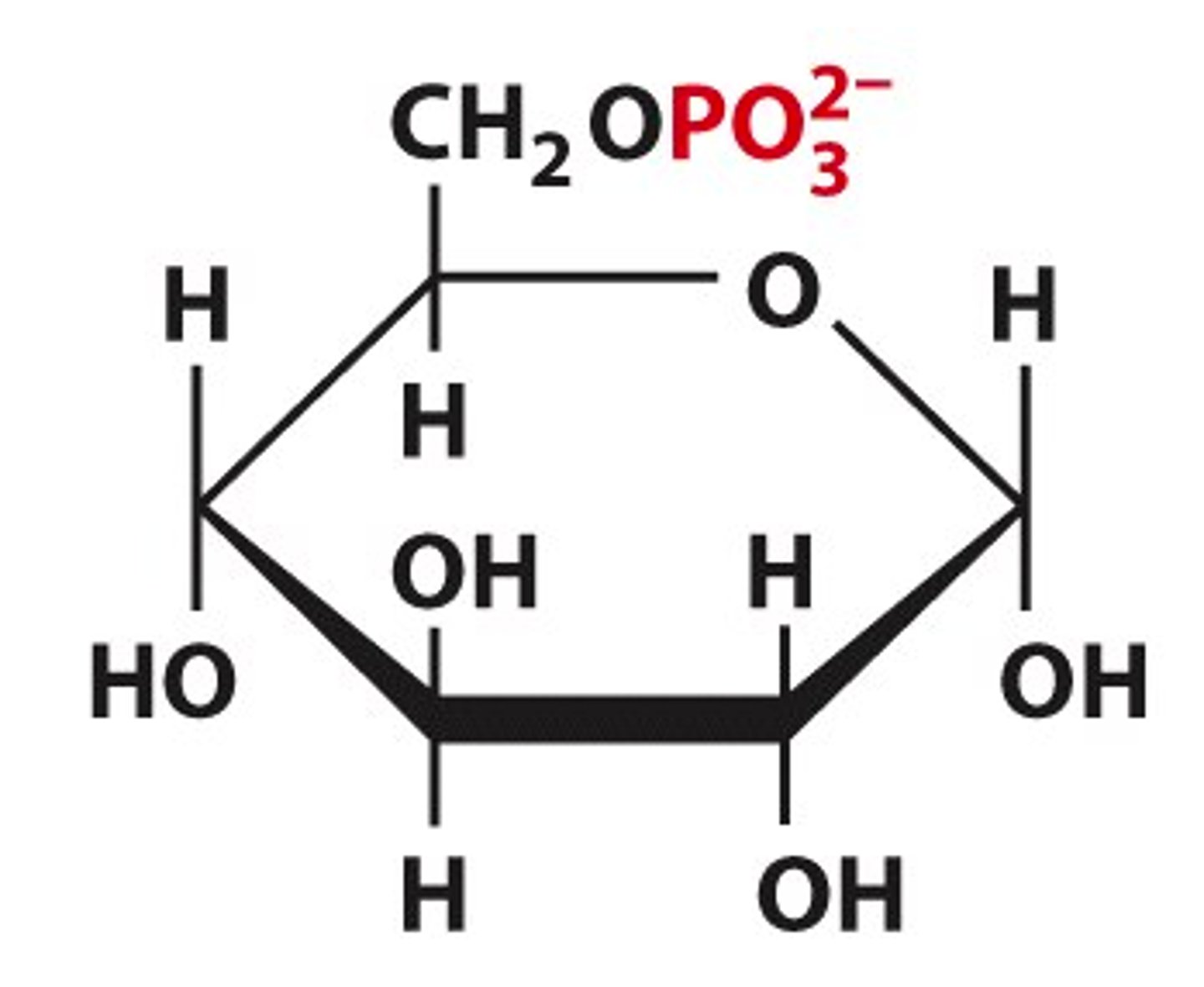
free anomeric carbon
- HOH group, usually on the left side
- common disaccharides have an unsubstituted anomeric carbon, except for sucrose
- the "reducing end"

is sucrose and reducing sugar?
no bc it does have a free anomeric carbon
glycosidic bonds are formed bu
- elimination of water between two hydroxyl groups
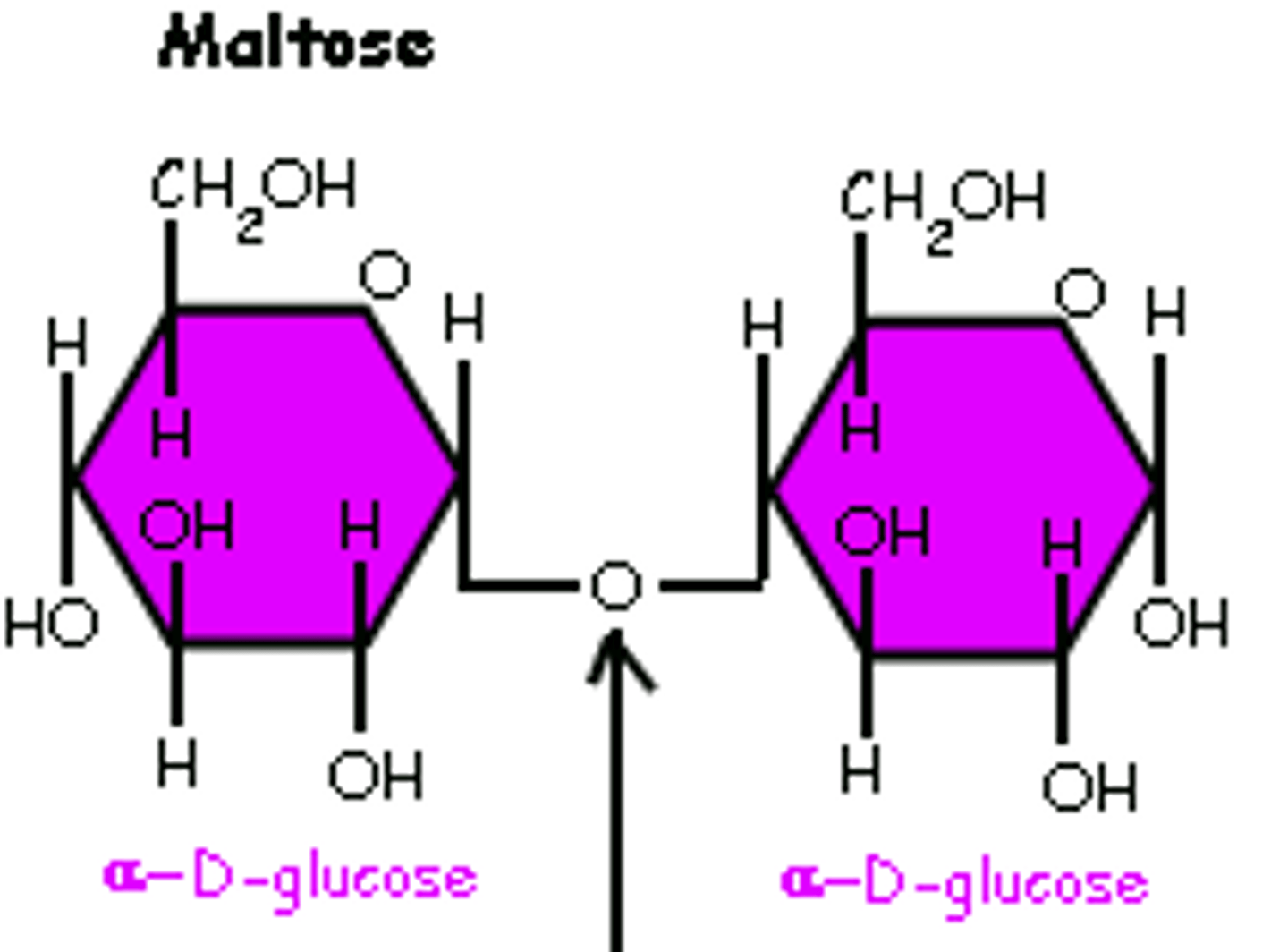
alpha 1,4 glycosidic bond
- both OH groups are facing down
|_o_|
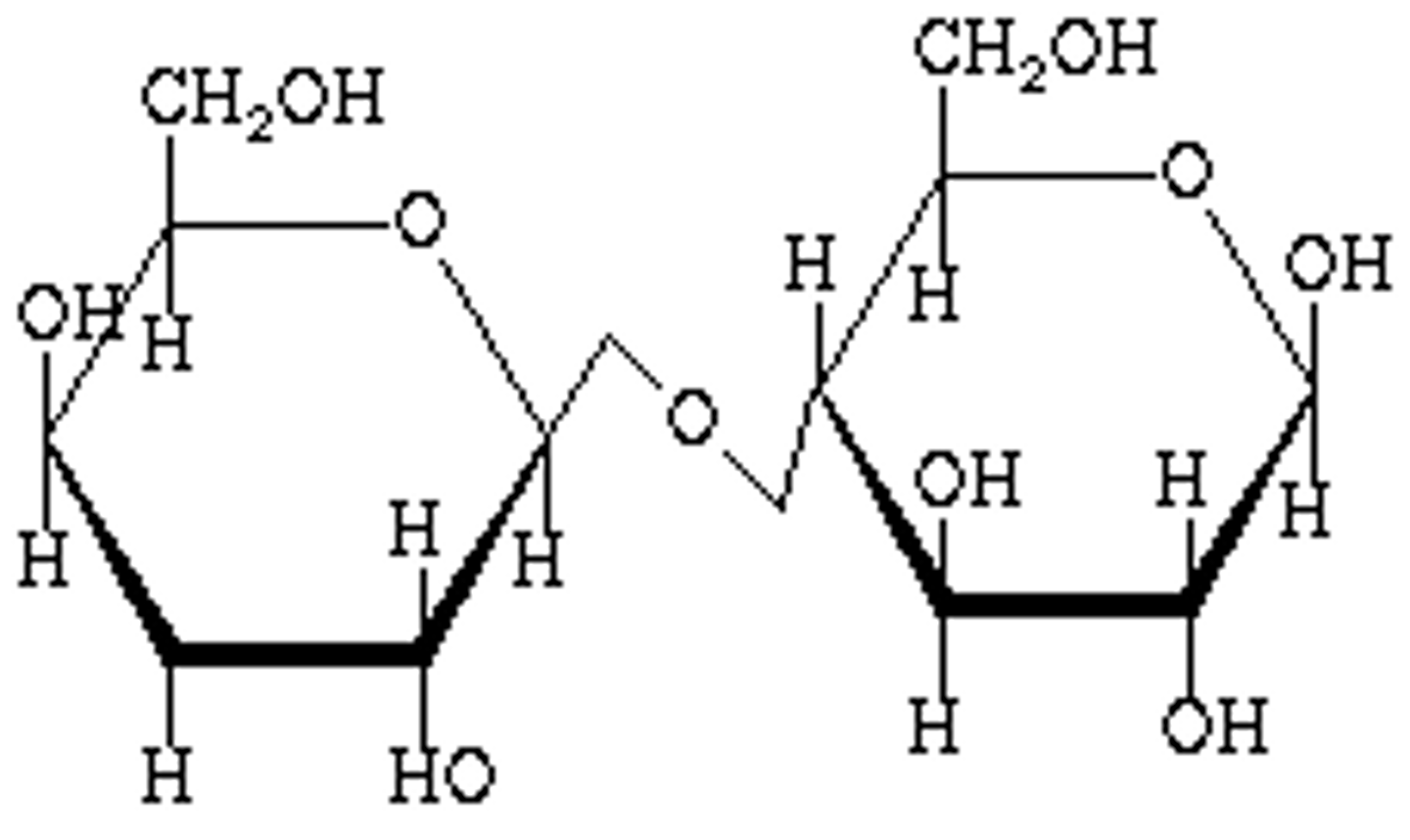
beta 1,4 glycosidic bond
- one OH is up (usually left one) and other OH is down (usually right one)
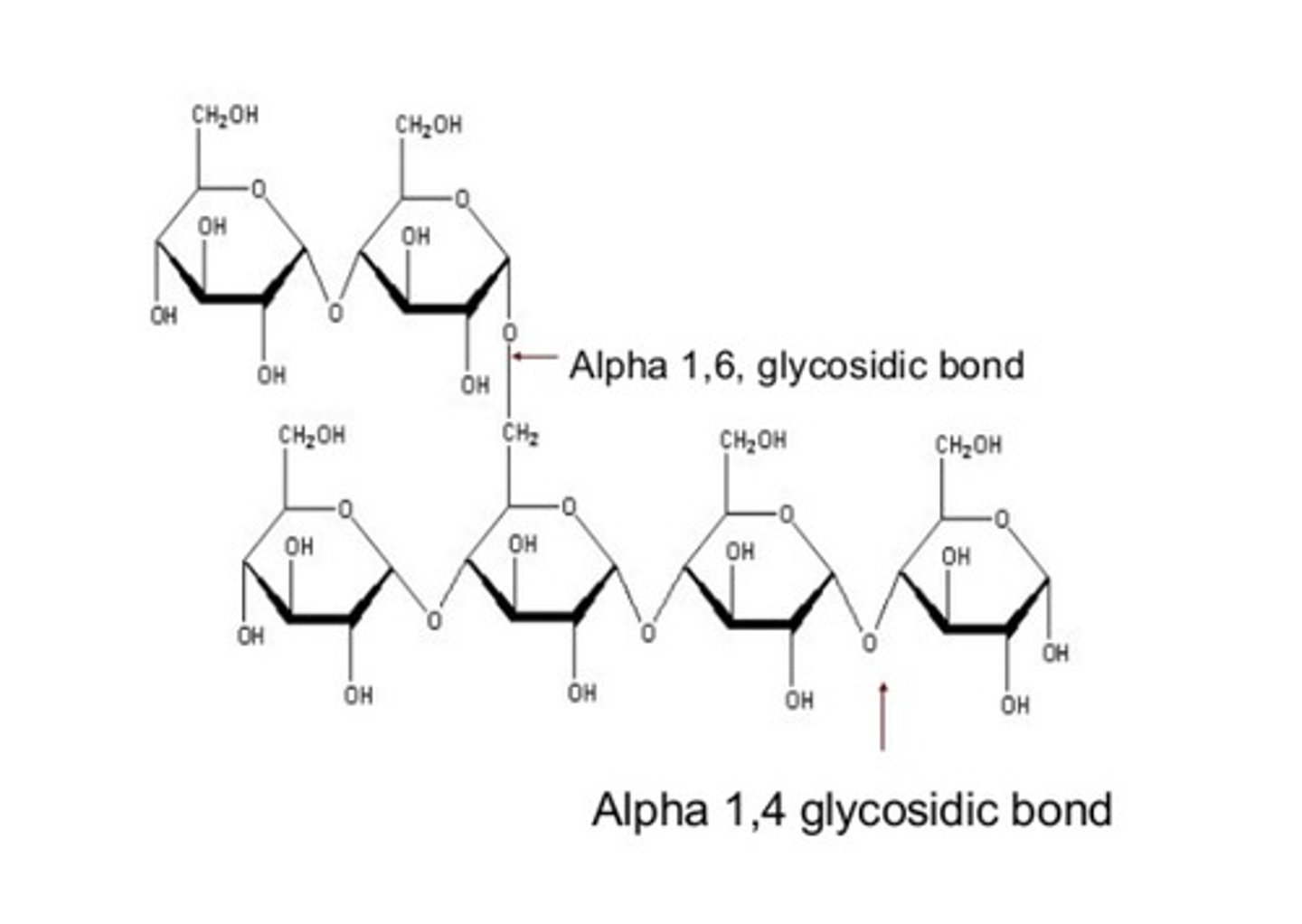
alpha 1,6 glycosidic bond
- Type of bond for glycogen branching
- connects the saccharides up and down, instead of left and right
glucose + glucose (alpha 1,4 connection) =
maltose
glucose + glucose (beta 1,4 connection) =
cellobiose
glucose + glucose (alpha 1,6 connection) =
isomaltose
galactose + glucose (beta 1,4 connection) =
lactose
- bond is hydrolyzed by lactase
- lactose intolerance is caused by lactase deficiency
glucose + fructose (alpha 1,2) =
sucrose
glycan
- aka starch
- polysaccharide
- mix of amylose and amylopectin
glucan
- long homopolysaccharide -> only contains glucose
amylose
- linear chain of glucose units in alpha 1,4 linkage
amylopectin
- branched chain
- branches are created by alpha 1,6 links and occur every 12,30 resides for about 24-30 residues
starch in plants
- starch phosphorylase release glucose phosphate -> catabolize by glycolysis
- cleavage at branch points -> needs alpha 1,6 glucosidase
- 1 ATP is "saved" since glucose is already phosphorylated in comparison to glycolysis
digestion of starch in animals start ...
in the mouth via salivary amylase
- salivary alpha amylase to break the alpha 1,4 linkage
- alpha 1,6 glucoside to break the alpha 1,6 linkage
glycogen
- glucose units joined by alpha 1,4 linkages and alpha 1,6 branches
- major form of storage polysaccharides in animals
how are starch and glycogen different?
by the number/degree of branching
- note: starch is stored in plants, glycogen is stored in animals
how are amylose and cellulose differ?
- in the configuration of the glycosidic linkages
- amylose is alpha 1,4
- cellulose is beta 1,4
- leads to different properties of cellulose
cellulose
- structural polysaccharide
- found in the cell walls of nearly all plants
- ex wood and bark of trees -> highly organized structure of cellulose and lignin -> insoluble
- alternating 180 degree flips to generate an extended ribbon conformation -> Hbonding bt chains
- resistant to hydrolysis by acid and amylases to can degrade starch and glycogen -> animals that digest cellulose need specific bacteria that can hydrolyze cellulose
in water, amylose structure becomes
helical conformation
chitin
- found in the cell walls of fungi and the exoskeletons of crustacea and insects
- identical to cellulose, except for the addition of NHCOCH3 at the C2 position -> repeating units is N-acetyl-D-glucosamine
agarose
- component of agar that is obtained from marine red algae -> chain of alternating D-galatase and 3,6-anhydro-L-galactose
- agarose gels used in labs to separate biomolecules via size
glycosaminoglycans
- linear chains of repeating disaccharides in which one unit is an amino sugar and one or both is negatively charged
- usually have to do with connective tissues
- ex heparin -> anticoagulant
- ex hyaluronates -> synovial fluid for joints and liquid humor in eyes
- ex chrondroitins and keratan sulfate -> tendons, cartilage and other connective tissue
- ex dermatan sulfate -> for the skin